What Is The Prevalence Of Autism
The exact prevalence of autism in Australia and internationally is unknown.
The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that there were 205,200 Australians with autism in 2018, which is around 1% of the population or 1 in 100.
Internationally this rate varies significantly, from 1 person in every 59 people in the USA, to the average prevalence across Asia, Europe, and North America is between one and two percent.
Statistics also show that:
- the number of Australians diagnosed with autism increased by 42% between 2012 and 2015;
- three out of four people diagnosed with autism are young people, aged between 5 and 24 years; and
- 1-2 out of 4 Australians diagnosed with autism are female.
While the reported prevalence of autism varies around the world, there has been a clear increase in the number of people diagnosed on the autism spectrum in recent years, but this doesnt necessarily suggest that there are more autistic people in the world than there were ten or twenty years ago.
Evidence suggests that the increase is the result of a number of cultural and clinical factors, including social influences driving greater awareness of autism, and improved diagnostic procedures and changes in diagnostic criteria allowing more people to access a diagnosis.
According to Professor Whitehouse, from Australias Autism CRC, research shows the majority of the increase in autism prevalence over this period was due to an increase in diagnosing children with less severe behaviours.
Development Of Repetitive Or Restrictive Habits
Repetitive habits are another sign of high-functioning autism. Those habits could interfere with the persons ability to do what they need to do or what others want them to do. One type of repetitive habit might be related to movement. The individual might have to tie and untie their shoes multiple times before they are satisfied and are able to start walking or leave the house. Some people develop restrictive habits that interfere with socially accepted living. For example, an individual might refuse to wear any other kind of shirt than a tee shirt. This could impact their health and well-being if they live in a place with cold weather.
Challenges Of Identifying High
High-functioning individuals with ASD pose particular challengesâboth for identification and for determining eligibility for services. These individuals often have either verbal or nonverbal intelligence within or above the average range and appear to succeed in some or most academic subjects, particularly in early school years. As a result, many are not diagnosed until later school age, adolescence, or even adulthood.
Long-term outcomes for these individuals show that challenges with social engagement and social communication can significantly affect their ability to adjust to social demands in later academic and community settings and in the workplace . These findings suggest the importance of providing intervention to address the gap between cognitive potential and social adaptive functioning.
School-age Children
Determining eligibility for educational services requires using a variety of strategies for gathering information, including
- standardized measures of social adaptive functioning,
- naturalistic observation across a range of settings, and
- caregiver/teacher interviews or questionnaires.
Regardless of the assessment measures or tools used, the clinician needs to be aware of any subtle signs and symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of ASD.
Adult Diagnosis
For a comprehensive discussion of individuals with ASD as they transition into and through adulthood, see IACC, 2017.
Consistent with the WHO framework, treatment is designed to
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Terms For Types Of Autism That Are No Longer Used Today
When autism was categorized by types, the lines between the different types of autism could be blurry. Diagnosis was, and still is, complicated and often stressful for families.
If you or your child received a diagnosis before the DSM-5 changed, you may still be using the older terminology . Thats OK. Your doctor may continue to use those terms if they help.
Why This Terminology Is No Longer Used By Doctors
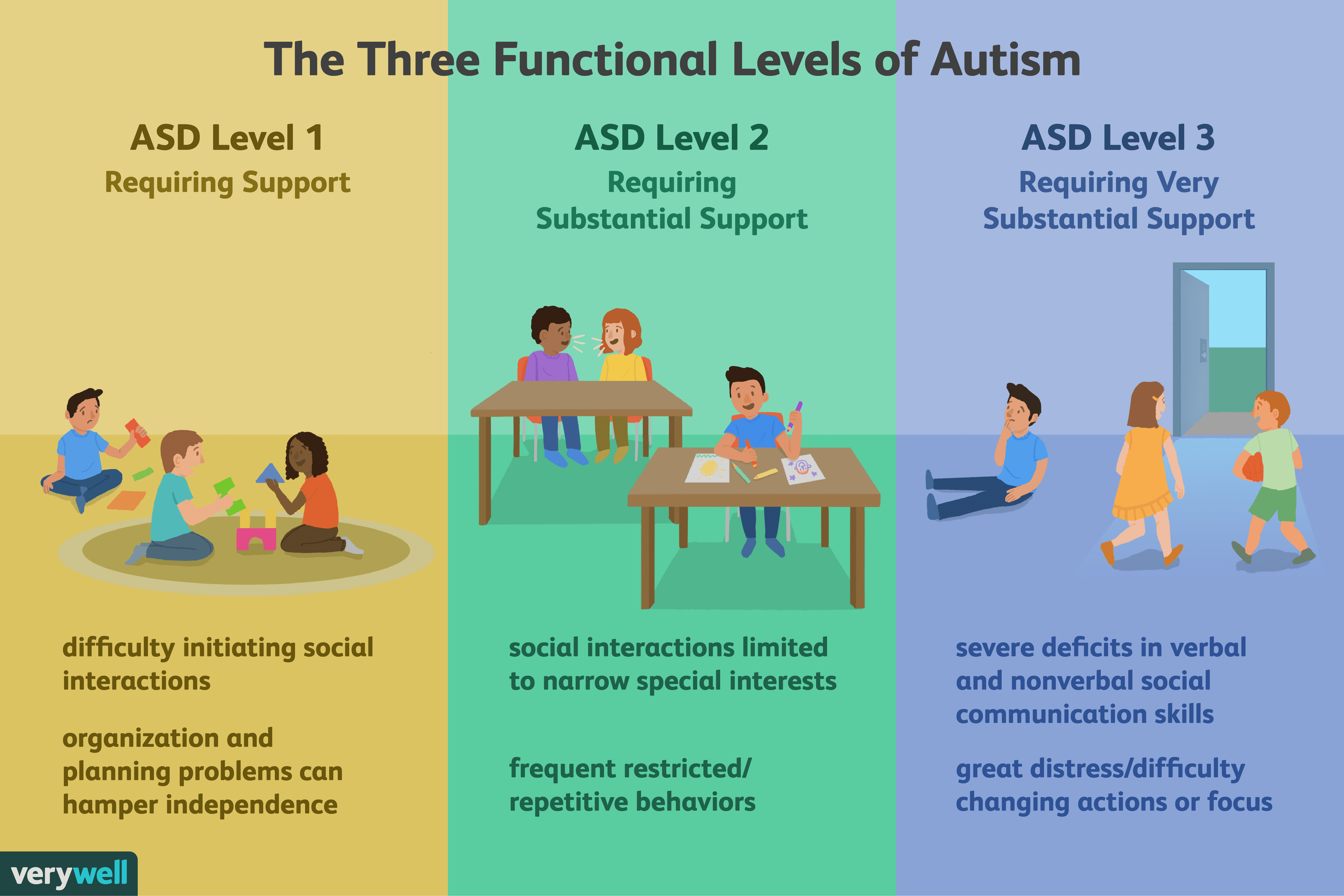
The spectrum illustrates a broad range of developmental delays and symptom severity.
ASD includes people who have a few mild autistic traits to those who need help with day-to-day functioning. It represents every intelligence level, as well as varying degrees of communication and social abilities.
The differences between one type and another type can be subtle and difficult to determine.
Don’t Miss: Life Expectancy For Autism
A Note Re Terminology
In New Zealand, the term used in diagnosis is Autism Spectrum Disorder .
This is the term used in the NZ Autism Spectrum Disorder Guideline and in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders Fifth Edition criteria which is the guide clinicians use when making a diagnosis.
Some autistic people prefer to use the term autism as they dislike the negative meaning implied by the word Disorder in Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Altogether Autism uses the term autism except when talking about diagnosis, where the term Autism Spectrum Disorder is used.
Other commonly used terms are Autism Spectrum, Autism Spectrum Condition, Aspergers Syndrome, Aspie, High Functioning Autism, Pervasive Developmental Disorder not otherwise specified .
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world.; NINDS and several other NIH Institutes and Centers support research on autism spectrum disorder.;
Nearly 20 years ago the NIH formed the Autism Coordinating Committee to enhance the quality, pace, and coordination of efforts at the NIH to find a cure for autism. The NIH/ACC has been instrumental in promoting research to understand and advance ASD. The NIH/ACC also participates in the broader;Federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee , composed of representatives from various U.S. Department of Health and Human Services agencies, the Department of Education, and other governmental organizations, as well as public members, including individuals with ASD and representatives of patient advocacy organizations. One responsibility of the IACC is to develop a strategic plan for ASD research, which guides research programs supported by NIH and other participating organizations.
Read Also: What Kind Of Autism Does Symmetra Have
What Is Aspergers Syndrome
In 1994 Aspergers Syndrome appeared as a separate presentation of a pervasive developmental disorder in standard diagnostic manuals, characterised by many as a milder type of autism.
The key characteristics of Asperger syndrome identified at the time were:
- Difficulties with social interaction and social communication
- Restricted and repetitive behaviours
- No intellectual disability
- No delay in verbal speech development
However, the idea that Aspergers is milder than autism has proven to be problematic, because it implies that living with Aspergers is less challenging than living with autism.
In May 2013, the diagnostic criteria for autism changed with the release of the latest diagnostic manual .
Since then Autistic Disorder and Aspergers syndrome are no longer differentiated as separate presentation of pervasive developmental disorders, but are now included under the single diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder or referred to as autism or the autism spectrum.
Role Of The Slp In Diagnosis
Interdisciplinary collaboration in assessing and diagnosing ASD is important due to the complexity of the disorder, the varied aspects of functioning affected, and the need to distinguish ASD from other disorders or medical conditions.
Ideally, the SLP is a key member of an interdisciplinary team with expertise in diagnosing ASD. When there is no appropriate team available, an SLPâwho has been trained in the clinical criteria for ASD and who is experienced in diagnosing developmental disordersâmay be qualified to diagnose these disorders as an independent professional .
Some state laws or regulations may restrict a licensee’s scope of practice and may prohibit the SLP from providing such diagnoses. SLPs should check with their state licensure boards and/or state departments of education for specific requirements.
Assessment
See the Assessment section of the Autism Spectrum Disorders Evidence Map for pertinent scientific evidence, expert opinion, and client/caregiver perspective.
Interdisciplinary collaboration and family involvement are essential in assessing and diagnosing ASD. The SLP is a key member of an interdisciplinary team that includes the child’s pediatrician, a pediatric neurologist, and a developmental pediatrician. There are a number of available algorithms and tools to help physicians develop a strategy for early identification of children with ASD .
Recommended Reading: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Restricted Or Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior Or Activities
These can include:
- an increase or decrease in sensitivity to specific sensory information from their surroundings, such as a negative reaction to a specific sound
- fixated interests or preoccupations
Autistic people are evaluated within each category, and the intensity of their symptoms is noted.
To receive an autism diagnosis, a person must display all three symptoms in the first category and at least two symptoms in the second category. Get more information on symptoms and how they may manifest in kids.
The exact cause of ASD is unknown. The most current research demonstrates theres no single cause.
Some suspected risk factors for ASD include:
- having an immediate family member whos autistic
- genetic mutations
An ASD diagnosis involves several screenings, genetic tests, and evaluations.
Communication And Interaction Tips For Asd
There are no hard-and-fast rules on how to communicate with a child with ASD. But many family members have had success with these tips:
It can be challenging to interact with a child or grandchild with ASD. But it is one of the most important things you can do to help that child learn. Research shows that early, frequent, and loving involvement of family members is one of the best ways to help children with ASD.;
Read Also: Autistic Life Expectancy
Foundation And History Of Autism
For many, the simple term conjures a static image of Dustin Hoffmans character in Rain Man. This belies the complexity and variation of neurological disorders that fall within the category. Aspergers Syndrome is a single manifestation of the spectrum of disorders, which has also been mischaracterized as high-functioning autism in the past.
At the end of the 19th century, Dr. Langdon Down described individuals with what was characterized as mental retardation or developmental slowness. This proved to be an incorrect assessment. However, the term coined in 1911 was also incorrectly applied and would continue to be misused until the 1940s, when it was finally associated with behavioral and social difficulties.
However, the diagnosis based on an observed suite of behavioral characteristics alone was the cause of continued misapplication and an entrenched misunderstanding of what caused the disorders such as Aspergers. It was assumed as late as 1950 that autism was caused by cold or unloving parenting approaches by mothers, and was most likely to occur in the children of highly intellectual households. Of course, this was a sterling example of inherent bias and a complete misunderstanding of organic brain disorders.
Getting The Right Environment

Environment is important to quality of life for autistic people. There are ways you can adapt and improve your environment to make it as comfortable and supportive as possible for you or your child.
The social model of disability is a way of looking at the world that treats the difficulties people with disabilities have as being caused by barriers in society, rather than just the disabilities themselves. These barriers can be physical for example, buildings not having accessible toilets. Barriers can also be caused by peoples attitudes for example, many people will assume someone is lying because they dont make eye contact while talking.
The social model of disability can be a helpful way of considering the difficulties someone faces, and how to adapt their environment so it works for them.
Common changes to an environment that can help autistic people include:
- sensory changes for example, being given a quiet space to work, being able to use sensory toys like fidget spinners, or being allowed to make noises while working
- communication changes for example, using email or apps to communicate, using very clear language, allowing additional time to ask questions, or using visual communication such as photos or pictures as well as written words
- routine keeping to a regular routine and giving warning of any changes as far in advance as possible
- infections
Read Also: Does Gestational Diabetes Cause Autism
Read Also: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Autism And Your Environment
Sometimes, when a situation is too much to cope with due to sensory input , or being asked to do things that cause stress or distress, an autistic person can become overwhelmed.
Meltdowns and shutdowns
When an autistic person becomes overwhelmed and isnt able to use or benefit from their coping strategies, they might have meltdowns or shutdowns.
Its important, for parents of autistic children in particular, to be aware that a meltdown isnt a tantrum. A tantrum is something that a child can control, and tantrums often happen because a child wants something. A meltdown or shutdown isnt something an autistic person can control, and its caused by being overwhelmed.
During a meltdown, an autistic person might try to make themselves feel less overwhelmed. This can include doing things like:
- trying to get away from people for example by running away or hiding
- trying to get people away from them for example by shouting, screaming, hitting, or acting aggressively;
During a shutdown, an autistic person might try to block everything out for example by not responding to anything or anyone around them.
Challenging behaviour
Like everyone else, autistic people can display challenging behaviour if theyre in the wrong environment. While it can be challenging for the people around them, this behaviour is often a result of distress or frustration, particularly if an autistic person has difficulty with communicating.
Can Diet Have An Impact On Autism
Theres no specific diet designed for autistic people. Nevertheless, some autism advocates are exploring dietary changes as a way to help minimize behavioral issues and increase overall quality of life.
A foundation of the autism diet is the avoidance of artificial additives. These include preservatives, colors, and sweeteners.
An autism diet may instead focus on whole foods, such as:
Some autism advocates also endorse a gluten-free diet. The protein gluten is found in wheat, barley, and other grains.
Those advocates believe that gluten creates inflammation and adverse bodily reactions in certain autistic people. However, scientific research is inconclusive on the relationship between autism, gluten, and another protein known as casein.
You May Like: What Kind Of Autism Does Symmetra Have
How Is Autism Diagnosed
Fortunately, the way autism is diagnosed has changed and improved over the last 80 years.
We now recognise a wider range of signs and characteristics as forming part of the autism spectrum.
As awareness increases, parents and professionals are getting better at identifying early signs of autism and are more likely to seek an autism assessment.
This explains why people think autism is more prevalent today than it was ten or twenty years ago.
High Functioning Autism Symptoms
- Fixation on Particular Subjects or Ideas
- Linguistic Oddities
- Development of Repetitive or Restrictive Habits
- Dislike of Change
- Focus on Self
- Unusual Movement Patterns
Diagnosis rates for autism continue to rise, especially as parents and professionals become more familiar with the symptoms of high-functioning autism. Many patients are getting the assistance they need to live full, productive lives because their unusual behaviors are no longer seen as simple social awkwardness or eccentricity. As more caring medical and mental health professionals learn to recognize the most common symptoms of autism, the number of interventions available to people with autism will rise.
Read Also: What’s The Difference Between Autistic And Autism
What Is The Outlook For People With Autism Spectrum Disorder
In many cases, the symptoms of ASD become less pronounced as a child gets older. Parents of children with ASD may need to be flexible and ready to adjust treatment as needed for their child.
People with ASD may go on to live typical lives, but there is often need for continued services and support as they age. The needs depend on the severity of the symptoms. For most, it’s a lifelong condition that may require ongoing supports.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Through research, there has been much that has been learned about autism spectrum disorder over the past 20 years. There is ongoing active research on the causes of ASD, early detection and diagnosis, prevention and treatments.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/29/2020.
References
Autistic People May Act In A Different Way To Other People
Autistic people may:
- find it hard to communicate and interact with other people
- find it hard to understand how other people think or feel
- find things like bright lights or loud noises overwhelming, stressful or uncomfortable
- get anxious or upset about unfamiliar situations and social events
- take longer to understand information
- do or think the same things over and over
If you think you or your child may be autistic, get advice about the signs of autism.
Also Check: High Frequency Autism
What Is The Difference Between Autism And Autism Spectrum Disorder
The term autism was changed to autism spectrum disorder in 2013 by the American Psychiatric Association. ASD is now an umbrella term that covers the following conditions:
- Autistic disorder.
- Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified .
- Asperger syndrome.
People with ASD have trouble with social interactions and with interpreting and using non-verbal and verbal communication in social contexts. Individuals with ASD may also have the following difficulties:
- Inflexible interests.
- Insistence on sameness in environment or routine.
- Repetitive motor and sensory behaviors, like flapping arms or rocking.
- Increased or decreased reactions to sensory stimuli.
How well someone with ASD can function in day-to-day life depends on the severity of their symptoms. Given that autism varies widely in severity and everyday impairment, the symptoms of some people arent always easily recognized.
What Does Atypical Autism Mean
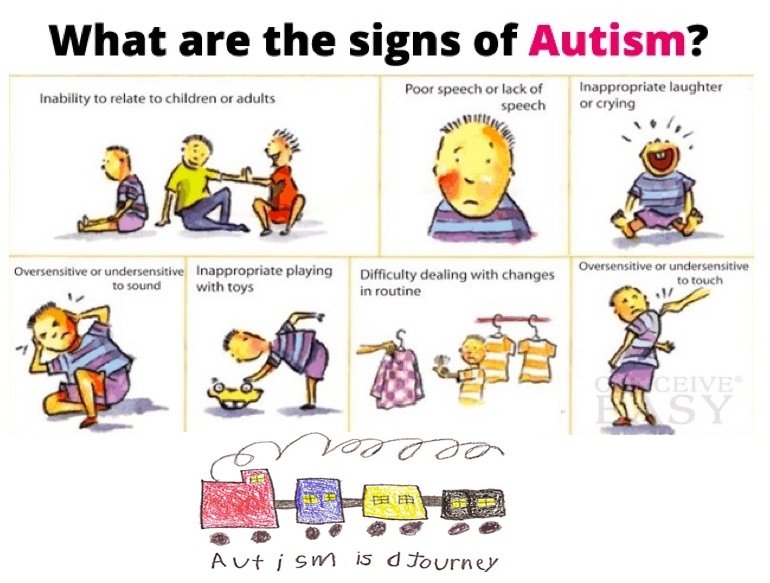
A person has atypical autism when they display some symptoms of autism spectrum disorder , but not enough to fit a diagnosis. Atypical autism is another term for pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified .;
The not otherwise specified part of PDD-NOS explains the purpose of this diagnosisto catch the people who dont quite align with other conditions.
It has also been called subthreshold autism, indicating that it doesnt fully meet the diagnostic criteria of ASD.
Read Also: Alex And Ani Autism Speaks