Autism Spectrum Disorder 29900
A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by the following, currently or by history :
Specifiers For Autism Spectrum Disorder
DSM-5 has introduced specifiers to help the clinician to describe associated or additional conditions, eg intellectual impairment, language impairment, genetic conditions, behavioural disorder, catatonia.
One of the specifiers relates to the severity of social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behaviour. There are three levels: requiring support, requiring substantial support, requiring very substantial support. This can allow the clinician to give an indication of how much someones condition affects them and how much support an individual needs.
However, people who receive a diagnosis are not automatically eligible for support. DSM-5 explains that severity levels may vary by context and also fluctuate over time, that the descriptive severity categories should not be used to determine eligibility for and provision of services, and that ‘these can only be developed at an individual level and through discussion of personal priorities and targets’.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know the primary causes of ASD, but studies suggest that a persons genes can act together with aspects of their environment to affect development in ways that lead to ASD. Some factors that are associated with an increased likelihood of developing ASD include:
- Having a sibling with ASD
- Having older parents
- Having certain genetic conditions
- Having a very low birth weight
You May Like: How To Make Friends With Autism
From A Single Autism Diagnosis To A Broad Spectrum
The most salient change from the DSM-IV to a new version DSM-5 has been the understanding of autism as a spectrum varying in severity and functioning. Over time, researchers have used a lot of resources to identify a clear etiology for autism. It seems to us that the most likely cause might be a combination of different proteins and genes. Studies found dozens and hundreds of genes related to ASD but not a clear specific single one .
Another issue was that the profiles were not consistent. These two reason led to conceptualizing autism as a spectrum . The classification is as follows:
Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period
Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity must be present .
ASD can be diagnosed with or without accompanying language impairment.
Peculiar speech patterns are not required for a diagnosis. However, echolalia and idiosyncratic phrases are considered examples of Stereotyped or repetitive movements, use of objects, or speechone of four non-social features.
Any two of the following must be present : Stereotyped use of objects Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or non-verbal behavior Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus Hyper- or hypo-reactivity to sensory input or unusual interest in sensory aspects of the environment.
Hallucinations and delusions, which are defining features of schizophrenia, are not features of ASD.
Aspergers Disorder And The Broader Autism Spectrum
Aspergers disorder and the broader autism spectrum have their own interesting and complex, and to some extent, interrelated, histories. In some respects, Aspergers original report stood in contrast to Kanners earlier paper. The cases that Asperger described, all boys with marked social difficulties , somewhat presaged the awareness over the past decades of the broader autism phenotype . This awareness has also reflected the similarly growing awareness of the complexity of the genetics of autism . Until Wings review of Aspergers original paper , however, there was relatively little awareness of the condition . Wing herself saw the condition as clearly being part of the autism spectrum and her paper became the inspiration for what can only be described as a plethora of differing diagnostic views on the concept , with no fewer than 5 distinctive approaches to Aspergers disorder emerging .
Also Check: How To Get Custody Of A Autistic Child
Social And Linguistic Training As An Example Followed In Norway For Normalizing Social Functionning
When it comes to early intervention, Norway is no different from most western countries. Early intervention in children with ASD is still a little bit tricky. This is specially the case for girls and individuals in the higher end of the spectrum.
In both Sweden and Norway, there are public programs which provide early intervention for young children with ASD. Both countries use the supervision of special pedagogues and clinical specialists in order to provide an adapted learning environment to the child with ASD . So far, the national guidelines for both countries are quite general. There are regulations including all children with disabilities of course but when it comes to the actual intervention, it is a general practice to focus on the individual profile of each child and try to address his needs with the aim of improving at all different levels. As the word spectrum suggests, there is a huge variance in profiles dispite a similar diagnosis.
EIBI takes into consideration the present biological and environmental conditions and the potential impact and influence that these can have on the child’s functioning, which can include for instance play, social skills, empathy, etc. The main goal is to start simple from simple situations, use these as a basis for developing new skills and abilities and reduce deviant or undesired behaviors .
Dimensional Approach To Core Asd Symptoms And Dsm
The dimensional approach to DSM-5 captures the homogeneity of core ASD symptoms with the aim of relatively high specificity, while allowing for heterogeneity in the quantity and quality of these symptoms. For example, while individuals must meet two of the four broad principles within the RRBs domain to receive an ASD diagnosis, individuals can vary on the number of principles met and the quality or severity of these impairments. This flexibility was improved through DSM-5s addition of unusual sensory responses/interests as a principle within the RRBs domain, supported by research about its prevalence in ASD and its usefulness in differentiating ASD from other disorders . This new principle provides an additional symptom description through which individuals can meet diagnostic criteria.
Recommended Reading: Can’t Focus On Studying Adhd
What Is The New Diagnosis Of Social Communication Disorder Who Will It Affect
This new diagnosis applies to people who have persistent problems with the social use of language, but dont have restricted interests or repetitive behaviors.
Some people who would have previously received a diagnosis of PDD-NOS may now receive a diagnosis of social communication disorder. However, this should apply only to newly diagnosed people. It should not be applied retroactively to someone already diagnosed with PDD-NOS under the DSM-IV criteria.
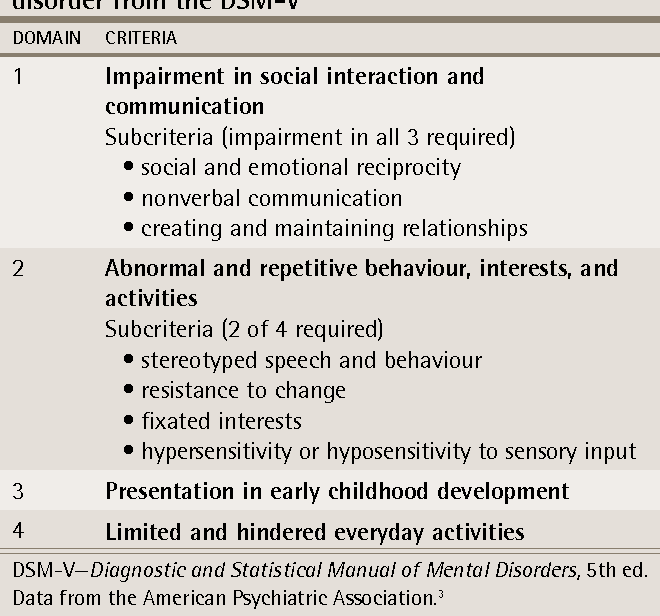
Diagnostic Criteria For Autism Spectrum Disorder In The Dsm
DSM stands for “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,” which is a manual published by the American Psychiatric Association. The manual includes classifications of psychiatric disorders for use by medical and mental health professionals. Clinicians may refer to versions of the DSM to look for diagnostic codes of different disorders and examine criteria for diagnosis. About 25% of the disorders are specific to children and are in the section of “Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence.” Autism and related disorders have been specifically included in different versions of the DSM since 1980.
The latest edition of the DSM, DSM-5, made significant changes to the diagnostic criteria for autism and related disorders. In DSM-IV, five separate diagnoses were classified under the heading “Pervasive Development Disorders:” Autistic disorder, Asperger Syndrome, Pervasive Development Disorder Not Otherwise Specified , Rett Syndrome, and Childhood Disintegrative Disorder. The Pervasive Development Disorder category no longer appears in DSM-5, and Autistic disorder, Asperger Syndrome, and PDD-NOS have now been combined into one label: Autism Spectrum Disorder .
Recommended Link
Don’t Miss: How Do You Punish An Autistic Child
What Are The New Criteria For Diagnosing Autism
The DSM-5 criteria for autism fall under two categories:
In addition, clinicians are asked to rate the severity of these problems, based on the level of daily support they require.
Read the full text of the DSM-5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder.
How will these DSM-5 changes affect people already diagnosed with Asperger syndrome, PDD-NOS or other previous autism categories?
The DSM-5 states, Individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnoses of autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
What if I or my child want to keep the diagnosis of Asperger syndrome?
Many people strongly identify with their diagnosis of Asperger syndrome. Healthcare providers can still indicate a diagnosis of Asperger syndrome in a patients medical record, alongside the current DSM-5 coding for autism spectrum disorder. Colleges and school districts may vary in their policies for educational records.
What is the new diagnosis of social communication disorder? Who will it affect?
This new diagnosis applies to people who have persistent problems with the social use of language, but dont have restricted interests or repetitive behaviors.
Is social communication disorder on the autism spectrum?
Have additional questions? Send them to
Associated Features Supporting Diagnosis
Many individuals with autism spectrum disorder also have intellectual impairment and/ or language impairment . Even those with average or high intelligence have an uneven profile of abilities. The gap between intellectual and adaptive functional skills is often large. Motor deficits are often present, including odd gait, clumsiness, and other abnormal motor signs . Self-injury may occur, and disruptive/challenging behaviors are more common in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder than other disorders, including intellectual disability. Adolescents and adults with autism spectrum disorder are prone to anxiety and depression. Some individuals develop catatonic-like motor behavior , but these are typically not of the magnitude of a catatonic episode. However, it is possible for individuals with autism spectrum disorder to experience a marked deterioration in motor symptoms and display a full catatonic episode with symptoms such as mutism, posturing, grimacing and waxy flexibility. The risk period for comorbid catatonia appears to be greatest in the adolescent years.
Read Also: What Are Symptoms Of Autism In A Child
Difficulties In Social Networking
A lot of children and adults with autism have trouble networking with social interaction. To be diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder, infants must have problems in the field of social interaction.
Signs of problems in this field include:
- Not using words to communicate with other people
- Not communicating at all
- Rarely responding while talking to others.
- Not communicating interests or successes with parents
- Seldom using or knowing signs such as nodding or smiling
- using only small facial features to connect
- Not expressing interest in peers or experiencing trouble making friends
- Not participating in creative play.
Summing Up On How To Cite A Dsm

The DSM-5 refers to a handbook used by clinicians and psychiatrists in the United States. Basically, the manual contains information regarding all mental-related health disorders for adults and children. When looking for descriptions, symptoms, and other details required for diagnosing psychological health conditions, writers use this manual. Then, other important details may include statistics about the gender differences concerning the psychiatric conditions, the age of onset, effects of management, and conventional treatment approaches. In this case, the APA 6th and 7th editions have specific guidelines that one should follow. Hence, some of the essential tips include:
1. Bibliographic entries in the 6th and 7th edition should appear as:
- Publishing Organization. . Title of the DSM-5 . DOI or Link
2. Bibliographic entries that contain a chapters title should appear as:
- The Publishing Organization. . Title of the chapter cited. In Title of the DSM-5 . DOI or Link
3. Parenthetical in-text citations in the APA 6th edition should appear as:
4. Parenthetical in-text citations in the APA 7th edition should appear as:
5. The main difference between APA 6th and 7th editions is the use of initials and versions in the in-text citation.
6. Students may use the acronym DSM-5 inside the text. In this case, APA formatting rules require one to write the full transcription of the acronym followed by its short form in the bracket.
Dont Miss: Can Autism Be Diagnosed By Blood Test
Also Check: How To Get Your Autistic Child To Talk
A022 Autismspectrum Disorder Without Disorder Of Intellectual Development And Withimpaired Functional Language
All definitional requirements forautism spectrum disorder are met, intellectual functioning and adaptivebehaviour are found to be at least within the average range , and there is marked impairment infunctional language relative to the individuals age, withthe individual not able to use more than single words or simple phrases forinstrumental purposes, such as to express personal needs and desires.
Social Communication And Interaction Skills
Social communication and interaction skills can be challenging for people with ASD.
Examples of social communication and social interaction characteristics related to ASD can include
- Avoids or does not keep eye contact
- Does not respond to name by 9 months of age
- Does not show facial expressions like happy, sad, angry, and surprised by 9 months of age
- Does not play simple interactive games like pat-a-cake by 12 months of age
- Uses few or no gestures by 12 months of age
- Does not share interests with others by 15 months of age
- Does not point to show you something interesting by 18 months of age
- Does not notice when others are hurt or upset by 24 months of age
- Does not notice other children and join them in play by 36 months of age
- Does not pretend to be something else, like a teacher or superhero, during play by 48 months of age
- Does not sing, dance, or act for you by 60 months of age
You May Like: Non Pharmacological Treatment For Adhd
Severity Levels In The Dsm 5 S New Autism Spectrum Disorder Requiring
Dsm 5 Levels Of Autism. Here are a number of highest rated Dsm 5 Levels Of Autism pictures on internet. We identified it from trustworthy source. Its submitted by dealing out in the best field. We receive this kind of Dsm 5 Levels Of Autism graphic could possibly be the most trending topic considering we ration it in google benefit or facebook.
Dsm 5 Criteria For Autism Spectrum Disorder Franzcalvo, Dsm 5 Autism Spectrum Disorder Guidelines, Autism Spectrum Disorders Understanding And Supporting Learners With,
Authtool2.britishcouncil.org is an open platform for users to share their favorite wallpapers, By downloading this wallpaper, you agree to our Terms Of Use and Privacy Policy. This image is for personal desktop wallpaper use only, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, DMCA report please Contact Us
The Purpose Of This Revision In The Dsm
A general overview of diagnostic criteria, per the DSM-5, is persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts . This can include problems with:
-
- Social-emotional reciprocity
- Developing, maintaining, and understanding social relationships.
Autism spectrum disorder also requires:
-
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities such as stereotyped or repetitive motor movements
-
- Ritualized patterns or inflexible adherence to routines
-
- Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus
- and/or hyper- or hypo reactivity to sensory input .
Other criteria also include that symptoms:
-
- Must be present in the individuals early developmental period
-
- Must cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of current functioning
- Are not better explained by intellectual disability or global developmental delay .
Severity specifiers are given for social communication impairments and restricted repetitive patterns of behavior . Severity for both criterion A and B are listed at three different levels:
-
- Level 1 requiring support
-
- Level 2 requiring substantial support
- Level 3 requiring very substantial support.
Read Also: What Foods Does Your Autistic Child Eat
Behavioral Psychological And Educational Interventions
People with ASD may be referred to a health care provider who specializes in providing behavioral, psychological, educational, or skill-building interventions. These programs are typically highly structured and intensive, and they may involve caregivers, siblings, and other family members. These programs may help people with ASD:
- Learn social, communication, and language skills
- Reduce behaviors that interfere with daily functioning
- Increase or build upon strengths
- Learn life skills necessary for living independently
Autism Spectrum Disorder And Identity
Being diagnosed with a disorder such as autism cannot help but influence both how one sees oneself and how one is seen by others. In other words, it becomes an imperative identity, meaning a facet of one’s social self that becomes relevant in almost all situations and over who’s content one has only limited control. Identity is often defined as how someone presents themselves, and sees themselves, as belonging to a group . We all inhabit multiple identities which may complement or overlap each other, but which may also be in conflict. Not only is the individual’s own self-presentation important for identity construction, but also those imposed by the other members of the target group, and society at large. Some identities are more central, and tend to bleed over and influence others, and it is these we refer to as imperative identities. This may be problematic, as autism is stigmatized and subject to numerous myths and misunderstandings in the broader culture .
Huynh et al. highlight the nosological social change that results from a new diagnostic criteria for individuals with AS both for them as individuals as well as their social groups.
Recommended Reading: What Does Autism Look Like In Girls