How Does It Work Differently
The connections within a brain bring it to life. And its the brain cells or neurons that act as the messengers. When a brain cell is active, it creates an electrical impulse and that gets propagated to other cells in the brain. We think that electrical activity holds the basis of thought and behavior and how the brain functions, Dr. Anderson says.
Researchers indirectly measure these electrical impulses by looking at how synchronized regions of the brain are. When regions are working together, they tend to have brain activity at the same time. Functional connectivity is the measurement of how much two regions of the brain seem to be synchronized or talking together.
Neuroscience : Brain Connectivity And Pruning
Congrats, you passed Neuroscience 101. Time now for Neuroscience 102 so lets talk about how Brain Connectivity and Pruning works.
In the critical growth stage in early development and early childhood, every time we learn something new, we strengthen, shape, or form new connections between the neurons in our brain. We know that the brain reaches the maximum number of its synaptic connections sometime in early childhood, between 2-4 years of age.
Neurologically, an abundant number of neurons and synapses develop, while also allowing different brain regions to communicate with each other. As this is happening in early childhood development, the synapses that are forming are strengthened, while unused connections become smaller or are removed. This is known as synaptic pruning.
Pruning is a natural brain maturation process as the brain begins to eliminate excess neurons that are not being used or strengthened basically, your brain says, use it or lose it. Pruning helps to refine the neural circuits and increase efficiency in the brain.
Overly Intense World Hypothesis
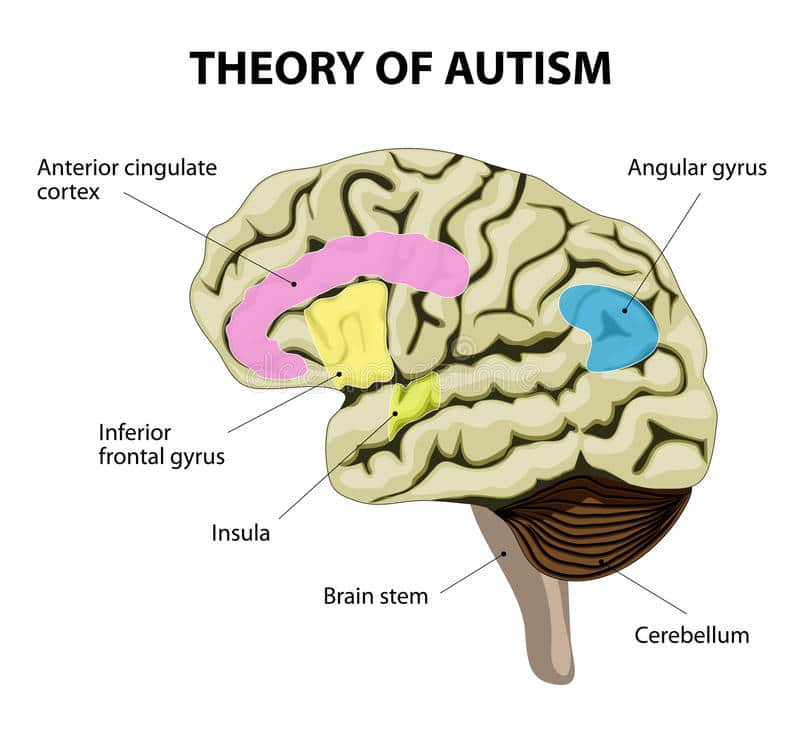
The overly intense world hypothesis focuses on both social behavior and sensory symptoms. Children with autism might have too much brain activity, which makes it hard to selectively pay attention to some things and not pay attention to others. They experience the world as overwhelming and overly intense. That could explain why they often experience sounds as too loud or fabric and as too scratchy or rough.
In terms of social behavior, the overly intense world hypothesis explains why children with ASD have difficulties. As far as we know, people with autism are often overwhelmed by social interactions, which are unpredictable. The hypothesis considers that the root of both social deficits and sensory sensitivity in Autism Spectrum Disorder might be the same, which is over-responsivity in certain areas of the brain.
The areas of the brain might be over-active. These areas include the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala. The prefrontal cortex is where higher-order brain function happens. It means complex brain functions such as attention, memory, executive function and planning, and social cognition.
Important functions such as regulation of body functions, related-oriented communication, emotion regulation, postponement of reactions, empathy, intuition, social skills, plan, control, logic, problem-solving, detailed thinking, management related to the prefrontal cortex. These functions are mostly impaired in individuals with autism.
Don’t Miss: How To Get A Child With Autism To Do Chores
Resources For Families Affected By Autism
Autism spectrum disorder is a complex developmental disability that affects a persons ability to communicate and interact with others. ASD is characterized by social-interaction difficulties, communication challenges and repetitive behaviors. Symptoms can be mild, moderate or severe.
There is no one cause of autism. Research suggests that its a combination of genetic and environmental factors. ASD affects boys more often than girls, and symptoms typically appear before a child is 3 years old.
There is no medical test for ASD. Doctors look at the childs behavior and development to make a diagnosis. There is no cure for ASD, but there are treatments that can help children and adults manage the symptoms and improve their quality of life.
If you think your child might have ASD, talk to your doctor. The sooner you get a diagnosis, the sooner you can start treatment.
Were Here To Help You Deal With This Unique And Often Misunderstood Disorder
Theres a reason the puzzle piece is a symbol for autism even the foremost experts would agree that they have much to learn as they work towards a greater understanding of the disorder. When youre dealing with a disorder that is not well-understood and a complicated set of legal rules, you need the right attorney on your side someone who not only has legal training, but also has an understanding of autism gained from experience handling cases like yours. At Keller & Keller, we have this experience, and can apply it in your case.
Special thanks to Keller & Keller paralegal Cassie Smith for research assistance.
Recommended Reading: Symmetra Autistic Comic
You May Like: What Does Autism Do To A Child
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
How Does Autism Affect The Brain
Image credit: CC0
Autism is a brain disorder that affects how people interact with others. It occupies a spectrum, with severe autism at one end and high-functioning autism at the other. People with severe autism usually have intellectual impairments and little spoken language. Those with high-functioning autism have average or above average IQ, but struggle with more subtle aspects of communication, such as body language. As well as social difficulties, many individuals with autism show repetitive behaviors and have narrow interests.
The brains of people with autism process information differently to those of people without autism. The brain as a whole shows less coordinated activity in autism, for example. But whether individual brain regions themselves also work differently in autism is unclear. Watanabe et al. set out to answer this question by using a brain scanner to compare the resting brain activity of high-functioning people with autism to that of people without autism.
The findings of Watanabe et al. suggest that changes in the structure and activity of small brain regions give rise to complex symptoms in autism. If these differences also exist in young children, they could help doctors diagnose autism earlier. Future studies should investigate whether the differences in brain activity cause the symptoms of autism. If so, it may be possible to treat the symptoms by changing brain activity, for example, by applying magnetic stimulation to the scalp.
Recommended Reading: Does A Child With Autism Qualify For Ssi
How Does Autism Affect Brain Development
In the study, Characteristics of Brains in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Structure, Function and Connectivity across the Lifespan, Magnetic Resonance Imaging scans were conducted. There were differences noted in those with autism.
The differences in the scans were found in the gray and white matter of the cerebral cortex. The differences were noted between the autistic brain and a neurotypical brain.
The Effect Of High Functioning Autism On Gender Orientation
The Autism Europe conference in Edinburgh had research presentations on the topic of gender dysphoria and its connection to high functioning ASD. Dr. Mark Stokes from from La Trobe University in Melbourne Australia spoke about his recent study examining this topic. The results from the international study found a higher percentage of those with ASD have gender distress, ambivalence and/or neutrality.
When compared to controls, individuals with ASD demonstrated significantly higher sexual diversity, reported gender-identities incongruent with their biological sex, and higher gender-dysphoric symptomatology.
The ASD group reported higher rates of asexuality decreased heterosexual attraction and contact increased homosexual attraction ASD females reported higher homosexual contact and were not concerned with the gender of their romantic partner. ASD individuals who were gender non-conforming reported better relationships with their opposite-sex peers during their schooling years than their gender-conforming peers did. The ASD group reported poorer mental health than controls and belonging to a sexual or gender-diverse group worsened this effect.
Increased non-heterosexuality in ASD may particularly fit predictions from the Extreme Male Brain theory of autism. An androgynous self-concept, gender ambivalence and dissatisfaction with culturally-dictated sex-roles emerged as major themes, which together may permit more fluid sexual-identities.
Recommended Reading: How Do They Diagnose Autism
Gene Mutation In The Brain May Be Early Clue To Autism Study Suggests
Mutations of a certain gene may contribute to autism by interfering with normal brain development, a new study suggests.
The gene, which is mutated in some people with autism, affects cells that set up the framework for the organization of a fetuss developing cortex, according to the study published in Neuron.
Those cells, called radial glia, can be viewed like the framing timbers of a house under construction. If the houses framing is off, then the rest of the construction will be affected.
Each of the radial glia divide and make neurons and serve as the guide for where those neurons go, said study coauthor Eva Anton, a professor at the University of North Carolina Neuroscience Center. They enable the organization of neurons in the brain that underlies functional circuits.
Disruption of this early organization, may be one of the contributors causing some of the brain malformations associated with autism, Anton said.
How Autism Affects The Mental Health
Autism spectrum disorder is a complex neurobehavioral disorder that includes impairments in social interaction, developmental language and communication skills, and restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior. Autism can be diagnosed as early as 18 months of age.
While ASD occurs in all ethnic and economic groups, boys are four times more likely than girls to have autism. There is no medical detection for ASD. Instead, parents or teachers usually notice unusual behaviors in children, which leads to evaluation by a specialist.
ASD affects the normal functioning of the brain by interfering with how nerve cells and their chemical messengers connect and interact with each other. The exact cause of ASD is currently unknown though research suggests that both genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of ASD.
You May Like: How Can I Get Diagnosed With Adhd
Brain Structures In Asd
Since neuroimaging approach is one of the few methods that enable to make direct observation of the brain in vivo, Magnetic Resonance Image studies have provided many implications of neurodevelopmental characteristics underlying ASD . Although various results were shown from structural MRI studies over the past decade, there are abnormalities in gray and white matter with some regional brain differences between ASD and typically developing control . Many sMRI studies have investigated volumetric and morphometric brain in order to examine atypical brain anatomy and neurodevelopment in ASD. Reviewing these findings provides insights into the neural substrates and autistic symptoms across the human lifespan.
Multiple Causes Multiple Effects
One of the biggest problems in succinctly dening autismand consequently in recommending treatmentis that the disorder exhibits such a broad array of characteristics. Autism is dened by the presence of multiple communication, social, and stereotyped behavioral difculties that begin before three years of age. Furthermore, autistic behaviors vary according to both developmental level and chronological age. Problems in communication can range from no language at all to more-subtle language difculties, such as delay in word acquisition or pronoun reversal. Stereotyped behaviors such as hand apping and spinning are typical of young children with the disorder, whereas older, high functioning people with autism often evidence a need for sameness or a focused interest in a particular activity or topic. In addition, many autistic children suffer from a host of other complaints, such as extreme reactions to sensory stimuli that would not bother most people and aggressive or self-injurious behavior.
Despite the diverse causes that may underlie autistic behavior, we cannot exclude the possibility of a few common neurochemical features. One of these may involve the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter critical to normal development in the brain.
Developmental disorders, including autism, result from errors in the normal sequence and duration of the programs of brain development.
Don’t Miss: Is Humming A Sign Of Autism
How Is Asd Diagnosed
ASD symptoms can vary greatly from person to person depending on the severity of the disorder. Symptoms may even go unrecognized for young children who have mild ASD or less debilitating handicaps.
Autism spectrum disorder is diagnosed by clinicians based on symptoms, signs, and testing according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-V, a guide created by the American Psychiatric Association used to diagnose mental disorders. Children should be screened for developmental delays during periodic checkups and specifically for autism at 18- and 24-month well-child visits.
Very early indicators that require evaluation by an expert include:
- no babbling or pointing by age 1
- no single words by age 16 months or two-word phrases by age 2
- no response to name
- excessive lining up of toys or objects
- no smiling or social responsiveness
Later indicators include:
- impaired ability to make friends with peers
- impaired ability to initiate or sustain a conversation with others
- absence or impairment of imaginative and social play
- repetitive or unusual use of language
- abnormally intense or focused interest
- preoccupation with certain objects or subjects
- inflexible adherence to specific routines or rituals
Infants Toddlers And Children
Social communication and social interaction
Language development is a critical neurobiological process to communicate each other. Delayed language development is one of the early warning signs of ASD . Children with ASD commonly show impaired language development that leads to social communication deficits. Some fMRI studies have examined the neurobiological differences of impaired language development between children with ASD and TD children . Wang et al. used fMRI to examine the neurobiological deficits in understanding irony in high-functioning children with ASD. In contrast to previous studies showing hypo-activation of regions involved in understanding the mental states of others, children with ASD showed hyper-activation than TD children in the right IFG as well as in bilateral temporal regions. Greater activity children with ASD fell within the network recruited in the TD children and this may reflect more efforts needed to interpret the intention of a word. They concluded that children with ASD have impairments interpreting the communicative intention of others’. These results also indicated that children with ASD can recruit regions activated as part of the normative brain circuitry when task requires some degree of explicit attention to socially relevant cues .
Restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities
Recommended Reading: Does The Good Doctor Have Autism
How Autism Affects The Appetite
Anorexia and other feeding problems are common in autism. They can stem from issues with the senses, gastrointestinal problems, or anxiety.
Some people with autism have a heightened sense of smell or taste, which can make certain foods unpalatable. Others may be sensitive to the textures of certain foods. Many children with autism also have gastrointestinal issues that lead to pain or discomfort after eating. And some people with autism are anxious about trying new foods or eating in unfamiliar environments.
Feeding problems can lead to weight loss, malnutrition, and other serious health problems. If your child is having trouble eating, its important to talk to their doctor about possible causes and treatment options.
What Part Of The Brain Does Autism Affect
Autism spectrum disorder is a complex developmental disability that affects a persons ability to communicate and interact with others. ASD is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is characterized by challenges with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
There is no one part of the brain that is affected by autism. Rather, it is a brain-wide disorder that affects many different areas of the brain. These areas include the hippocampus, cerebellum, frontal lobe, and temporal lobe. Each of these areas plays an important role in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
Recommended Reading: When Is World Autism Awareness Day
Brain Structure Changes In Autism Explained
Angie Voyles AskhamSpectrum
Listen to this story:
Autism is a neurodevelopmental condition. Although it is diagnosed based on the presence of two core behaviors restricted interests and repetitive behaviors, as well as difficulties with social interactions and communication those traits are thought to arise because of alterations in how different parts of the brain form and connect to one another.
No research has uncovered a characteristic brain structure for autism, meaning that no single pattern of changes appears in every autistic person. Studies of brain structure often turn up dissimilar results there is great variety across individuals in general. But some trends have begun to emerge for subsets of autistic people. These differences might one day provide some insight into how some autistic peoples brains function. They may also point to bespoke treatments for particular subtypes of autism.
Here is what we know about how brain structure differs between people with and without autism.
Which brain regions are known to be structurally different betweenautistic and non-autistic people?Studies that make use of a brain-scanning technique called magnetic resonance imaging have highlighted a few brain regions that are structurally distinct in people with autism.
Other structural differences, such as the rate of brain growth and amount of cerebrospinal fluid, appear similar between the sexes6,9.
How Autism Affects The Behavior
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disorder that affects communication and behavior. Although ASD can be diagnosed at any age, it is usually diagnosed in children between the ages of 3 and 5.
There is no single cause for ASD, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests that ASD occurs in families and may be linked to certain genes.
ASD affects the way the brain develops and processes information. People with ASD may have difficulty understanding or responding to social cues, such as body language or eye contact. This can make it hard for them to interact with others.
People with ASD may also have repetitive behaviors, such as hand-flapping or rocking back and forth. These behaviors can help ease anxiety or provide a sense of comfort.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Autism In Infants