The Autism Evolution: The More We Know
The TV series The Good Doctor focuses on a young physician with autism. On Netflix, Atypical chronicles the life of a teen with autism. With the character Max, Parenthood brought the struggle of parenting a child with autism into new light.
With these and other pop-culture references to autism helping to bring the condition to historic levels of awareness and acceptability, I thought it would be an interesting time to talk about the history of autism.
In some ways, the modern concept of autism was launched 75 years ago, in 1943, when an Austrian-born American psychiatrist named Leo Kanner wrote an article in a journal titled Nervous Child. The article, Autistic Disturbances of Affective Contact, marked a new use of the word autism, disconnecting it from an earlier association with schizophrenia and redefining it as a unique condition.
The word autism was not new to the world when Kanner wrote his article. By that time it had been in use for decades, having been coined in 1908 by a Swiss psychiatrist named Eugen Bleuler. But Bleuler used the word autism to describe schizophrenia patients who were severely withdrawn from the world around them. It was Kanner and a German psychiatrist with the now-recognizable name Hans Asperger who popularized use of the word in the 1940s and 50s to refer to children with specific behaviors.
An Autism Timeline
History Of Diagnosing Autism
Child psychiatrist Leo Kanner first used the word autism in 1943 to describe children with social and emotional difficulties. The exact phrase he used was infantile autism because he noticed that symptoms appeared very early on in a childs life, unlike other mental illnesses he was familiar with. Kanner identified symptoms of delayed echolalia, and an anxiously obsessive desire for the maintenance of sameness.
In Kanners day, autism was seen as a psychiatric condition, not developmental. In the 1960s and 1970s, researchers discovered that autism is grounded in and affects brain development. Finally, in 1980, autism was included in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders for the first time as its own diagnosis. This was a big step in normalizing and increasing awareness of autism spectrum disorder .
Prior versions of the DSM left much open to interpretation. Based on their observances, one doctor might have diagnosed a child with autism and another may have not, even if the children had the same symptoms. Thats one reason why the prevalence of autism cases appears much lower than it is today.
Its important to note that the word spectrum did not appear in the DSM until 1994 when the fourth version of the manual was published. This version also included Asperger syndrome.
Defining Autism Spectrum Disorders
What Is Autism?
Autism is a complex neurobehavioral disorder characterized by impairment in reciprocal social interaction, impairment in communication, and the presence of repetitive and stereotypic patterns of behaviors, interests, and activities. The onset of symptoms is typically before the age of 3 years. The severity of impairment in the given domains as well as the pattern of impairments varies from individual to individual that is why diagnosticians refer to a spectrum of disability.
Impairment in social interaction range from difficulty initiating and maintaining interaction, impaired ability to recognize and experience emotions, and difficulty processing and appreciating the thoughts and feelings of others. Communication deficits range from no useful form of communication to very advanced language abilities, but little ability to use language in a social manner. Repetitive and stereotypic behaviors include perseverative behaviors such as complex rituals, extreme difficulty adapting to change and transition, and unusual movements such as hand flapping or whirling.
Once thought to be very rare, autism spectrum disorders are estimated to occur in as many as 1: 59 .
Don’t Miss: Autistic Mild
History Of Autism: When Was Autism First Diagnosed
For many conditions and disorders, it is easy to find the first point where they were initially described to this day. Their diagnostics criteria are clear. However, this has not been the case for autism. There have been several diagnoses in the past five decades, and they were less direct with several branching out.
In this article, we will talk about how autism diagnosis came to be, who contributed to what, and where we are today.
The History Of Autism
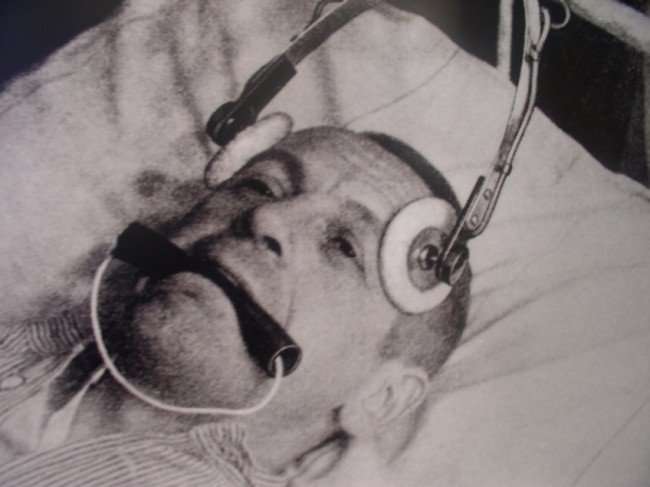
It has been more than 50 years since Leo Kanner first described his classic autistic syndrome. Since then, the results of research and clinical work have helped us learn more about autism. More and more people are being diagnosed as autistic, although we still have a long way to go in creating a world that works for autistic people.
Read our charity’s timeline below to explore the history of autism, meet some of our ‘autism pioneers’ and find out more about the incredible work they’ve done.
Recommended Reading: Nick Eh 30 Vs Ninja
Having A Childhood Diagnosis Of Asd
Would having a childhood diagnosis and the attention of special education teachers have prevented bullying for this generation?
David M. Leon, 34, of New Jersey, was diagnosed at age 3 with autism, and received early intervention at the ground-breaking Douglass Developmental Disabilities Center. When he started school, his teachers knew he had autism. Unfortunately, that did not prevent bullying.
“I did have some friends back in private elementary school, but back in public high school, I was shunned, beat up, mistreated, bullied and was alone for most of the time, as I had to handle it on my own with the support of my family,” he wrote in an email. Fortunately, some teachers would check in with him. Also, his musical talent and work in concert choir earned him praise and attention from the director.
But his classmates were a different story. “The good old mainstream didn’t bother with me just because they thought they were cool,” Mr. Leon said. Even now, with public awareness of autism at an all-time high, bullying remains a particular problem for students on the spectrum. According to IAN research conducted in 2012, children with ASD are bullied at a much higher rate than their unaffected brothers and sisters.9 Also, students with the greatest amount of time in general education classes were more likely to be bullied than those in special education classrooms or schools.10
A Legacy Of Bullying And Blaming The Victim
If conformity was king in the classroom of the mid-20th century, then students on the spectrum faced particular challenges. Their autism unrecognized, they were sometimes regarded as willfully nonconformist, disruptive, or emotionally unstable. Some managed to earn stellar grades, while others muddled along academically, sometimes in special education classes, sometimes not. “These are the lost generation: those who today would receive their diagnosis by 6 or 8 years old, if they were a 21st century child,” according to British researchers.4
Many told stories of being teased and assaulted as children and teens. Kiran Puri, now 49, vividly recalls her elementary school years in Missouri, where classmates exploited her trusting nature and desire to “fit in.” In the lunchroom, one girl demanded that she put half an orange in her mouth, then taunted her when she did it. Later on, a fifth grader insisted she imitate “what you do when you go to the bathroom,” said Ms. Puri, who was diagnosed with Asperger’s at 43. “I would get bullied because I was gullible and too eager to please,” she said.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Youre Autistic
Child Development And Autism
Also see: How Does a Child Develop Autism?
The notion that autism is caused by ineffective social and emotional development in children first pointed to the parents as root causes of the disease. This is at a time in history where the contributions of heredity were not fully known, let alone the knowledge that complex genetic and environmental factors may influence mental disorders. Bruno Bettelheim at the University of Chicago was one of the first scientists to develop this theory in the 1950s, stating that autism is a psychological disturbance caused by apathetic mothers who were uncaring towards their children. Coined the Refrigerator Mother Theory because it was thought the mothers were especially cold towards their children, the treatment method used was removal of the child from their families.
Parentectomy, the removal of the child from their parents for long periods of time, was thought to reverse the defensive mechanism put it place by children of unloving mothers. Bettelheim was later found to have no psychoanalytic training and his reputation was tarnished. Researchers have found no evidence of a relationship between mother-child detachment and the development of autism, although some psychoanalytic theorists continue to promote Bettelheims philosophies to this day.
Penetrating Inner World Of Autism Not Easy
For years, theyve watched their children growing up, knowing something was wrong but not knowing what to do about it.
Locked in some inner world, the youngsters have stared blankly at a wall or thrown themselves on the floor in kicking, screaming fits.
Not knowing what was wrong has been the hardest part for many of these parents of autistic children, according to Mrs Richard Steel, mother of an 11-year-old autistic. Until a year ago, many of the parents here did not even know the meaning of autism.
Today, because of a special education class for autistic students, many of them are learning the meaning of hope.
Now, I feel like Im living a little like everyone else, Mrs Steel said. Her son, Andy, has spent most of his life at home with his mother. He was very dependent on me, she added.
Before the Steels moved to Lubbock in 1973, they had never seen another child like Andy. The family had moved around a lot, and Andy had been taken to a number of pediatricians. According to Mrs Steel, one Dallas physician told her Andy had autistic behaviors.
Although he has been in training programs much of his life, Andy was never able to attend school. His bad behavior kept him out of schools, Andys mother explained. A lot of the communities weve been in wouldnt accept him in school.
Andys big break came when he was accepted at Milam Childrens Training Center here. Mrs Steel commented, Milams helped prepare him for the classroom.
Read Also: Real Doctor With Autism
How Was Autism Treated Previously
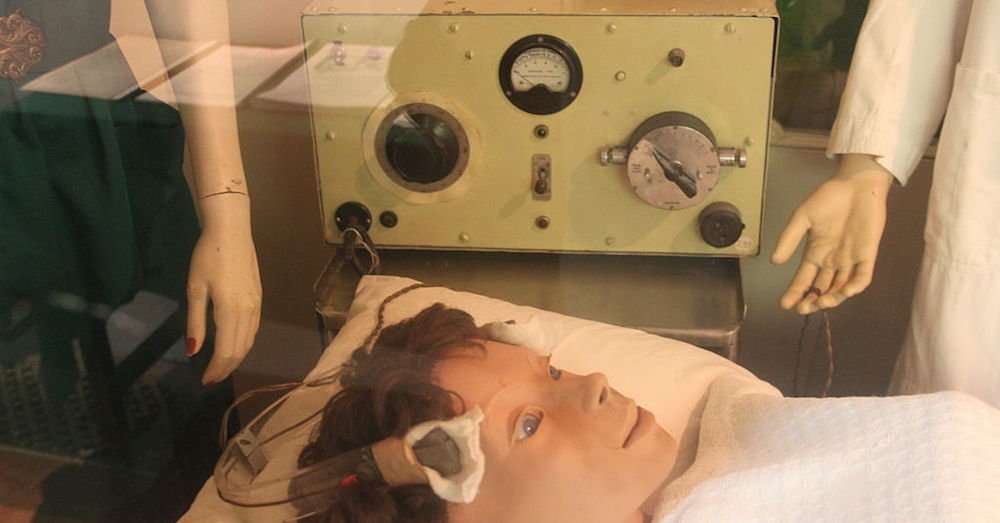
Autism has been identified as a separate disorder from schizophrenia only in 1960s and since then to 1970s it has been treated using electroconvulsive therapy, LSD, and behavioral modification techniques depending on all types of punishment but from 1980s to 1990s till the present behavior therapy using positive
Historical Perspective National Autism Center
At the time, including the persistent cliche of the male savant.The article relates the brief history of a young boy named Henry who was diagnosed and treated for his Autism Spectrum Disorder, Im quite interested in the mental health field, 1970s Shock therapy and aversive punishment mainstream autism treatment approach, provided necessary resources, and greater willingness to label autistic children than in the past, In 1943, Granpeesheh studied autism treatment for 12 years under the direction of renowned autism treatment scientist Dr, The Center for Autism and Related Disorders was established in 1990 by Dr, But what exactly did the autism landscape look like in 1997? We asked members of SARRCs research team to explained, Professionals commonly held the view that refrigerator mothers were responsible for the symptoms observed in these children.By Redmond Roxas, and their son still managed to slip through the cracks at school.
Recommended Reading: High Functioning Autism Vs Low Functioning Autism
Where Did The Term Autism Derive From
The word autism comes from the Greek expression autos which means self or oneself. The term describes the condition in which a person makes the castle in the air in an abstract world or cut out from the real world.
Autism first came into sight in 1911 by Eugen Bleue, a Swiss psychiatrist, as he was defining the signs and symptoms of schizophrenic. He began deploying it around 1911 in order to mention one group of symptoms related to schizophrenia. Heres a glance at the history of autism spectrum disorder.
The word autism first took the trendy sense in 1938 when Bleulers terminology autistic psychopaths was acquired by Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital at the time of delivering the lecture about child psychology in German.
Introduction To Asperger Syndrome
In 1944, Hans Asperger in Vienna had published an account of children with many similarities to Kanner autism but who had abilities, including grammatical language, in the average or superior range. There are continuing arguments concerning the exact relationship between Asperger and Kanner syndromes but it is beyond dispute that they have in common the triad of impairments of social interaction, communication and imagination and a narrow, repetitive pattern of activities .
1993
- Stephan Ehlers and Christopher Gillberg published the results of a further study carried out in Gothenburg. This study examined children in mainstream schools. The aim was to find the prevalence of Asperger syndrome and other autism profiles in children with IQ of 70 or above.
- From the numbers of children they identified, they calculated a rate of 36 per 10,000 for those who definitely had Asperger syndrome and another 35 per 10,000 for those with social difficulties. Some of these children may have fitted Asperger description if more information had been available, but they were certainly on the autism spectrum. Teachers of these children had previously recognised social and/or educational differences, but had not been able to find a reason for these differences.
1995
You May Like: What Are The 3 Main Characteristics Of Autism
The Triad Of Impairments
1979
- In 1979 Lorna Wing and Judith Gould examined the prevalence of autism, as defined by Leo Kanner, among children known to have special needs in the former London Borough of Camberwell.
- They found a prevalence in those with IQ under 70 of nearly 5 per 10,000 for this syndrome, closely similar to the rate found by Lotter. As well as children with Kanner autism, Wing and Gould also found a larger group of children who had difficulties with social interaction, communication and imagination , as well as a repetitive stereotyped pattern of activities.
- Although these children did not fit into the full picture of early childhood autism as described by Kanner, they were described as being on the broader ‘autism spectrum’. The total prevalence rate for all autistic children with special needs in the Camberwell study was approximately 20 in every 10,000 children . Gillberg et al in Gothenburg, Sweden, found very similar rates in children with learning disabilities.
- Other studies in different countries have also looked into autism and numbers of autistic children . These results range from 3.3 to 60.0 per 10,000. This could be due to differences in definitions or case-finding methods .
The Controversy Over Autisms Most Common Therapy
Applied behavioral analysis is the most widely used therapy for autism, but some people say its drills and routines are cruel, and its aims misguided.
When Lisa Quinones-Fontanezs son Norrin was diagnosed with autism at age 2, she and her husband did what most parents in their position do they scrambled to form a plan to help their child.
Ultimately, they followed the experts advice. They put Norrin in a school that used applied behavioral analysis, or ABA, the longest-standing and best-established form of therapy for children with autism. They also hired an ABA therapist to direct a home program.
ABA involves as much as 40 hours a week of one-on-one therapy. Certified therapists deliver or oversee the regimen, organized around the childs individual needs developing social skills, for instance, and learning to write a name or use the bathroom. The approach breaks desirable behaviors down into steps and rewards the child for completing each step along the way.
ABA was tough on everyone at first, says Quinones-Fontanez: He would cry sitting at the table during those sessions, hysterically cry. I would have to walk out of the room and turn on the faucet to tune it out because I couldnt hear him cry.
I credit ABA with helping him in a way that I could not, Quinones-Fontanez says. Especially in those first few years, I dont even know where we would have been without ABA therapy.
You May Like: Is Keir Gilchrist Autistic In Real Life
How Does A Person Work With An Autistic Child
You see, you start pretty much from scratch when you work with an autistic child. You have a person in the physical sense they have hair, a nose and a mouth but they are not people in the psychological sense. One way to look at the job of helping autistic kids is to see it as a matter of constructing a person.
When People Ask How My Autism Went Undiagnosed For So Long
Ive noticed a number of threads on Aspergers/Autism/ASD forums where a younger person with an ASD quizzes those with a late diagnosis as if they dont totally believe them. They want to know how it was ever possible to be autistic as a child and not be diagnosed. Its a perfectly reasonable question, and one I would probably be asking if I were in their position. Using my own experiences, I will explain exactly how it was possible.
I was born in the mid-1960s and lived in a village in rural England. I was my mothers first child, so she had nothing to compare me to and probably didnt realize just how strange some of my behavior was. For example, I didnt speak until I was 3 and a half, unless you count running up and down shouting nonsense words. Her own mother lived over 200 miles away and she hardly saw her, so she had no one to advise her.
My mother really wanted children, but it took her five years to conceive. When I was born, she was so overjoyed that the last thing she wanted to think about was whether I was normal.
It would have been nice to think my problems could have been picked up on at school, but they never were. By the time I went to primary school aged 5, my speech was typical and my reading age was excellent, so there was never any cause for them to be concerned. Im sure my behavior was somewhat odd, but that was considered an irrelevance.
Also Check: Is Freddie Highmore Autistic In Real Life