What Are Some Common Signs Of Asd
Even as infants, children with ASD may seem different, especially when compared to other children their own age. They may become overly focused on certain objects, rarely make eye contact, and fail to engage in typical babbling with their parents. In other cases, children may develop normally until the second or even third year of life, but then start to withdraw and become indifferent to social engagement.
The severity of ASD can vary greatly and is based on the degree to which social communication, insistence of sameness of activities and surroundings, and repetitive patterns of behavior affect the daily functioning of the individual.
Social impairment and communication difficultiesMany people with ASD find social interactions difficult. The mutual give-and-take nature of typical communication and interaction is often particularly challenging. Children with ASD may fail to respond to their names, avoid eye contact with other people, and only interact with others to achieve specific goals. Often children with ASD do not understand how to play or engage with other children and may prefer to be alone. People with ASD may find it difficult to understand other peoples feelings or talk about their own feelings.
Understanding The Three Levels Of Autism
Steven Gans, MD, is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
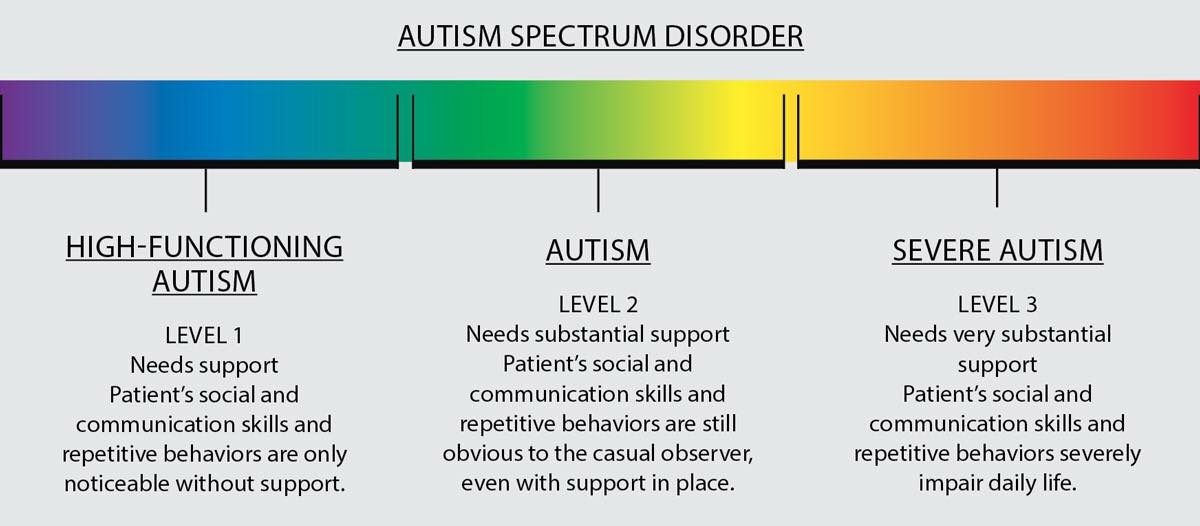
There are three levels of autism spectrum disorder , which are described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition .
Each person with ASD is further diagnosed with either ASD level 1, level 2, or level 3, depending on how severe their disorder is and how much support they need in their daily life.
The levels range from least to most severe, with ASD level 3 describing an individual who has the most severe level of ASD symptoms, and ASD level 1 describing someone with symptoms on the milder end of the spectrum.
This article discusses the symptoms that are typical of each of the three ASD levels. It also includes realistic examples of the strengths and limitations that are unique to each level.
Verywell / Cindy Chung
Are Repetitive Behaviors A Problem
These types of behaviors aren’t unique to people with autism. Most people engage in some such behaviors. Common forms of perseveration include:
- Nail biting
- Compulsive cleaning
- A “need” to watch the same TV shows or sporting events without fail
For some people with autism, the problem of perseveration is really no problem at all, since it only arises at the same times as it would for other peopleusually under stressand the behaviors are fairly unobtrusive.
Perseveration can even be a plus for people with autism, since it may relate to a passionate interest that can lead to friendships or even careers. Someone with perseverative interest in computer games, for example, can join gaming clubs and find others with a similar passion.
For many people with autism, though, perseveration or repetitive behavior is not only disturbing to others but it’s also a major roadblock to communication and engagement in the world.
A person who compulsively flicks his hands to the exclusion of anything else is clearly unable to attend to the world around them or take part in real-world activities.
And while there is nothing intrinsically wrong with talking about the same subject in the same way over and over again, such behavior can cause a variety of social and practical problems.
Don’t Miss: How To Hypnotize A Child
Level : Requires Substantial Support
People with ASD level 2 will have more obvious problems with verbal and social communication than those diagnosed with level 1. Likewise, they will find it harder to change focus or move from one activity to the next.
Children with level 2 tend to have very narrow interests and engage in repetitive behaviors that can make it difficult for them to function in certain situations. For example, they may pace back and forth or say the same thing over and over again.
A person diagnosed with ASD level 2 tends to speak in simple sentences and also struggles with nonverbal forms of communication.
Autism Aspergers Advocacy Australia
By Aaron Kandola, Reviewed by Karen Gill, MD
Autism is a spectrum disorder that causes social and behavioral problems. There are three different levels of autism, which range from mild to severe.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , about one in 59 children have autism. Signs of the condition are usually present at a young age, but occasionally people do not receive a diagnosis until adulthood.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 , doctors categorize autism by assigning level 1, 2, or 3 to two of the domains of symptoms.
One severity score is for impairment in social function, while a second severity score is for restrictive, repetitive behaviors. The levels the doctor assigns depend on the severity of the symptoms.
A correct autism diagnosis that includes the levels of severity can help doctors and other specialists work with the individual to provide the right treatment and support. In this article, learn more about the levels of autism.
Don’t Miss: Asd Level 3
Assigning A Functioning Level
At the completion of the child’s in-depth testing and assessment, specialists assign one of three autism functioning levels from mild to severe based on DSM-5 criteria for this assignment. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention factsheet gives an example of rating various areas of function, such as intelligence and social and communication skills. The following sections summarize the DSM-5 three levels of autism as outlined by Autism Speaks.
Variations In The Level Of Impairments
Every person with autism is different, and there can variations in the level of each functional impairment in the same person. In addition, among individuals diagnosed with the same level of autism, some dysfunctions might be more prominent in some people than in others. The functioning level assigned to a child or adult also serves as a guide for what treatments, interventions, and support he or she needs to achieve the best functional outcome.
You May Like: Does Freddie Highmore Have A Twin
Understanding The 3 Different Levels Of Adult Autism
Autism spectrum disorder, or ASD, is complex and nuanced.
Usually, there is not just one but several issues that affect a person with ASD. These can include symptoms related to the condition. Additionally, there also can be secondary symptoms. These are typically connected to other mental health issues that also go along with autism.
To break down the symptoms of autism into more distinct categories, researchers have created a system. There are three categories, or levels, of autism. The criteria for these categories is formalized in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, or DSM-5.
Of course, nobody likes being labeled. And these classifications are not meant to discriminate. Rather, they help to better focus the care, attention, and services needed to best help someone with autism.
Lets take a closer look at all three.
Level : Require Substantial Support
- A deficit with verbal/nonverbal communication skills.
- Limited or no social interaction and no respond to people trying to interact with them
- Interaction is possible up to a limit with non-verbal communication
- Nervousness and shyness when watched by unfamiliar faces
- reduced ability to function and participate in their daily activities
- Repetitive behaviour is obvious
Read Also: How To Set Up A Classroom For Students With Autism
The Autism Diagnosis Process
Now, you are probably wondering: but how do I know that these unique symptoms are autism? To be diagnosed with autism , the Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee explains that there have to be a couple of certain symptoms across multiple contexts of social interaction and communication.
These contexts include:
- Is it difficult for them to hold a back-and-forth conversation?
- Are their responses to social situations unnatural?
- Have they spoken few or no words by age two?
- Are they using words strangely or in an unnaturally flat voice?
- Are they not responding to their name even though their hearing is fine?
- Deficits in nonverbal communication.
- Is their body language abnormal?
- Is eye contact a challenge?
- Do you see them commonly rocking or flapping as a way to calm themselves?
- Do you notice an abnormal over or under-sensitivity to sensations?
- Deficits in developing and maintaining relationships.
- Are they having a hard time making friends?
- Is imaginative play a stretch when playing with other children difficult?
- Do they tend to line up toys instead of playing with them?
- Do changes to a game overly upset them?
Challenges In Severe Autism
The extreme behaviors of severe autism may result from frustration, sensory overload, or physical pain.
Some people with severe autism express themselves through frightening behaviors. If the behaviors can’t be managed, they can become dangerous.
In many cases, it’s not safe for family members to live with a severely autistic teen or adult.
Also Check: Life Expectancy Of Autistic Person
How Diagnosis Of Autism Changed With Dsm
The DSM is the official publication of the American Psychiatric Association which defines psychiatric and developmental disorders. While it has no legal status, the DSM does have an enormous impact on the way insurers, schools, and other service providers think about and treat autism.
Until 2013, the DSM described the autism spectrum as a disorder that included five distinct diagnoses. Asperger syndrome was, essentially, a synonym for “high functioning autism,” while autistic disorder meant almost the same thing as “severe autism.” People with PDD-NOS had some but not all of the symptoms of autism . Rett syndrome and Fragile X syndrome, rare genetic disorders, were also considered to be part of the autism spectrum.
Then, in May 2013, the DSM-5 was published. The DSM-5, unlike the DSM-IV, defines autism as a single spectrum disorder, with a set of criteria describing symptoms in the areas of social communication, behavior, flexibility, and sensory sensitivity Anyone who had already been diagnosed with one of those disorders was “grandfathered” into the new autism spectrum disorder. A new diagnosis, social communication disorder, was created to classify people with very mild versions of autism-like symptoms.
The Three Levels of Support
The autism spectrum is incredibly wide and varied. Some people with autism are brilliant while others are intellectually disabled. Some have severe communication problems while others are authors and public speakers.
Where Can I Get More Information

For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
You May Like: Nick Eh 30 Social Blade
Level : Requiring Support
A person who meets the criteria for level 1 may face social challenges that require some support.
They may find it difficult to:
- initiate conversations with others
- respond as others would expect
- maintain interest in the conversation
As a result, it can be hard to make friends, especially without the right support.
The person may also:
Terms For Types Of Autism That Are No Longer Used Today
When autism was categorized by types, the lines between the different types of autism could be blurry. Diagnosis was, and still is, complicated and often stressful for families.
If you or your child received a diagnosis before the DSM-5 changed, you may still be using the older terminology . Thats OK. Your doctor may continue to use those terms if they help.
Recommended Reading: Definition High Functioning Autism
How Autism Spectrum Disorders Are Described
Psychiatrists and other clinicians rely on the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders to define autism and its symptoms. The DSM-5 definition recognizes two main symptom areas:
- Deficits in social communication and interaction
- Restricted, repetitive behaviors, interests, or activities
These symptoms appear early in a childs developmentalthough diagnosis may occur later. Autism is diagnosed when symptoms cause developmental challenges that are not better explained by other conditions.
The definition of autism has been refined over the years. Between 1995 and 2011, the DSM-IV grouped Aspergers Syndrome and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified with autism. Aspergers syndrome was an autism spectrum disorder marked by strong verbal language skills and, often, high intellectual ability. PDD-NOS was a more general diagnosis for people who did not fit clearly into the other two categories.
However, the DSM-5 no longer recognizes Aspergers syndrome or PDD-NOS as separate diagnoses. Individuals who would previously have received either of these diagnoses may now receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder instead.
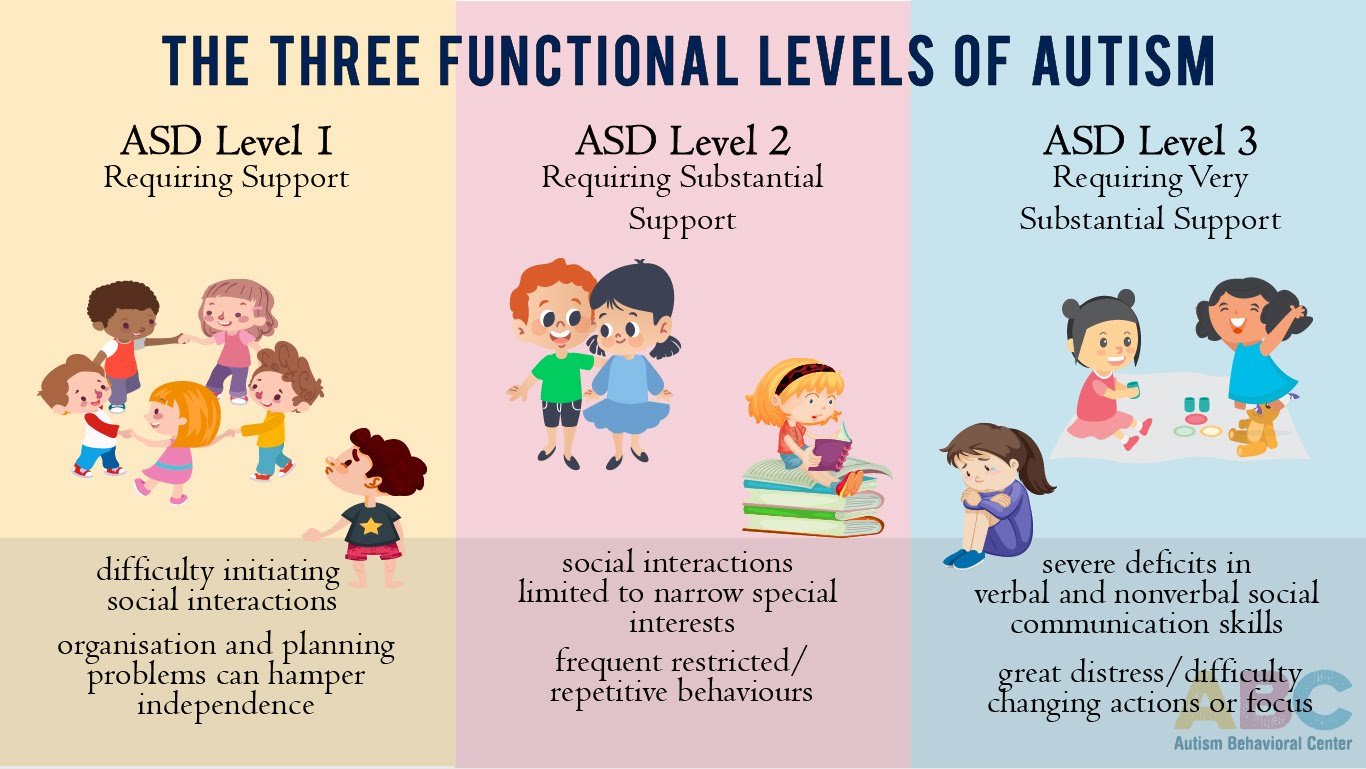
The Three Functional Levels Of Autism
When talking about Autism Spectrum Disorder , it features various levels starting from mild to severe symptoms. People diagnosed with the disorder are further diagnosed into the level of symptoms they have. The levels pave the way for more clarity for a persons diagnosis of where they fit in on the spectrum.
To be precise, there are three levels of ASD level 1, level 2, and level 3. These levels define the severity of the autistics social skills and behaviours the two domains of symptoms to which the levels are assigned. They are based on the individuals strengths and limitations in communicating, adapting to new situations, and managing daily lives, indicating the support they need. Lets look at each of them in detail.
ASD Level 1 Requiring Support
Level 1 is the least severe and most high-functioning of all. This is mild autism. People suffering from Level 1 ASD find it difficult to initiate social interactions they may not understand cues and body language at times. They even have trouble organising and planning, which can come in the way of their independence. Level 1 autistics may even want to stick to their already established routines and not welcome changes or unexpected events. However, they only require little support to function according to their routine.
ASD Level 2 Requiring Substantial Support
ASD Level 3 Requiring Very Substantial Support
Recommended Reading: Is The Actor In The Good Doctor Autistic
The Different Levels Of Autism
Does the phrase if youve met one person with autism, youve met one person with autism ring a bell? It might seem like a no-brainer, but it is surprising how often we forget that autism spectrum disorder is exactly that: a range of symptoms on a spectrum.
Asking questions is an important part of the human journey, and we want to celebrate that journey of understanding each other. So weve gathered a few of those questions on this topic from people like YOU. Hopefully, we can shed some light on it!
What Are The Dsm
In 2013, the American Psychiatric Association released the fifth edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders .
The DSM-5 is now the standard reference that healthcare providers use to diagnose mental and behavioral conditions, including autism.
By special permission of the American Psychiatric Association, you can read the full-text of the new diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder and the related diagnosis of social communication disorder below.
Also see: Answers to frequently asked questions about DSM-5 criteria for autism
Also Check: Optimal Outcome Autism
What Are The Three Types Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Just like there is more than one type of anxiety disorder, diabetes, or developmental disorder, there is more than one type of autism. In anxiety, for example, there are five completely separate types, each with their own symptoms, some unique to the other types and some types sharing similar symptoms on a spectrum. Autism Spectrum Disorder is considered the broad term for autism, but there are actually three separate sub-types that fit within the ASD category.
When you think about a spectrum, think of seeing different shades of blue all together in one band. All of the shades are technically blue, but they range from lightest to darkest. You can also think of a rating scale with two extremes or opposite points. The term autism spectrum disorder should be viewed similarly there is a spectrum of symptoms that someone with autism can exhibit, ranging from mild to severe.
You may be one of the millions of people around the world affected by autism. Or you might know someone personally affected by the disorder or have realized its impact on people and the world. Either way, it is encouraged that you educate yourself on what autism is and what the three types of autism spectrum disorders are. In doing so, you will have a better understanding about the disorder, which can help you to interact and communicate more effectively with individuals who are on the spectrum and to put yourself in their shoes.
The three types of ASD that will be discussed are:
Other Terminology You May Have Heard For Types Of Autism
Terms like mild or high functioning arent official diagnoses. Some people find these terms useful, but many in the autistic community havent found them to be helpful or accurate, largely due to the range of abilities that can be present in an autistic person.
You may also have heard about three levels of autism, with level 1 being the mildest and level 3 the most severe.
Don’t Miss: Is Keir Gilchrist Autistic