Terminology And Distinction From Schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism; while in 2007 it was believed to be one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed, parents continue to feel social stigma in situations where their child’s autistic behavior is perceived negatively, and many primary care physicians and medical specialists express some beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely.Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
The Normative Implications Of Biological Interpretations
In the first part of this paper I argued autism is, besides a heterogeneous concept, also a polysemous concept. Disability scholars have demonstrated that this polysemy need not be problematic, as it opens up possibilities for different possible narratives about the autistic person. The biological explanation helps exculpating autistic people and their parents, as they are now considered less responsible for, and thus less to blame for, their or their child’s behaviour, an insight that may be helpful in a therapeutic context. A biological explanation also serves to underscore the realness of the autistic experience; it is not merely a quirk in one’s personality that one can overcome. However, an emphasis on biologicaletiological explanations in research can actually have the opposite effect: mechanisticbiological explanations of autism may redirect resources from research into what it is like to be autistic, and what purpose certain autistic behaviours serve, to the investigation of autistic mice and fruit flies, whose behaviour is explained solely through the genes that were knocked out. In the next part, I suggest a way to conceptualize autism that does not deny its biological basis, but does so in a non-reductionist way, and that sees experiences as necessary ingredients for understanding behaviour.
What Challenges Are Associated With Autism
Autism is often linked with physical, developmental or mental health conditions such as intellectual disability, epilepsy, gastro-intestinal issues, ADHD, dyspraxia, anxiety or depression.
However, many of the disabling challenges associated with autism come about when individuals dont have the respect, understanding and supports that allow them to be comfortable in a non-autistic world.
Lawful Basis For Processing Your Data
Social Communication And Social Interaction Challenges

Social communication
Autistic people have difficulties with interpreting both verbal and non-verbal language like gestures or tone of voice. Some autistic people are unable to speak or have limited speech while other autistic people have very good language skills but struggle to understand sarcasm or tone of voice. Other challenges include:
- taking things literally and not understanding abstract concepts
- needing extra time to process information or answer questions
- repeating what others say to them
Social interaction
Autistic people often have difficulty ‘reading’ other people – recognising or understanding others’ feelings and intentions – and expressing their own emotions. This can make it very hard to navigate the social world. Autistic people may:
- appear to be insensitive
- seek out time alone when overloaded by other people
- not seek comfort from other people
- appear to behave ‘strangely’ or in a way thought to be socially inappropriate
- find it hard to form friendships.
Read more about social communication and social interaction challenges here
A Short History Of Autism
Researchers have been working on autism and autism-like disorders since the 1940s. At that time, autism studies tended to be small in scale and used varying definitions of the disorder. Autism was also sometimes lumped in with other conditions.
Focused research into ASD became more common in the 1980s when the DSM-III established autism as a distinct diagnosis. Since then, researchers have explored the causes, symptoms, comorbidities, efficacy of treatments, and many other issues related to autism.
Researchers have yet to discover a cause for autism. Many of the ideas put forth thus far have been disproven. Likely a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors are at work, which is the case with many psychiatric disorders and conditions.
Challenges Parents Face While Understanding Autism
Fig 3
The medical definition of autism is quite technical. That is perhaps why parents and family members strive to have a doctor or therapist who could easily explain what is autism in simple terms. Technically, autism is a complex neurobehavioral disorder which includes impairments in social, developmental and communicative skills combined with rigid and/or repetitive behaviors. Autism covers such a large spectrum of skills and impairments, which can sometimes lead to varying degrees of disabilities, thus requiring institutional care.
Domain A: Social Communication And Social Interaction
Differences or challenges relating to language and social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, both currently or historically. These include difficulty or differences in:
- Social-emotional communication and personal exchanges.
- Non-verbal communicative behaviours used for social interaction.
- Developing, maintaining and understanding relationships.
What Is The History Of Autism
The understanding of autism has developed over a number of decades. While the term autism was defined by Kanner, there is varying evidence that other professionals, including Grunya Efimovna Sukhareva and Paul Bleuler, had recognised the unique presentation of symptoms much earlier than this. Since the 1940s the diagnostic criteria has evolved and shifted as we learn more but now autism is widely understood as a spectrum of conditions with wide-ranging degrees of impairment
Autism Is Not An Illness
Being autistic does not mean you have an illness or disease. It means your brain works in a different way from other people.
It’s something you’re born with or first appears when you’re very young.
If you’re autistic, you’re autistic your whole life.
Autism is not a medical condition with treatments or a “cure”. But some people need support to help them with certain things.
When Was Autism Identified
Autism was first described in the early 1940s by two doctors who were working independently of each other. Leo Kanner and Hans Asperger identified a common set of symptoms they found among the children they were studying.
Both used the word autism from the Greek word for self to describe these children, who seemed enclosed in their own solitary worlds.
Kanner was a child psychologist at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Md. Asperger, whose work was published a year after Kanner’s, was a pediatrician in Vienna.
Since Asperger included people who had average to high IQs in his definition, the scientific community reserved “Asperger syndrome” to describe prodigies and certain high-functioning people with an autistic disorder.
It has been suggested by some that Microsoft founder Bill Gates exhibits the characteristics of Asperger syndrome. He has often been seen rocking and tends to speak in monotones both habits acknowledged to be symptoms.
Trying To Make Sense Of A Confusing World
When a rewrite of psychiatry’s diagnostic guide is released in San Francisco later this month, it will include a revised definition of autism, expanding it into a full spectrum disorder that can range from mild to heartbreakingly severe.
This new and already controversial fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders will add the term “autism spectrum disorder,” which is currently used by many experts.
Asperger’s disorder or syndrome a condition where people often have high intelligence and vast knowledge of narrow subjects but lack social skills will be dropped and incorporated under the umbrella austism-spectrum diagnosis.
The new definition will incorporate a wide range of symptoms that range from mild to severe, psychiatrists say.
In a child, the signs can include ritualistic physical activity like spinning or flapping arms wildly in the air, expressing frustration by pushing a teacher or teacher’s aide aside, or retreating into playing computer games instead of spending time with other children.
Autism is now felt to be a common neurological disorder. Estimates of the number of people afffected by it range from one in 200 to one in 300, according to a study by the National Epidemiological Database for the Study of Autism in Canada.
“Some of the increase is due to the way children are identified, diagnosed and served in their local communities, although exactly how much is due to these factors is unknown,” the CDC said.
The Thing About Echolalia
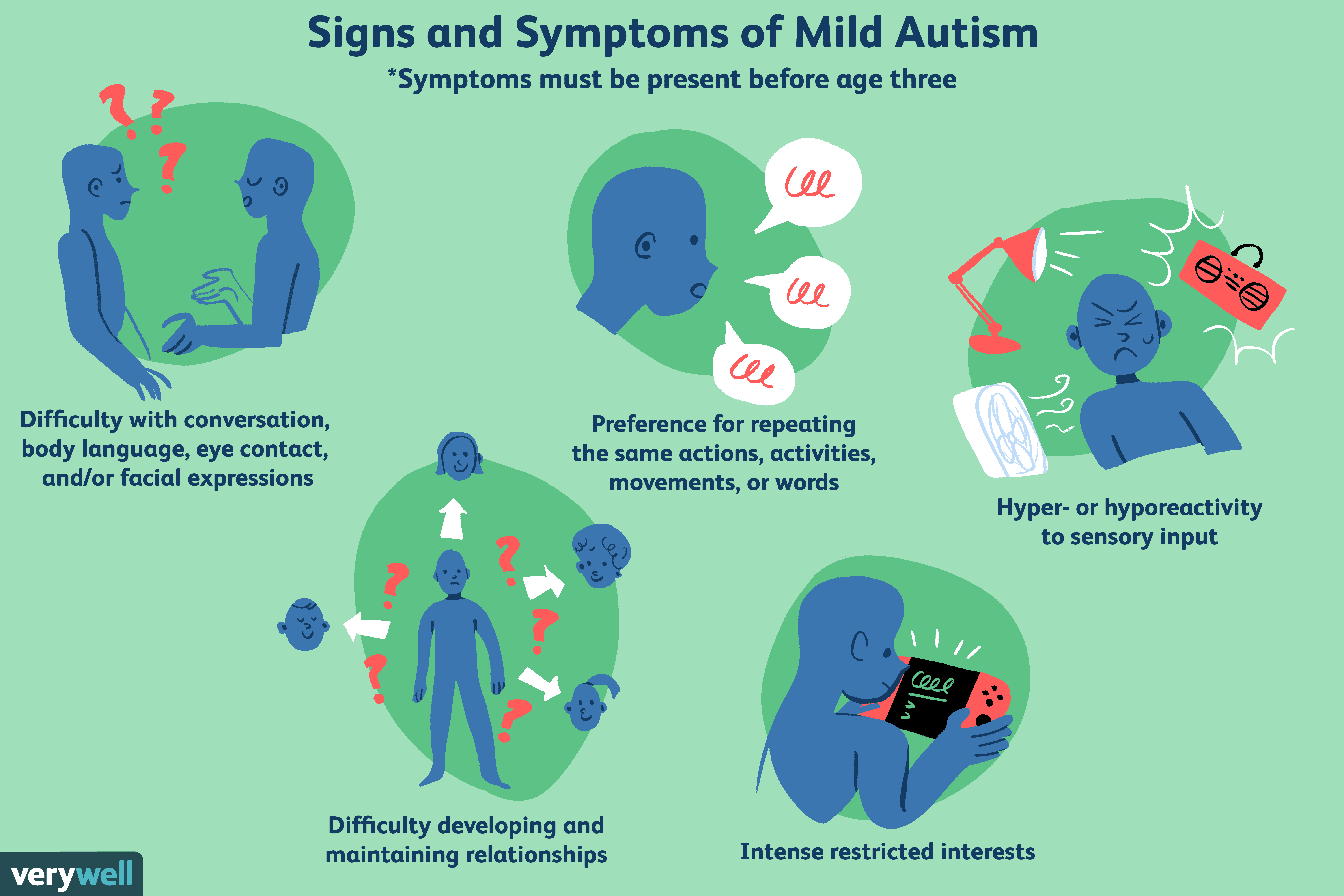
Fig 5
Echolalia is another form of borderline autism. What is Echolalia Autism? It is another form of Autism which is very similar in nature to borderline autism but with one differentiating factor Speech. Echolalia Autism is a rhythmic way of mimicking the cadence and tones of our language. Children with Echolalia Autism often mimic and repeat phrases to entire sentences. This is called gestalt which means whole. Learning a language the gestalt way would be like learning a language in chunks, just like a parrot. For example, such children know who mommy is by the repetition of the word mommy whenever she is involved in anything. Echolalia Autism is often observed when the toddler is about two and a half years old.
Many children with this form of autism can echo or mimic what is being said by associating a predefined sequence of words to repetitive actions. Some even lead to use the same voice inflections as the person that spoke the word or phrase. If a child stays with this echolalia type of speech it could indicate that the growth in communication skills of an autistic child may have stagnated at a particular level. Reassessment and a new therapy plan would be needed at this time to move the child along to future levels.
What Is Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity is the idea that variation in brain function exists across the population. Differences such as autism and ADHD have existed throughout human history and are not due to faulty neural circuitry. Rather than viewing them as such, neurodiversity embraces autism as a different way of thinking and behaving.
Proponents of neurodiversity believe that society should work to eliminate stigma, create accommodations, and fully accept people with autism as capable of contributing to society. The paradigm stands in contrast to the medical model, which conceives of autism as a disease to be treated or cured.
The term was coined by an Australian sociologist, Judy Singer, who had autism herself. It was popularized by American journalist Howard Blume beginning in the late 1990s. Although neurodiversity primarily refers to autism, there are also conversations around neurodiversity and Tourettes syndrome, epilepsy, dyslexia, and bipolar disorder.
How Is Asd Diagnosed
There is no single test that will confirm that someone has an ASD. A diagnosis is based on the number and pattern of typical characteristics and on the observation of specific behaviours and disabilities.
Someone with a mild case could go undiagnosed for years, and it might only be detected when the person goes through a crisis that brings contact with professionals who are able to recognize the disorder.
What Are The Causes Of Autism
Its natural to want to know what causes autism, however it is likely that there is not one single cause. While genetic differences are known to cause some types of autism, the causes of autism are largely unknown.
We do know that autism is a neurobiological difference, meaning that the brain processes information differently for people with autism, than it does for people who do not have autism.
We also know that parenting styles do not cause a child to develop autism.
Autism is not caused by vaccinations during or before pregnancy, and the falsely-reported link between the measles-mumps-rubella immunisation and autism has been retracted from the paper it was published in, and completely discredited by the research, scientific and medical community.
For more information about the current studies being undertaken into the causes of autism, visit our what causes autism section.
How Is Autism Diagnosed
Fortunately, the way autism is diagnosed has changed and improved over the last 80 years.
We now recognise a wider range of signs and characteristics as forming part of the autism spectrum.
As awareness increases, parents and professionals are getting better at identifying early signs of autism and are more likely to seek an autism assessment.
This explains why people think autism is more prevalent today than it was ten or twenty years ago.
Examples Of Autism In A Sentence
autism Dallas NewsautismAZCentral.comautismThe New Yorkerautism AZCentral.comautism Washington Postautism PEOPLE.comautism PEOPLE.comautism Fox News
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘autism.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Possible Causes And Risk Factors
The cause of autism remains unclear. However, it appears that both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the disorder. A study published in 2011 that assessed pairs of twins in which at least one twin was affected by an ASD suggested that, while genetic factors contribute moderately to susceptibility, environmental factors contribute to a greater degree. Other research has indicated that genetic vulnerability to autism differs between males and females, with more mutations being needed to produce the condition in females compared with males. Increased genetic resiliency to autism in females lends support to the so-called female protective model, which attempts to explain the increased prevalence of autism in males. Interactions between genes and the environment likely play an important role in influencing susceptibility to autism.
An environmental risk factor that has been proposed for autism and other ASDs is maternal infection during pregnancy. Indeed, certain maternal infections have been associated with an increased incidence of neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring. Infection with agents such as the rubella virus activate the mothers immune system, and such immunological activity in the early stages of pregnancy has been linked with damage to the developing brain of the embryo or fetus.
What Causes Autism
- Research indicates that genetics are involved in the vast majority of cases.
- Children born to older parents are at a higher risk for having autism.
- Parents who have a child with ASD have a 2 to 18 percent chance of having a second child who is also affected.
- Studies have shown that among identical twins, if one child has autism, the other will be affected about 36 to 95 percent of the time. In non-identical twins, if one child has autism, then the other is affected about 31 percent of the time.
- Over the last two decades, extensive research has asked whether there is any link between childhood vaccinations and autism. The results of this research are clear: Vaccines do not cause autism.
What Is A Savant

Savant syndrome is when an individual with autism or another disability has extraordinary skills in a particular domain. For example, a savant may be a gifted classical musician or complete puzzles extremely quickly. One explanation for a savants ability is that additional brain regions are recruited and rewired to support memory.
Kim Peeks, on whom the movie Rain Man was based, falls in line with that theory. Peeks read with remarkable speed: He read both pages of a book at the same time, each with one eye, with excellent content retention. He also had an incredible memory for directions, history, politics, and sports statistics. Peeks did not have a corpus callosum, which facilitates communication between the two hemispheres of the brain. Reading is typically rooted in the left hemisphere, but Peeks may have developed the ability in both hemispheres, leading to his savant abilities.
Who Resolution On Autism Spectrum Disorders
In May 2014, the Sixty-seventh World Health Assembly adopted a resolution entitled “Comprehensive and coordinated efforts for the management of autism spectrum disorders ,” which was supported by more than 60 countries.
The resolution urges WHO to collaborate with Member States and partner agencies to strengthen national capacities to address ASD and other developmental disabilities.
Clinical Development And Diagnoses
Leo Kannerearly infantile autism
The word autism first took its modern sense in 1938 when Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital adopted Bleuler’s terminology autistic psychopaths in a lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD now known as Asperger syndrome, though for various reasons it was not widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981.Leo Kanner of the Johns Hopkins Hospital first used autism in its modern sense in English when he introduced the label early infantile autism in a 1943 report of 11 children with striking behavioral similarities. Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner’s first paper on the subject, notably “autistic aloneness” and “insistence on sameness”, are still regarded as typical of the autistic spectrum of disorders. It is not known whether Kanner derived the term independently of Asperger.
Kanner’s reuse of autism led to decades of confused terminology like infantile schizophrenia, and child psychiatry’s focus on maternal deprivation led to misconceptions of autism as an infant’s response to “refrigerator mothers“. Starting in the late 1960s autism was established as a separate syndrome.
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disability that can cause significant social, communication and behavioral challenges. There is often nothing about how people with ASD look that sets them apart from other people, but people with ASD may communicate, interact, behave, and learn in ways that are different from most other people. The learning, thinking, and problem-solving abilities of people with ASD can range from gifted to severely challenged. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives; others need less.
A diagnosis of ASD now includes several conditions that used to be diagnosed separately: autistic disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified , and Asperger syndrome. These conditions are now all called autism spectrum disorder.
Restrictive / Repetitive Behaviors May Include:
- Repeating certain behaviors or having unusual behaviors. For example, repeating words or phrases, a behavior called echolalia
- Having a lasting intense interest in certain topics, such as numbers, details, or facts
- Having overly focused interests, such as with moving objects or parts of objects
- Getting upset by slight changes in a routine
- Being more or less sensitive than other people to sensory input, such as light, noise, clothing, or temperature
People with ASD may also experience sleep problems and irritability. Although people with ASD experience many challenges, they may also have many strengths, including:
- Being able to learn things in detail and remember information for long periods of time
- Being strong visual and auditory learners
- Excelling in math, science, music, or art
Causes And Risk Factors
We do not know all of the causes of ASD. However, we have learned that there are likely many causes for multiple types of ASD. There may be many different factors that make a child more likely to have an ASD, including environmental, biologic and genetic factors.
- Most scientists agree that genes are one of the risk factors that can make a person more likely to develop ASD.4, 19
- Children who have a sibling with ASD are at a higher risk of also having ASD. 5-10
- Individuals with certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis, can have a greater chance of having ASD. 11-14, 20
- When taken during pregnancy, the prescription drugs valproic acid and thalidomide have been linked with a higher risk of ASD.15-16
- There is some evidence that the critical period for developing ASD occurs before, during, and immediately after birth.
- Children born to older parents are at greater risk for having ASD.
ASD continues to be an important public health concern. Like the many families living with ASD, CDC wants to find out what causes the disorder. Understanding the factors that make a person more likely to develop ASD will help us learn more about the causes. We are currently working on one of the largest U.S. studies to date, called Study to Explore Early Development . SEED is looking at many possible risk factors for ASD, including genetic, environmental, pregnancy, and behavioral factors.
Autism Screening And Diagnosis
It can be hard to get a definite diagnosis of autism. Your doctor will focus on behavior and development.
For children, diagnosis usually takes two steps.
- A developmental screening will tell your doctor whether your child is on track with basic skills like learning, speaking, behavior, and moving. Experts suggest that children be screened for these developmental delays during their regular checkups at 9 months, 18 months, and 24 or 30 months of age. Children are routinely checked specifically for autism at their 18-month and 24-month checkups.
- If your child shows signs of a problem on these screenings, theyâll need a more complete evaluation. This might include hearing and vision tests or genetic tests. Your doctor might want to bring in someone who specializes in autism disorders, like a developmental pediatrician or a child psychologist. Some psychologists can also give a test called the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule .
If you werenât diagnosed with autism as a child but notice yourself showing signs or symptoms, talk to your doctor.
What Are The Different Types Of Autism
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition is published by the American Psychiatric Association . Clinicians use it to diagnose a variety of psychiatric disorders.
The most recent fifth edition of the DSM was released in 2013. The DSM-5 currently recognizes five different ASD subtypes, or specifiers. They are:
- with or without accompanying intellectual impairment
- with or without accompanying language impairment
- associated with a known medical or genetic condition or environmental factor
- associated with another neurodevelopmental, mental, or behavioral disorder
Someone can receive a diagnosis of one or more specifiers.
Before the DSM-5, autistic people may have received a diagnosis of:
- autistic disorder
- pervasive development disorder-not otherwise specified
- childhood disintegrative disorder
Its important to note that a person who received one of these earlier diagnoses hasnt lost their diagnosis and wont need to be reevaluated.
Symptoms of ASD typically become clearly evident during early childhood, between 12 and 24 months of age. However, symptoms may also appear earlier or later.
Early symptoms may include a marked delay in language or social development.
The DSM-5 divides symptoms of ASD into two categories: problems with communication and social interaction, and restricted or repetitive patterns of behavior or activities.
Restricted Or Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior Or Activities

These can include:
- an increase or decrease in sensitivity to specific sensory information from their surroundings, such as a negative reaction to a specific sound
- fixated interests or preoccupations
Autistic people are evaluated within each category, and the intensity of their symptoms is noted.
To receive an autism diagnosis, a person must display all three symptoms in the first category and at least two symptoms in the second category. Get more information on symptoms and how they may manifest in kids.
The exact cause of ASD is unknown. The most current research demonstrates theres no single cause.
Some suspected risk factors for ASD include:
- having an immediate family member whos autistic
- genetic mutations
An ASD diagnosis involves several screenings, genetic tests, and evaluations.