How This Project Is Making A Difference
The team found that parents from the SOLACE group reported improved mental health, higher self-esteem and self-compassion after the intervention period. They also reported lower self-stigma and increased positive feelings about the role of caregiving. The “control” group did not show these imporovements. Parents particularly welcomed being able to share their experiences with other parents and learning about self-compassion.
The team will now use the findings and learnings from this project to develop a much larger randomised controlled trial. This is an essential step towards the therapy being adopted and rolled out to more parents and carers.
First Steps After Receiving An Autism Diagnosis
You have just learned that your child has been diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. For some parents, the news comes as a shock, while other parents may have been expecting it. However, almost all parents who receive this diagnosis for their child struggle with reimagining their childs future with this pervasive developmental disability. You are not alone, and it is normal to feel this way. The important thing to know is that, although there is no known cure for autism, there is hope. Your child will be able to learn, grow and gain new skills within their potential. The important first steps are educating yourself about the diagnosis, adjusting the childs home environment to best meet their needs, and seeking professional therapeutic services.
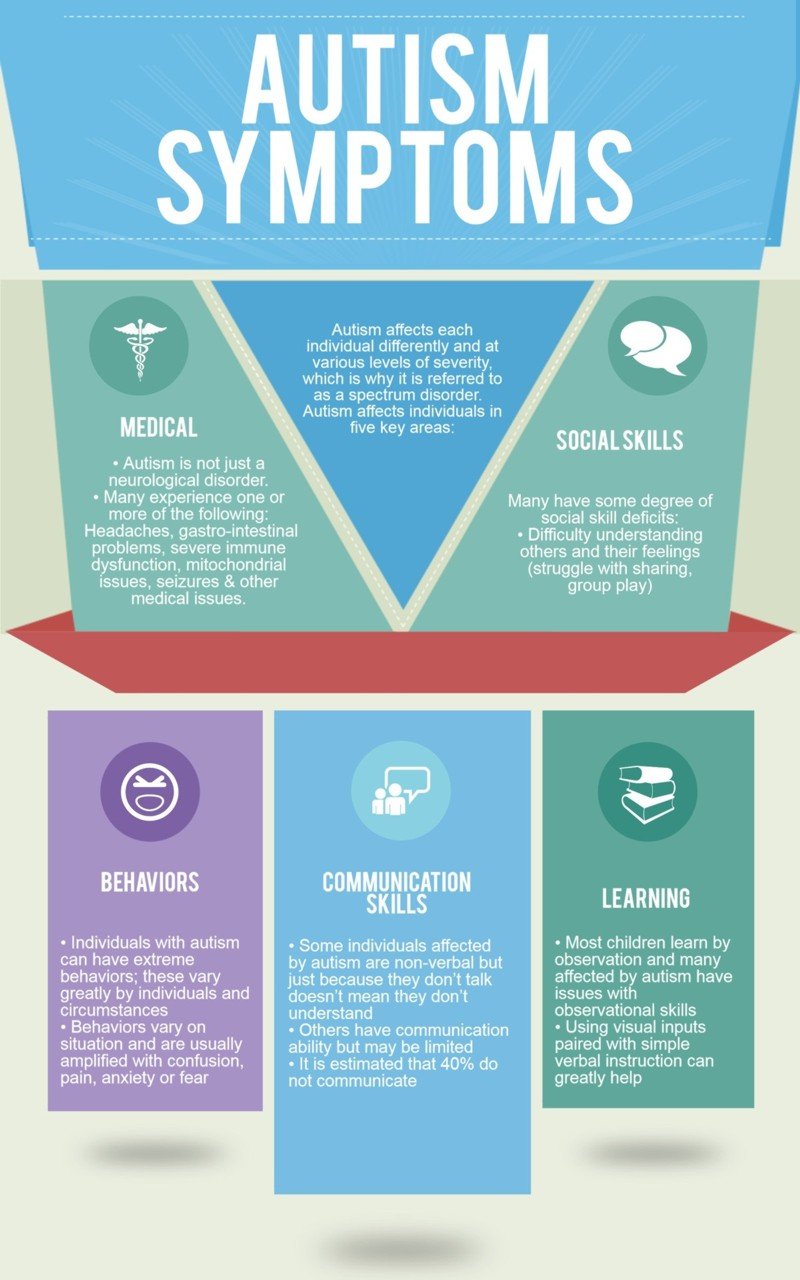
What is autism spectrum disorder?
As the name suggests, children with this diagnosis fall along a spectrum of symptoms that can vary from children who are fairly verbal and described as high functioning to those who have no language abilities and are described as lower functioning. Your childs symptoms and abilities will fit into one of three diagnostic levels to indicate the severity and where they fall on the spectrum:
Level 2:;This level requires substantial support. These children may have some verbal or cognitive deficits, and their social impairments are apparent even with supports in place.
What can I do at home to help my child?
Use Visuals
Increase Structure
What To Do Next
- Attend one or more parent support groups, or join a parent email listserve: Parents can be a wonderful source of support and information.
- If you dont already have one, get a proper diagnosis; you will need it to secure appropriate services. Some practitioners will give you a softer diagnosis in order to spare your feelingsthis is not actually a kindness, because it will impede your ability to get the services your child needs and is entitled to.
- Contact your states Developmental Disabilities program and apply for services. Be persistent.
- Contact your local school district and ask about school programs. See what they have to offer.
- Find a local physician who offers an integrated medical approach to autism. Some physicians will be open to medical and nutritional testing and medical and nutritional treatments, but others will not find one who is willing to help your child, as opposed to just monitoring the severity of your childs problems. Do not take your child to a physician who does not support you or respect your viewpoint.
- Attend the Autism Research Institutes free online webinars and continuing education events.
- Make sure you still find some time for your other children and spouse/significant other. Having a child with autism can result in many challenges, and you need to be prepared for the long term.
- Continue trying to learn all you can. Good luck!
Read Also: What’s The Definition Of Autism
Can You Grow Out Of Autism
The short answer is no. Autism is a lifelong diagnosis, and there is no known cure.
As a spectrum disorder, there are varying degrees of autism and levels of disability. Some children with milder symptoms can learn how to manage the disorder more effectively than others.
Autism impacts communication, behavior, emotion, and social skills. The earlier it is diagnosed, the more effectively a child can learn how to improve these skills through early intervention techniques.
There have been several studies documenting that between 3% and 25% of children diagnosed with autism seem to grow out of their diagnoses. These children were often diagnosed young. In follow-ups, they show no characteristics of the disorder later in life. This is called an optimal outcome, or OO.
Other studies show that children in the OO group who were diagnosed with autism before 5 years old, and tested through the standard autism diagnostic test and personality tests, no longer show social characteristics of autism. These children no longer fall into the diagnostic parameters of autism.
There are several possible reasons for this outcome. It does not mean that a child can truly outgrow an autism diagnosis.
How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Treated
ASD is most often a life-long condition. Both children and adults with autism benefit from behavioral interventions or therapies that can teach new skills to address the core deficits of autism and to reduce the core symptoms. Every child and adult with autism is unique. For this reason, the treatment plan is individualized to meet specific needs. It is best to begin interventions as soon as possible, so the benefits of therapy can continue on throughout the course of life.
Many people with ASD often have additional medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal and feeding issues, seizures and sleep disturbances. Treatment can involve behavioral therapy, medications or both.
Early intensive behavioral treatments involves the entire family and possibly a team of professionals. As your child ages and develops, treatment may be modified to cater to their specific needs.
During adolescence, children benefit from transition services that promote skills of independence essential in adulthood. The focus at that point is on employment opportunities and job skill training.
Also Check: Who Can Diagnose Autism Spectrum Disorder
Going Forward Achieving Better Outcomes For All
The World Health Organization declares that the highest attainable standard of health is a fundamental right for all human beings. Leaving aside entirely the idea of a cure for autism, people with autism deserve much better health care and health research than they currently enjoy.
By adequately identifying and addressing medical issues associated with autism, a wide range of individuals challenges and difficulties can potentially be reduced, including anxiety, impulsivity, headaches, poor sleep, depression, aggression, self-injury, obsessive and compulsive behaviours, gastrointestinal problems to name a few.
No one should be expected to suffer a lower standard of health simply because of an autism diagnosis, yet diagnostic overshadowingattributing medical symptoms and conditions to the diagnosis of autism and therefore not offering appropriate investigation or treatmentis widespread.
If an individuals experience of autism does not involve health problems that result in suffering, and if the symptoms of autism are not perceived to be an impediment to happiness, independence, success, an enjoyable social and personal life, and to being in control of their lives, then there would no reason to seek intervention. However, for the majority of those diagnosed with autism, there is sufficient suffering and serious disability to rightfully deserve thorough investigation and appropriate intervention.
What Does This Mean For People Currently Awaiting Diagnosis
When it comes to looking at the pros and cons of these changes, I understand that most people who are waiting for a diagnosis are less than impressed. Despite this, today I wanted to create a balanced argument for the DSM-5, as I believe that the publication does have the potential for good and then I will discuss its blatant flaws and come to a conclusion on why it is indeed rubbish.
Pros:
- A more accurate title: Changing the name of autism to Autistic Spectrum Disorder may seem like a small change to most. However, for people who are freshly diagnosed with autism, it lets them know immediately that, even though they are now autistic, this word wont define them: as there is still a whole spectrum of possibilities .
- It makes things clearer : I understand that most people who are autistic dislike change, but if you look at the old way of diagnosing, its hard to say it was perfect. With previous types of autism including names such as: Aspergers Syndrome, Atypical Autism and Autistic Disorder, most people with autism didnt understand what their diagnosis means, even after receiving it.
- Levels is better than Functioning: As stated in the intro, there isnt/never was such a thing as high/low functioning autism. This is for good reason, as it makes people who are described as low function feel like they have nothing to offer, which of course we/they do.
Cons:
Recommended Reading: Will My Child Be Autistic
Autism As A Natural Variation
I am a Proud Autistic. Tito Mukhopadhyay15
Some adults with ASD have led a neurodiversity movement that celebrates autism as a natural variation of the human condition and opposes efforts to cure it. These advocates prefer supports and accommodations for people with ASD, rather than treatments that would erase harmless autistic behaviors.16
As professor Ralph J. Savarese explained in Disability Studies Quarterly, neurodiversity means “a willingness to make room for difference as difference .”17
Some neurodiversity advocates with milder forms of autism have garnered media attention, but what about those with severe autism? They appear in the mainstream media most often when they have been given the opportunity to demonstrate extraordinary skills or to challenge preconceptions of autism.
The poet Tito Mukhopadhyay was diagnosed with severe, nonverbal autism in India in the 1990s. His mother, Soma Mukhopadhyay, taught him to communicate through writing, by using her own style of teaching. Mother and son have been the subject of television shows, articles and blogs. The author of The Mind Tree and other books, Mr. Mukhopadhyay looks forward to a world beyond stigma. He writes: “One day I dream that we can grow in a matured society where nobody would be ‘normal or abnormal’ but just human beings, accepting any other human being ready to grow together.”18
Mom Uses Junk Science To Treat Child With Autism Shares It Online
I think that given the complexity and the variability of the causes and the manifestations of autism, trying to come up with a cure is probably not the right approach, said autism researcher and psychologist Len Abbeduto, director of the University of California, Davis, MIND Institute in Sacramento.
An estimated 80 percent of autism cases involve genetic factors, and it tends to run in families, but there is no single autism gene, Abbeduto explained. In fact, research has shown that more than 100 genes, and maybe upwards of 1,000, may play a role. Researchers also suspect that environmental factors such as exposures to infectious agents, pesticides or other toxins in pregnancy may play a role.
Scientists are investing a lot of work into understanding the genes but were also realizing its a lot more complicated than anybody ever thought when they started out, psychologist Ann Wagner, national autism coordinator for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, said.
Its highly likely that there are different causes for different kinds of ASD.
We do know that its highly genetic, we just havent identified how particular kinds of genes might interact with each other or with other factors to cause autism spectrum disorder, Wagner said. Autism is such a heterogenous disorder, so its highly likely that there are different causes for different kinds of ASD.
Don’t Miss: How To Explain Autism To Your Autistic Child
Carry On The Conversation
Am I wrong for feeling this way? Possibly. So let me know what you would like to see introduced in the next edition of the DMS in the comments below.
Dont forget you can sign up to the blogs newsletter by completing the online form, found on the sidebar .
As always, I can be found on Twitter and via my email: AutisticandUnapologetic@gmail.com
If you like what you have seen on the site today, then show your support by liking the .
Thank you for reading and I will see you next Saturday for more thoughts from across the spectrum.
Emotional And Behavioral Difficulties
- You have trouble regulating your emotions and your responses to them.
- Changes in routines and expectations cause outbursts or meltdowns.
- When something unexpected happens, you respond with an emotional meltdown.
- You get upset when your things are moved or rearranged.
- You have rigid routines, schedules, and daily patterns that must be maintained no matter what.
- You have repetitive behaviors and rituals.
- You make noises in places where quiet is expected.
Recommended Reading: How To Get My Child Tested For Autism
‘i Felt Like An Alien’
But the pieces didn’t quite fit – until he watched a TV programme about autism.
“The stereotyped view that I’d always had of autistic people was that they were either very severely disabled and unable to communicate, or formidable computer geeks.
“But seeing people in the documentary who seemed perfectly normal getting diagnosed, and identifying with them in so many different ways, was a revelation.”
Robert felt “immense relief” following his diagnosis.
“Finally I had a name for the thing that had made me feel like an alien for so long. Finally I could stop feeling bad about being different.”
Barney and Robert are just two of an unknown number of older adults who have spent much of their lives not knowing why they feel different.
With autism first classified as a mental disorder in 1980, people born before then may have gone undiagnosed or been misdiagnosed.
Around 700,000 people are thought to be autistic in the UK, and more are being diagnosed all the time, says Anna Bailey-Bearfield, policy and public affairs manager at the National Autistic Society.
“Autism is often seen only to affect children but more autistic adults are now appearing on TV and people are starting to see themselves represented.”
But the impact of not knowing for 40 or 50 years “can be very traumatic”, she says, leaving people feeling anxious and socially isolated.
National guidance says people should wait no longer than 13 weeks, but 2019 NHS data showed a significant number waiting longer.
What Is The Diagnostic Manual Of Mental Disorders

So Im going out on a limb here, but Im guessing the question most of you are currently asking is, since when wasnt Aspergers a form of autism? The answer to this is simple: 2013 The reasoning is a bit more complex.
In 2013, the world of autism was rocked when the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders was released. If this means as little to you as it did to me, all you need to know is that the DSM has been dubbed the psychiatrists bible, and 5 years ago it was rewritten.
From changing the very name of autism from Autistic Disorder, to Autistic Spectrum Disorder, to changing the way in which its diagnosed. Once the DSM-5 was released, there were very few similarities between what we had come to know of autism, and what it is now .
Read Also: How To Get Autistic Child To Listen
Replacing Asd Diagnosis With Another One
Sixty-one children lost their autism spectrum diagnosis by age 8. But almost all of them had at least one other diagnosis, such as Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder , developmental delay, or language delay. Fifty of the 61 children were receiving special education help at school, which suggests ongoing academic challenges.
The children who no longer had autism also tended to have been diagnosed earlier, at or before 30 months of age. Does that mean they benefited from earlier autism intervention, or were they misdiagnosed?
The researchers can’t say, because the study involved reviewing records, not examining children. “We cannot determine whether this change in classification represented an improvement in functioning or a substitution in diagnosis . However, these results suggest that ASD may be difficult to distinguish from other developmental conditions in some children, said team leader Lisa D. Wiggins PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, in an email.
One caveat: This study did not follow children past age 8, so any children who may have lost their diagnosis in late childhood or beyond would not be counted.
Dr. Blumberg’s team studied 1,420 children who were currently diagnosed with autism, and 187 who used to have autism. The children were ages 6 to 17, meaning some were younger or older than the 8-year-olds in Dr. Wiggins’ study.
The Stigma Of Autism: When All Eyes Are Upon You
What parent of a child with autism hasn’t had one of those moments in public? Your child is screaming, spinning or making noises, and you’re on the receiving end of disapproving stares or outright hostility from The Annoyed. “Control your child,” The Annoyed says coldly. Maybe he assumes your child lacks discipline; maybe he recognizes the disability but blames you for subjecting him to such behavior. The Annoyed can be a stranger, an acquaintance or cousin Pat.
At that moment, you feel the stigma that societies around the globe attach to autism. In different ways and to different degrees, people in many countries view autism as a source of disappointment, annoyance, shame or worse. According to some researchers, stigma may keep families from seeking a diagnosis and services for their children, from participating fully in their communities, and from enjoying the same quality of life as their neighbors. Simply put, stigma influences public health.1
Stigma is born of culture, so it may look different depending on whether you are living in South Korea, Australia, the West Bank, Japan or the United States. Pope Francis recently told Roman Catholics worldwide to help with “breaking down the isolation and, in many cases, the stigma burdening people with autism spectrum disorders, and just as often their families.”2
Don’t Miss: Why Blue For Autism Awareness
A Day In The Life Of A Woman With Autism
The most striking case of a child who was misdiagnosed with autism at the age of three was a young boy with big blue eyes and sandy blond hair. He was adorable, but he didnt speak and used only gestures and crying to protest and to request. He was hanging onto his mother with both hands gripped around her neck during our first meeting. He looked away from me. I walked over to the train set and gave the mom a Thomas train that made a giggle sound. He buried his head in her lap. She explained how he resisted the ABA therapy and wanted to leave the room. He had been seen by seven speech pathologists and he had refused to say anything. But, with careful, slow work, three sessions later, he was playing with the train set. A train fell off of the train track. He giggled and looked at me. I said, Oh, you need tape! I was just using my sense of humor since I could see the expression on his face. He smiled. I walked toward my desk and picked up some scotch tape, giggling back at him. He was unintelligible, but he tried to say, I see tape!
This was our beginning and from then on he was able to use some language; it was unintelligible, but he was trying to connect with me. He had a few vowel sounds, and unclear consonant sounds. As we progressed in sound production therapy, I gave him the Apraxia Profile test and found that he clearly met the criteria for Developmental Verbal Dyspraxia .
References