How Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder Play
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder tend to be less spontaneous than other kids. Unlike a typical curious little kid pointing to things that catch their eye, children with ASD often appear disinterested or unaware of whats going on around them. They also show differences in the way they play. They may have trouble with functional play, or using toys that have a basic intended use, such as toy tools or cooking set. They usually dont play make-believe, engage in group games, imitate others, collaborate, or use their toys in creative ways.
What Is The Difference Between Autism And Autism Spectrum Disorder
The term autism was changed to autism spectrum disorder in 2013 by the American Psychiatric Association. ASD is now an umbrella term that covers the following conditions:
- Autistic disorder.
- Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified .
- Asperger syndrome.
People with ASD have trouble with social interactions and with interpreting and using non-verbal and verbal communication in social contexts. Individuals with ASD may also have the following difficulties:
- Inflexible interests.
- Insistence on sameness in environment or routine.
- Repetitive motor and sensory behaviors, like flapping arms or rocking.
- Increased or decreased reactions to sensory stimuli.
How well someone with ASD can function in day-to-day life depends on the severity of their symptoms. Given that autism varies widely in severity and everyday impairment, the symptoms of some people arent always easily recognized.
Are There Different Types Of Asd
ASD used to be called Pervasive Developmental Disorder . These terms mean the same thing. PDD is the diagnostic classification in the DSM-IV . In the DSM-IV, PDD included five types or categories: autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder, childhood disintegrative disorder, Retts syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified .
The American Psychiatric Association released the new fifth edition of the DSM in May 2013. In the DSM-5 the term ASD has replaced PDD. Additionally, the DSM-5 does not have any catego-ries under ASD so that all individuals meeting the diagnostic criteria will fall under one autism spectrum. This change was made because research indicates the categories that were under PDD cannot be reliably distinguished. This means the categories of autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder, and PDD-NOS will no longer be usedinstead the diagnosis of ASD will be used to cover the full spectrum.
You May Like: How To Tell If My Child Is Autistic
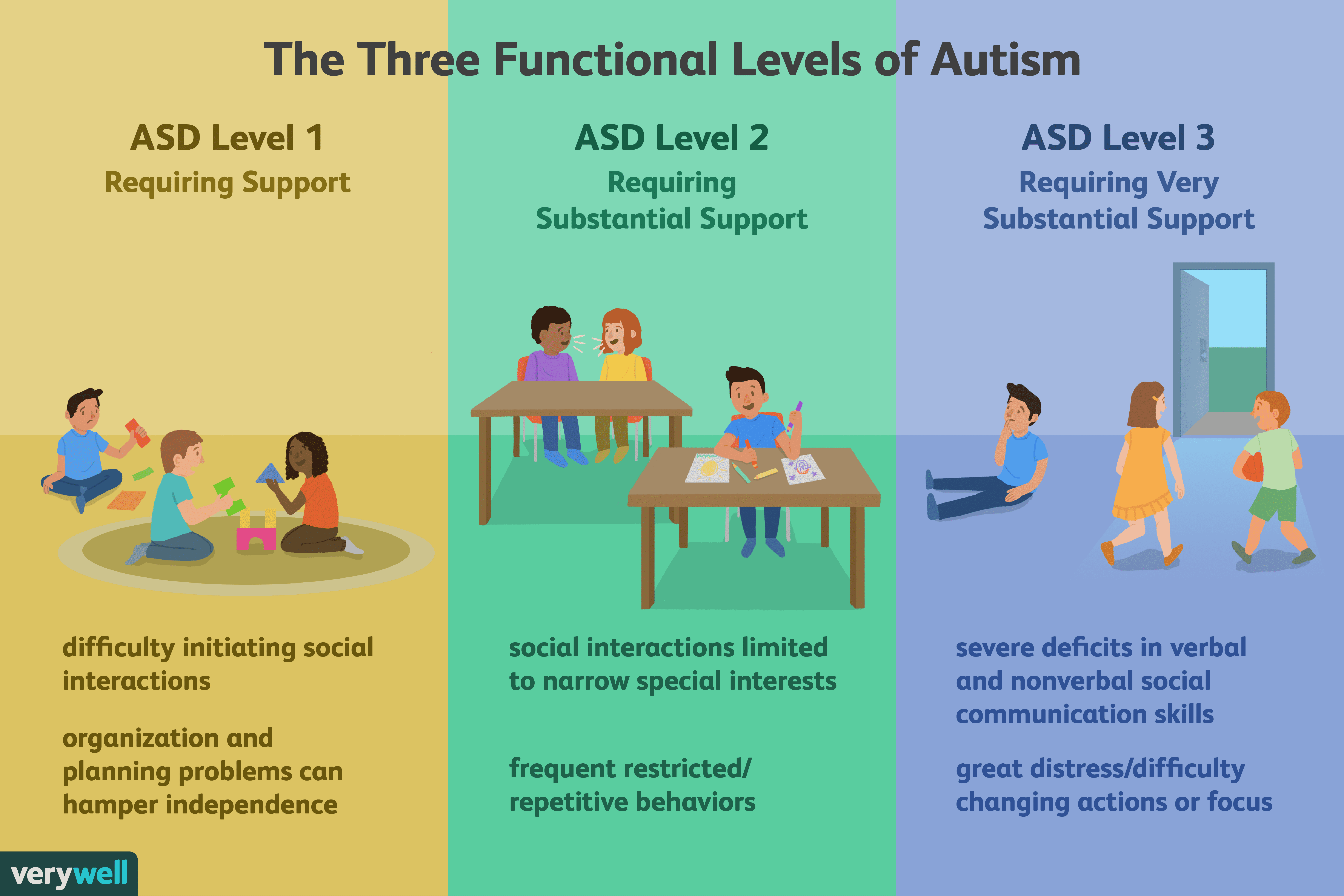
Level 1: Requiring Support
The communication issues that a person with Level 1 ASD may face include:
- difficulty initiating social interactions
The repetitive behavioral issues a person with Level 1 ASD may face include:
- inflexible behavior that interferes with general functioning in one or more contexts
- problems switching between activities
- issues with organization and planning, which can impact independence
Discussing Different Types Of Autism In Brief
Autism is considered to be a spectrum disorder implying that individuals with autism may have an extensive range of severe, moderate or mild symptoms. However, does every person with an autism spectrum analysis have a similar disorder, regardless of his/her symptoms?
How autism analysis has changed recently
The autism spectrum is represented by 5 spectrum diagnoses that include PDD-NOS , Asperger Syndrome, Childhood Disintegrative Syndrome, Autistic Disorder, and Rett Syndrome.
But this analysis is confusing. Not just were they tricky to define, but various practitioners chose various analysis for similar patients. To describe their analysis, practitioners used terms like high functioning autism, mild autism, and severe autism. Nevertheless, these terms are not true analysis also; they are only descriptions. And when they are meant to help teachers and parents better understand the status of a child on the autism spectrum, every practitioner had their own concept of what severe or mild might appear like.
How people consider autism these days
Everybody with an autism analysis, regardless of his/her symptoms, is currently sectioned under a single analysis. 3 autism levels, alongside nonverbal descriptors, are meant to create analysis clearer and easier.
What are the different types of Autism?
Autism terms are not always useful
Read Also: How Do You Get Diagnosed With Autism
Conditions Related To Autism
Autism diagnosis doesnt just begin and end with these 5 conditions though as, like the 2 previous conditions demonstrate, there are many MANY types of diagnosis out there which overlap in the causes and effects of autism.
As such, while you may have seen many things labelled a rare type of autism in a newspaper or journal, the reality is that many of these condition are close to the spectrum but not on in. These include:
Are Siblings At Greater Risk For Autism Spectrum Disorder
The truth is that genetics do play a role in autism. When one child is diagnosed with ASD, the next child to come along has about a 20% greater risk of developing autism than normal. When the first two children in a family have both been diagnosed with ASD, the third child has about a 32% greater risk of developing ASD.
You May Like: Can You Stop Being Autistic
Treatment And Development Strategies For The Types Of Autism
Children with less extreme forms of autism, such as Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder, can benefit from social skills classes as well as taking part in behavioral modification to help with possible obsessive tendencies. In some cases, an altered diet free of preservatives, gluten, artificial sugars, and food coloring can be beneficial. Since many children with Level 1 ASD are advanced learners, looking into differentiated curriculum to challenge and hold their attention can provide numerous benefits.
Similarly, children diagnosed with PDD-NOS can greatly benefit from strategic changes in nutrition combined with occupational therapy and classes in life-skills development.
Girls with Rett Syndrome often need lifelong care because other symptoms may appear or grow more severe as the child ages. Difficulty breathing, cognitive disabilities, grinding teeth, seizures, and growth delays may all need ongoing treatment options. Physical therapy can help increase mobility and straighten limbs, while occupational therapy may help reduce involuntary movements and promote self care. Finally, speech therapy, diet modification, and certain medications can help control seizures.
Childhood Disintegrative Disorder requires early intervention on the part of doctors and parents via specialized and focused nutrition and speech and occupational therapy. Behavior modification helps children cope with this type of autism.
What Are The Signs Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Signs of ASD range from mild to severely disabling, and every person is different. The following signs are considered to be red flags that indicate your young child may be at risk for autism. If your child shows any of the following signs, please get in touch with your childs healthcare provider to discuss a referral for an autism evaluation.
The signs include the following:
- Your child doesnt respond to their name being called at all or responds inconsistently.
- Your child doesnt smile widely or make warm, joyful expressions by the age of 6 months.
- Your child doesnt engage in smiling, making sounds and making faces with you or other people by the age of 9 months.
- Your child doesnt babble by 12 months.
- No back-and-forth gestures such as showing, pointing, reaching or waving by 12 months.
- No words by 16 months.
- No meaningful, two-word phrases by 24 months.
- Any loss of speech, babbling or social skills at any age.
Recommended Reading: How To Teach Empathy To Autistic Child
How Common Is Autism
An autism diagnosis occurs in one of every sixty-eight births. An early intervention program can be helpful when autism is discovered in younger children. In some cases, with the right treatment program, a child can even outgrow some of the issues associated with autism and begin to display better social and communication skills.
Repetitive Behaviors And Restricted Interests
- Unusual ways of moving their hands, fingers, or whole body
- Develops rituals such as lining objects up or repeating things over and over
- Very focused on or attached to unusual kinds of objects such as strips of cloth, wooden spoons, rocks, vents, or doorstops
- Excessive interest in particular objects, actions, or activities that interferes with social interaction
- Unusual sensory interests such as sniffing objects or looking out of the corner of their eye
- Over- or under-reaction to certain sounds, textures, or other sensory input
Read Also: Does Chelation Therapy Work For Autism
Why The Types Of Autism Shifted To One Diagnosis
The current diagnosis autism spectrum disorder debuted in the latest edition of the DSM , published in 2013. Prior to that, they were categorized as five different types of autism: autistic disorder, pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified , Asperger syndrome, Childhood Disintegrative Disorder and Rett Syndrome .;
But research found that these categories were not reliably diagnosed, according to Thomas W. Frazier, a doctor of clinical psychology and Autism Speaks chief science officer. The diagnosis would shift over time and was partly dependent on the provider who made the diagnosis, he says.
Therefore, experts landed on a single diagnosis, which allows for a more nuanced understanding of the disorder. While people on the autism spectrum share common characteristics related to social communication, repetitive, restricted behaviors, sensory issues, etc., there is great diversity within the autism spectrum, says Stephen Shore, a doctor of education and clinical assistant professor at Adelphi Universitys College of Education and Health Sciences in New York. When youve met one person on the autism spectrum, youve met one person on the autism spectrum.;
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorders

Autism is not a single disorder, but a spectrum of closely related disorders with a shared core of symptoms. Every individual on the autism spectrum has problems to some degree with social interaction, empathy, communication, and flexible behavior. But the level of disability and the combination of symptoms varies tremendously from person to person. In fact, two kids with the same diagnosis may look very different when it comes to their behaviors and abilities.
If youre a parent dealing with a child on the autism spectrum, you may hear many different terms including high-functioning autism, atypical autism, autism spectrum disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder. These terms can be confusing, not only because there are so many, but because doctors, therapists, and other parents may use them in dissimilar ways.
But no matter what doctors, teachers, and other specialists call the autism spectrum disorder, its your childs unique needs that are truly important. No diagnostic label can tell you exactly what challenges your child will have. Finding treatment that addresses your childs needs, rather than focusing on what to call the problem, is the most helpful thing you can do. You dont need a diagnosis to start getting help for your childs symptoms.
Whats in a name?
Don’t Miss: Which Month Is Autism Awareness
What Are The Levels Of Autism
Along with diagnosing a child with autism spectrum disorder , doctors now assign a functional level 1, 2 or 3 that correlates to a particular type and amount of support.
This way of categorization avoids placing people into proverbial boxes in favor of describing the type and amount of support needed across the two major characteristic areas: social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors, explains Shore.
Heres what each level means, according to the DSM-5:
Level 1: Requires support;
People in this category require support for social communication, as they might have difficulty initiating interactions or responding to social overtures. They may exhibit decreased interest in social interaction, inflexibility of behavior, difficulty switching between activities or problems with organization and planning that hamper independence.
Level 2: Requiring substantial support
People given this diagnosis have trouble with verbal and nonverbal social communication and might struggle even with supports in place. Their initiation of social interactions is limited and they have reduced or abnormal responses to social overtures from others. They might have distress and/or difficulty changing focus or action.;
Level 3: Requiring very substantial support
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism
The most obvious symptoms tend to involve communication and interaction with others.
Autistic people may have different ways of learning, thinking, and problem-solving. Intellectually, autistic people can fall on a range from severely challenged to gifted.
Everybody is different. Some people will have many symptoms, and some will have only a few. Signs of autism in a 3-year-old or 4-year-old may look different from those who are teens or adults. Some autistic people may be able to mask their symptoms.
General signs of autism may include:
- not responding to their name
- avoiding eye contact or not showing an awareness when others are speaking
- not understanding sharing or taking turns
- not looking at objects shown to them
- not pointing or responding to pointing
- having difficulty understanding facial expressions
In older children and adults, you might also notice:
- having difficulty reading body language, facial expressions, and other social cues
- not getting sarcasm, teasing, or figures of speech
- speaking in monotone
Recommended Reading: Is Aspergers Autism Spectrum Disorder
Social Behavior And Social Understanding
Basic social interaction can be difficult for children with autism spectrum disorders. Symptoms may include:
- Unusual or inappropriate body language, gestures, and facial expressions .
- Lack of interest in other people or in sharing interests or achievements .
- Unlikely to approach others or to pursue social interaction; comes across as aloof and detached; prefers to be alone.
- Difficulty understanding other peoples feelings, reactions, and nonverbal cues.
- Resistance to being touched.
- Difficulty or failure to make friends with children the same age.
Is Rett Syndrome An Asd
Children with Rett syndrome often have behaviors similar to autism, and experts used to group it among spectrum disorders. But now that itâs known to be caused by a genetic mutation, itâs no longer considered an ASD.
National Institute of Mental Health: “Autism Spectrum Disorders.”
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: “Asperger Syndrome Fact Sheet.”
Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry: âSpecifying PDD-NOS: A Comparison of PDD-NOS, Asperger Syndrome, and Autism.â
Psychiatric Clinics of North America: âThe autistic spectrum: subgroups, boundaries, and treatment.â
Spectrum: âReclassification of Rett syndrome diagnosis stirs concerns.â
Rettsyndrome.org: âWhat is Rett Syndrome?â
Autism Speaks: âAsperger Syndrome,â âAbout Autism: Why Was My Child Diagnosed with Autism? And What Does It Mean?â
Centers for Disease Control: âFacts About ASD.â
You May Like: How To Increase Attention Span In Autism
What Are The 3 Main Characteristics Of Autism
These are some of the characteristics of ASD:
- problems with social interaction with others.
- unusual interest in objects.
- need for sameness.
- great variation in abilities.
- under or over reaction to one or more of the five senses: sight, touch, taste, smell, or hearing.
- repeated actions or body movements.
Is Autism Inherited From The Mother Or Father
Clues to the first two questions come from studies that have shown that at least 30% of individuals with autism have spontaneous de novo mutations that occurred in the fathers sperm or mothers egg and disrupt genes important for brain development, these spontaneous mutations likely cause autism in families where
Also Check: Is Autism Genetic Or Hereditary
Does Autism Worsen With Age
Change in severity of autism symptoms and optimal outcome
One key finding was that childrens symptom severity can change with age. In fact, children can improve and get better. We found that nearly 30% of young children have less severe autism symptoms at age 6 than they did at age 3.
Can Autism Go Away With Age

There is no known cure for autism. But recent research might make parents wonder if it ever goes away either through therapy or through a child simply growing older. Around 13 percent of these children lost the diagnosis later meaning they no longer had signs and symptoms that fit on the autism spectrum.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Difference Between Autistic And Autism
What Are The 5 Different Types Of Autism
The different kinds of autism include:
- Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder , previously called Aspergers Syndrome;
- Rhett Syndrome, although this has been removed from the spectrum;
- Childhood Disintegrative Disorder ;
- Kanners Syndrome or Classic Autistic Disorder; and
- Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified .
Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Accepted Term
Autism spectrum disorder is the accepted term for people with autism symptoms. This one acronym encompasses many people, behaviors, and levels of impairment.;
Autism Speaks explains that no one is exactly sure what causes ASD. It’s likely that a combination of genetics and environment is to blame. Similarly, researchers aren’t sure what causes some people to live with mild impairment, while others need around-the-clock caregivers. There’s a lot we just don’t know about autism despite years of intense research.;
Years of observation highlight typical autism signs and symptoms. Those include changes in:
- Responses to stimulus. People with autism may not point at objects to highlight interest, and they may not look at things others point to.
- Relationships. They may not relate to other people. Some don’t seem troubled by their lack of connection, while others want to get close and aren’t sure how to make it happen.
- Touch. Some dislike being hugged, held, patted, or squeezed, even by people they know and trust.
- Speech. Some echo or repeat words while forming few full sentences. Others don’t talk at all. Some talk extensively, but only about subjects that interest them.
- Routine. Many like to stick to the same schedule every day, and they feel distressed when things change.;
- Senses. Some people with autism feel overwhelmed by loud noises, strong scents, or high levels of visual stimuli.
Don’t Miss: Is Autism A Neurodevelopmental Disorder
In 2013 Doctors Stopped Diagnosing 4 Different Types Of Autism
Until 2013, there had been four separate diagnoses within the category of autism: autistic disorder, Asperger’s syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder . The change was made because these distinct diagnoses were not always made consistently and may have limited treatment options for some individuals on the spectrum.
The American Psychiatric Associations revision to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders;, published in May 2013, did not include four subtypes of autism. According to the DSM-5, anyone on the autism spectrum should be diagnosed simply with autism spectrum disorder. The revised diagnosis represents a new, more accurate, and medically and scientifically useful way of diagnosing individuals with autism-related disorders, the APA noted in a statement released with the DSM-5 revision.
The change was made in part because these diagnoses were not consistently applied across the board, according to the APA. Doctors approached each of these diagnoses differently. Rolling the diagnoses into a single category offered a more cohesive approach to treating autism.