Cause Of Fragile X Syndrome
Fragile X syndrome is caused by a change to a gene on the X-chromosome called the FMR1 gene. This gene produces a protein that helps the brain to function normally. If this gene is changed or altered in any way, it cannot produce its normal protein, which can result in Fragile X syndrome. Fragile X syndrome is inherited in a way that is known as ‘X-linked’, as the changed gene is on the X chromosome. This means that men with Fragile X syndrome are often more severely affected than women. This is because men only have one X chromosome, whereas women have two X chromosomes, only one of which is changed.
Suggestions For Working With Individuals With Fragile X
Everyone with Fragile X is unique. However, those with this disorder often share some particular behaviors and intellectual characteristics. For example, children with Fragile X can easily become overwhelmed by crowds, noise, and touch. Other common characteristics include weak abstract thinking skills and poor quantitative skills. However, these children often have unique strengths as well, including visual memory. By taking these unique strengths and weaknesses into account, teachers can promote the best learning for these children.1
Suggestions:
- Know the learning style of the individual.
- Develop a consistent daily schedule or routine.
- Use visual signs and concrete examples or materials to present ideas, concepts, steps, etc.
- Prepare the individual for any changes in routine by explaining these changes ahead of time, possibly by using visual signs.
- Include functional goals with academic goals for instance, teach the individual the names of different pieces of clothing as well as how to dress himself/herself.
- Provide opportunities for the child to be active and move around.
- Use computers and interactive educational software.
- Provide a quiet place where the child can first retreat and then regroup.
Developmental Trajectory Of Asd Symptoms In Fxs And Non
Additional insight into the nature of the psychological impairments underlying ASD in FXS and non-syndromic ASD can be gleaned by studying the developmental course of ASD symptoms in the two conditions. More generally, Karmiloff-Smith has argued that similar phenotypes often belie important mechanistic differences that can only be discovered through studying the emergence of the phenotypes over the life course. In one stunning example, Karmiloff-Smith et al. have demonstrated that in infants with Williams syndrome numerosity skills are a relative strength and language a relative weaknesses, whereas in adults with Williams syndrome numerosity skills are relatively weak and language skills relatively strong.
In this vein, McDuffie et al. used retrospective data to track age-related changes in ASD symptoms in adolescents with FXS. In particular, these investigators conducted an in-depth analysis of ADI-R interviews completed by the biological mothers of 50 children and adolescents with FXS , comparing the responses for those who met and did not meet criteria for autism. Assignment to the comorbid autism and no autism groups was determined following standard ADI-criteria for verbal individuals . Change over the life course was examined by comparing maternal responses to the 29 ADI-R items that are queried both for current functioning and for the lifetime, or diagnostic, algorithm, with the latter items generally being anchored to functioning between the ages of 4 and 5 years.
Don’t Miss: Asd And Adhd Comorbidity
Inheriting Fragile X Syndrome
Fragile X syndrome is inherited, which means it is passed down from parents to children. Anyone with the FMR1 gene mutation can pass it to their children. However, a person who inherits the gene mutation may not develop Fragile X syndrome. Males will pass it down to all of their daughters and not their sons. Females have a 50/50 chance to pass it along to both their sons and daughters. In some cases, an FMR1 premutation can change to a full mutation when it is passed from parent to child. Read more about how FMR1 changes as it is passed from parent to child.
Awkward Interactions With Peers
Even children with high-functioning autism display problems when interacting with peers. Ã Adults working closely with kids may notice this through their play behaviors.
These children have major deficits in communicating with those outside their limited social circle. Ã This makes it difficult for them to form new relationships.
For toddlers, it might be that they have a problem with sharing toys. Ã For teens, it might be difficulty completing group work assignments. Ã This presents a challenge for peers who dont quite understand the person with autism. Ã And when the autistic person cant explain these feelings, it intensifies the awkwardness.
Also Check: How To Tell If My Child Is Autistic
Low Functioning Vs High Functioning Autism
In contrast, the phrase low functioning is often used to describe someone who has significant challenges that may prevent them from participating in normal activities such as going to school or work. These individuals are often non-verbal and may engage in a variety of behaviors others find strange. When an individual is labeled low functioning assumptions may be made about what that person is capable of achieving, or even how aware they may be of what is going on around them.
Has The Definition Of High Functioning Autism Changed
Yes, absolutely. There is a lot of confusion about the definition of High Functioning Autism and you may get a variety of definitions depending on who you ask.
Lets take the internet for example.
Type high functioning autism definition into the Google search engine and the first page of results is a mixed bag of definitions.
Here are four examples* I have chosen to illustrate the many differences you can find.
High-functioning autism is autism without an intellectual disability .
people with autism spectrum disorder who read, write, speak, and manage life skills without much assistance.
Although diagnosed formally with ASD, people with HFA often lead remarkably normal lives and have less difficulty assimilating into society than other ASD patients.
High-Functioning Autism specifically applies to children with autism who have an IQ of 70 or higher and exhibit milder symptoms. For example, these children exhibit fewer language delays, few to no cognitive deficits, and better spatial skills.
Alarmingly, some of these definitions include statements that I have included above in the What High-Functioning Autism Does Not Mean section.
It seems the term, High Functioning Autism, has had a range of additional qualifying statements attached to it that has skewed its original meaning and purpose.
Also Check: Autism Symbol Meaning
Personal Information Collection And Processing
We collect and process several types of personal information from and about users of our websites and of our products and services, including:
- Personal and sensitive information: some of our products and services may involve testing of biological samples that we or our customers use to create test reports, genotyping or sequencing services for research or clinical purposes and the receipt, creation, or analysis of genomic or other data derived from samples, including through our customers use of our software as a service product. In receiving samples and providing our products and services, we may obtain your name and surname, date of birth, email address, home address, telephone number, gender, ethnicity and other health related information.
- Computer, device and browsing information: as you interact with our products and services online, including this website, we may use automatic data collection technologies to collect certain information about your computer or device, as well as browsing actions and usage patterns. This data may include your IP address, browser type or version. The technologies we use for this automatic data collection may include cookies. You can control cookies by adjusting your cookies settings.
Information about children
Development Of Mechanisms And Phenotypes In Animal Models Of Fxs
There is an extensive literature on preclinical animal models of FXS, mostly in mice. Many of these studies have examined phenotypes during early development either due to convenience of methodology or to examine developmental trajectory. Almost all of the developmental trajectory studies in animal models use a cross-sectional approach. Such studies conducted before 2014 have been comprehensively reviewed elsewhere . Here, we summarize key studies done in the past few years and focus on the gaps and paradoxes in the developmental literature on animal models. The major point made by these studies is that many of the phenotypic differences between KO and WT mice are developmentally transient, suggesting the importance of studying trajectories. This is all the more relevant if altered brain responses attributed to an imbalance in excitatory and inhibitory function reflects compensatory plasticity, and is not necessarily the primary defect driven by the genetic mutation causing neurodevelopmental disorders .
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Sensory Processing Disorder And Autism
Fragile X Is Inherited
A mother who carries Fragile X has a 50% chance of passing the mutated gene to each of her children. Her children will either be carriers or they will have Fragile X syndrome.
Carrier men will pass the premutation to all their daughters but none of their sons. These daughters are carriers but they do not have Fragile X syndrome.
The Fragile X premutation can be passed silently down through generations in a family before a child is born with the syndrome.
More About Genes and Inheritance
Each cell in the body contains forty-six chromosomes. These chromosomes consist of genetic material necessary for the production of proteins which lead to growth, development and physical and intellectual characteristics. The first twenty-two pairs of chromosomes are the same in males and females. The remaining two chromosomes, X and Y, determine whether a person is male or female. Males have only one X chromosome which is inherited from the mother. They receive a Y chromosome from the father. Females inherit two X chromosomes, one from each parent.
Explaining Autism To Your Family And Friends
After receiving your childs autism diagnosis, youll likely have new questions every day. One thing that most parents struggle with at first is how to explain autism to their friends and family. Being honest about your childs diagnosis and how it affects him/her is important. The more you educate people in your childs life, the more successful interactions will be.
Give people concrete ideas on how to support your child and interact with him/her. Explain to family and friends how autism affects your child. Give specific examples and explain your childs reactions. To the extent that you are comfortable, provide comprehensive answers to their questions.
People will likely have lots of questions. It is okay to tell people you are still figuring things out. It is fine to say that you do not have all the answers and refer them to a helpful article. These conversations are ongoing ones. Each time you start a new conversation, it will likely get easier.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Meaning Of Autism In Hindi
How Is Fragile X Syndrome Diagnosed What Tests Are Done
Diagnosing fragile X syndrome requires DNA from blood, amniotic fluid or other tissues. Your healthcare provider will send the sample to a laboratory that will determine if your child has the FMR1 gene.
If youre pregnant and concerned that your child has fragile X syndrome, you can see a genetic counselor where you may undergo the following prenatal tests:
- Amniocentesis: The healthcare provider takes a sample of the amniotic fluid for testing.
- Chorionic villus sampling: The healthcare provider takes a sample of cells from the placenta for testing.
Five Things You May Not Know About Fragile X Syndrome

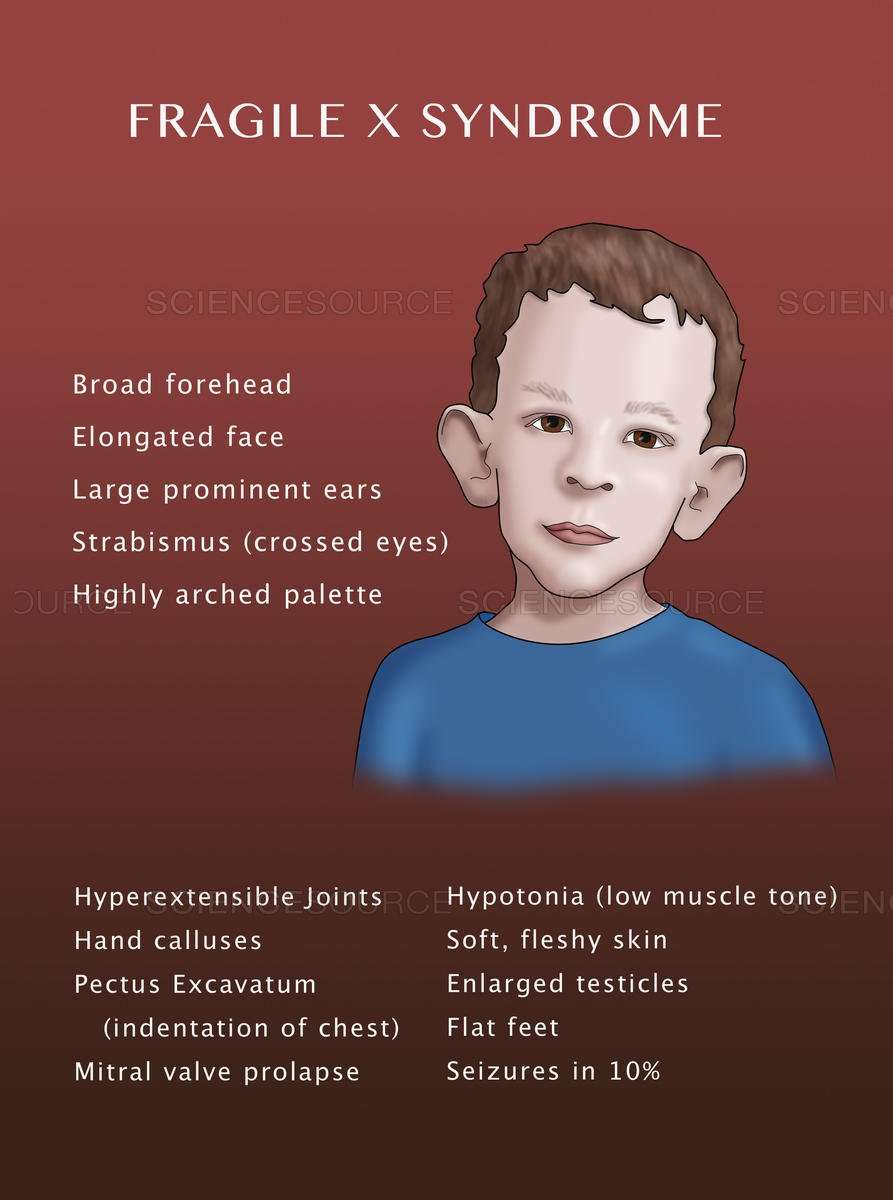
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder. Because of changes in their genetic material , people who have FXS do not make a protein called FMRP, which is needed for normal brain development. People who have other fragile X-associated disorders also have changes in the FMR1 gene, but usually make some of the FMRP protein.
Signs and symptoms of FXS include:
- Developmental delays
- Learning disabilities and
- Social and behavior problems , trouble paying attention, hand flapping, acting and speaking without thinking, and being very active).
Having FXS is associated with an increased chance of intellectual disability, particularly in males, and of having autism spectrum disorder .
As part of CDCs work to educate people about the condition and to celebrate fragile X awareness month, here are five things you may not know about FXS.
You May Like: Average Lifespan Of Autistic Person
Emergence And Rate Of Autism In Fragile X Syndrome Across The First Years Of Life
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 November 2020
- Department of Psychology, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA
- Jessica Bradshaw
- Department of Psychology, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA
- Elizabeth Will
- Department of Psychology, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA
- Abigail L. Hogan
- Department of Psychology, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA
- Samuel McQuillin
- Department of Psychology, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA
- Kimberly Hills
- Department of Psychology, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA
- *
What Is Difference Between Metabolic Syndrome And Insulin Resistance
Some individuals still use the term insulin resistance syndrome but now the term metabolic syndrome is more commonly used to describe the aggregation of multiple CHD and T2D risk factors. Insulin sensitivity/resistance is closely related to MS and the major manifestation of MS is coronary artery disease .
You May Like: Autism And Adhd Comorbidity
Asd Symptom Profiles In Fxs And Non
Perhaps the most direct approach to addressing the question of whether ASD in FXS reflects the same underlying psychological impairments as in non-syndromic ASD is to compare the behaviors that lead to the diagnosis in the two conditions. Presumably, if ASD in FXS is true ASD, the symptom profiles leading to the diagnosis should be indistinguishable in the two conditions. In a recent study , we compared the ASD symptom profiles of 4- to 10-year-old boys with FXS who met criteria for ASD to chronological age-matched boys with ASD for whom FXS had been ruled out , with the ASD diagnostic classification determined by the combined use of the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule and Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised using the procedures described by Risi et al. . Because, as noted, FXS is almost invariably associated with below average IQ in males, the sample was restricted at the outset to boys whose non-verbal IQs were under 85 on the Leiter International Performance Scale-Revised . Symptom profiles were examined using the scores assigned for the childs current functioning on 28 items of the ADI-R .
Paradoxical Reactions To Chemical Substances
An additional sign of a structural altered signal processing in the are the more frequently observed in patients with ADD. This are unexpected opposite reactions to what would usually be expected, or other deviating reactions. Substances which play hereby a role are neuroactive substances like local anesthesia , tranquilizers, caffeine, antihistamine, low-potency neuroleptic as well as central and peripheral pain killers. Due to that paradoxical reactions may at least partly have a genetical cause, it may be reasonable to ask in a critical situation, like a surgery, if such reactions occurred in the patient or relatives.
You May Like: Is Freddie Highmore On The Spectrum
Symptom Profiles In Fxs With And Without Comorbid Asd
Numerous studies, including several we have conducted, have been designed to understand the symptoms and correlates distinguishing individuals with FXS who receive an ASD diagnosis from those with FXS who do not receive the diagnosis . Although perhaps a more indirect approach than those considered in previous sections, these studies can provide insight into the essential impairment distinguishing the two FXS subgroups and whether the difference is best explained as the result of the core impairments that define ASD in the non-syndromic case.
In the McDuffie et al.s study described previously, ADI-R profiles were compared for 50 children and adolescents with FXS divided into those who met and did not meet criteria for autism. Comparisons were made for both the lifetime, or diagnostic, items and the items assessing current functioning. Importantly, McDuffie et al. controlled for the expected differences in IQ between the two groups, using non-verbal IQ as a covariate in all comparisons.
It should be noted that, in contrast to McDuffie et al. , Hernandez et al. found that the groups with and without autism in their prospective longitudinal study of 3- to 8-year-olds with FXS were most discriminated by differences in adaptive socialization. IQ differences between the subgroups existed at two of three assessment points and were not controlled for in the Hernandez et al.s study, complicating interpretation of their findings.
Not Everyone Who Has Fxs Has The Same Symptoms And Fxs Doesnt Just Affect Boys
Both boys and girls can have FXS. FXS is more common in boys, and the symptoms are usually more severe in boys than in girls. Boys with FXS usually have some degree of intellectual disability, whereas girls range from normal intelligence to having an intellectual disability. But both boys and girls can have symptoms that range from mild to severe.
Don’t Miss: Examples Of Restricted Repetitive Behaviors In Autism
Testing For Fragile X Syndrome Before Or During Pregnancy
If youre pregnant or planning a pregnancy you might want to have testing done to find out whether youre at risk of having a child with Fragile X syndrome.
All women can have Fragile X carrier testing, but Medicare funding is available only for women with a family history of Fragile X syndrome. If youre pregnant and find out youre a Fragile X carrier, your baby can be tested for Fragile X syndrome by chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis.
Before you go ahead with antenatal testing for Fragile X syndrome, you might want to think about genetic counselling. Genetic counselling will help you understand your options and the effect a diagnosis might have on you and your family. A genetic counsellor can also support you as you make .
DNA tests are important for diagnosing genetic conditions like Fragile X syndrome. Our article on genetic testing has more information about DNA tests, what you can expect and some of the things you need to know beforehand.