What Causes Autism Researchers Id 102 Genes Linked To Condition
- A large genetic study provided scientists with a greater understanding of how genes cause changes in the brain that lead to autism spectrum disorder.
- Researchers analyzed more than 35,000 participant samples, including almost 12,000 from people with ASD.
- Scientists believe that both genes and environment are involved in the development of ASD, with genetics playing a big part.
In the largest genetics study of its kind to date, scientists have identified 102 genes associated with the risk for autism spectrum disorder .
Researchers also gained further insight into which of these genes are associated with both ASD and other disorders that cause intellectual disability and developmental delay.
For the study, an international team of researchers analyzed more than 35,000 participant samples, including almost 12,000 from people with ASD.
Researchers used a genetic technique called exome sequencing, which looks at all the regions of a persons genetic information or genome that are translated into proteins. This testing can pick up rare genetic mutations that might not show up with other methods.
Dr. Lonnie Zwaigenbaum, a professor in the Department of Pediatrics and the Stollery Childrens Hospital Foundation Chair in Autism at the University of Alberta, called this an exciting study, both for the sophisticated methods used and the large sample size.
The study results were published January 23 in the journal Cell.
Genetic Bases Of Autism
Several psychiatric diseases have strong evidences of genetic involvement in their origin, and among them are schizophrenia, bipolar disturbance and autism. In 1977, a study with mono and dizygotic twins described for the first time the genetic predisposition of autism .
Nowadays, population studies suggest that the model that better describes DASs is multifactorial with a concordance of 60-92% in monozygotic twins and 0-10% in dizygotic twins . Differences found in studies between monozygotic twins support the multifactorial model, demonstrating the importance of environmental factors.
Several studies were performed to clarify genetic factors associated with the disease. Autism symptoms that suggest a strong genetic component are convulsions, mental deficiency, neurons and synapse decrease in amygdala, hippocampus and cerebellum, increased size of encephalon, and increased level of circulating serotonin. Even studies with monozygotic twins show a significant concordance, as opposed to dizygotic twins. Non-twin siblings present a risk of developing autism ranging from 0-30%, and this risk is much higher than in the general population .
The comparison of the mentioned populational groups, as well as the difference between men and women, shows epistatic effects that involve an interaction between several genes, suggesting the role of environmental factors .
Definition And Evolution Of Asd
Autism is a developmental neuropsychiatric syndrome with onset before the age of three. The fundamental conceptualization of the disorder is based on the initial observation of Kanner in 1943 , where he described 11 children with autism, mostly boys with a combination of severe social and variable language dysfunction and the presence of repetitive restrictive behaviors. Kanner made numerous interesting observations based on these case studies, including the identification of large head size in about half of the subjects and postulated a biological, genetic basis for the disorder. However, until the 1980s autism was not considered a distinct disorder in the manuals of psychiatric diagnosis, nor was it considered by most to be biologically based.
Also Check: High Functioning Autism Vs Adhd
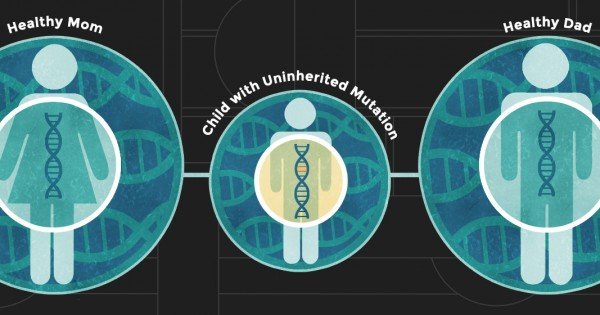
Rare Gene Variants Passed On From Parents May Significantly Increase Risk Of Autism
Autisms cause is not something science has completely figured out yet. Studies have discovered several different links which appear to play a role in children developing the condition. Now, researchers have identified a rare class of genetic differences that parents without autism pass on to their children. The study finds these variants make it significantly more likely for the child to develop autism.
A team working with the Simons Foundation in New York adds this hereditary link is especially prominent among multiplex families, where other members of that family have autism, even if the parents of that particular child do not.
Clinical Implications And Future Perspectives
When autism was first described, it was hypothesized to be an environmentally caused disease. Decades of research have since revealed that autism is a highly heterogeneous and extremely complex genetic condition. Even though great progress had been made in identifying hundreds of risk genes, very little is known about the different types of modifiers that may exacerbate or ameliorate disease severity. Such modifiers could include epigenetics, sex-linked modifiers, CNVs, double-hit mutations, or environmental factors .
Figure 1. Genetic modifiers in autism spectrum disorder. Autism is estimated to be 4080% heritable. However, both genetic and non-genetic factors modulate the penetrance of risk genes, resulting in a highly heterogeneous disease phenotype for similar pathogenic variants. Examples of genetic modulators include CNV, epigenetics, and double-hit mutations. Examples of non-genetic modifiers include environmental exposures and sex-linked modifiers.
Also Check: Can A Child With Autism Have Dyslexia
Treatment For Your Child With Autism
At Therapeutic Pathways, our therapists and behavior technicians follow the most up-to-date practices extensively researched and backed by leaders in the scientific community. After your child has been diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder, come to Therapeutic Pathways for individualized treatment. We provide family training and support as well as comprehensive Applied Behavior Analysis treatment for children, adolescents, and adults.
For more information, call 422-3280.
Brain Development And Autism
The brain develops differently in autistic children compared with typically developing children.
In young children, the brain is developing all the time. Every time a child does something or responds to something, connections in the brain are reinforced and become stronger.
Over time, the connections that arent reinforced disappear theyre pruned away as theyre not needed. This pruning is how the brain makes room for important connections those needed for everyday actions and responses, like walking, talking or understanding emotions.
In autistic children, the brain tends to grow faster than average during early childhood, especially during the first three years of life. The brains of autistic babies appear to have more cells than they need, as well as poor connections between the cells.
Also, pruning doesnt seem to happen as much in autistic children. This means that information might be lost or sent through the wrong connections. The lack of pruning might also explain why the brain seems to be growing faster in autistic children than in typically developing children.
Its not yet clear what causes this difference in brain development.
You May Like: Does Nick Eh 30 Have Autism
Identification Of Candidate Asd Risk Genes
Following the classification of autism by Kanner, research efforts were undertaken to determine the disease etiology. Though it was initially assumed to be of environmental origin, an improved understanding of the role of genetics in human health soon suggested otherwise. In 1977, Folstein and Rutter conducted twin studies upon the observation that incidence among siblings was 50× higher than average. They found that monozygotic twins were more likely to share a diagnosis than dizygotic twins, suggesting a genetic influence. Bailey et al. supported this finding, documenting 60% concordance for monozygotic twins versus no concordant dizygotic pairs. In addition, risk of a child having ASD was found to be proportional to the percentage of the genome they shared with an affected sibling or parent . By the turn of the century, ASD was established to have some genetic component, though which genes were involved remained a mystery.
Somatic Mosaicism and ASD Risk
CNVs Contribute to ASD Susceptibility
Epigenetic Regulation and ASD
Traits In Mothers May Signal Gene Variants For Autism
by Taylor White / 16 October 2020
Topics:
Talking traits:
Autistic childrens traits track more with subtle, autism-like behaviors in their mothers than with those in their fathers, according to a new study1.
In particular, autistic children whose mothers have problems with pragmatic language communicating in social settings tend to have especially prominent social-communication difficulties themselves, the study shows. Whats more, those mothers also have many common genetic variants linked to autism. These common variants are thought to account for as much as half of autisms genetic basis.
The findings suggest that the same genetic factors that contribute to autism also underlie a collection of mild traits known as the broad autism phenotype. The presence of these traits may be a sign that a woman carries a genetic predisposition to autism.
I was really excited to see that features of broad autism phenotype, and especially language-related features, seem to be really important in understanding how genetic liability is expressed and really linked to molecular genetic variation, says co-lead investigator Molly Losh, director of the Neurodevelopmental Disabilities Lab at Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois.
It shows that autism traits and expression of the conditions genetics roots may differ for mothers and fathers, says co-lead investigator Lea Davis, assistant professor of genetic medicine at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tennessee.
Recommended Reading: Autism Symbols Puzzle Piece
Are A Whole New Batch Of Genes Leading To Autism
The SPARK Consortium contributed more than half of the genetic data researchers used for this project. In total, the team reviewed genetic material from over 21,000 SPARK participants, including more than 6,500 with autism spectrum disorder . Despite knowing about many genes and mutations which show a connection to autism, the results reveal these new ultra-rare inherited variants are not coming from the typical pool of autism genes.
Interestingly, the vast majority of those variants are not found in genes already known to be autism genes, indicating that there is much more to be learned about autism genetics, says Dr. Feliciano. While the current study is not large enough to confidently identify individual genes that have these rare inherited variants, we are learning more about these genes. Future research that focuses on multiplex families is increasingly important to yield novel insights.
What Age Does Autism Usually Show Up
Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life. In others, symptoms may not show up until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD gain new skills and meet developmental milestones, until around 18 to 24 months of age and then they stop gaining new skills, or they lose the skills they once had.
Also Check: What Causes Autism Exploring The Environmental Contribution
You May Like: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Behaviour Analysis Of Asds
Although now a days knowledge concerning autism is much more prefound, it still surprises due to the diversity of characteristics that patients can show.
Usually, the autistic child has normal physical . However, these children also show an irregular profile of development that is detectable in the first three years of life, being present till adulthood. The Triade of Social Impediments is characterized by a strict and continuous pattern with intelligence levels varying from mental retardation to an extraordinary performance in certain cognitive domains or savant capacities . Although 80% of autistic children show mental retardation, savant capacities can exist, however the global intelligence ratio is low . The difference between mental retardation and autism should be pointed out: The first one shows a uniform development deficit while the last presents an irregular profile, with differentiated degrees of commitment.
The following classification and diagnosis systems allow to distinguish autism from other disorders: International classification of Diseases of the World Health Organization and the Manual of Diagnosis and Statistics of Mental Disorders from the American Academy of Psychiatry . In these systems the term Child Autism was replaced by Autistic Disturbance, officially separating it from Asperger syndrome .
Epigenetic Dysregulation In Autism
Although most of the epigenetic modifications described above are underpinned by genetic mechanisms, the evidence of the contribution of epigenetic dysregulation in autism raises the issue of the role of epigenetic modifications by environmental factors. An example is assisted conception. Indeed, while it was shown that in vitro fertilization and ovulation induction can result in abnormal methylation and dysregulation of imprinted genes, epidemiologic studies on the use of assisted reproductive technology and the risk of autism found conflicting results.
You May Like: Can A Child With Autism Have Dyslexia
New Technology Reveals New Gene Ties To Autism
Study authors, led by Amy B. Wilfert, Ph.D. from the University of Washington, say new technology and dropping costs on genetic research have allowed them to gather information of thousands of genes from people with autism and their relatives. Researchers analyzed nearly 11,000 people with autism to identify the new mutations which pass from healthy parents to children on the autism spectrum.
The team notes most autism genes discovered to date come from research on de novo mutations. These are genetic variations that first develop in a person with autism and are not present in their parents genes at all. The new findings reveal that rare inherited variants which lead to autism are likely in a different batch of genes from the ones de novo mutations affect.
While most autism studies focus on de novo mutations, this study focuses on rare inherited mutations, which are often understudied in autism, says Dr. Wilfert in a media release. We find that these variants are individually less damaging than de novo mutations but have the potential to contribute almost as much risk and impact the same molecular pathways, through a distinct set of genes. These variants, however, are only able to persist in the general population for a few generations before being selected out by evolution.
Indirect Evidence Suggesting A Contribution Of Environmental Factors
Prevalence
Prevalence studies of autism spectrum disorders conducted in recent years have been the source of an important debate because of a steady and highly significant increase of estimates of the total prevalence of pervasive developmental disorders. Indeed, while the prevalence was estimated at 6 per 1000 in a population of school children in 2005, recent studies have gone so far as to estimate the prevalence to be one child in 38.The last prevalence estimates in the United States, released by the Centers for Disease Control recently, reached 1 in 88 child in 2008, while their previous estimate was one in 110 in 2006. However, most of the studies are not comparable in method or in the populations studied. One hypothesis is that this increase is the result of enlargement of diagnostic criteria, and the growing importance of screening for ASDs. The results of an epidemiological study from England, based on a national sample from 2007, support this hypothesis. Indeed the authors found a rate of about 1% in adults across the entire age range, without a significant reduction in the older part of the sample, as one would expect if the prevalence had increased in recent years. However, another study suggested that diagnostic substitution, especially for the most severe cases, and better ascertainment, especially for children at the less severe end of the spectrum, explain only a part of the linear increase observed in the California registry.
Immune dysfunction
Transcriptome
Also Check: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Causes Of Autism Remain Mysterious
While autism is increasingly common, its cause is usually unknown. In a general way, researchers believe that there is a strong genetic component to autism and that there are environmental “triggers” that may cause certain individuals to develop symptoms for any individual, however, the precise nature of the genetic and environmental triggers is unknown.
When autism is of known origin , it is referred to as secondary autism. When autism is of unknown origin, it is called idiopathic autism.
Key Points About Autism Spectrum Disorder In Children
-
Autism spectrum disorder is a problem that affects a childs nervous system and growth and development.
-
A child with ASD often has problems communicating. He or she may have trouble developing social skills.
-
Genes may play a role in ASD.
-
All children should be screened for ASD before age 2.
-
Diagnosis may include imaging and genetic tests.
-
Children with ASD need a special treatment plan. It may include programs that change behavior and teach social skills.
Also Check: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
How Is Asd Diagnosed In A Child
No single medical test can diagnose ASD. Healthcare providers use certain guidelines to help diagnose ASD in children before age 2. The guidelines can help diagnose the disorder early. Children diagnosed with ASD early can be treated right away.
The guidelines say that all children should be screened for ASD and other development disorders before age 2. The screening is done at well-child checkups. Children who have symptoms of development or behavior disorders will need to get more testing for ASD.
Healthcare providers look for the following problems during well-child visits before age 2:
-
No babbling, pointing, or gesturing by age 12 months
-
No single words spoken by age 16 months
-
No 2-word phrases by age 24 months, just repeating words or sounds of others
-
Loss of any language or social skills at any age
-
No eye contact at 3 to 4 months
If a child has any of the above problems, the healthcare provider will do more screening. This will help show if your child has ASD or another developmental disorder. Your child may need to see a healthcare provider with special training to diagnose and treat ASD. Your child may also need these screening tests:
-
Nervous system exam
-
Genetic tests to look for gene problems that cause ASD or other developmental disorders
Inclination For Mental Illness
With age, the quality of sperm decreases. This is why elderly people can pass on mutated genes to their children. This increases the risk of developing mental illnesses, autism, hyperactivity, or bipolar disorder. Also, children born to fathers who are over 45 years old or more are more likely to be suicidal and have learning difficulties.
At any age, men who have coronary heart disease are likely to pass it on to their sons. And men who were infertile and the conception was done artificially, often have sons with the same problem.
Recommended Reading: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic