Social And Communication Skills
Impairments in social skills present many challenges for individuals with ASD. Deficits in social skills may lead to problems with friendships, romantic relationships, daily living, and vocational success. One study that examined the outcomes of adults with ASD found that, compared to the general population, those with ASD were less likely to be married, but it is unclear whether this outcome was due to deficits in social skills or intellectual impairment, or some other reason.
Prior to 2013, deficits in social function and communication were considered two separate symptoms of autism. The current criteria for autism diagnosis require individuals to have deficits in three social skills: social-emotional reciprocity, nonverbal communication, and developing and sustaining relationships.
Social skills
Some of the symptoms related to social reciprocity include:
- Lack of mutual sharing of interests: many children with autism prefer not to play or interact with others.
- Lack of awareness or understanding of other people’s thoughts or feelings: a child may get too close to peers without noticing that this makes them uncomfortable.
- Atypical behaviors for attention: a child may push a peer to gain attention before starting a conversation.
Symptoms related to relationships includes the following:
- Defects in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships.
- Difficulties adjusting behavior to fit social contexts.
Comparison Of Cars Scores By Age And Diagnostic Group
Mean CARS total scores were calculated for each diagnostic group. In order to assess whether differences in autism severity varied across diagnostic groups, a one-way ANOVA was conducted for each age group. In the 2-year-old sample, the analysis produced a main effect of diagnostic group = 286.89, p< 0.001), indicating that mean CARS scores differed significantly by diagnostic group. Post hoc comparisons indicated that the autistic disorder sample had the highest mean CARS score , which was significantly higher than the mean CARS score of the PDD-NOS group , which was significantly higher than the mean CARS score of the non-ASD group , which in turn was significantly higher than the mean CARS score of the no diagnosis group .
Similar results were found in the 4-year-old sample. There was a main effect of diagnostic group = 216.37, p< 0.001) and post hoc comparisons indicated that the autistic disorder sample had the highest mean CARS score , which was significantly higher that the mean CARS score of the PDD-NOS group , which was significantly higher than the mean CARS score of the non-ASD group , which was significantly higher than the mean CARS score of the no diagnosis group .
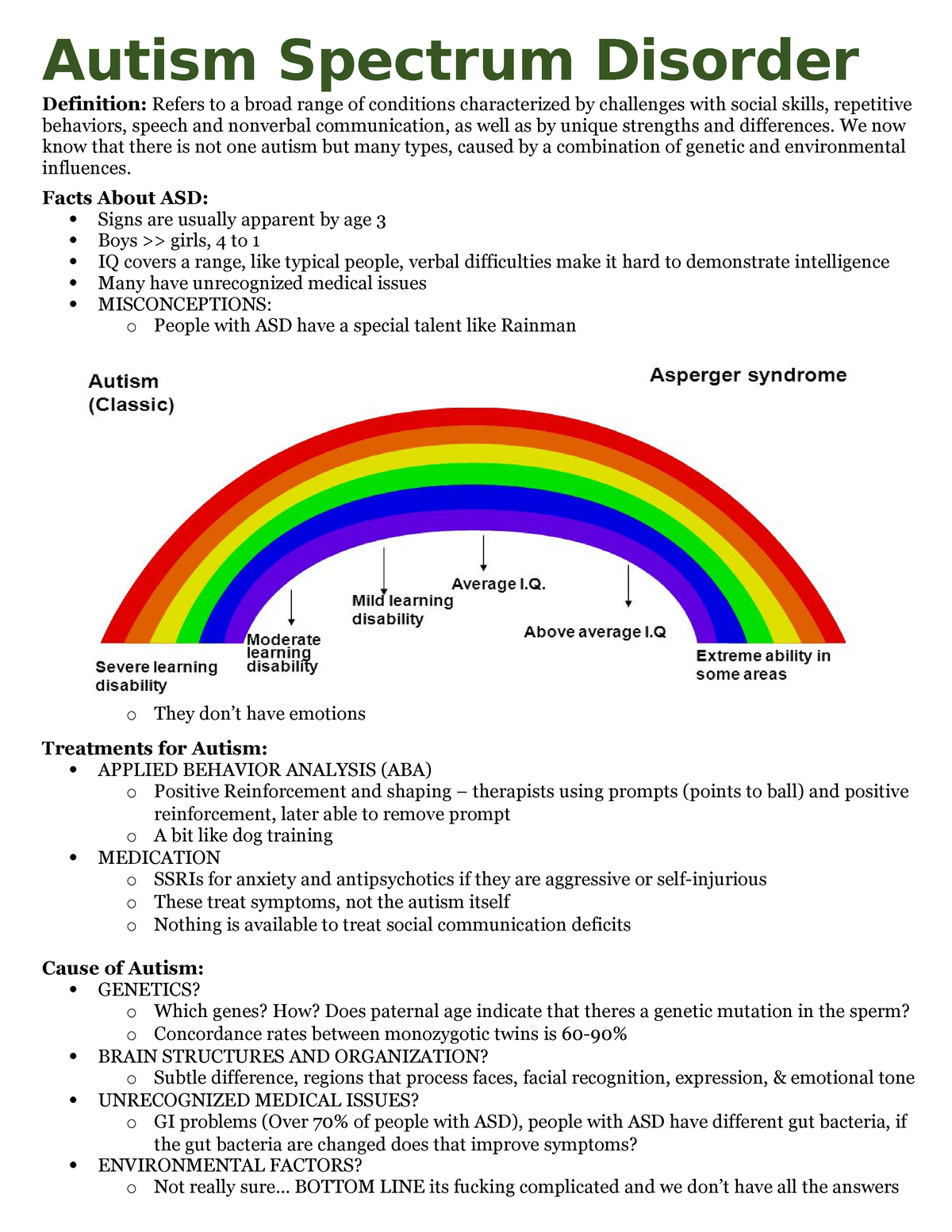
Signs And Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disability caused by differences in the brain. Some people with ASD have a known difference, such as a genetic condition. Other causes are not yet known. Scientists believe there are multiple causes of ASD that act together to change the most common ways people develop. We still have much to learn about these causes and how they impact people with ASD.
There is often nothing about how people with ASD look that sets them apart from other people. They may behave, communicate, interact, and learn in ways that are different from most other people. The abilities of people with ASD can vary significantly. For example, some people with ASD may have advanced conversation skills whereas others may be nonverbal. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives others can work and live with little to no support.
ASD begins before the age of 3 years and can last throughout a persons life, although symptoms may improve over time. Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life. In others, symptoms may not show up until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD gain new skills and meet developmental milestones, until around 18 to 24 months of age and then they stop gaining new skills, or they lose the skills they once had.
Don’t Miss: Puzzle Symbol For Autism
Causes And Risk Factors
We do not know all of the causes of ASD. However, we have learned that there are likely many causes for multiple types of ASD. There may be many different factors that make a child more likely to have an ASD, including environmental, biologic and genetic factors.
- Most scientists agree that genes are one of the risk factors that can make a person more likely to develop ASD.4, 19
- Children who have a sibling with ASD are at a higher risk of also having ASD. 5-10
- Individuals with certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis, can have a greater chance of having ASD. 11-14, 20
- When taken during pregnancy, the prescription drugs valproic acid and thalidomide have been linked with a higher risk of ASD.15-16
- There is some evidence that the critical period for developing ASD occurs before, during, and immediately after birth. 17
- Children born to older parents are at greater risk for having ASD. 18
ASD continues to be an important public health concern. Like the many families living with ASD, CDC wants to find out what causes the disorder. Understanding the factors that make a person more likely to develop ASD will help us learn more about the causes. We are currently working on one of the largest U.S. studies to date, called Study to Explore Early Development . SEED is looking at many possible risk factors for ASD, including genetic, environmental, pregnancy, and behavioral factors.
What Is Autism Screening
Autism screening is usually administered by a pediatrician during a routine well-child checkup. The doctor may observe the child or ask you questions about his or her behaviors at home and while interacting with other children on the playground. The purpose of an autism screening is to identify common early signs of autism. The following are early signs of autism, however, they do not necessarily need to be present.
- Delays in communicating with others including speech and gestures
- Not responding to ones own name
- Getting upset over minor changes in routine
- Avoiding many, if not most, forms of physical contact
- Showing little interest in objects or people
The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests that autism screenings should be part of standard 18 and 24-month well-child checkups, whereas the National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities recommends that all children be screened at 9, 18, and 24 or 30 months.
Screenings administered during well-child checkups are only designed to indicate whether a child may be showing some early signs of autism. These screenings identify areas requiring further assessment and do not replace a formal diagnosis. Although many doctors follow the AAP and NCBDD guidelines, parents should also be proactive. If you suspect your child may have autism, please ask your childs pediatrician to administer screening or request a referral to a qualified specialist.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Restricted Or Repetitive Behaviors Or Interests
People with ASD have behaviors or interests that can seem unusual. These behaviors or interests set ASD apart from conditions defined by only problems with social communication and interaction.
Examples of restricted or repetitive interests and behaviors related to ASD can include:
- Lines up toys or other objects and gets upset when order is changed
- Repeats words or phrases over and over
- Plays with toys the same way every time
- Is focused on parts of objects
- Gets upset by minor changes
- Has obsessive interests
- Flaps hands, rocks body, or spins self in circles
- Has unusual reactions to the way things sound, smell, taste, look, or feel
Is Rett Syndrome An Asd
Children with Rett syndrome often have behaviors similar to autism, and experts used to group it among spectrum disorders. But now that itâs known to be caused by a genetic mutation, itâs no longer considered an ASD.
National Institute of Mental Health: “Autism Spectrum Disorders.”
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: “Asperger Syndrome Fact Sheet.”
Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry: âSpecifying PDD-NOS: A Comparison of PDD-NOS, Asperger Syndrome, and Autism.â
Psychiatric Clinics of North America: âThe autistic spectrum: subgroups, boundaries, and treatment.â
Spectrum: âReclassification of Rett syndrome diagnosis stirs concerns.â
Rettsyndrome.org: âWhat is Rett Syndrome?â
Autism Speaks: âAsperger Syndrome,â âAbout Autism: Why Was My Child Diagnosed with Autism? And What Does It Mean?â
Centers for Disease Control: âFacts About ASD.â
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
What Challenges Are Associated With Autism
Autism is often linked with physical, developmental or mental health conditions such as intellectual disability, epilepsy, gastro-intestinal issues, ADHD, dyspraxia, anxiety or depression.
However, many of the disabling challenges associated with autism come about when individuals dont have the respect, understanding and supports that allow them to be comfortable in a non-autistic world.
Autism Spectrum Rating Scales Complete Kit
| Item | |
|---|---|
| Autism Spectrum Rating Scales, Complete Kit | $495.00 |
| ASRS Complete Software Scoring Kit*DISCONTINUED | $0.00 |
| Autism Spectrum Rating Scales, Kit ages 2-5 | $295.00 |
| ASRS Software Scoring Kit for ages 2-5*DISCONTINUED | $0.00 |
| Autism Spectrum Rating Scales, Kitages 6-18 | $295.00 |
| ASRS Software Scoring Kit for ages 6-18*DISCONTINUED | $0.00 |
| ASRS Parent Response Forms, ages 2-5, pkg/25 | $88.00 |
| ASRS Teacher Response Forms, ages 2-5, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Short Response Forms, ages 2-5, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Parent QuikScore Forms, ages 2-5, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Teacher QuikScore Forms, ages 2-5, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Short QuikScore Forms, ages 2-5, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Parent Response Forms, ages 6-18, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Teacher Response Forms, ages 6-18, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Short Response Forms, ages 6-18, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Parent QuikScore Forms, ages 6-18, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Teacher QuikScore Forms, ages 6-18, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Short QuikScore Forms, ages 6-18, pkg/25 | $80.00 |
| ASRS Scoring Software, unlimited use*DISCONTINUED | $0.00 |
You May Like: Dyslexia And Autism In Adults
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school are often first recognized by parents and teachers and then evaluated by the schools special education team. The schools team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend these children visit their primary health care doctor or doctors who specialize in ASD for additional testing.
Parents may talk with these specialists about their childs social difficulties including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication issues may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. Parents may also find that their child has trouble forming friendships with peers.
Do Symptoms Of Autism Change Over Time
For many children, symptoms improve with age and behavioral treatment. During adolescence, some children with ASD may become depressed or experience behavioral problems, and their treatment may need some modification as they transition to adulthood. People with ASD usually continue to need services and supports as they get older, but depending on severity of the disorder, people with ASD may be able to work successfully and live independently or within a supportive environment.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
How Could The Levels Of Autism Spectrum Disorder Be Diagnosed
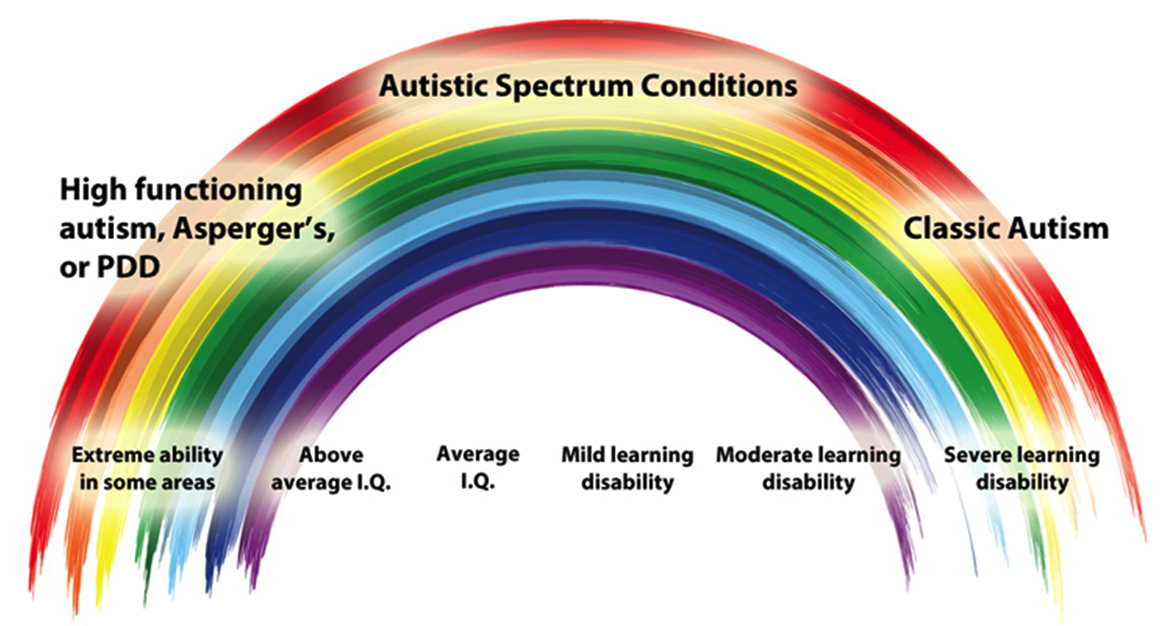
To get diagnosed as having autism, there is no medical testing, for example, blood testing, imagining test or scan test. Instead of those testings, behavioral symptoms, communication problems and family history are taken into account in order to help to rule out any potential genetic disorders or conditions.
Experts will ask a variety of questions about an individuals daily habits and aspects of their social life. They may refer the individuals for psychological testing and in order to that they are consulted to mental health professionals, such as psychologists or psychiatrists. Diagnosis is based on the level with which the symptoms are most consistent.
It should be remembered that levels of autism spectrum disorder are not black and White, which means they are not certain. Not each individual with autism clearly fits into one level. However, they can provide a useful baseline in order to help experts come up with effective management plans to set achievable goals.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Difficulty With Verbal Communication
A child with HFA will typically have no problems understanding language. Learning individual words, grammar rules, and vocabulary may not be an issue for them.
The use of language to communicate, however, can be problematic. Someone with HFA may have difficulty understanding sarcasm, metaphors, or idioms. This is known as “pragmatic” language.
In addition, some people with HFA may struggle to speak when under stress or overwhelmed.
Research Validating The Autism Research Evaluation Checklist
Users frequently have questions about interpreting ATEC scores and research validating the ATEC for evidence-based treatments. Here we report the results of the subgroup analyses of an observational cohort of children whose parents completed the Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist over the period of several years. A linear mixed effects model was used to evaluate longitudinal changes in ATEC scores within different patient subgroups. All groups decreased their mean ATEC score over time indicating improvement of symptoms, however there were significant differences between the groups. Younger children improved more than the older children. Children with milder ASD improved more than children with more severe ASD in the Communication subscale. There was no difference in improvement between females vs. males. One surprising finding was that children from developed English-speaking countries improved less than children from non-English-speaking countries.
You May Like: What Is The Symbol For Autism
Influence Of The Cars Cutoff On Diagnostic Agreement
To assess the influence of a CARS ASD cutoff on rates of agreement among autism diagnostic instruments and clinical judgment, kappa analyses were conducted to assess agreement for ASD diagnoses based on DSM-IV criteria, the ADOS, and the CARS using the traditional CARS cutoff of 30 and the proposed ASD cutoff score of 25.5. Kappa analyses were conducted with sub-samples of the original 2-year-old and 4-year old samples children were excluded if they did not have sufficient ADOS data available. Levels of clinical significance are defined by criteria.
Using the CARS cutoff of 30 for the children in the 2-year-old sample, there was 76% agreement and 268 cases of agreement between ASD diagnoses made by the CARS and diagnoses based on DSM-IV criteria. In the sample, 155 children received ASD diagnoses from both the CARS and clinical judgment based on DSM-IV criteria, 5 children received diagnoses from the CARS but did not receive a diagnosis based on DSM-IV criteria, 81 children met DSM-IV criteria for ASD diagnoses but did not meet criteria on the CARS, and 113 children did not receive a diagnosis from the CARS or clinical judgment. Kappa analyses revealed fair agreement between the CARS and DSM-IV criteria using a cutoff score of 30 on the CARS.
The Michigan Autism Spectrum Questionnaire: A Rating Scale For High
M. Ghaziuddin
1Department of Psychiatry, University of Michigan Medical Center, Plymouth Road, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-0277, USA
2Center for Statistical Consultation and Research , University of Michigan Medical Center, Plymouth Road, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-0277, USA
Abstract
Although the DSM-5 has recently created a single category of autism spectrum disorder , delineation of its putative subtypes remains clinically useful. For this process, screening instruments should ideally be brief, simple, and easily available. The aim of this study is to describe the validity of one such instrument. We administered the Michigan Autism Spectrum Questionnaire , a 10-item questionnaire, to 42 patients with ASD and 18 patients with other psychiatric disorders . Responses to each item were scored from 0 to 4 yielding a total score of 30. Patients with intellectual disability were excluded. As a group, patients with ASD scored higher than those with other psychiatric disorders . Within the ASD group, a linear discriminant analysis found that the best cut-off points were 22 or above for Asperger syndrome, 14 to 21 for autism/PDDNOS, and less than 14 for those with other psychiatric disorders. We propose that the MASQ can be used as a brief measure to screen high-functioning ASD from other psychiatric disorders and to identify its possible subtypes.
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
Read Also: Lifespan Of Autistic
Social Communication / Interaction Behaviors May Include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Tending not to look at or listen to people
- Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing or showing things to others
- Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or to other verbal attempts to gain attention
- Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions