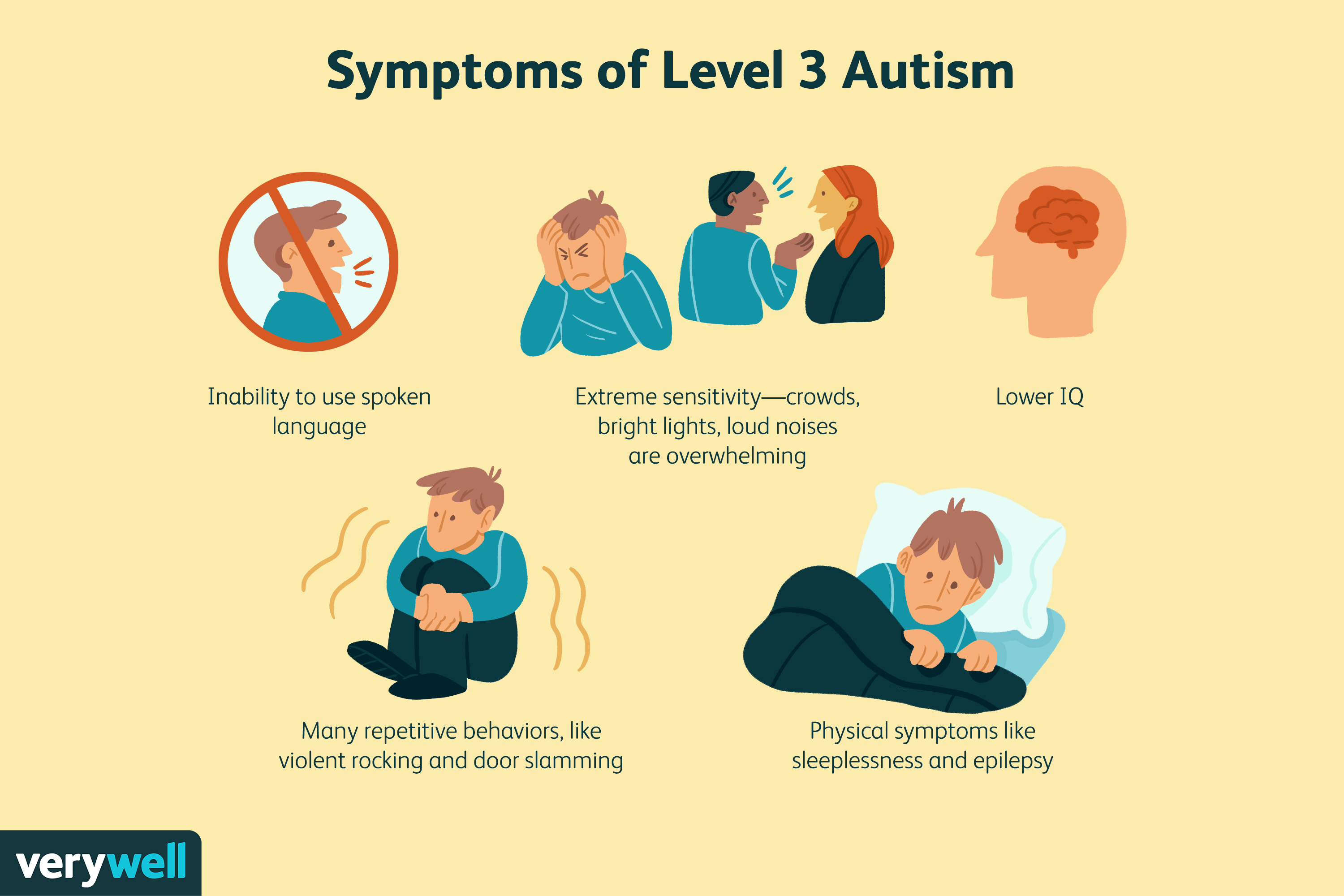
What Are Signs Of Autism In A 3
Autism symptoms in a 3-year-old
- doesn’t respond to name.
- prefers playing alone to playing with others.
- doesn’t share with others, even with guidance.
- doesn’t understand how to take turns.
- isn’t interested in interacting or socializing with others.
- doesn’t like or avoids physical contact with others.
Why This Terminology Is No Longer Used By Doctors
The spectrum illustrates a broad range of developmental delays and symptom severity.
ASD includes people who have a few mild autistic traits to those who need help with day-to-day functioning. It represents every intelligence level, as well as varying degrees of communication and social abilities.
The differences between one type and another type can be subtle and difficult to determine.
Types Of Autism Tests
On average, half of the families of children with autism notice their childrens unusual behavior after 18 months of age. Also, on average 4/5 of families notice after 24 months. At this point, the autism test which is performed at an early stage has great importance in case of intervention and treatment.
Children with autism are not very well connected with the people around them. Children with autism who have difficulty speaking compared to their peers experience communication problems. Early diagnosis is of paramount importance, especially in the case of autism, which is manifested by the lack of eye contact. Due to the fact that autism has no definitive treatment. However, with the comprehensive training applied as a result of early diagnosis, the symptoms of autism are reduced by up to 70%.
The attention of families is very important for the diagnosis of autism. For example, if the child does not bawl when he/she is 12 months old, if there are no hand signals, if the child does not say a word when he/she is 16 months old, and if the child cannot speak even two words when he/she is 24 months old. So, if the parents observe those kinds of behaviors and take their children to the experts, it means that they can help to establish an early diagnosis of autism. Therefore, it should be kept in mind that parents should observe the different behaviors that exist in their children.
You May Like: Asd Level 2 Symptoms
Terms For Types Of Autism That Are No Longer Used Today
When autism was categorized by types, the lines between the different types of autism could be blurry. Diagnosis was, and still is, complicated and often stressful for families.
If you or your child received a diagnosis before the DSM-5 changed, you may still be using the older terminology . Thats OK. Your doctor may continue to use those terms if they help.
Are Siblings At Greater Risk For Autism Spectrum Disorder
The truth is that genetics do play a role in autism. When one child is diagnosed with ASD, the next child to come along has about a 20% greater risk of developing autism than normal. When the first two children in a family have both been diagnosed with ASD, the third child has about a 32% greater risk of developing ASD.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Read Also: Asd And Adhd Comorbidity
Treatment And Therapy For Low Functioning Autism
A childs first years are crucial to their level of development and future learning and growth. By taking action and getting support right away, parents can help their children realize the best possible outcome. Early intervention also has a positive impact on the parents, by providing them with insight and tools to use as they learn to navigate their relationship with their special needs child.
Every child and adult with autism has varying degrees of symptoms and although they may share similarities, no two people with autism are alike, especially considering the fact that they often are diagnosed with numerous medical conditions that can include suffering from Sensory Processing Disorder, anxiety disorder, ADHD, Tourettes Syndrome, and many others.
Regardless of the childs diagnosis, early intervention is the key to helping children with autism progress. Therapy and intervention can include applied behavioral analysis, speech therapy, augmentative and alternative communication, physical therapy, occupational therapy, dietary restrictions, and treatment and diagnosis of comorbid medical conditions. Some parents also opt for less conventional music therapy and pet therapy.
Parentscould My Baby Have Autism New Resource Aims To Identify Asd Early
Another important aspect of autism spectrum disorder relates to deficits in social communication.
This can impact ones manner of speech, ability to engage in typical social communication such as humor, sarcasm or use of idioms, and more, Pipkin said. Social skills deficits can also be much more nuanced. It can be very like landing in the middle of a foreign land with a language you do not speak and rules that everyone else seems to know but of which you are unaware. Reading body language, facial expressions, changes in tone or picking up on hints, such as recognizing the specific interest about which you have been talking for the last two hours is not how the listener would like to spend their afternoon.
Also Check: Autism Life Expectancy
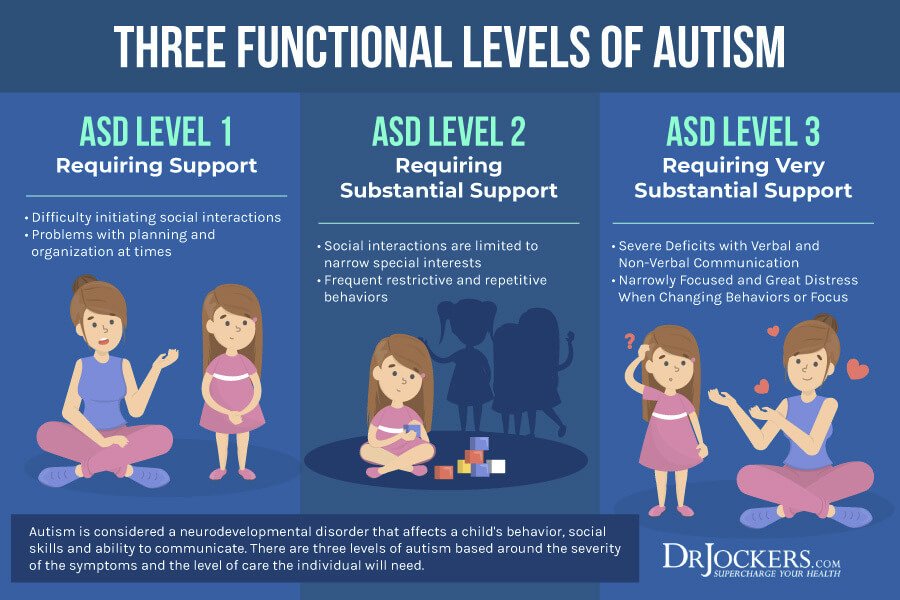
Autism Spectrum Disorder Level : Requiring Substantial Support
According to DSM-5, individuals with level 2 autism require substantial support. Generally, they need more support than individuals with level 1 autism. Even with support, they might have a hard time adjusting to changes in the environment around them.
There are a variety of therapies can help them. For example, sensory integration therapyhelps individuals learn how to deal with sensory input. In other respect, individuals with level 2 autism tend to benefit from occupational therapy. This type of therapy helps them develop the skills that they need to complete daily tasks in order to make easier their daily routines, such as decision-making or job-related skills.
A person with level 2 autism, meaning that with moderate autism, may exhibit normal or below normal mental functioning. They may have some degree of mental retardation or they may have a normal IQ of about 100. This person with level 2 autism might find self-care tasks difficult and challenging.
The symptoms which are associated with level 2 autism include more severe lack of both verbal and nonverbal communication skills compared to level 1 autism. To put it in a different way, they have a significant lack of verbal and nonverbal communication skills. They might have an unusual or reduced response to social cues, communication or interactions. They mostly use overly simple sentences during the conversation.
Levels Of Autism: What The Dsm
The diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder themselves are fairly straightforward:
- “Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts” this may refer to differences in body language, different ways of communicating with others that neurotypical people find hard to understand, and a different way of expressing or feeling emotions.
- “Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities” this can refer to physically repetitive movements or the repitition of sounds , a need for rigid routines, being really interested in a particular topic or a few, and things like wanting or needing to eat the same foods every day.
- Symptoms have to show up in childhood, even though they may not have been recognized as autism.
- Symptoms affect daily functioning in a negative way.
- Another diagnosis couldn’t better explain the symptoms.
There’s quite a few more “specifiers”, terms that further describe any given autistic person’s personal autism, such as “with” or “without” intellectual or language impairment.
The levels of autism are quite interesting:
Rather than referring to levels, it’s also common to hear talk of “low-functioning” vs “high-functioning” autism.
Read Also: Can Autistic Adults Get Married
How Do Kids Get Autism
Genetics. Several different genes appear to be involved in autism spectrum disorder. For some children, autism spectrum disorder can be associated with a genetic disorder, such as Rett syndrome or fragile X syndrome. For other children, genetic changes may increase the risk of autism spectrum disorder.
What Causes Autism
The exact cause of autism is unknown, and the most current research has not identified any single genetic or environmental cause. It is most likely a combination of genetic and environmental influences of which ongoing health research continues to investigate the exact cause. However, there are some known risk factors for ASD which help elucidate its origins:
- Genetic mutations
- Fragile X syndrome and other genetic disorders
- If an immediate family member is also autistic
- Low birth weight
- Having older than average parents
- Metabolic imbalances
- A history of viral infections
Thankfully, clear and explicit research has shown that there is no linkage between vaccines and autism. A previously controversial study on the topic published in 1998 was discredited, and subsequently retracted, in 2010.
Also Check: Why Is A Puzzle Piece The Symbol For Autism
How Is Asd Treated
There arent any standardized treatment recommendations for different levels of ASD. Treatment depends on each persons unique symptoms.
People with different levels of ASD may all need the same kinds of treatment, but those with level 2 or level 3 ASD will likely need more intensive, long-term treatment than those with level 1 ASD.
Potential ASD treatments include:
Level : Requiring Substantial Support
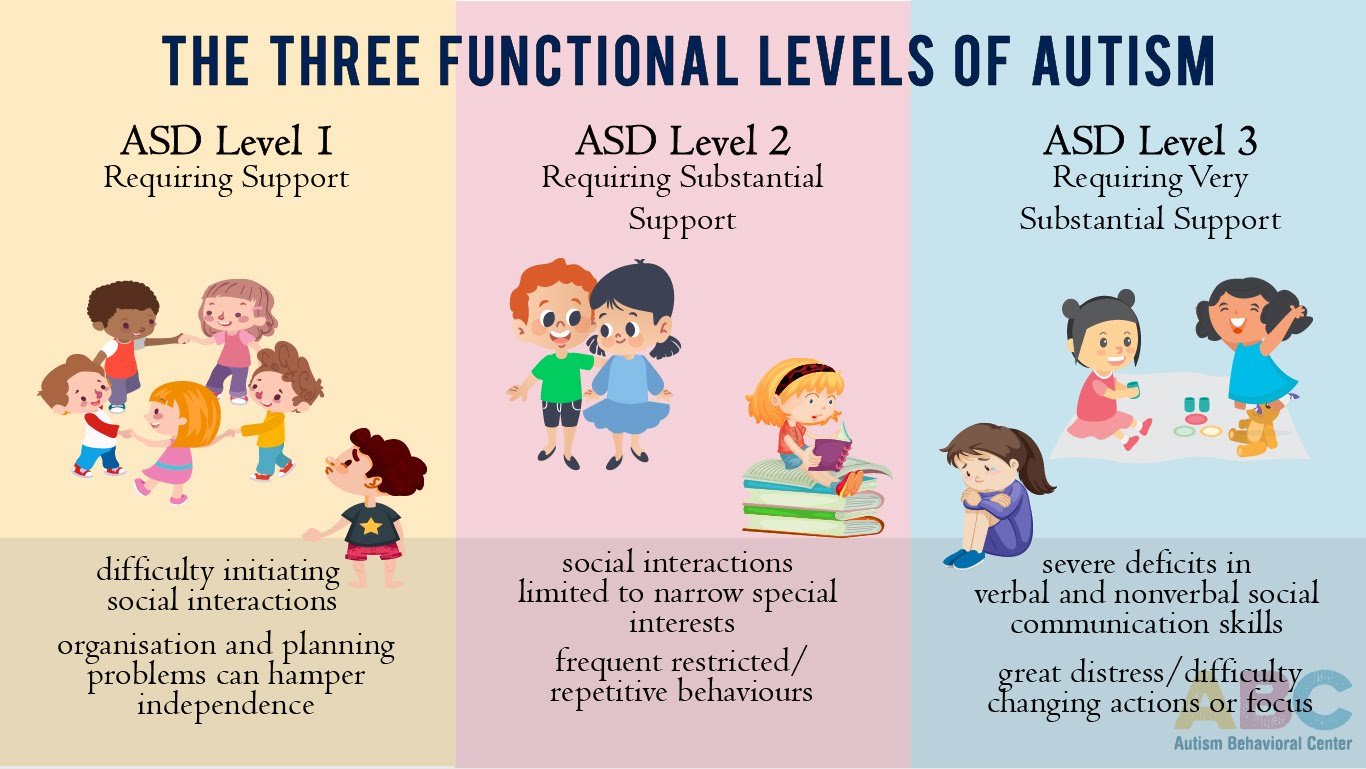
People who meet the level 2 criteria need more support than those with level 1 autism. Social challenges can make holding a conversation very difficult.
Even with support, the person may find it hard to communicate coherently, and they are more likely to respond in ways that neurotypical people consider surprising or inappropriate.
The person may:
- only discuss very specific topics
- have difficulty understanding or using nonverbal communication, including facial expression
For example, they may face away from the person with whom they are communicating.
People with level 2 autism may also find daily functioning difficult due to the challenges of coping with change. Facing change might cause them to experience significant distress.
Don’t Miss: What Is Pivotal Response Training
Autism Levels Of Severity
Autism is referred to as a broad spectrum because the autism levels of severity can be extremely different amongst those diagnosed. Despite this, the DSM-5 has categorized autism into three levels of severity. Level 1 refers to those who require support but are able to live independently with symptoms that may not be overly obvious, this is controversially labeled as high functioning autism. Level 2 autism requires more substantial support with much more apparent symptoms. Level 3 refers to those who require the most substantial support and is often referred to as low functioning autism, these individuals also tend to have an intellectual disability. They display the most severe symptoms of autism and usually have the hardest time socializing and communicating with many being nonverbal. Although there are treatments and several ways to help them experience a better quality of life, they require the most support and it is nearly impossible for them to gain independence as they continue to need help with basic activities throughout their lives. They are also more likely to have other conditions like epilepsy, tuberous sclerosis, and Fragile X syndrome.
Autism Symptoms In Adults At Work
Symptoms of ASD vary greatly from person to person based on the severity of the condition. These or similar manifestations of ASD may be apparent at work:
- When youre having a conversation with your boss, you prefer to look at the wall, her shoes, or anywhere but directly into her eyes.
- Your co-workers say that you speak like a robot.
- Each item on your desk has a special place, and you dont like when the cleaning company rearranges it to dust.
- You are really good at math, or software coding, but struggle to succeed in other areas.
- You talk to your co-workers the same way you talk with your family and friends.
- During meetings, you find yourself making involuntary noises, like clearing your throat over and over.
- When talking with your boss, you have difficulty telling if he is happy with your performance or mad at you.
In addition, individuals with ASD may exhibit extraordinary talents in visual skills, music, math, and art. And roughly 40 percent of individuals with ASD have average or above-average intelligence.
If you experience these or similar symptoms of ASD, consult a doctor or mental-health professional for a formal autism evaluation and learn more about treatment options for autism symptoms in adults.
Also Check: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder Level : Requiring Support
According to the DSM-5, individuals on level 1 autism require support. They can live by themselves and maintain a high quality of life with little support. Usually, this support is taken in the form of behavioral therapy or other types of therapy, depends on the individuals need. Both of these approaches can help improve social skills and communication skills. Also, behavioral therapy can help develop positive behaviors of individuals that might not come naturally.
Theory of Mind is one of the most effective ways in order to treat level 1 autism. Both ToM and adaptive skill-based treatments target executive function, emotional regulation, cognitive flexibility, social communication skills and reduction in anxiety. These aspects are very important in the field of level 1 treatment.
Individuals with level 1 autism have noticeable impairments, communication problems and problems in socializing. They can have a conversation, however, it might be difficult to maintain a back-and-forth conversation. Some of them at this level might find it hard to reach out and make new friends.
At this level, individuals may show decreased interest in social interactions or activities. They might have difficulties initiating social interactions and communications, such as talking to a person. They are able to engage with a person but they may struggle to maintain a give-and-take of a typical conversation. Some of them who attempt to make friends are seen as odd and typically unsuccessful.
What Causes Autism Spectrum Disorder
There is no clear-cut cause of ASD. Some causes that are supported by research include genetic and some environmental factors. Specific genetic causes can only be identified in 10% to 20% of cases. These cases include specific genetic syndromes associated with ASD and rare changes in the genetic code.
Risk factors include older parental age, low birth weight, prematurity and maternal use of valproic acid or thalidomide during pregnancy, among others. This field of study is an active one for reasearch.
Recommended Reading: Psycom Autism Test
What Are The Dsm
In 2013, the American Psychiatric Association released the fifth edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders .
The DSM-5 is now the standard reference that healthcare providers use to diagnose mental and behavioral conditions, including autism.
By special permission of the American Psychiatric Association, you can read the full-text of the new diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder and the related diagnosis of social communication disorder below.
Also see: Answers to frequently asked questions about DSM-5 criteria for autism
What Are The Different Types Of Autism
Prior to the 2013 transition, the levels of autism were explained using terminology that classified people with autism into different phenotypes, or groupings of symptoms, of the disorder, rather than the severity. This caused some misunderstandings and confusion surrounding autism spectrum disorder as it was generally non-specific and open to interpretation. You may have heard of some of the specific terms previously used for autism, which included:
Don’t Miss: Autism Puzzle Symbol
What Is Low Functioning Autism
The difference between high functioning autism and low functioning autism is behavioral. Low functioning autism causes behaviors that inhibit the ability to conduct daily life. Children with high functioning autism have similar abilities to his/her neurotypical peers.
This is especially true when the child receives early intervention therapies. Children diagnosed with low functioning autism need more support. They struggle to communicate and manage their behaviors.
Symptoms are identifiable in infancy or early childhood. Children with autism spectrum disorder will not meet neurodevelopmental benchmarks on time or at all. These children experience delays in learning how to self-soothe, forming bonds, and talking. They usually experience severe communication and behavioral challenges.
Children with low functioning autism struggle to complete activities of daily living. They generally need help with most activities. Children with severe autism are more likely to have co-morbid conditions. These include such as Fragile X syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, and epilepsy.
What Is Missing From Asd Levels Of Support
ASD Levels of Support is a helpful guide in determining the persons place on the spectrum. However, these levels also bring up many questions in addition to those they answer.
Although the idea of ASD levels of support makes sense in terms of logic, clinicians still have a difficult time when assigning a level. These levels can be subjective in a way. In addition, as the skills of the individual and other issues improve in time, it may be possible that the level of the individual may change.
It may not always be clear what type of support the American Psychiatric Association had in mind when they were developing these functional levels. This can range from a personal care assistant to a college advisor, but it is not really clear. Heres our definitive autism guide where you can find more information on DSM-5 and much more.
People with autism, especially those who are high functioning, may have anxiety. This can cause challenges in typical settings, despite these people being bright and verbal. When people with ASD are depressed or anxious, they may need significant support to function in daily life. This makes it complicated to fit these people into a certain level.
Similarly, some people with ASD do just fine at home but need extensive help in school. They are expected to meet specific demands. Some do well at school but struggle at home. The support needed by people at various levels becomes vague.
Recommended Reading: Autism Awareness Colors Meaning