Maternal Qats In Pedigrees Consistent Or Not Consistent With Silent Maternal Transmission
We next explored a more stringent manifestation of maternal carrier status for ASD risk to determine whether this was associated with differences in maternal QATs. In families from existing WUSTL studies and the Second Generation Project , we compared SRS-2 T-scores between mothers of ASD-affected children with versus without a pedigree consistent with silent maternal transmission of ASD .1). These pedigrees included mothers with a first-degree ASD-affected relative or two ASD-affected offspring who were maternal half-siblings. Mean SRS-2 scores were again numerically higher for the group suspected of silent maternal transmission but the difference did not reach statistical significance .
A Variety Of Problems
The genetic defect has widespread consequences in the body, and people with even the trait or carrier status may have a variety of physical, emotional, intellectual and behavioral problems or they may be normal. Early menopause is a common problem for women who are carriers. Also, older carriers can develop tremor and balance problems as they age. All of these problems can vary widely in severity among individuals.
Although many children with fragile X syndrome clearly desire socialization, they are often overwhelmed by stimuli, leading to behaviors typical of autism.
About 80 percent of boys with fragile X syndrome demonstrate intellectual disability, compared to about one third of females. Intellectual abilities range from a normal IQ with subtle learning disabilities to severe intellectual disability. Female carriers who are intellectually normal are often found to share characteristic disturbances, such as difficulty in learning math, and emotional problems such as extreme shyness, anxiety, obsessive worrying and mood swings.
Health problems, related to the variety of underlying physical abnormalities, include frequent sinus and ear infections, a lazy eye, dental problems, and heart murmurs indicative of a floppy heart valve. Seizures are common, but are often outgrown by adulthood.
Genetic Causes Of Autism: Trio Of Studies
In two of the new studies, researchers analyzed more than 1,000 families who have one autistic child and unaffected siblings. They evaluated their DNA from blood samples. The researchers used a highly sophisticated technique that can detect duplications or deletions of one or more sections of DNA.
These duplications or deletions are called copy number variants or CNVs. If they occur at random, or sporadically, and aren’t inherited, they are known as de novo CNVs.
Some CNVs ”are normal parts of being human,” Sanders tells WebMD. “It’s very difficult to find the ones that matter. We looked for ones that were new in the child.”
They found more new CNVs in autistic children than in unaffected children, which they expected.
They zeroed in on many regions linked with these rare sporadic mutations, Sanders says, confirming previous research on which areas matter. “Basically five regions really stand out now,” he says.
These include areas of chromosome 7, 15, 16, 17 and Neurexin 1.
The team estimates ”there are 130-234 CNV regions that could be linked with autism,” he says.
The researchers also found that the long arm of chromosome 7, a region associated with Williams syndrome, a genetic disorder in which people are highly social and overly friendly with strangers, may also be associated with autism.
“For a long time it has been known if you have a deletion there, it causes Williams syndrome,” Sanders says.
You May Like: Autism Level 2 Meaning
Currently Available Autism Genetic Testing Panels
Below weve included a list of labs and tests that are both marketed for autism spectrum disorder and include the FMR1 gene. Though we tried to locate and verify as many as we could, we do not assume this list is exhaustive. Because they can change at any time, please review the information carefully and follow up with your health professional and/or the lab for the most current information.
Please note that the commercial labs in this list may or may not also offer specific Fragile X DNA testing. Our intent with this list is to assist people facing an autism diagnosis with an unknown cause, and who would benefit from testing that includes all currently known autism-related genes.
Please in interpreting any of the information here:
Note that the following are as of May 2019. We will update this list periodically and note the date of last revision. These are not Fragile X DNA tests, they are tests for an autism diagnosis of unknown cause that include the FMR1 gene.
| Lab |
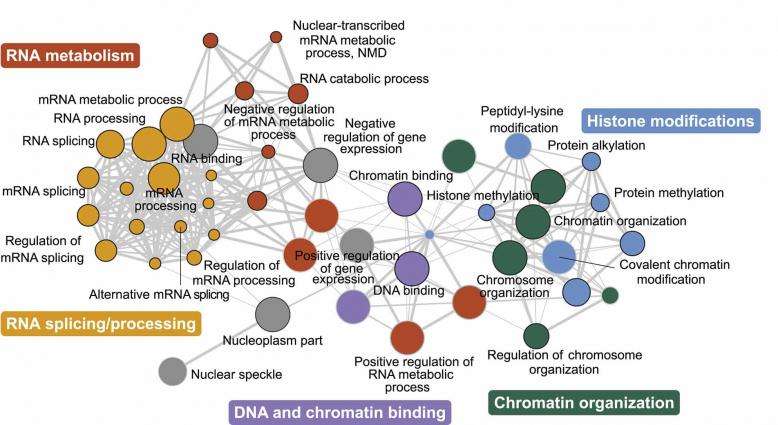
Several Biological Pathways Identified
Individuals with ASD vary in language ability, ranging from absent speech to fluent language, and in cognitive development, ranging from profound intellectual disability to above-average intellectual functioning. Individuals may also show associated medical comorbidities including epilepsy and minor physical anomalies, as well as psychiatric comorbidities, thus showing a wide clinical heterogeneity. The clinical heterogeneity of autism has long been a hindrance to understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms involved. However, although many questions remain and new questions are being raised, the last several years of investigation have brought important pieces to the autism puzzle. Indeed, the identification of specific alleles contributing to ASD has shed light on pathogenic mechanisms.
Going back to an individual approach, already used in mental retardation, the search for rare mutations or chromosomal rearrangements was then used, allowing new hypotheses about the mechanisms involved in autism. While the existence of many genetic syndromes associated with autism first led to considering the existence of genetic heterogeneity mirroring the clinical variability, genetic studies in idiopathic autism confirmed the existence of different defects in common pathways. The results suggest that autism may be caused by a multitude of genetic alterations that ultimately affect only limited biological pathways of brain development and plasticity.
Read Also: How To Self Diagnose Autism
Definition And Evolution Of Asd
Autism is a developmental neuropsychiatric syndrome with onset before the age of three. The fundamental conceptualization of the disorder is based on the initial observation of Kanner in 1943 , where he described 11 children with autism, mostly boys with a combination of severe social and variable language dysfunction and the presence of repetitive restrictive behaviors. Kanner made numerous interesting observations based on these case studies, including the identification of large head size in about half of the subjects and postulated a biological, genetic basis for the disorder. However, until the 1980s autism was not considered a distinct disorder in the manuals of psychiatric diagnosis, nor was it considered by most to be biologically based.
Endophenotypes Common Variants And Domain Specificity In Asd
The relationship of specific genetic variants with specific cognitive processes, such as language, highlight the notion that the broad syndrome of ASD can be broken down into many component, or intermediate phenotypes, referred to as endophenotypes. The familial segregation of endophenotypes provides a genetic basis for the broader phenotype described earlier. A logical extension of this concept is that these endophenotypes represent one end of the continuum of the normal spectrum of behavior and cognition . Several groups have demonstrated that this is indeed the case with respect to CNTNAP2 , as the same allele that increases risk for language delay in ASD, increases risk for specific language impairment and modifies language ability in the general population. Similarly, common variation in different ASD-associated CNTNAP2 single nucleotide polymorphism , has been shown to modulate brain morphology in several ASD related cortical regions in normal controls .
Recommended Reading: Autism Type 2
Massive Project Doubles List Of Genes Tied To Autism
Nicholette ZeliadtStrong signal
The largest analysis of genetic sequences from autistic people implicates 184 genes in the condition nearly doubling an estimate from last year.
Researchers presented the unpublished results today at the 2019 American Society of Human Genetics meeting in Houston, Texas.
The researchers analyzed sequences of exomes the protein-coding portions of the genome pooled from multiple datasets. They built off their unpublished analysis of nearly 35,000 sequences. That analysis, which the team presented at a conference last year, tied 99 genes to autism.
The new work incorporates 27,000 additional sequences and increases the proportion of autistic people whose condition can be tied to a genetic cause to roughly 20 percent.
The results reflect the rapid increase in the number of sequences and a briskly evolving set of strategies to analyze the data, says Kyle Satterstrom, a computational biologist in s lab at the Broad Institute in Cambridge, Massachusetts, who presented the findings. This is very much a work in progress.
Maternal Qats In Simplex Families With Versus Without A De Novo Variant In Asd
We next examined whether maternal QAT burden was lower among mothers of ASD-affected children whose conditions were associated with de novo mutations. In participants from the SSC ,1), for whom one third of ASD cases would be expected to be at least partly influenced by a de novo pathogenic variant , we compared SRS-2 scores in mothers of an affected child with or without a known ASD-associated de novo variant , as defined in the methods . We hypothesized that in families with sporadic cases of ASD, lower familial ASD liability, as indexed by parental QATs on the SRS-2, would be observed for cases in which the proband carried a known ASD-associated de novo variant. As predicted, mean SRS-2 scores were significantly lower for mothers whose child had an ASD-associated de novo variant versus mothers of children without such variants =â3.04, p=.003). Despite this highly significant result, the between-group difference had a small effect size . A parallel analysis based on SRS-2 scores in fathers and mean parental SRS-2 scores for cases in which scores of both parents were available revealed a comparable result .
Don’t Miss: Difference Between Sensory Processing Disorder And Autism
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder refers to a group of complex neurodevelopment disorders characterized by repetitive and characteristic patterns of behavior and difficulties with social communication and interaction. The symptoms are present from early childhood and affect daily functioning.
The term spectrum refers to the wide range of symptoms, skills, and levels of disability in functioning that can occur in people with ASD. Some children and adults with ASD are fully able to perform all activities of daily living while others require substantial support to perform basic activities. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders includes Asperger syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorders not otherwise specified as part of ASD rather than as separate disorders. A diagnosis of ASD includes an assessment of intellectual disability and language impairment.
ASD occurs in every racial and ethnic group, and across all socioeconomic levels. However, boys are significantly more likely to develop ASD than girls. The latest analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1 in 68 children has ASD.
Greater Understanding Of Genetics Of Asd
ASD is a group of neurological and developmental conditions that affect communication and behavior. Theres wide variation in the type and severity of symptoms in people with ASD.
Scientists believe that both genes and environment are involved in the development of ASD, with genetics playing a big part.
We know that inherited and unique mutations in the genome are a major source of risk for developing ASD, but specific causes of ASD are not yet well understood, said Lori J. Warner, PhD, director of the Center for Human Development and Ted Lindsay Foundation HOPE Center at Beaumont Childrens Hospital in Royal Oak, Michigan, who wasnt involved in the study.
Although environmental factors play some role in ASD, scientific have found that theres no link between receiving vaccines and developing ASD.
The new study marks an important step forward in scientists understanding of the genetic basis of ASD.
Researchers identified both inherited genetic mutations and de novo mutations ones that occur spontaneously when an egg or sperm form.
They also found that the ASD genes identified in the study can affect brain development or brain function. And they showed that two major types of nerve cells can be affected in ASD.
Of the 102 genes identified in the study, 49 were associated with other developmental delays.
Zwaigenbaum said the overlap between ASD and other neurodevelopmental disorders fits with previous research.
Don’t Miss: Autistic Friendly Movies
The Role Of Rare Mutations Versus Common Polymorphisms In Asd
A series of important findings over the last four years clearly challenges the notion that autism is mainly caused by combinations of common variants by identifying a large number of rare, recurrent, and non-recurrent mutations that lead to ASD. At the same time, whole genome association studies with common variants, while identifying a few loci with very small effect sizes, have not yielded independently replicated results . These rare mutations, mostly in the form of sub-microscopic chromosomal structural variation, called copy number variants , are now known to account for up to 10% of cases of idiopathic autism . Since many of these CNV have large effect sizes and thus are thought sufficient to cause ASD, they are predicted to significantly reduce reproductive fitness. Consistent with this, these causal CNV are often not transmitted from the parent, but instead occur de novo in the germline . However, in some cases, such as CNV at 16p11 and 15q11-13, the CNV are transmitted from an unaffected parent to cause the disorder in an offspring . The genetic or epigenetic mechanism for the reduced penetrance for ASD in the mutation-carrying parent is not known. However, it is also very likely that the parent carriers of such CNV have more subtle neuropsychiatric or cognitive phenotypes that have not yet been systematically identified.
Autisms Genetic Risk Factors
Research tells us that autism tends to run in families. Changes in certain genes increase the risk that a child will develop autism. If a parent carries one or more of these gene changes, they may get passed to a child . Other times, these genetic changes arise spontaneously in an early embryo or the sperm and/or egg that combine to create the embryo. Again, the majority of these gene changes do not cause autism by themselves. They simply increase risk for the disorder
Don’t Miss: What Is Mild Autism
About The Center For Autism And Neurodevelopment At Northwestern
The centers mission is to spur interdisciplinary research collaborations aimed at understanding the biological bases of autism and related neurodevelopmental disorders and to facilitate the translation of this knowledge into new treatments.
Autism is a highly prevalent neurodevelopmental disorder. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, one in 68 children are identified as having Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Over the past few years, many genetic causes of autism and related disorders have been found, which could provide insight into its neurobiological bases, Penzes said. The next major challenge is to understand the function of these genes in shaping the development of brain circuits and how their improper function may derail neurodevelopment. These genes and neurodevelopmental processes could serve as targets for new drugs aimed at treating autism and related disorders.
Other Northwestern authors are Sehyoun Yoon, PhD, Euan Parnell, PhD, and Marc Forrest, PhD.
The research was supported by grant R01MH107182 from the National Institute of Mental Health of the National Institutes of Health.
What Might The Doctor Recommend For Your Child If You Have A Family Health History Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Knowing about your family health history of ASD can help your childs doctor better care for your child. The doctor may check your child more closely for early signs of ASD and might refer your child to a specialist for further evaluation. When a child is closely monitored, signs of ASD can sometimes be noticed at 18 months or youngerexternal icon. A reliable diagnosis of ASD is more common around 2 or 3 years of ageexternal icon and usually made by a developmental specialist. If a child is diagnosed at a young age with ASD, treatment is more effective. Also, a diagnosis of ASD is important for tailoring childrens education once they start school. Learn how early intervention leads to better outcomes for children with ASD.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, your doctor might recommend carrier screening if you have a family health history of a genetic disorder, such as fragile X syndrome.
Read Also: Can You Outgrow Autism
Asd And Associated Genetic Conditions
Autism Spectrum Disorder and features of ASD can occur as part of some genetic conditions. Approximately 20% of children with ASD will have a diagnosable genetic syndrome. These syndromes can be due to missing or extra stretches of DNA, misspellings in genes, or biochemical abnormalities.
Some of these conditions are easy for a general pediatrician to recognize , while other conditions can be subtle and require specialized testing . For this reason, the American College of Medical Genetics recommends that anyone with an ASD diagnosis receive an evaluation by a clinical geneticist. Accurate diagnosis is important because there can be other health implications for the affected child, as well as differences in the risk of having another child on the autism spectrum.
In addition to genetic causes of ASD, exposure to certain medications during pregnancy can cause ASD. During your childs visit with a clinical geneticist, they will review any medications that you may have taken during pregnancy.
Examples of genetic abnormalities that can be associated with ASD are listed below.
22q deletion syndrome
Angelman syndrome
CHARGE
Cornelia de Lange syndrome
Down syndrome
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Fragile X
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition that causes a range of developmental delay. Usually males are more severely affected than females. Children may be hyperactive or have a secondary diagnosis of ADHD.
Prader-Willi syndrome
Rett syndrome
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
Evidence For Converging Molecular Pathways
Several recent studies have suggested that in addition to convergent brain pathways, that there may as well be convergence at the level of molecular mechanisms in ASD. One class of such studies has asked whether putative ASD susceptibility genes are enriched in members for specific molecular or biological processes more than expected by chance. The value of this approach depends on the level of experimental support for the specific genes tested and the degree to which current pathway annotations represent reality . For genes identified within CNV this can be particularly problematic, as most known pathological CNV contain more than one gene and it is not expected that all genes within the CNV contribute to ASD, potentially increasing noise in this analysis. One recent study reduced such background by using a new phenotype-driven method to group genes within high confidence de novo CNV , identifying significant enrichment for several categories of genes, including axon outgrowth, synaptogenesis, cell-cell adhesion, GTPase signaling, and the actin cytoskeleton. These results replicate and extend earlier composite pathway analysis of putative ASD susceptibility genes compiled from the literature , and CNV pathway analysis in the Autism Genetic Resource Exchange and other cohorts . Still, these studies place ASD genes within a multiplicity of pathways, several of which are broad and do not necessarily demonstrate convergence on final common molecular processes in individuals.
Recommended Reading: Level 1 High Functioning Autism