Asd Level : Requiring Support
Level 1 is the mildest, or highest functioning form of autism, which includes those who would have previously been diagnosed with Aspergers syndrome. Individuals with ASD level 1 may have difficulty understanding social cues and may struggle to form and maintain personal relationships. A child with level 1 autism may understand and speak in complete sentences, but have difficulty engaging in back-and-forth conversation.
Children with ASD level 1 experience some inflexibility of behavior, like difficulty switching between tasks, staying organized, and planning.
Most Common Signs Of High Functioning Autism
Sometimes, the signs of high functioning autism are hiding in plain sight! And if youre not careful, you might mistake them for something else. Or even worse, miss them altogether.
Given the overall increase in autism diagnoses in recent years, it might be helpful to be familiar with the signs. But first, its important to note a few things.
First, the medical community no longer uses the terms Asperger Syndrome or High Functioning Autism. Click here for more on that.
And secondly, though the terms have changed, understanding how to effectively parent regardless of the different expressions of autism is way more important now than before. Find out how to do so by clicking here.
So here are the 4 most common signs of what people often refer to as high functioning autism.
Signs And Symptoms Of Autism
There are many signs and symptoms that could indicate a person has autism spectrum disorder. Not all adults or children with autism will have every symptom, and some adults and children without autism may display some of the same behaviors and symptoms.
People with autism spectrum disorder often have difficulties with communication, and connecting emotionally and socially with others. They may also process sensory information, such as sounds and smells, differently from other people. These differences can underlie some of the behavioral signs of autism that people may display.
When looking for early signs of autism spectrum disorder, there are developmental milestones that children are expected to reach by certain ages, such as babbling by four months old and being able to use simple sentences by two years old. If a child reaches these milestones later, or does not develop the skills at all, it may indicate a developmental disorder such as autism spectrum disorder.
Autism can be diagnosed by age two, though symptoms may be apparent much earlier.
Recommended Reading: Does Freddie Highmore Have Autism
Theories And Empirical Research
Confucianism
is a study and theory of relationships especially within hierarchies. Social harmonyâthe central goal of Confucianismâresults in part from every individual knowing his or her place in the social order, and playing his or her part well. Particular duties arise from each personâs particular situation in relation to others. The individual stands simultaneously in several different relationships with different people: as a junior in relation to parents and elders and as a senior in relation to younger siblings, students, and others. Juniors are considered in Confucianism to owe their seniors reverence and seniors have duties of benevolence and concern toward juniors. A focus on mutuality is prevalent in East Asian cultures to this day.
Minding relationships
The mindfulness theory of relationships shows how closeness in relationships may be enhanced. Minding is the âreciprocal knowing process involving the nonstop, interrelated thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of persons in a relationship.â Five components of âmindingâ include:
What Is The Difference Between High

High-Functioning Autism and Low-Functioning Autism are different degrees of a spectrum of the same developmental disorder. While children with HFA and LFA may occasionally have similar behavioral characteristics, these characteristics are much more pronounced in children with LFA.
Many times, children with HFA are able to live relatively normal lives, though they may need specialized tutoring, therapy, or other treatments to improve their quality of life. However, children with LFA will need to attend special schools and will have very different lives from average children.
Its important to understand the differences between these two types of autism. Parents of autistic children must know that HFA and LFA does not determine a childs:
- Perseveration levels
Most of these traits and behaviors vary among all children and individuals. Some HFA children are very aggressive, while some LFA children are quite docile.
Some LFA children are very talented, and some HFA children may perform well in other areas of life, but struggle with certain repetitive behaviors. The primary difference between these types of autism is the severity of a childs struggle to learn and their ability to relate to other people, form relationships, and communicate with others.
The signs and symptoms of LFA are listed below to help you understand this disorder more clearly:
Don’t Miss: Does Autism Affect Lifespan
Symptoms Of Low Functioning Autism
The symptoms of low functioning autism can include all or some of the typical signs and symptoms of autism like limited social abilities, inflexible and repetitive behaviors, and impaired communication skills. However, these symptoms are more pronounced and severe than with others on the spectrum. In addition, those with low functioning autism also generally display signs and suffer from one or more forms of intellectual disability as described below.
Being a parent brings with it several challenges, fears, hopes, and new experiences. Every parent wants their child to be happy and healthy, but it is becoming more and more apparent that Autism Spectrum Disorder is on the rise and a growing concern among new parents.
Autism is the fastest growing developmental disability with new statistics showing it has been steadily growing over the past 20 years, with 1 in 59 children now being affected in the U.S. . In addition, over half of all autistic children also have mild to severe intellectual disability a diagnosis that indicates an autistic child has low-functioning autism. Although there is no cure for autism, early detection and treatment can have a huge impact on a childs quality of life, regardless of the level of severity of their symptoms.
Why Do Some Young People Get A Late Diagnosis
It is common for a young person to get a late diagnosis if they are high functioning or academically able. This also occurs more in girls than in boys, as girls are generally more adept at copying neuro-typical behaviours, including verbal and non-verbal communication in order to mask their autism.
Late diagnosis can happen because there is some ambiguity which makes it difficult to be sure a young person has autism, or because other conditions have presented as being their primary need e.g. challenging behaviour or ADHD. Typically, children are also often able to cope in a primary school environment but find the increasing demand of secondary school very stressful, leading to their difficulties becoming more apparent.
Recommended Reading: Can A Child Outgrow Autism
Level : Requiring Support
A person who meets the criteria for level 1 may face social challenges that require some support.
They may find it difficult to:
- initiate conversations with others
- respond as others would expect
- maintain interest in the conversation
As a result, it can be hard to make friends, especially without the right support.
The person may also:
How Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder Play
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder tend to be less spontaneous than other kids. Unlike a typical curious little kid pointing to things that catch their eye, children with ASD often appear disinterested or unaware of whats going on around them. They also show differences in the way they play. They may have trouble with functional play, or using toys that have a basic intended use, such as toy tools or cooking set. They usually dont play make-believe, engage in group games, imitate others, collaborate, or use their toys in creative ways.
Don’t Miss: What Color Stands For Autism
High Functioning Autism Explained
Ill never forget the look on her face when I told her my older son was autistic. She was completely dumbfounded, and stood speechless for a moment. Immediately following an epic public meltdown, this lady had reprimanded me for having such an unruly child. After she regained her composure, all she could blurt out was, But hes so high functioning! With that, she scurried off. I dont know who gave her the right to label him as such, but what is high functioning autism anyway?
Also Check: Can Autism Be Passed Down
What Are The Signs Of Autism In A 3 Year Old
Autism symptoms in a 3-year-olddoesnt respond to name.avoids eye contact.prefers playing alone to playing with others.doesnt share with others, even with guidance.doesnt understand how to take turns.isnt interested in interacting or socializing with others.doesnt like or avoids physical contact with others.More items
You May Like: Difference Between Autism And Sensory Processing Disorder
Getting Evaluated For Autism Spectrum Disorder
Parent interview In the first phase of the diagnostic evaluation, you will give your doctor background information about your childs medical, developmental, and behavioral history. If you have been keeping a journal or taking notes on anything thats concerned you, share that information. The doctor will also want to know about your familys medical and mental health history.
Medical exam The medical evaluation includes a general physical, a neurological exam, lab tests, and genetic testing. Your child will undergo this full screening to determine the cause of their developmental problems and to identify any co-existing conditions.
Hearing test Since hearing problems can result in social and language delays, they need to be excluded before an Autism Spectrum Disorder can be diagnosed. Your child will undergo a formal audiological assessment where they are tested for any hearing impairments, as well as any other hearing issues or sound sensitivities that sometimes co-occur with autism.
Observation Developmental specialists will observe your child in a variety of settings to look for unusual behavior associated with the Autism Spectrum Disorder. They may watch your child playing or interacting with other people.
Lead screening Because lead poisoning can cause autistic-like symptoms, the National Center for Environmental Health recommends that all children with developmental delays be screened for lead poisoning.
Dont Miss: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Brain Development And Asd
The development of the brain and how it functions is different in some way in children with DS-ASD than their peers with Down syndrome. Characterizing and recording these differences in brain development through detailed evaluation of both groups of children will provide a better understanding of the situation and possible treatments for children with DS-ASD.
A detailed analysis of the brain performed at autopsy or with magnetic resonance imaging in children with autism shows involvement of several different regions of the brain:
- The limbic system, which is important for regulating emotional response, mood and memory,
- The temporal lobes, which are important for hearing and normal processing of sounds,
- The cerebellum, which coordinates motor movements and some cognitive operations, and
- The corpus callosum, which connects the two hemispheres of the cortex together.
At Kennedy Krieger Institute, we have conducted MRI studies of 25 children with DS-ASD. The preliminary results support the notion that the cerebellum and corpus callosum is different in appearance in these children compared to those with Down syndrome alone. We are presently evaluating other areas of the brain, including the limbic system and all major cortical subregions, to look for additional markers that will distinguish children with DS-ASD from their peers with Down syndrome alone.
Read Also: Treatment Of Autism Spectrum Disorders Prelock
Characteristics Of People With High
Most people with high-functioning autism receive the diagnosis as adults. This might be because they tend to have a keen intelligence that allows them to overcome difficulties.
However, their families and their social environment suffer certain limitations. Thus, they tend to attribute such deficiencies to their personality. Thus, they rarely suspect that autism spectrum disorder is behind their behavior. Continue reading to find out more about what people with high-functioning autism are like.
Current Classifications Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
While the old system of classification may seem a little more cut-and-dried, the subtle differences that often distinguished one from the other left room for a lot of confusion and much was open to interpretation. To address this, ASD is now categorized into three different levels, indicating what level of support a patient may need.
- ASD Level 1 Level 1 ASD is currently the lowest classification. Those on this level will require some support to help with issues like inhibited social interaction and lack of organization and planning skills.
- ASD Level 2 In the mid-range of ASD is Level 2. In this level, individuals require substantial support and have problems that are more readily obvious to others. These issues may be trouble with verbal communication, having very restricted interests, and exhibiting frequent, repetitive behaviors.
- ASD Level 3 On the most severe end of the spectrum is Level 3 which requires very substantial support. Signs associated with both Level 1 and Level 2 are still present but are far more severe and accompanied by other complications as well. Individuals at this level will have limited ability to communicate and interact socially with others.
Read Also: What Is High Functioning Aspergers
Previous Autism Spectrum Disorder Terminology
Much of the misconception surrounding ASD comes from terminology that was used prior to 2013. In this prior classification system, children fell into one of the following three categories:
- Autistic Disorder More severe cases of ASD were previously classified as autistic disorder. The condition was often defined by communication troubles, repetitive behaviors, and social challenges among other symptoms.
- Aspergers Syndrome On the opposite end of the spectrum was Aspergers syndrome which was characterized by milder symptoms which may impact an individuals communication or social skills.
- Pervasive Development Disorder, Not Otherwise Specified For children who fell in the middle and didnt fully meet the requirements for either autistic disorder or Aspergers, a diagnosis of PDD-NOS was often given.
Getting An Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis
The road to an ASD diagnosis can be difficult and time-consuming. In fact, it is often two to three years after the first symptoms of ASD are noticed before an official diagnosis is made. This is due in large part to concerns about labeling or incorrectly diagnosing the child. However, an ASD diagnosis can also be delayed if the doctor doesnt take a parents concerns seriously or if the family isnt referred to health care professionals who specialize in developmental disorders.
If youre worried that your child has ASD, its important to seek out a clinical diagnosis. But dont wait for that diagnosis to get your child into treatment. Early intervention during the preschool years will improve your childs chances for overcoming their developmental delays. So look into treatment options and try not to worry if youre still waiting on a definitive diagnosis. Putting a potential label on your kids problem is far less important than treating the symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Psycom Autism Test
Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder In Adults
Common symptoms of autism in adults include:
- Difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling
- Trouble interpreting facial expressions, body language, or social cues
- Difficulty regulating emotion
- Trouble keeping up a conversation
- Inflection that does not reflect feelings
- Difficulty maintaining the natural give-and-take of a conversation prone to monologues on a favorite subject
- Tendency to engage in repetitive or routine behaviors
- Only participates in a restricted range of activities
- Strict consistency to daily routines outbursts when changes occur
- Exhibiting strong, special interests
Autism spectrum disorder is typically a life-long condition, though early diagnosis and treatment can make a tremendous difference.
What Age Does Autism Usually Show Up
Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life. In others, symptoms may not show up until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD gain new skills and meet developmental milestones, until around 18 to 24 months of age and then they stop gaining new skills, or they lose the skills they once had.
Don’t Miss: Is Nonny Autistic
What Is Level 2 On The Autism Spectrum
Level 2: Requiring Substantial Support: Marked difficulties in verbal and nonverbal social communication skills. Markedly odd, restricted repetitive behaviors, noticeable difficulties changing activities or focus. Level 3: Requiring Very Substantial Support: Severe difficulties in verbal and nonverbal communication.
Signs And Symptoms Vary
Although we are documenting some similarities in the way DS-ASD presents, autism is what is considered a spectrum disorder. This means every child with DS-ASD will be different in one way or another. Some will have speech, some will not. Some will rely heavily on routine and order, and others will be more easy-going. Combined with the wide range of abilities seen in Down syndrome alone, it can feel mystifying. It is easier if you have an understanding of ASD disorders separate from Down syndrome.
Autism, autistic-like condition, autistic spectrum disorder , and pervasive developmental disorder are terms that mean the same thing, more or less. They all refer to a neurobehavioral syndrome diagnosed by the appearance of specific symptoms and developmental delays early in life. These symptoms result from an underlying disorder of the brain, which may have multiple causes, including Down syndrome. At this time, there is some disagreement in the medical community regarding the specific evaluations necessary to identify the syndrome or the degree to which certain core-features must be present to establish the diagnosis of ASD in a child with Down syndrome. Unfortunately, the lack of specific diagnostic tests creates considerable confusion for professionals, parents, and others trying to understand the child and develop an optimal medical care and effective educational program.
There is general agreement that:
- Autism is a spectrum disorder: it may be mild or severe.
ASD include:
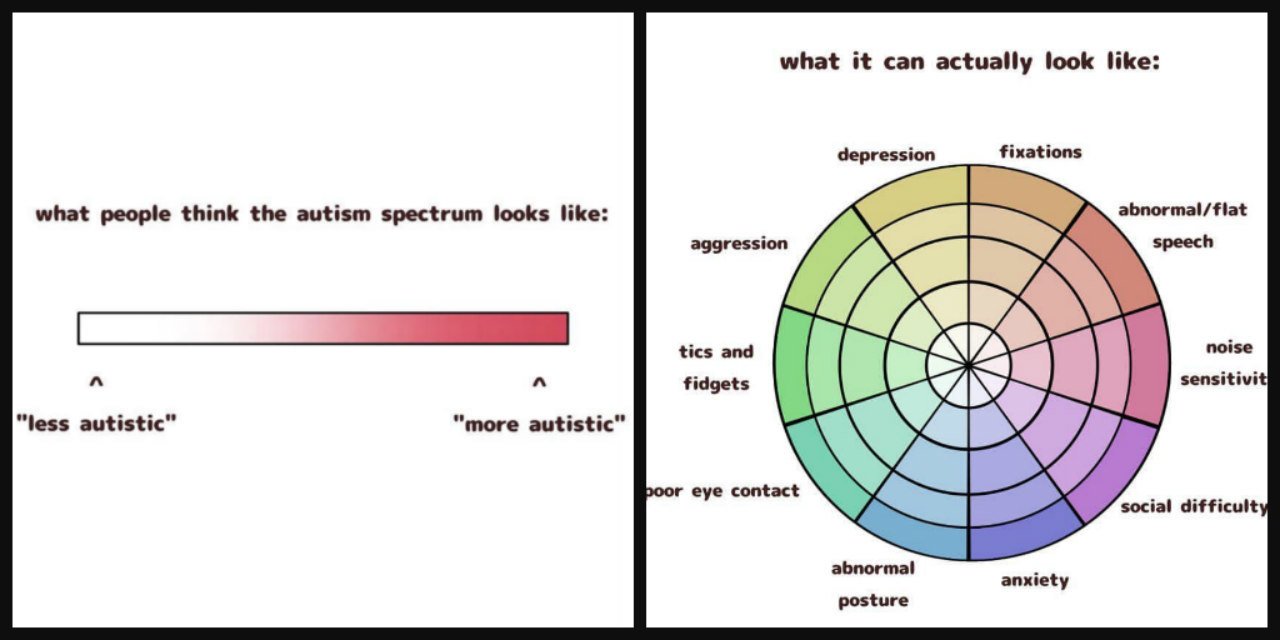
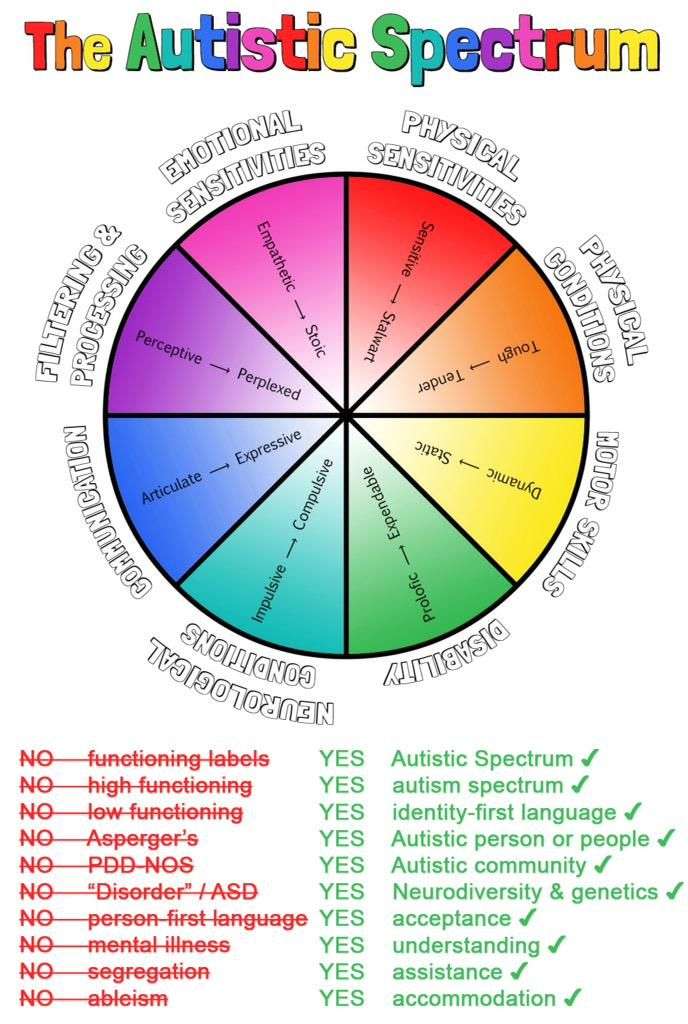
You May Like: Severity Levels Of Autism