How Autism Spectrum Disorders Are Described
Psychiatrists and other clinicians rely on the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders to define autism and its symptoms. The DSM-5 definition recognizes two main symptom areas:
- Deficits in social communication and interaction
- Restricted, repetitive behaviors, interests, or activities
These symptoms appear early in a childs developmentalthough diagnosis may occur later. Autism is diagnosed when symptoms cause developmental challenges that are not better explained by other conditions.
The definition of autism has been refined over the years. Between 1995 and 2011, the DSM-IV grouped Aspergers Syndrome and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified with autism. Aspergers syndrome was an autism spectrum disorder marked by strong verbal language skills and, often, high intellectual ability. PDD-NOS was a more general diagnosis for people who did not fit clearly into the other two categories.
However, the DSM-5 no longer recognizes Aspergers syndrome or PDD-NOS as separate diagnoses. Individuals who would previously have received either of these diagnoses may now receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder instead.
Biological Risk Factors For Autism
Recent studies have also found that random or spontaneous gene mutations can lead to a higher risk of autism. Spontaneous gene mutations are not passed down from the parents but instead occur randomly in the egg or sperm during fertilization.
As the fertilized egg divides itself, the mutation can continue to occur in each cell. What happens with these mutations? Research is ongoing, but it appears that the mutation can affect single genes or entire strands of DNA.
When a full strand of DNA is affected, multiple genes may be duplicated or deleted. Studies have recently found that people with autism have more duplicated genes than people without autism.
As with genetic risk factors, the spontaneously mutated genes do not seem to cause autism, but it appears that they can increase the risk factor.
How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Treated
ASD is most often a life-long condition. Both children and adults with autism benefit from behavioral interventions or therapies that can teach new skills to address the core deficits of autism and to reduce the core symptoms. Every child and adult with autism is unique. For this reason, the treatment plan is individualized to meet specific needs. It is best to begin interventions as soon as possible, so the benefits of therapy can continue on throughout the course of life.
Many people with ASD often have additional medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal and feeding issues, seizures and sleep disturbances. Treatment can involve behavioral therapy, medications or both.
Early intensive behavioral treatments involves the entire family and possibly a team of professionals. As your child ages and develops, treatment may be modified to cater to their specific needs.
During adolescence, children benefit from transition services that promote skills of independence essential in adulthood. The focus at that point is on employment opportunities and job skill training.
Don’t Miss: Which Country Has The Highest Autism Rate
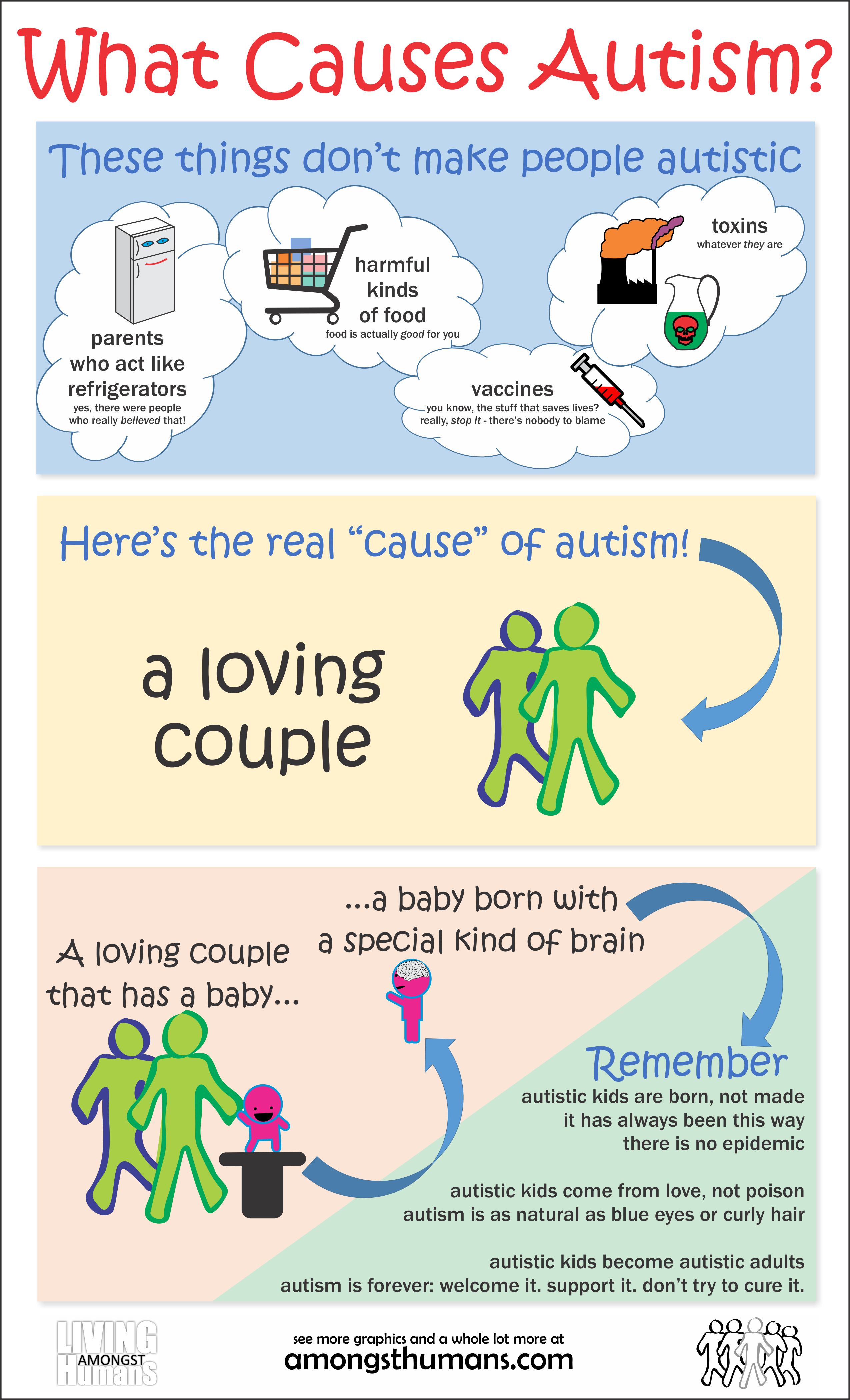
What Causes Autism Spectrum Disorder
There is no clear-cut cause of ASD. Some causes that are supported by research include genetic and some environmental factors. Specific genetic causes can only be identified in 10% to 20% of cases. These cases include specific genetic syndromes associated with ASD and rare changes in the genetic code.
Risk factors include older parental age, low birth weight, prematurity and maternal use of valproic acid or thalidomide during pregnancy, among others. This field of study is an active one for research.
What Is The Outlook For People With Autism Spectrum Disorder
In many cases, the symptoms of ASD become less pronounced as a child gets older. Parents of children with ASD may need to be flexible and ready to adjust treatment as needed for their child.
People with ASD may go on to live typical lives, but there is often need for continued services and support as they age. The needs depend on the severity of the symptoms. For most, it’s a lifelong condition that may require ongoing supports.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Through research, there has been much that has been learned about autism spectrum disorder over the past 20 years. There is ongoing active research on the causes of ASD, early detection and diagnosis, prevention and treatments.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/29/2020.
References
Don’t Miss: How To Know If You Have Autism
A Short History Of Autism
Researchers have been working on autism and autism-like disorders since the 1940s. At that time, autism studies tended to be small in scale and used varying definitions of the disorder. Autism was also sometimes lumped in with other conditions.
Focused research into ASD became more common in the 1980s when the DSM-III established autism as a distinct diagnosis. Since then, researchers have explored the causes, symptoms, comorbidities, efficacy of treatments, and many other issues related to autism.
Researchers have yet to discover a cause for autism. Many of the ideas put forth thus far have been disproven. Likely a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors are at work, which is the case with many psychiatric disorders and conditions.
Do Environmental Factors Cause Autism
Several environmental factors increase the risk of autism, and they center around experiences in the pregnancy or infancy that may influence brain development. Premature birth and low birth weight raise the risk of autism, as do diabetes, high blood pressure, and infection during pregnancy. Having an older father is also a risk factor, likely because the chance of spontaneous genetic mutations increases with age.
There is some evidence of a correlation between exposure to air pollution during pregnancy or early childhood and the onset of autism. However, researchers are still working to understand this relationship. Pinning down the connection between autism and any single environmental factor is difficult because its nearly impossible to isolatethere are so many variables at play.
Don’t Miss: Can Trauma During Pregnancy Cause Autism
Learn More About Applied Behavior Analysis Therapy
If a family member has been diagnosed with autism, it can be frustrating not to know the exact causes. However, that doesnt mean autistic people cant get the help and support they need.
When it comes to treatment options, early intervention is the best path to success for autistic children. Evaluate your child for signs of autism early and always attend important checkups. Communicate any signs you see to your doctor so they can determine if a full evaluation is necessary.
Once the evaluation and diagnosis are complete, you can begin exploring treatment options. Applied Behavior Analysis is a customizable, evidence-based treatment for autism that focuses on each clients innate skills and strengths.
Contact us for a free consultation about ABA therapy at our treatment centers or our in-home services in New Hampshire and Massachusetts.
Use Of Information Collected From You
Recommended Reading: How To Transition A Child With Autism
Is There A ‘cure’ For Autism
There is no known ‘cure’ for autism. We also believe that autism does not need a ‘cure’ and should be seen as a difference, not a disadvantage. We also warn people about fake cures and potentially harmful interventions here.
This does not mean that autistic people do not face challenges, but with the right support in place, they are more than capable of living fulfilling and happy lives. Because autism is a ‘spectrum’ condition it affects different people in different ways. It is therefore very difficult to generalise about how an autistic person will develop over time. Each person is different, and an intervention or coping strategy which works well with one person may not be appropriate or effective with another.The characteristics of autism can present themselves in a wide variety of combinations. Two people with the same diagnosis can have a very different profile of needs and skills.
Possible Environmental And Genetic Causes
Autism is believed to be caused by the influence of both environmental and genetic factors. However, till date no specific cause has been assigned to this disorder. Diagnosis of autism has detected that in autistic patients certain areas of the brain fail to connect properly to other areas which is attributed to developmental anomalies that occur in the brain prior to the birth of the child. Often prematurely born children have exhibited higher frequency of autism. Autism is also considered to have a familial linkage as in the case of twins, where, when one individual is affected, the other has a 35 to 95% chance of being autistic. In some cases, families with autistic children have also been found to have members affected by other mental disorders like schizophrenia and bipolar disorders, at a frequency greater than the average case. Parents of children with autism have, in certain cases, also been found to exhibit some type of mild but unusual behavior. Though familial studies have pointed towards heredity as one of the causes of autism, a specific gene responsible for autism has not yet been identified conclusively. Sporadic mutations in the egg or sperm cells of the autistic childs parents before fertilization or in the zygote after fertilization could also be responsible for autism in cases where there is no familial linkage to the disease.
Don’t Miss: Why Is There More Autism Now
Is Autism A Brain Disorder
There is a specific condition that has an association with neurological development, which affects social interaction as well as communication and how an individual perceives and socializes with others. A pattern of repetitive behavior, limitations in behavior, and limited information are also known to contribute to the disorder.
Do Symptoms Of Autism Change Over Time

For many children, symptoms improve with age and behavioral treatment. During adolescence, some children with ASD may become depressed or experience behavioral problems, and their treatment may need some modification as they transition to adulthood. People with ASD usually continue to need services and supports as they get older, but depending on severity of the disorder, people with ASD may be able to work successfully and live independently or within a supportive environment.
Also Check: Does Anthony Hopkins Have Autism
Autism Treatment Center Of America
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
Pre-Requisites for this course are:
- Your child is 7 years or older.
- Your child uses sentences, asks and answers questions and might even be able to have back and forth conversations with other people.
- You have completed one of the following: The Son-Rise Program Start-Up, The Son-Rise Program Online Course, or you have done Son-Rise Program Consultations.
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
NOTE: Attendance of live sessions via Zoom are required to complete this course.
Please note, this is a per-person registration
Please make sure you understand the following pre-requisites for this course before registering.
Personal Statement
What Causes Autism Study Of 100000 Kids Reveals New Clues
From genetics to fevers, Columbia psychiatrist and epidemiologist Mady Hornig discusses the possible roots of this mysterious condition.
Autism is, for the most part, an inherited disorder: scientists estimate that up to 80 percent of a childs risk of developing it is determined by DNA. But environmental and behavioral risk factors may also play a role, and since rates of autism in the US are at an all-time high, new and expecting parents are eager to learn more about the roots of this complex condition.
For the past two decades, a team of researchers including Michaeline Bresnahan 99PH, Mady Hornig, W. Ian Lipkin, and Ezra Susser 74CC, 82VPS, 93PH, all epidemiologists at Columbias Mailman School of Public Health, has been searching for nongenetic clues to explain why some kids develop autism and others do not. The researchers, in collaboration with the Norwegian Institute of Public Health and other Columbia scientists, have scrutinized the medical histories of more than one hundred thousand children, as well as those of their parents. Armed with unprecedented amounts of data, the researchers are investigating dozens of hypothesized risk factors for autism everything from parental age to maternal infections to vitamin deficiencies. Columbia Magazine recently spoke to Hornig, who is herself the mother of an adult son with autism, about the teams research.
What are the major risk factors for autism?
Does it matter what causes the fever?
Don’t Miss: How To Get Your Autistic Child To Talk
Myths About Autism Causes
One 1998 study explored a potential link between childhood vaccines and autism spectrum disorder. However, several later studies found no evidence of a link between vaccines and ASD. The original study scientists even retracted the statement about vaccines in 2010. Vaccines to prevent childhood infectious diseases have been proven to be safe and not linked to autism.
Our Commitment To Privacy
The Autism Treatment Center of America® are committed to your privacy. This notice serves to help you better understand what information we collect, how we use that information, and with whom we may share a limited portion of that information. If you have questions or concerns regarding this policy, you should contact Customer Support by email .
We know that you value your personal information, and we strive to protect your privacy as if it were our own. The Autism Treatment Center of America uses of your information is limited to the ways outlined in this notice, except as required by law and/or to comply with a judicial proceeding, court order, or legal process served on us.
You May Like: What Is The Main Difference Between Autism And Aspergers
What Role Do Genes Play
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
Brain Development And Autism
The brain develops differently in autistic children compared with typically developing children.
In young children, the brain is developing all the time. Every time a child does something or responds to something, connections in the brain are reinforced and become stronger.
Over time, the connections that arent reinforced disappear theyre pruned away as theyre not needed. This pruning is how the brain makes room for important connections those needed for everyday actions and responses, like walking, talking or understanding emotions.
In autistic children, the brain tends to grow faster than average during early childhood, especially during the first three years of life. The brains of autistic babies appear to have more cells than they need, as well as poor connections between the cells.
Also, pruning doesnt seem to happen as much in autistic children. This means that information might be lost or sent through the wrong connections. The lack of pruning might also explain why the brain seems to be growing faster in autistic children than in typically developing children.
Its not yet clear what causes this difference in brain development.
Don’t Miss: Is Dyspraxia Related To Autism
Using Milestones To Track Development
Families can also benefit from an awareness of key developmental milestones as their child grows. These milestones help all families, regardless of concern about autism, understand their childs development as compared to typically developing children at the same age. Tracking your childs development can help you recognize potential concerns and identify areas where your child could benefit from specific supports and services.
The Baby Navigator provides a timeline of detailed milestones for babies and toddlers from 1 to 24 months. The CDC provides milestones in different categories from 2 months to 5 years of age, and additional material through Learn the Signs, Act Early. Previously, CDC milestones indicated what was expected to be achieved by 50% of children at each age. As of February, 2022, this has been updated to instead reflect what the majority of children can be expected to achieve.
Below are some highlights of the milestones your child should reach at each age. This is not an exhaustive list, and is focused on milestones that can be easily observed through interacting with your child. Please go to the CDC Learn the Signs Act Early website or Baby Navigator for more examples of what you should expect your child to achieve at each age.