How Does Adhd Interfere With Peer Relationships
Exactly how ADHD contributes to social problems is not fully understood. Children who are inattentive sometimes seem shy or withdrawn to their peers. Children with symptoms of impulsivity/hyperactivity may be rejected by their peers because they are intrusive, may not wait their turn, or may act aggressively. In addition, children with ADHD are also more likely than those without ADHD to have other disorders that interfere with getting along with others.
Problem: Adhd Onset Age Is Arbitrarily Fixed In Dsm
The DSM-5 states that several symptoms of ADHD must present before age 12 to merit a diagnosis. But nature does not respect a number like 12 the onset of ADHD symptoms in peoples lives can actually occur at any point in time. In the vast majority of cases, ADHD symptoms do present before age 18 or 21. But theres still a small percentage who fit outside these parameters, or who may even develop acquired ADHD. An extreme sports athlete, for example, who sustained lots of head traumas can theoretically develop a form of ADHD secondary to traumatic brain injury .
Whats more, parents of children with ADHD tend to inaccurately recall the age of onset of symptoms. Most parents are actually off by about three to five years, far later than actually documented in charts, according to our research. Adults make the same mistake when assessing their own symptoms. Thus, the age of onset criterion is too unreliable for us in diagnosis.
Studies Considered By The Committee During Revisions To The Age Of Onset Criterion
We identified one document that we considered the key document describing the evidence to support the ADHD criteria revision process . The document refers to a systematic literature review published by the workgroup age-of-onset subcommittee and one published study as evidence for the change to the age of onset criterion. The review included 32 studies related to the age of onset criterion of varying designs and with different objectives. Based on these studies, the Committee commented on a) the magnitude of change , b) the reason/evidence for change, c) the potential negative consequences considered and d) additional objections and response. This key document had been available previously on the American Psychiatric Association website, but is no longer publicly available. On full text review of the 33 studies referred to by the key document, 17 studies addressing the checklist items were categorised and analysed .
Fig. 1
Our searches of the available literature found 20 relevant studies . We did not locate any studies of prevalence, precision, benefit or harm additional to those used by the Committee. However, we identified a further 3 studies related to prognosis .
Don’t Miss: Grants For Autistic Business Owners
Suicidal Behavior And Nonsuicidal Self
Non-suicidal self-injury is defined as the purposeful self-inflicted destruction of ones body without the goal of suicide. Research shows that the incidence of these behaviors may be as high as 40% among adolescents, absolutely warranting clinical attention.
The designation of this gives clinicians the ability to flag these behaviors independent of a specific diagnosis so that one may get the proper care. Additionally, these behaviors have been isolated clinically and diagnostically to encourage research on treating them specifically, rather than just addressing their manifestation in other disorders.
NSSI, specifically, had previously only been included as a symptom in borderline personality disorder, which means that it failed to capture those with other disorders or no diagnosable disorder who engaged in self-mutilation. This may also help clinicians to estimate risk factors for future suicide attempts or death.
Problem: Dsm Symptoms Do Not Reflect Adult Adhd
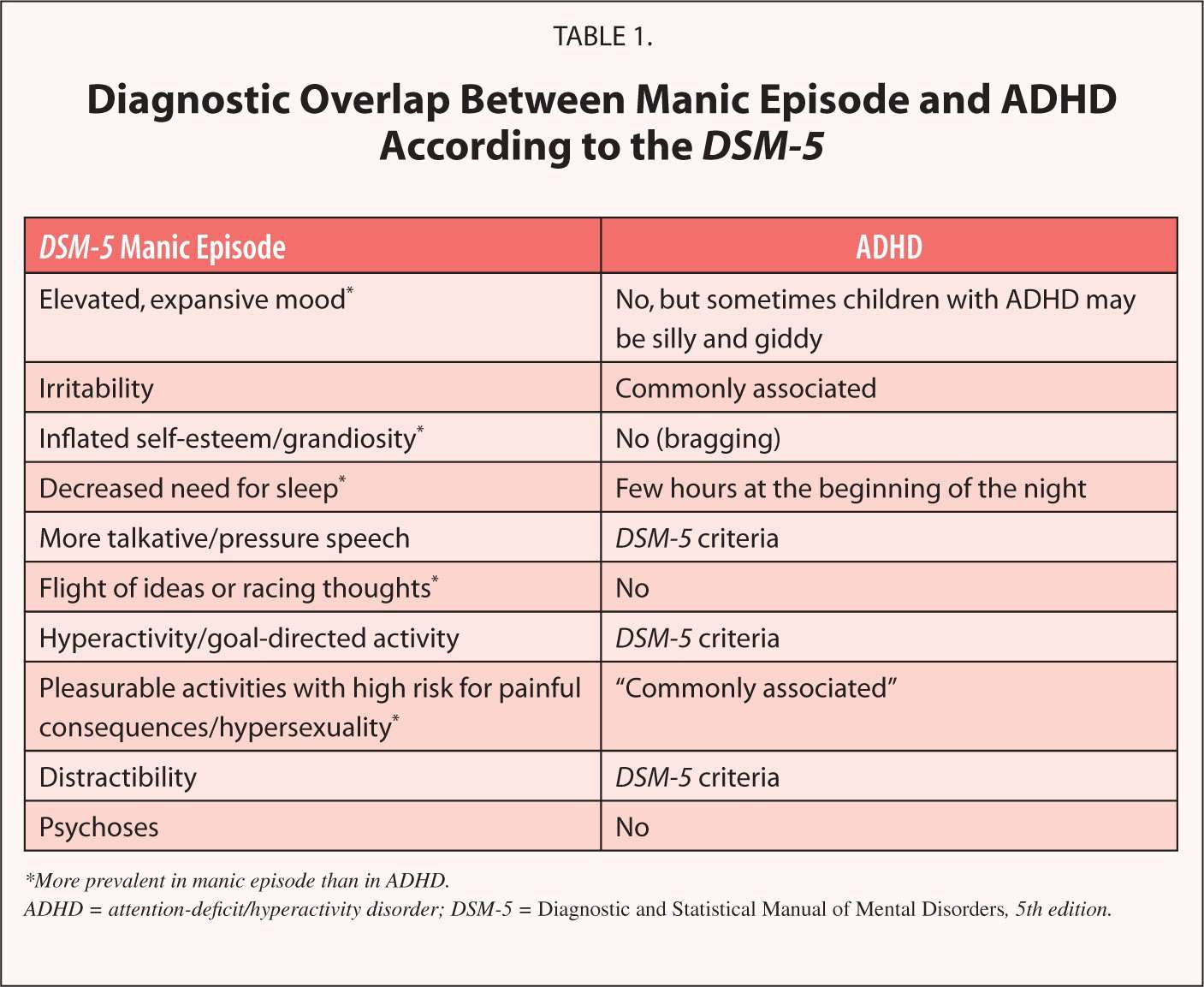
The ADHD symptoms listed in the DSM were developed for children. We can see this in the phrasing of certain symptoms, such as cant play quietly or driven by a motor in the hyperactive/impulsive items. These phrasings dont translate well to the adult experience. Few adults with ADHD would use these terms to describe their daily experience with the condition, leaving clinicians to extrapolate these items into clinical practice with adults.
Some DSM-5 symptoms do include parenthetical clarifications meant to capture adolescent and adult experiences. These changes may have led to a rise in ADHD diagnoses, because they count as additional symptoms even when the root symptom they modify is not endorsed. But the lingering issue is that these phrases were essentially invented by DSM-5 committees. Little to no effort was made to empirically test them for their relationship to ADHD, to the root symptom they clarify, and to the extent they facilitate accurate diagnosis. Additionally, no guidance was offered as to whether these phrases should clarify existing symptoms or be treated as new symptoms. This is a significant problem.
Our recent research found a very low correlation between many of these clarifications and their root symptoms in the DSM-5. In the parenthetical comment for the inattentiveness symptom of seeming absentmindedness when spoken to, for example, the symptom actually appears to be as much or more related to anxiety, making it a poor symptom for ADHD.
Also Check: Why Do People Make Fun Of Autism
Behavior Or Conduct Problems
Children occasionally act angry or defiant around adults or respond aggressively when they are upset. When these behaviors persist over time, or are severe, they can become a behavior disorder. Children with ADHD are more likely than other children to be diagnosed with a behavior disorder such as Oppositional Defiant Disorder or Conduct Disorder.
What Are Adhd And Add
ADHD describes a neurodevelopmental disorder that features a variety of symptoms. These may include poor attention, hyperactivity, and poor impulse control.
For a diagnosis of ADHD, the symptoms must be severe enough to interfere with a persons functioning.
There are three subtypes of ADHD:
Predominantly inattentive ADHD features forgetfulness, disorganization, and lack of focus. This was previously known as ADD.
Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive ADHD involves restlessness and impulsive decisions, but not inattention.
Combined ADHD features inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
The signs and symptoms of ADHD vary depending on the type of disorder.
The DSM-5 lists the diagnostic criteria for a range of mental conditions, including ADHD.
Also Check: Why Do Kids Have Autism
Are There Any Benefits To Having Adhd
Everyone with ADHD should know that their condition can be an asset. Its especially helpful to kids to be given a positive framework in which to see themselves and their ADHD brains. Parents and caregivers can help children find a metaphor that feels good to them. For example, having a neurodevelopmental disorder is boring, but having a race car brain is awesome! Especially when you can help write the owners manual.
People with ADHD can be incredibly creative, especially when they find an outlet that really engages them. They can be great problem-solvers. They can be hyperfocused and energetic, bright and clever, spontaneous and adaptable. Everyone who has ADHD is unique, with their own personal strengths that arent always traditionally valued in society. Parents of kids with ADHD can help their children find those strengths and amplify them.
Screening And Diagnostic Scales For Use With Adults
To aid physicians and psychologists in the diagnostic process, several validated behavior scales have been developed to help screen, diagnose, evaluate, and track symptoms of ADHD in adults.
These scales are not to be used as sole diagnostic tools, nor should they replace the full clinical assessment based on the DSM-5® criteria however, they may help review and quantify symptoms.2
Don’t Miss: How Does Someone Get Autism
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
ADHD is a condition that can be managed, but the protocols for managing it must be followed effectively in order to achieve a fruitful result. The management involves an interprofessional team that includes the specialist psychiatrist, pediatrician, pharmacist, and other health care professionals, including nurse practitioners who help in diagnosing the disorder. The collaboration on the part of the family and the health care team becomes important so as to know the exact history of the events that the patient has gone through.
Open communication between the interprofessional team is the key to improve outcomes. The team should have a conference as that everyone knows what message is to be sent to the caregiver, who often gets upset with mixed messages.
Outcomes
Despite decades of research, the outcomes for patients with ADHD are guarded. Noncompliance with medications is common, and follow-up is difficult as many patients seek alternative treatments. Many parents do not trust the drugs and often seek alternative care. There is no question that currently available treatments do help some patients improve functionally. Still, without treatment, the individuals continue to deteriorate and eventually end up in financial, legal, and social difficulties.
Common Behavior Rating Scales Used In Adults To Assess Adhd And Monitor Adhd Symptoms2
ADULT ADHD SELF-REPORT SCALE SYMPTOM CHECKLIST
An 18-item scale that can be used as an initial symptom assessment to identify adults who may have ADHD2-3
- The scale has a question for each of the 18 symptom domains identified by the DSM-IV® criteria, with modifications to account for the adult presentation of ADHD symptoms
- Measures the frequency of how often symptoms occur based on a 0 to 4 rating scale
ADULT ASRS-v1.1 SCREENER
A 6-question subset of the full 18-item ASRS-v1.1 Symptom Checklist that can be used to screen for adults who may have ADHD2-4,6
- Can be used as an initial self-assessment tool to identify adults who may have ADHD but it is not diagnostic in and of itself
- The 6-question subset of the ASRS Symptom Checklists comprised of questions that were found to be most predictive of ADHD symptoms
- Scoring is based on how often a symptom occurs
ADULT ADHD CLINICAL DIAGNOSTIC SCALE v1.2
A diagnostic measure developed to establish the presence of current adult symptoms of ADHD5-6
- The 18-item, clinician-based, semistructured interview employs adult-specific language to ensure adequate probing of adult manifestations of ADHD symptoms
- The 18 items in the scale correspond to the 18 symptoms in the DSM-IV® criteria
BROWN ATTENTION-DEFICIT DISORDER RATING SCALE FOR ADULTS
A broad-based, 40-item rating scale providing a rating of the frequency of symptoms in many domains3
ADHD RATING SCALE IV WITH ADULT PROMPTS
You May Like: What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Autism
Adhd Symptoms And Risks
ADHD symptoms can include difficulty in maintaining focus, excess movement that is not appropriate with the setting, and frequent bouts of impulsivity.¹²
Despite its prevalence, the causes and risk factors for ADHD remain known, but some research has shown there may be a genetic factor.² The CDC states that other risk factors may include:
-
brain injury
-
exposure to environmental risks, such as lead
-
alcohol and tobacco use during pregnancy
-
premature delivery
-
low birth weight
Previously, it was popularly thought that ADHD might be caused by overconsumption of sugar, watching too much television, poor parenting, or poverty. While these environmental factors might worsen symptoms, the CDC notes that there is not enough evidence to conclude that these are causative factors for ADHD development.²
See also, how race and culture can impact a diagnosis. Plus, diagnosis seekers
Identifying Documents Describing The Proposed Changes And Supportive Evidence
We first sought to identify documents outlining the proposed or actual changes to the DSM-IV-TR ADHD age of onset criterion and the evidence used by the Committee to inform these changes. We searched websites and bibliographic databases, asked manuscript authors and colleagues for studies known to them, and conducted reference checks, forward citation and PubMed similar articles searches .
Also Check: Is Sensitivity To Loud Noises A Sign Of Autism
Assessment Of The Factor Solution That Provides The Best Fit For Adhd Symptoms
The data fit indexes for several factorial models tested in CFA are presented in Table 3. The model with the best factor structure for DSM-5 symptoms was the bifactor model with one general factor and two specific factors . The most important implication from these findings is that a general factor substantially influences all of the ADHD symptoms whereas the specific factors account for additional variance related to inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity.
Other Considerations When Getting Diagnosed With Adhd
In addition to determining the type of ADHD, your clinician may also give you a rating based on the status of your condition and the severity.
Status of your ADHD
If you previously met the criteria for ADHD but are currently experiencing fewer symptoms, you may get labeled as in partial remission. In this case, you still have impairments but dont meet enough symptoms to have a full diagnosis. Oftentimes, people who are receiving effective treatment may fall into this category.
Severity of ADHD
Your clinician may also give you a rating of severity based on your symptoms. You may be rated as:
-
Mild: Few, if any, symptoms in excess of those required to make the diagnosis are present, and symptoms result in only minor functional impairments.
-
Moderate: Symptoms or functional impairment between mild and severe are present.
-
Severe: Many symptoms in excess of those required to make the diagnosis, or several symptoms that are particularly severe, are present, or the symptoms result in marked impairment in social or occupational functioning
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Adhd In Adults
Cultural Changes To The Dsm
Members of the American Psychiatric Associationwhich publishes the DSMas well as other mental health professionals were calling for race, racism, and discrimination to be handled more appropriately in the DSM.
Particular attention was paid to misdiagnosis in socially oppressed racial groups as well as variations of symptom expression across races and possible causes for disorders.
The Cross-Cutting Review Committee on Cultural Issues and an Ethnoracial Equity and Inclusion Work Group collaborated on the following changes:
- The term “racialized” is used instead of “race/racial” to underscore that race is a social construct
- “Ethnoracial” is used to define and combine the U.S. Census categories that encompass both ethnicity and race, such as White, African-American, and Hispanic
- “Minority” and “non-White” are no longer used, as they are thought to describe racial groups in relation to White people, creating a social hierarchy
- “Latinx” is used instead of “Latino” or “Latina” in an effort to promote gender equality
- “Caucasian” is no longer used because of its obsolete description of the origins of the pan-European ethnicity
- Data about the prevalence of certain disorders in specific ethnoracial groups was added when existing research included reliable data
What Is An Adhd Person Like How Does Adhd Affect Functioning
The ADHD brain has been compared to a Ferrari with Model-T brakes a sprinter, not a marathoner a busy intersection with no streetlights a butterfly, and a television with hundreds of channels and someone else wielding the remote control. Many experts conceptualize ADHD as an executive function disorder affecting a number of cognitive and emotional domains, sometimes categorized as hot and cold pathways. Those domains are the following:
Another thing to highlight about the ADHD brain is that its often caught in the default mode network , the brain process responsible for daydreaming, mind wandering, and even ruminating. But if the ADHD brain gets super engaged in something task-positive that requires conscious attention, the DMN deactivates.
Read Also: Why Does Mmr Vaccine Cause Autism
Other Concerns And Conditions With Adhd
The combination of ADHD with other disorders often presents extra challenges for children, parents, educators, and healthcare providers. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to screen every child with ADHD for other disorders and problems. This page provides an overview of the more common conditions and concerns that can occur with ADHD. Talk with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your childs symptoms.
Every child with ADHD should be screened for other disorders and problems.
Common Adhd Diagnosis Mistakes And Challenges
Depression, anxiety, or other psychiatric conditions may be mistaken for ADHD, Solanto says. So may some learning disabilities, as well as medical issues including thyroid problems, seizure disorders, and sleep disorders.And children, teens, and adults with ADHD may be able to work around the challenges of the condition and perform at a high level in school or work, essentially hiding or not really recognizing that theyre dealing with the condition until they meet a major challengesuch as moving from elementary to middle school, from high school to college, or into the working world.
Some people can compensate, she notes. Thats why its important to have a thorough, good evaluation.
ADHD may also be overlooked in girls and women because the condition is more likely to have symptoms related to inattentiveness rather than hyperactivity and impulsivity. Research indicates that females with ADHD that begins in childhood are less likely to be recognized and diagnosed than males, she says. Theyre not disruptive in the classroom. Theyre quiet. Theyre encountering insults to their self-esteem, so they may start thinking of themselves as incompetent or unintelligent. And theyre more likely to be socially ignored by their peers.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Your Baby Has Autism
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patients with ADHD must be followed up regularly to check upon their symptoms and comorbidities. In order to achieve treatment goals, the role of patient education cannot be emphasized enough. For children who have ADHD, the parents should be formally educated about the disorder so that they understand the concept behind the diagnosis. Medication treatment can only be optimized if there is an ongoing interaction between the primary caregiver and the family.
The American Psychiatric Associations Diagnostic And Statistical Manual Of Mental Disorders 5th Edition

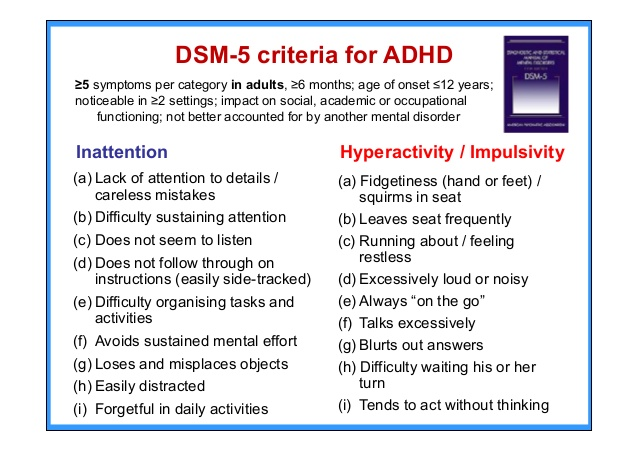
The DSM-5TM medical classification system for ADHD is published by the American Psychiatric Association, and is used in the US and the rest of the world. This classification system defines ADHD as a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development.7 The DSM-5TM includes ADHD among neurodevelopmental disorders, which comprise conditions associated with factors affecting brain development, and gives examples of how ADHD symptoms are expressed across the lifespan. The DSM-5TM states that at least five symptoms must be present prior to age 12 years, and that there should be clear evidence that symptoms interfere with or reduce the level of social, academic and occupational functioning for a diagnosis of ADHD.5
The DSM-5TM replaced the previous version in 2013.7,8 The NICE guidelines1 and other clinical guidelines2-5 refer to the DSM-5TM however, some clinical trials initiated before the new edition also refer to the DSM-IV.
You May Like: How To Deal With Autism Tantrums