How Is Autism Treated
There is no cure for ASD. Therapies and behavioral interventions are designed to remedy specific symptoms and can substantially improve those symptoms. The ideal treatment plan coordinates therapies and interventions that meet the specific needs of the individual. Most health care professionals agree that the earlier the intervention, the better.
Educational/behavioral interventions: Early behavioral/educational interventions have been very successful in many children with ASD. In these interventions therapists use highly structured and intensive skill-oriented training sessions to help children develop social and language skills, such as applied behavioral analysis, which encourages positive behaviors and discourages negative ones. In addition, family counseling for the parents and siblings of children with ASD often helps families cope with the particular challenges of living with a child with ASD.
What Are The Types Of Brain Damage And How Severe Are They
All traumatic brain injuries are head injuries. But head injury is not necessarily brain injury. There are two types of brain injury: traumatic brain injury and acquired brain injury. Both disrupt the brainâs normal functioning.
- Traumatic Brain Injury is caused by an external force — such as a blow to the head — that causes the brain to move inside the skull or damages the skull. This in turn damages the brain.
- Acquired Brain Injury occurs at the cellular level. It is most often associated with pressure on the brain. This could come from a tumor. Or it could result from neurological illness, as in the case of a stroke.
Both traumatic brain injury and acquired brain injury occur after birth. And neither is degenerative. Sometimes, the two terms are used interchangeably.
There is a kind of brain damage that results from genetics or birth trauma. It’s called congenital brain damage. It is not included, though, within the standard definition of brain damage or traumatic brain injury.
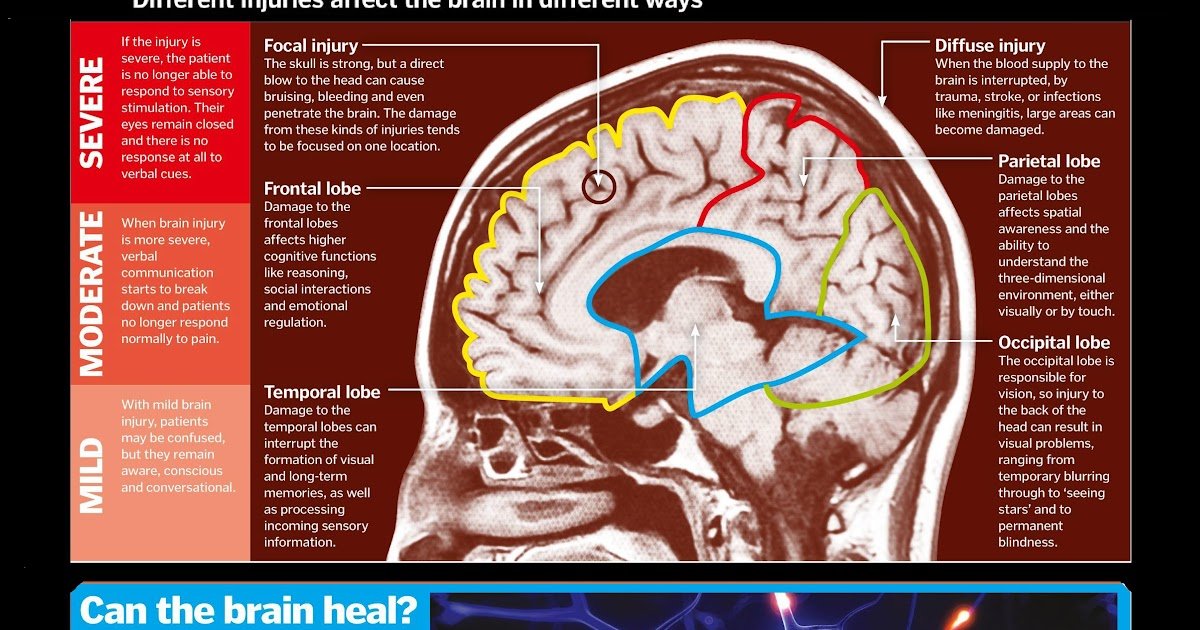
Some brain injuries cause focal — or localized — brain damage, such as the damage caused when a bullet enters the brain. In other words, the damage is confined to a small area. Closed head injuries frequently cause diffuse brain damage, which means damage to several areas of the brain. For example, both sides of the brain are damaged and the nerves are stretched throughout the brain. This is called diffuse axonal injury or DAI.
Things To Know About Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy is the most common motor disability in childhood, and children with CP and their families need support. Learn more about CP and what signs to look for in young children.
About 1 in 10 children identified with CP walk using a hand-held mobility device.
Many children with CP have one or more additional conditions or diseases along with their CP, known as co-occurring conditions. For example, about 4 in 10 children with CP also have epilepsy and about 1 in 10 have autism spectrum disorder.
Read Also: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Evidence That Cerebellum Is Involved In Autism And Asd
Although traditionally implicated in motor function, accumulating evidence indicates that the cerebellum is also involved in cognitive function . The cerebellum is structurally and functionally abnormal in patients diagnosed with autism or within the ASD spectrum . Syndromes that share cognitive symptomology with autism also frequently share genetic mutations associated with abnormal cerebellar development.
How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Treated
There is no cure for autism, but treatment can make a big difference. The younger kids are when they start treatment, the better.
Doctors, therapists, and special education teachers can help kids learn to talk, play, and learn. Therapists also help kids learn about making friends, taking turns, and getting along.
Also Check: Is The Good Doctor Actor Really Autistic
Researchers Find A Web Of Factors Behind Multiple Sclerosis
Researchers involved in the study came upon the myelination problem while looking for something else.
They were studying brain cells in mice with a gene mutation that causes Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, which can include features of autism spectrum disorder. “We saw a signature that suggested there might be something wrong with myelination,” Maher says. “So that was pretty surprising to us.”
More experiments confirmed that “there was a clear deficit,” in the cells that control myelination, which are called oligodendrocytes, he says. This was true not only in mice with the Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, but in other mouse models of autism, too.
Next, a biostatistics expert named Andrew Jaffe looked at a genetic analysis of brain tissue from people with autism who had died. And that experiment also found problems with the system that controls myelination.
To fully understand what’s going on though, the problem needs to be studied in developing brain tissue, Vaccarino says.
That should be possible, she says, using tiny clusters of human brain cells called brain organoids, which can be grown in a petri dish. Vaccarino’s lab has created brain organoids from the cells of people with autism spectrum disorder, which might reveal how the myelination problems begin, she says.
Brain myelination “really does not start in earnest until the first year or two of life,” Weinberger says. “And this is around the time that autism is first apparent.”
Chapter 6 Claim : Savant Skills Special Skills And Intelligence Vary Widely In Autism
Treffert reported that 50% of individuals with savant syndrome were diagnosed with autism, and Howlin and colleagues stated that one third of individuals with autism have special information-processing talents. However, the true prevalence of savant skills in autism has not been determined. Savant and special skills found in autism all occur in typical individuals. As noted earlier, Fabricius theorized that all individuals with autism had a variant of savant sensory information processing. He argued that while typical individuals compress sensory data to prototypes for association across brain systems, savants and individuals with autism who were not savants failed to make prototypes, but retained uncompressed sensory information. He further claimed that individuals with savant syndrome retained all primary sensory information to higher-level processing without compressing any sensory details.
Not only are savant skills an unexplained form of heterogeneity in autism, there is heterogeneity within savant and other special skills that has remained unexplained.
Lynn Waterhouse, in, 2013
Read Also: Dyslexia Comorbidity
What Are Some Common Signs Of Asd
Even as infants, children with ASD may seem different, especially when compared to other children their own age. They may become overly focused on certain objects, rarely make eye contact, and fail to engage in typical babbling with their parents. In other cases, children may develop normally until the second or even third year of life, but then start to withdraw and become indifferent to social engagement.
The severity of ASD can vary greatly and is based on the degree to which social communication, insistence of sameness of activities and surroundings, and repetitive patterns of behavior affect the daily functioning of the individual.
Social impairment and communication difficultiesMany people with ASD find social interactions difficult. The mutual give-and-take nature of typical communication and interaction is often particularly challenging. Children with ASD may fail to respond to their names, avoid eye contact with other people, and only interact with others to achieve specific goals. Often children with ASD do not understand how to play or engage with other children and may prefer to be alone. People with ASD may find it difficult to understand other peoples feelings or talk about their own feelings.
Traumatic Brain Injury And Cerebral Palsy
Page Medically Reviewed and Edited by Pierrette Mimi Poinsett, M.D.
This article has been fact checked by a Board Certified Pediatrician. Sources of information for the article are listed at the bottom.
For any content issues please Contact Us.
Traumatic brain injuries that occur during the labor and delivery process is one of the ways that infants can develop cerebral palsy. In fact, brain injuries are one of the leading reasons that children develop cerebral palsy. Traumatic brain injuries are considered a severe medical issue and treatment must be initiated quickly for the best possible outcome.
Don’t Miss: Best Dog Breed For Special Needs Child
How To Optimize Your Childs Prognosis
As a parent, you have a key role in helping your child heal and move past his or her brain injury. Together with your childs healthcare team, you will provide support for your child at home and school. Of course, you want what is best for your child, and you want them to have every opportunity to thrive.
There are some things that you can do to optimize your childs prognosis, such as:
- Talk to your childs doctors about things you can do at home to help your child.
- Work with therapists and create a list of activities that you can do at home with your child to support what they are learning during therapy sessions.
- Consider family counseling with a psychologist or psychiatrist who is experienced with brain injury cases. This can help your entire family better understand the changes that may happen in your home.
- Encourage your child to set small, reasonable goals. Praise him or her when those goals are met. Be supportive and encouraging when they are not.
- Develop a lifestyle routine for your home and family that is as normal as possible.
- Reach out to your community for support. There are often state and local networks dedicated to families suffering from certain types of injury or illness.
- When its time for school, work with your childs teachers to develop a plan for academic success. Your child may need special accommodations or an individualized education plan .
Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury And Autism: Elucidating Shared Mechanisms
Brandon P. Lucke-Wold
1Department of Neurosurgery, West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV 26505, USA
2Department of Basic Pharmaceutical Sciences, West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV 26505, USA
3Department of Medical Sciences, University of Florida School of Medicine, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA
4Department of Psychology, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC 27695, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Disorders
The Office of Special Education started collecting data for TBI as a disability category in the same year that it began collecting data for ASD. The prevalence of both ASD and TBI among successive births of US school-aged children showed a marked increase in the period between 1992 and 2001 . Cohort curves suggest that these two disorders exhibit similar increases in prevalence over that period. TBI from nonaccidental head injury may lead to substantial neurological and developmental deficits. A small study of children who suffered nonaccidental head injury showed speech and language difficulties consistent with a diagnosis of ASD .
2.1. Natural Progression of Pediatric TBI
The Glasgow Coma Scale is a grading system used to assess consciousness and thus grade the severity of TBI by stratifying the sum of three tests: verbal, eye, and motor responses . The GCS describes the severity of TBI as follows: mild , moderate , and severe . Since its inception, the original GCS has been modified for use in children .
| Symptom |
Recommended Reading: Level 2 Autism
How Does Autism Affect The Brain
- Open annotations. The current annotation count on this page is being calculated.
Image credit: CC0
Autism is a brain disorder that affects how people interact with others. It occupies a spectrum, with severe autism at one end and high-functioning autism at the other. People with severe autism usually have intellectual impairments and little spoken language. Those with high-functioning autism have average or above average IQ, but struggle with more subtle aspects of communication, such as body language. As well as social difficulties, many individuals with autism show repetitive behaviors and have narrow interests.
The brains of people with autism process information differently to those of people without autism. The brain as a whole shows less coordinated activity in autism, for example. But whether individual brain regions themselves also work differently in autism is unclear. Watanabe et al. set out to answer this question by using a brain scanner to compare the resting brain activity of high-functioning people with autism to that of people without autism.
Considerations For Cultural And Linguistic Variations
When selecting assessment tests, the SLP considers the influence of cultural and linguistic factors on the individual’s communication style and the potential impact of impairment on function.
Clinicians make appropriate accommodations and modifications to the testing process to reconcile cultural and linguistic variations. Comprehensive documentation includes descriptions of these accommodations and modifications. Scores from standardized tests are often invalidated in these cases and may not be appropriate to report. Rather than reporting scores, results can be stated descriptively See ASHA’s Practice Portal pages on Bilingual Service Delivery Collaborating With Interpreters, Transliterators, and Translators and Cultural Competence.
Due to the complexity of cognitive sequelae in TBI and its influence on bilingual language production , a thorough case history and interviews with the family and individual are particularly useful in identifying premorbid language proficiency, language preference for assessment and treatment of linguistic deficits, and communicative needs in the community .
See the Treatment section of the Traumatic Brain Injury Evidence Map for pertinent scientific evidence, expert opinion, and client/caregiver perspectives.
Treatment of persons with TBI considers
The goal of intervention in TBI is to achieve the highest level of independent function for participation in daily living. Consistent with the ICF framework , intervention is designed to
Read Also: What Is The Symbol For Autism
Nucleus Accumbens And Asd
Besides amygdala, nucleus accumbens is also considered as the key structure which is related with the social reward response in ASD. NAc borders ventrally on the anterior limb of the internal capsule, and the lateral subventricular fundus of the NAc is permeated in rostral sections by internal capsule fiber bundles. The rationale for NAc to be considered as the potential target of DBS for ASD is its predominant role in modulating the processing of reward and pleasure . Anticipation of rewarding stimuli recruits the NAc as well as other limbic structures, and the experience of pleasure activates the NAc as well as the caudate, putamen, amygdala, and VMPFC . It is well known that dysfunction of NAc regarding rewarding stimuli in subjects with depression. Bewernick et al. demonstrated antidepressant effects of NAc-DBS in 5 of the 10 patients suffering from severe treatment-resistant depression .
Anticipation of pleasurable stimuli recruits the NAc, whereas the experience of pleasure activates VMPFC . NAc is activated by incentive motivation to reach salient goals . Increased activation in the left anterior cingulate gyrus and left mid-frontal gyrus was noted during both the anticipatory and consummatory phase of the reward response . However, the activity within the ventral striatum was decreased in autistic subjects, which caused impairment in social reciprocity .
Autism And Morality: Outcomes Matter More Than Intentions
ByAmanda Chan30 May 2013
Imagine this: Janet and her friend are kayaking in a part of the ocean with many jellyfish. Janet had read that the jellyfish aren’t dangerous, and tells her friend it’s alright to swim. Her friend is stung by a jellyfish and dies.
Who’s to blame?
Researchers who used this scenario in a recent study found that people with autism were more likely to blame Janet for her friend’s death than people without autism . Most normally functioning people understand the death of Janet’s friend was accidental, because Janet didn’t realize the jellyfish were poisonous, they said.
But people with autism may perceive morality differently than normally functioning people because they focus more on the outcomes of situations, rather than the intentions of the people in those situations , said study researcher Liane Young, a researcher at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The ability to distinguish between intention and outcome is called “theory of mind.”
The study “shows that some of the ways in which we make moral judgments are rooted in the brain, in physical processes,” Young told MyHealthNewsDaily.
The study was published online today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The blame game
Young and her colleagues tested the theory of mind in 13 adults with autism and 13 normally functioning adults. They presented the people in the study with about 50 scenarios, including the jellyfish story.
Painting a picture of the mind
Also Check: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Diagnostic Models Based On Imaging Genetics
Imaging genetics in ASD has proven useful, and pathways that include common genetic variation in TD individuals at risk of developing ASD have been characterized. Prenatal transcription regulation and synapse formation in the developing brain is impacted by the genes associated with ASD . Alteration in frontal WM connectivity and structure and disturbance in the frontal, temporal, and occipital circuits involved in visual and language processing was found to be associated with NRXN superfamily genes. Neuropeptide signaling and emotional functioning was found to be influenced by the oxytocin and arginine vasopressin receptor genes via structural and functional modification in the amygdalahypothalamus circuitry. One study showed a relationship between frontal lobe connectivity and common genetic variants in CNTNAP2 using a functional neuroimaging study and the study found that ASD and TD individuals who were nonrisk allele carriers showed more reduction in the activation of mPFC during an fMRI task as compared to risk allele carriers. Another study showed decreased functional connectivity in the prefrontal cortex, cortical spinal tract, corpus callosum, and decreased integrity of WM in children and adolescents carrying MET rs1858830, C risk allele. Such studies suggest that the genes affect the brain regions that are involved in social and emotional processing.