How Is Autism Treated
Currently there is no cure for ASD. Therapies and behavioral interventions are designed to remedy specific symptoms and can substantially improve those symptoms. Some symptoms can be treated with medication. The ideal treatment plan coordinates therapies and interventions that meet the specific needs of the individual. Most health care professionals agree that the earlier the intervention, the better.
Educational/behavioral interventions: Early behavioral/educational interventions have been very successful in many children with ASD. In these interventions therapists use highly structured and intensive skill-oriented training sessions to help children develop social and language skills, such as applied behavioral analysis, which encourages positive behaviors and discourages negative ones. In addition, family counseling for the parents and siblings of children with ASD often helps families cope with the particular challenges of living with a child with ASD.
General Guidelines Of Citing A Dsm
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Health refers to a handbook used by clinicians and psychiatrists in the United States. Basically, these health practitioners use the DSM to diagnose mental illnesses. For instance, the DSM contains details about all mental-related health disorders for all people. In this case, one may find descriptions, symptoms, and other details required to diagnose psychological health conditions for children and adults. Besides, the manual contains statistics about the gender differences concerning psychiatric conditions. Then, other details include the age of onset, effects of management, and conventional treatment approaches. Moreover, mental health practitioners use the manual when classifying patients for billing purposes. Hence, students have to learn how to cite a DSM-5 in APA 7 and 6.
Read Also: Freddie Highmore Really Autistic
How Is Asd Diagnosed
ASD symptoms can vary greatly from person to person depending on the severity of the disorder. Symptoms may even go unrecognized for young children who have mild ASD or less debilitating handicaps.
Autism spectrum disorder is diagnosed by clinicians based on symptoms, signs, and testing according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-V, a guide created by the American Psychiatric Association used to diagnose mental disorders. Children should be screened for developmental delays during periodic checkups and specifically for autism at 18- and 24-month well-child visits.
Very early indicators that require evaluation by an expert include:
- no babbling or pointing by age 1
- no single words by age 16 months or two-word phrases by age 2
- no response to name
- excessive lining up of toys or objects
- no smiling or social responsiveness
Later indicators include:
- impaired ability to make friends with peers
- impaired ability to initiate or sustain a conversation with others
- absence or impairment of imaginative and social play
- repetitive or unusual use of language
- abnormally intense or focused interest
- preoccupation with certain objects or subjects
- inflexible adherence to specific routines or rituals
Read Also: Can An Mri Detect Autism
Diagnosis Of Other Co
Sometimes autism comes with other conditions. These are called co-occurring conditions.
If children have signs or characteristics that meet the criteria for other conditions, theyll be diagnosed as having two or more conditions for example, autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or intellectual disability.
Get To Know The Positive Side Of Adhd
Educate yourself on the positive traits that people with ADHD have. As a child, these traits may seem like a detriment. With maturity, the deficits become attributes.
Heres a small list:
- Inability to focus turns into creativity and flexibility
- Hyperactive turns into high energy
- Hypersensitivity turns into sensitivity to others and attention to detail
- Impulsivity becomes fearlessness and ingenuity
Recommended Reading: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Recommended Reading: Is Epilepsy Common In Autism
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
Components Of Aiims Modified Indt Asd Tool
The modified tool has two sections . Section A has 28 questions for 7 items representing domains of DSM-5 criteria for ASD diagnosis. Section A has 2 subsections: Subsection A1 has three subdomains namely, deficits in social-emotional reciprocity , non-verbal communication and deficits in developing and maintaining relationships and subsection A2 has 4 subdomains namely- Stereotyped movements or speech , Fixed routines , Fixed interests and Sensory symptoms .
Response to each question is marked as yes, no or unsure. Response of unsure is marked only when both parents and investigator are unsure of the response. Investigator assessment relies upon interview of primary caregivers and direct observation of child involved in spontaneous play activity. For any discrepancy in parental response and investigators assessment, it is indicated for each question whether parental response or assessors observation should take precedence. Based on question and indication in the tool, the response of either yes or no might be abnormal. Number of abnormal responses are calculated as total score for each patient. Hence a child may score anywhere between zero to 28.
Recommended Reading: What Does Aba Mean Autism
Restrictive / Repetitive Behaviors May Include:
- Repeating certain behaviors or having unusual behaviors, such as repeating words or phrases
- Having a lasting intense interest in specific topics, such as numbers, details, or facts
- Showing overly focused interests, such as with moving objects or parts of objects
- Becoming upset by slight changes in a routine and having difficulty with transitions
- Being more sensitive or less sensitive than other people to sensory input, such as light, sound, clothing, or temperature
People with ASD may also experience sleep problems and irritability.
People on the autism spectrum also may have many strengths, including:
- Being able to learn things in detail and remember information for long periods of time
- Being strong visual and auditory learners
- Excelling in math, science, music, or art
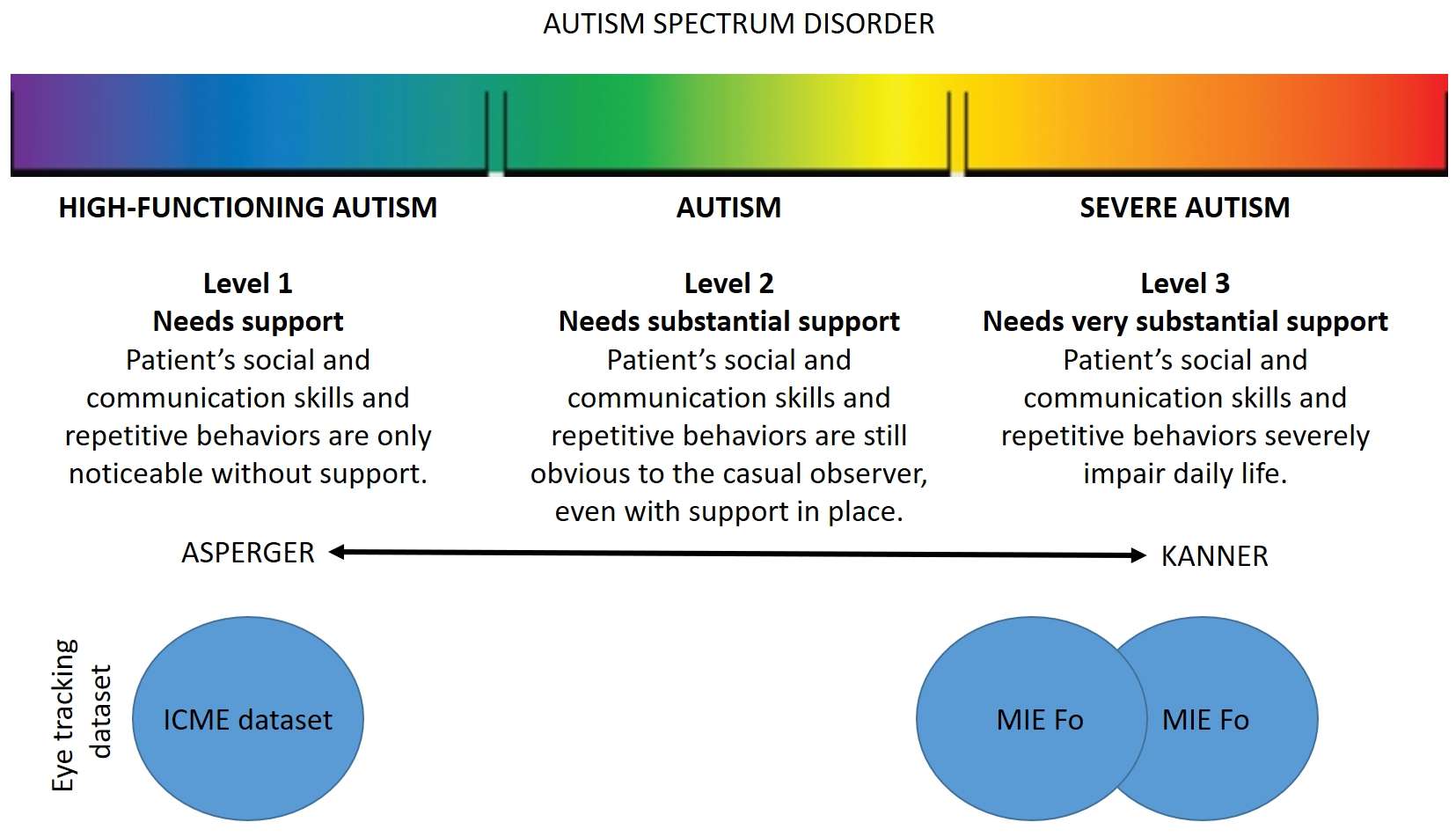
Level : Requires Very Substantial Support
Level 3 is the most severe form of autism. Children in this category will have many of the same behaviors as those with levels 1 and 2, but to a more extreme degree.
Problems expressing themselves both verbally and nonverbally can make it very hard to function, interact socially, and deal with a change in focus or location. Engaging in repetitive behaviors is another symptom of level 3 ASD.
A person with ASD level 3 will have a very limited ability to speak clearly and will rarely start interactions with other people. When they do, they will do so awkwardly. Someone with level 3 will also respond only to very direct social approaches from other people.
Recommended Reading: What Does The National Autistic Society Do
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Diagnostic Criteria For Autism Spectrum Disorder In The Dsm
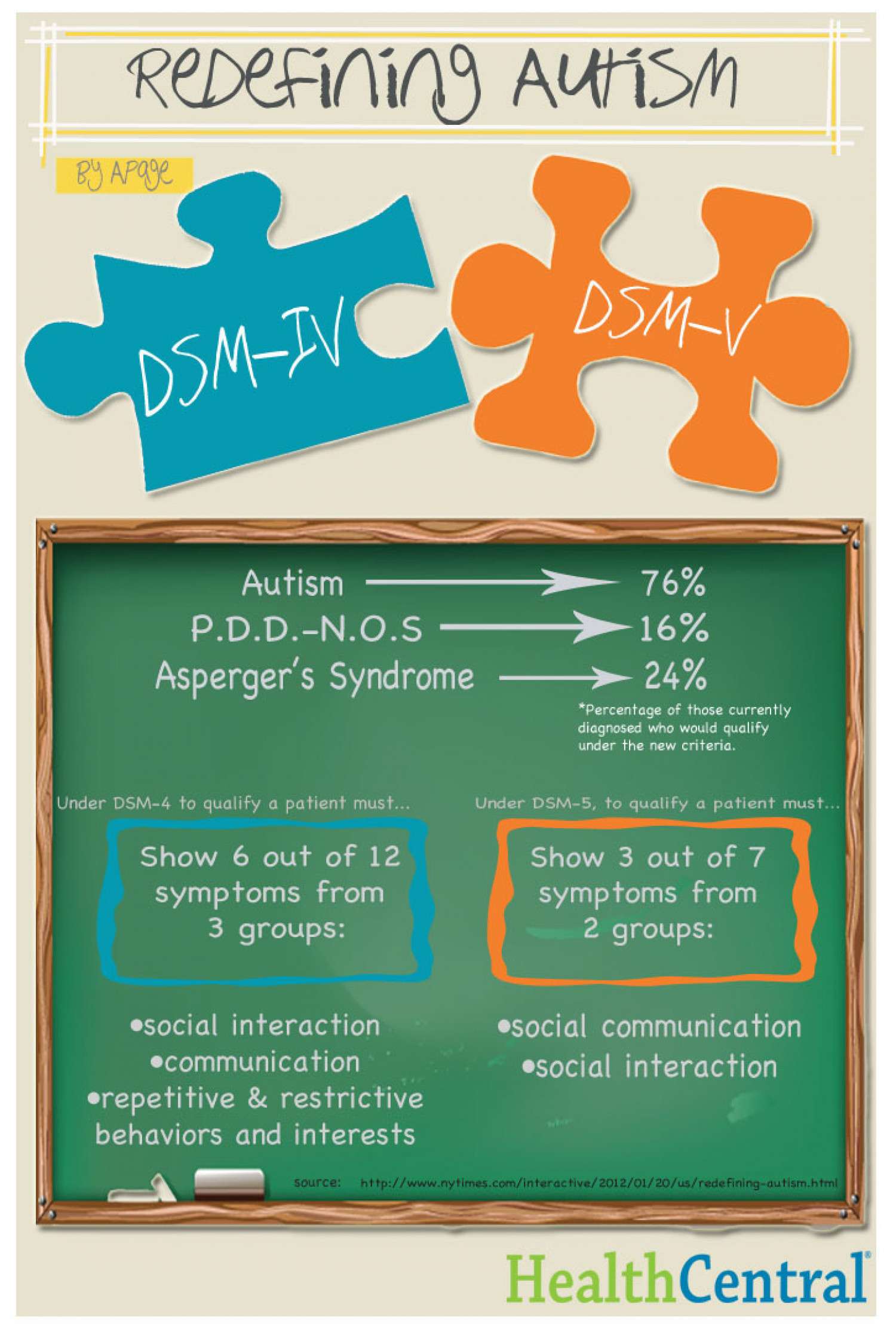
DSM stands for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, which is a manual published by the American Psychiatric Association. The manual includes classifications of psychiatric disorders for use by medical and mental health professionals. Clinicians may refer to versions of the DSM to look for diagnostic codes of different disorders and examine criteria for diagnosis. About 25% of the disorders are specific to children and are in the section of Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence. Autism and related disorders have been specifically included in different versions of the DSM since 1980.
The latest edition of the DSM, DSM-5, made significant changes to the diagnostic criteria for autism and related disorders. In DSM-IV, five separate diagnoses were classified under the heading Pervasive Development Disorders: Autistic disorder, Asperger Syndrome, Pervasive Development Disorder Not Otherwise Specified , Rett Syndrome, and Childhood Disintegrative Disorder. The Pervasive Development Disorder category no longer appears in DSM-5, and Autistic disorder, Asperger Syndrome, and PDD-NOS have now been combined into one label: Autism Spectrum Disorder .
Related Articles:
Read Also: How Can A Kid Get Autism
Specify Current Severity: Severity Is Based On Social Communication Impairments And Restricted Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior
B. Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history :
C. Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period .
D. Symptoms cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of current functioning.
E. These disturbances are not better explained by intellectual disability or global developmental delay. Intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder frequently co-occur to make comorbid diagnoses of autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability, social communication should be below that expected for general developmental level.
NOTE: Individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnosis of autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder, or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. Individuals who have marked deficits in social communication, but whose symptoms do not otherwise meet criteria for autism spectrum disorder, should be evaluated for social communication disorder.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know the primary causes of ASD, but studies suggest that a persons genes can act together with aspects of their environment to affect development in ways that lead to ASD. Some factors that are associated with an increased likelihood of developing ASD include:
- Having a sibling with ASD
- Having older parents
- Having certain genetic conditions
- Having a very low birth weight
Don’t Miss: How To Diagnose Autism Spectrum
Communications With The Workgroup
In 2009, ASAN made contact with the DSM-5 Workgroup through one of its members, hereby referred to as Member A, whom Ari had corresponded with earlier regarding early intervention methodology. The two had earlier found common ground over a shared critique of the excess rigidity of behaviorist interventions. Separately, Ari connected with the workgroup Chair at a meeting of the Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee and, after Member A provided the Chair and Workgroup with a favorable impression of ASAN, Ari was invited to provide written and verbal feedback to the workgroup at several teleconferences and semi-annual in-person meetings in Washington DC hotel rooms. Ari also used the IACC as a vehicle for highlighting autistic community priorities and concerns regarding the DSM-5 during his two years as a public member of the committee .
After an individual meeting with the Chair and phone calls with her and Member A, Ari met with the workgroup in person on the morning of April 8, 2010 . At this meeting, Ari stressed the importance of acknowledging mitigating measures and ensuring that individuals would not lose access to a diagnosis by virtue of their having learnt how to pass as non-autistic, a serious concern for many autistic adolescents and adults.
symptoms must be present in the early developmental period .
Symptoms must be present in early childhood .
Symptoms must be present in early childhood .
Evaluation Of Treatment Effectiveness
A 2019 review found sensory integration therapy to be effective for autism spectrum disorder. Another study from 2018 backs up the intervention for children with special needs, Additionally, the American Occupational Therapy Association supports the intervention.
In its overall review of the treatment effectiveness literature, Aetna concluded that “The effectiveness of these therapies is unproven”, while the American Academy of Pediatrics concluded that “parents should be informed that the amount of research regarding the effectiveness of sensory integration therapy is limited and inconclusive.” A 2015 review concluded that SIT techniques exist “outside the bounds of established evidence-based practice” and that SIT is “quite possibly a misuse of limited resources.”
You May Like: How To Be Diagnosed With Autism As An Adult
How Does The Dsm
Six major changes included:
1. Four previously separate categories of autism consolidated into one umbrella diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
The previous categories were:
- Pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified
2. Consolidation of three previous categories of autism symptoms
- Social impairment
into two categories of symptoms
- Persistent deficits in social communication/interaction and
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior
3. The addition of sensory issues as a symptom under the restricted/repetitive behavior category. This includes hyper- or hypo-reactivity to stimuli or unusual interests in stimuli
4. A severity assessment scale based on level of support needed for daily function.
5. Additional assessment for:
- Any known genetic causes of autism
- Language level
- Intellectual disability and
- The presence of autism-associated medical conditions
6. Creation of a new diagnosis of social communication disorder, for disabilities in social communication without repetitive, restricted behaviors.
What Dsm 5 Could Mean To Children With Autism And Their Families
Dsm 5 Autism Criteria Checklist. Here are a number of highest rated Dsm 5 Autism Criteria Checklist pictures on internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by processing in the best field. We undertake this kind of Dsm 5 Autism Criteria Checklist graphic could possibly be the most trending subject afterward we ration it in google gain or facebook.
Crumbtrail.org is an open platform for users to share their favorite wallpapers, By downloading this wallpaper, you agree to our Terms Of Use and Privacy Policy. This image is for personal desktop wallpaper use only, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, DMCA report please Contact Us
Read Also: Will My Child Grow Out Of Autism
Adhd Assessments Occupational Therapy And Child & Family Therapy
An ADHD assessment is not just a series of tests so that you can put the ADHD label on your child. It is these tests that will help you know your childs strengths and weaknesses. Your ADHD child will most likely be hyperactive with low impulse control and a short attention span. That pretty much defines ADHD! But that is not the entire breadth of their character.
Even so, lets first look at what an occupational therapist and child & family therapist can do to help the hallmark symptoms of ADHD. Your child is most likely running around like a perpetual motor and cant sit still. He wont sit down and join the group and he cant listen to instruction and rules. In elementary school, when my son showed these behaviors, the punishment was to sit on the sidelines during physical education.
Your therapists will know that this is absolutely counterproductive! These kids need an outlet for all of that energy. Help them find that outlet.
Therapy will also help teach your child the difficult concept of self-control. I will be good when Im six, my son said. He really wanted to be good so badly, he just found it impossible.
Your therapist will give your whole family tips and tricks to help him plug into his ability to monitor his actions. They will also help him understand that even when he fails, he is still loved and respected. And for a child constantly in trouble, this is important.
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder refers to a group of neurodevelopment disorders cthat affect how people communicate, learn, behave, and socially interact. People may have repetitive and characteristic patterns of behavior or narrow interests. Not everyone who has ASD may have these symptoms, which are usually present from early childhood and affect daily functioning. Both children and adults can have ASD.
The term spectrum refers to the wide range of symptoms, skills, and levels of disability in functioning that can occur in people with ASD. Some children and adults with ASD are fully able to perform all activities of daily living while others require substantial support to perform basic activities. Learning and thinking can range from extremely gifted to needing severe help.The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders includes Asperger syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorders not otherwise specified as part of ASD rather than as separate disorders. A diagnosis of ASD includes an assessment of intellectual disability and language impairment.
ASD occurs in every racial and ethnic group, and across all socioeconomic levels. However, boys are significantly more likely to develop ASD than girls.
Don’t Miss: How Is Adult Autism Diagnosed
Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnostic Criteria 29900
A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by all of the following, currently or by history :
1. Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back-and-forth conversation to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions.
2. Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction, ranging, for example, from poorly integrated verbal and nonverbal communication to abnormalities in eye contact and body language or deficits in understanding and use of gestures to a total lack of facial expressions and nonverbal communication.
3. Deficits in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships, ranging, for example, from difficulties adjusting behavior to suit various social contexts to difficulties in sharing imaginative play or in making friends to absence of interest in peers.
Specify current severity: Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior .
B. Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history :
1. Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech .
2. Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior .
Specify if: