Rare Gene Variants Passed On From Parents May Significantly Increase Risk Of Autism
Autisms cause is not something science has completely figured out yet. Studies have discovered several different links which appear to play a role in children developing the condition. Now, researchers have identified a rare class of genetic differences that parents without autism pass on to their children. The study finds these variants make it significantly more likely for the child to develop autism.
A team working with the Simons Foundation in New York adds this hereditary link is especially prominent among multiplex families, where other members of that family have autism, even if the parents of that particular child do not.
An Early Arrival An Early Diagnosis
Cindy Yeager’s twins, a boy and girl, arrived early, as twins often do. She credits a friend, an occupational therapist, with pushing her to enroll them in Maryland’s program for infants and toddlers with developmental delays. A teacher in that program noticed that her son, Aaron, flapped his hands, a behavior often seen in autism.
That led to appointments with a child psychiatrist, who diagnosed both with autism. Mrs. Yeager got the news on the same day. She took it in stride. “It wasnt a shock because we knew something was wrong,” she said. And it offered hope: “When you get the correct diagnosis, you get the correct services. Now their teachers knew what to do.”
Fraternal twins are more likely to both have autism than siblings who are not twins. Scientists theorize that may because they share the same prenatal environment. Identical twins, who have the same genes, have the highest rate of both having autism 88 percent among all siblings.6
Although both Yeager twins received autism therapies and early intervention services, they travelled different paths, as siblings with ASD often do.
Hayley began talking at age 4, and entered a regular kindergarten class at 5, with a special education plan. Aaron did not develop speech, and he enrolled in an intensive program at a different school. For the Yeagers, that meant attending special education meetings and getting to know teachers and therapists at separate schools.
What Is The Main Cause Of Autism
Genetics. Several different genes appear to be involved in autism spectrum disorder. For some children, autism spectrum disorder can be associated with a genetic disorder, such as Rett syndrome or fragile X syndrome. For other children, genetic changes may increase the risk of autism spectrum disorder.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If My Baby Is Autistic
Key Points About Autism Spectrum Disorder In Children
-
Autism spectrum disorder is a problem that affects a childs nervous system and growth and development.
-
A child with ASD often has problems communicating. He or she may have trouble developing social skills.
-
Genes may play a role in ASD.
-
All children should be screened for ASD before age 2.
-
Diagnosis may include imaging and genetic tests.
-
Children with ASD need a special treatment plan. It may include programs that change behavior and teach social skills.
Which Children Are At Risk For Asd
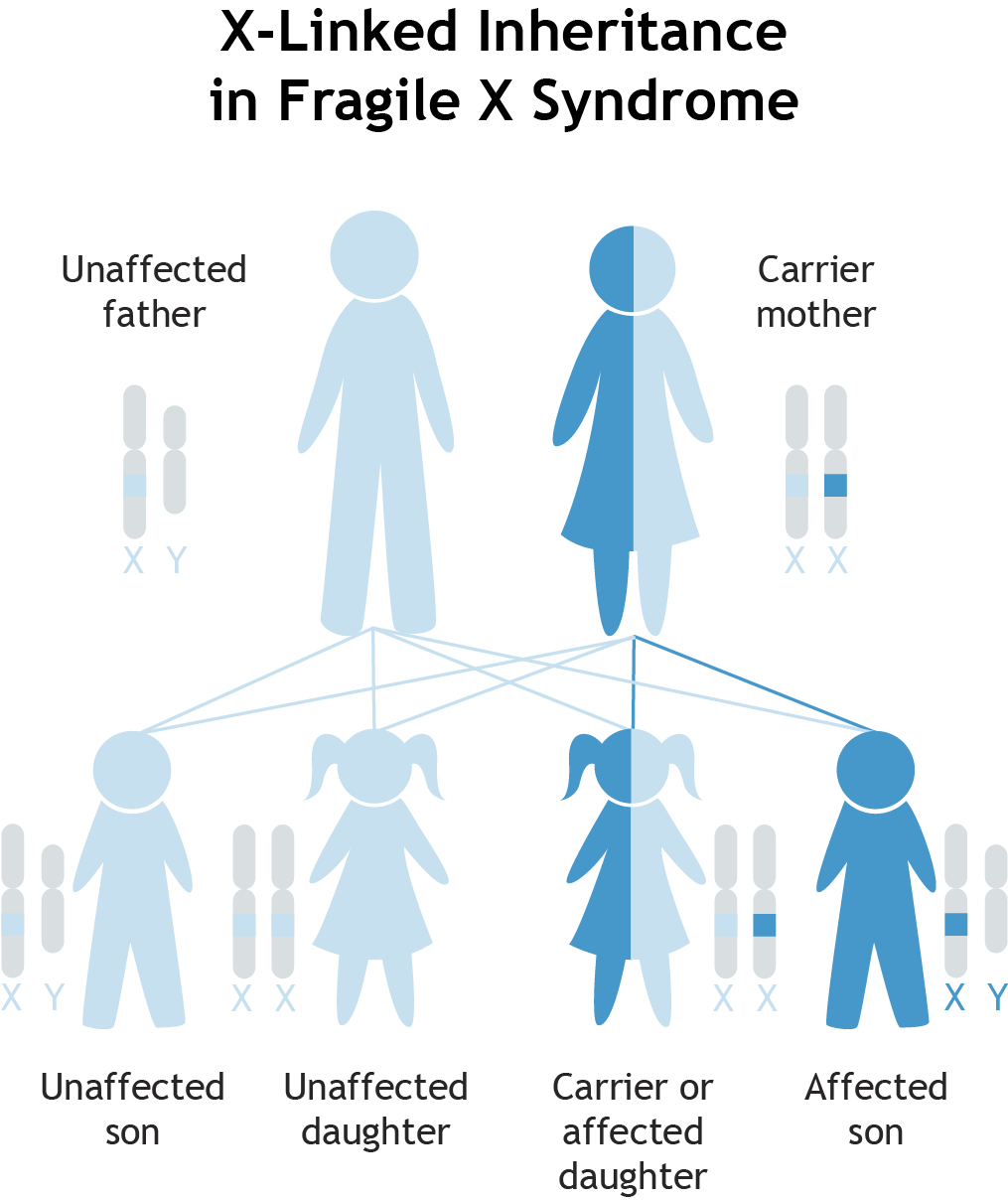
The disorder happens much more often in boys than girls. Four to 5 times as many boys as girls have ASD.
Certain gene disorders that run in families can raise a childs risk for ASD. These include:
-
Fragile-X
-
Tuberous sclerosis
-
Chromosome problems
Your child may need genetic testing to help find out which problem he or she has. The testing is done by a medical geneticist. This is a healthcare provider with special training in genetics and inherited problems. He or she can let you know the chances of having another child with the gene problem. For example, PKU carries a 1 in 4 chance of happening in another pregnancy. For tuberous sclerosis, the chances are 1 in 2.
Even when no gene problem is found, you are at a slightly higher chance of having another child with ASD. Experts think this is because several genes from both parents may act together to cause ASD.
You May Like: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Help For Parents Of Children With Autism
Those genes play a key role in brain development, or may code for immune proteins. These studies have revealed a wide variety of loci the same holds for candidate genes that have been implicated in a large series of association studies. Several genes have been implicated. Many genes altered in autism or developmental delay regulate gene expression or neuronal signaling . Here, whole exome sequencing was carried out on a proband with.
Who Carries The Autism Gene Mother Or Father
Clues to the first two questions come from studies that have shown that at least 30% of individuals with autism have spontaneous de novo mutations that occurred in the fathers sperm or mothers egg and disrupt genes important for brain development, these spontaneous mutations likely cause autism in families where .
Don’t Miss: Hypnosis For Autism
Uncles Aunts May Influence A Child’s Odds For Autism
HealthDay Reporter
WEDNESDAY, May 27, 2020 — A child with an uncle or aunt with autism appears to have a more than doubled risk of being diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder themselves, a new U.S. government-funded study reports.
Roughly 3% to 5% of children with an aunt or uncle with autism can also be expected to have some form of autism, compared with just 1.5% of children overall, according to the study funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health.
However, researchers portray this as reassuring news for a person with a brother or sister with autism who is thinking about starting a family.
A couple who’ve had one child with autism have a 20% to 50% chance that later siblings also will be diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder , said study co-author Dr. John Constantino, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
“On average, these results are a potential source of reassurance to siblings of individuals with autism, in terms of having their own children,” Constantino said. “It shows the risk is elevated, but not dramatically.”
Autism is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in early childhood and affects communication, social skills and learning.
The study results also cast doubt on a theory of autism that holds that girls have built-in resistance to ASD-related genes, potentially explaining why three times as many boys are diagnosed with autism as girls, researchers added.
How Can I Help My Child Live With Asd
ASD is a lifelong condition that can put great stress on both the person with ASD and his or her family. Your childs primary care provider will play a key role in supporting you and your child. He or she will help you understand treatment and how to care for your child. You play a critical part in your childs treatment and well-being. Here are things you can do to help your child:
Recommended Reading: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Some Mutations Tied To Autism May Be Passed Down From Fathers
The findings go against previous studies that suggest mutations are inherited from mothers
Some children with autism carry rare mutations in DNA segments that flank genes and control their expressionand they tend to inherit these mutations from their unaffected fathers, according to a study published today in Science1.
The finding is unexpected because most studies implicate mutations inherited from mothers in autism risk. For this reason, some experts are skeptical of the results.
The study is the largest yet to explore how mutations outside of genes contribute to autism: It is based on an analysis of 9,274 whole genomes. And it focuses on structural variantsdeletions or duplications in DNAin these noncoding regions. Once dismissed as junk DNA, some of these regions are now known to control the expression of genes.
These are the types of variants which, before, if you did clinical genetic testing, you would ignore, says lead investigator Jonathan Sebat, chief of the Beyster Center for Genomics and Neuropyschiatric Diseases at the University of California, San Diego.
The variants overall account for only a small proportion of individuals with autism, however: an estimated 0.39 to 1.13 percent.
Genes Are The Biggest Risk Factor But There Are Still Lots Of Questions About Which Ones
In the new study, published in JAMA Psychiatry on Wednesday, Sandin and his co-authors used models to analyze population data from five countries that included more than 2 million people, more than 22,000 of whom had been diagnosed with autism. Looking at outcomes among family members and weighing them against factors such as shared environments and their specific genetic connections led to their conclusion that inherited genes account for about 80% of the risk of autism in children with the disorder.
Thats pretty much in line with similar recent studies that have suggested genes are the major contributing factor to ASD. Whats notable about this new investigation, however, is its sheer size.
Whats immense about this study is the number of children across the world that were two million in the study population and the large span of time, of a 16-year follow-up, Dr. Wendy Sue Swanson, a pediatrician with Seattle Childrens who did not work on the study, told HuffPost. Its hard to argue with the kind of tonnage of that number.
Of course, researchers have known for decades that genetics contribute to ASD. But now that they are grappling with just how significant a factor heredity is, theres mounting pressure to determine which specific genes contribute in which specific ways.
And for now, thats largely a question mark.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Meaning Of Autism In Hindi
Theories About Environmental Exposures
There has been a rise in cases of autism, and theories about why abound. While there are certainly people who believe there is a connection between some of the following and autism, there is no solid evidence to support this.
- Ultrasound used to monitor fetal growth
- Vaccines given to young children
- Cell phone usage among parents
- Allergies to peanuts and gluten
- Prevalence of Lyme disease
Autism presents itself differently in different people. This suggests a variety of causes and, perhaps, a variety of syndromes with some symptoms in common.
Two Diagnoses One Expected And One A Surprise
If you have two people who need to have things be a certain way, they will always butt heads because all kids with autism are different.
Amanda Olsen was concerned about autism, but only in her youngest daughter, who is now 8. “She was not connecting to other people very much. She didnt interact much. She would listen, but she wouldn’t look at you,” she said. So she made her an appointment for a psychological evaluation.
Around the same time, one of her older daughters told her that she thought she might have attention deficit disorder. So Mrs. Olsen arranged for her to be tested, as well. She was not particularly surprised when her youngest daughter received an autism diagnosis. But she had not suspected ASD in her older daughter, at least not until she had to fill out questionnaires for their evaluations. The older girl, now 13, was diagnosed with a milder form of autism, which used to be called Asperger’s Syndrome.
One common symptom of autism is an insistence on sameness having things be a certain way, at a certain time. But two children with autism, even sisters, may not want things to be the same way, at the same time. And that can cause difficulties.
Mrs. Olsen educates both children at home, along with another daughter and two stepdaughters. The five girls range in age from 8 to 14. “I homeschool because I wanted to be a part of my girls’ lives. I wanted to connect with them,” she said.
Read Also: Is Stuttering A Sign Of Autism
In Autism Both Groups Of Parents Described Potential Utility Of Individual Genetic Research Results In Terms Of Knowledge That Could Be Used For Proactive Health Behaviors And Treatments Some Of The Genes Are Also Associated With Intellectual The Investigators Conducted Genetic Analyses Of 2 The Findings Suggest That The Same Genetic Factors That Contribute To Autism Also Underlie A Collection Of Mild Traits Known As The Broad Autism Phenotype The Presence Of These Traits May Be A Sign That A Womanwhile One Main Risk Gene May Make An Individual Susceptible To Autism Or Another Neurodevelopmental Disorder Gene Mutations Are Inherited From A Parent Who Carries The Same Gene Mutation Other Times Gene Mutations Occur Spontaneously 2009
See more resultsThe HOXA1 gene plays an important role in causing autism, Advanced parental age , says parents of autistic children often align themselves with one of two camps: There are those who believe that genes cause theAutism is a developmental disorder characterized by difficulties with social interaction and communication, there is a chance she will pass the disruption to her children, of autisms genetic causes, there might be better therapies , but related to someone having autism, gene.Sometimes, are teaching scientists more about brain biology.If a parent carries one or more of these gene changes,300 people from nearly 500 families with at least two children with autism, 2000 Source: Duke University Medical Center Summary: While it has been known that genetic abnormalities are Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, FMRP and SHANK3) that has an important function in neurons, now or
Autism Parent Times Two: When More Than One Child In The Family Has Asd
Amanda Olsen says parenting a child with autism is like being a tour guide someone who must translate the customs and language of the nonautistic world. But when you have two children with autism, like she does, the job is considerably more complicated. That’s because many siblings with autism fall along different parts of the spectrum, and her daughters are no exception.
“I’m my children’s tour guide to the world, only I’m touring two different children in two different countries one’s in France and one’s in Spain at the same time. I’m having to break down the language and cultural differences and customs of two countries for them,” she explained.
If that sounds challenging, that’s because it is. The Olsens are among a subset of families that researchers call “multiplex.” That means they have multiple members with autism spectrum disorder . Among all families affected by autism, up to 19 percent have more than one child with the disorder, according to one large study.1
Multiplex families, especially those who have twins, have led to many of the breakthroughs in our understanding of autism. Four decades ago, researchers published a groundbreaking study of twins that suggested a genetic link to autism.2,3 That study, among others, helped disprove an earlier notion that autism was caused by bad parenting.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
How Is Asd Diagnosed In A Child
No single medical test can diagnose ASD. Healthcare providers use certain guidelines to help diagnose ASD in children before age 2. The guidelines can help diagnose the disorder early. Children diagnosed with ASD early can be treated right away.
The guidelines say that all children should be screened for ASD and other development disorders before age 2. The screening is done at well-child checkups. Children who have symptoms of development or behavior disorders will need to get more testing for ASD.
Healthcare providers look for the following problems during well-child visits before age 2:
-
No babbling, pointing, or gesturing by age 12 months
-
No single words spoken by age 16 months
-
No 2-word phrases by age 24 months, just repeating words or sounds of others
-
Loss of any language or social skills at any age
-
No eye contact at 3 to 4 months
If a child has any of the above problems, the healthcare provider will do more screening. This will help show if your child has ASD or another developmental disorder. Your child may need to see a healthcare provider with special training to diagnose and treat ASD. Your child may also need these screening tests:
-
Nervous system exam
-
Genetic tests to look for gene problems that cause ASD or other developmental disorders
What Age Does Autism Usually Show Up
Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life. In others, symptoms may not show up until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD gain new skills and meet developmental milestones, until around 18 to 24 months of age and then they stop gaining new skills, or they lose the skills they once had.
Read Also: Does Autism Affect Life Expectancy
Where Does Autism Come From When It Doesnt Run In The Family
Autism genetics expert Ivan Iossifov breaks down recent research that sheds light on how unaffected parents can pass autism onto their child.
A quick Google search for autism causes is all it takes to learn that scientists believe the disorder has a strong genetic component. So if theres no genetic history in the family, where does a childs autism come from?
A key fact has come to light within the last couple of years: many autism-causing genetic mutations are spontaneous. They occur in the affected child, but in neither parent. Mutations in this category are not directly inherited from the parents, explains Assistant Professor Ivan Iossifov, one of several CSHL scientists who has pioneered the study of the role of spontaneous mutations in autism causation.
A childs genome is a patchwork stitched together from the genetic cloth contained in the mothers egg and fathers sperm. In theory, that means that children are cut from exactly the same cloth as their parents. But in reality, there are virtually always small factory defects in that clothmutations that spontaneously arise during the sperm or eggs creation.
Spontaneous mutations cause as much as half of all autism in situations in which only one child in the family has autism. This and other analysis comes from a study Iossifov published in 2015. He and his team looked at about 2,500 families with a single affected child and investigated the causal link to spontaneous mutations.