How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Treated
There is no cure for autism, but treatment can make a big difference. The younger kids are when they start treatment, the better.
Doctors, therapists, and special education teachers can help kids learn to talk, play, and learn. Therapists also help kids learn about making friends, taking turns, and getting along.
How Is The Structure Of The Brain Different
The neuroanatomy of autism is difficult to describe, Dr. Culotta says. So it might be easier to talk about the architecture of the brain and how the autistic brain may differ.
So whats different in the structure of this three-pound organ? Lets start with a quick anatomy refresher: First of all, the brain is split into two halves or hemispheres. It is these two hemispheres that we get the idea of a left brain and a right brain. In reality, our thinking and cognitive processes bounce back and forth between the two halves. There’s a little bit of difficulty in autism communicating between the left and right hemispheres in the brain. There’s not as many strong connections between the two hemispheres, Dr. Anderson says.
In recent years, science has found that the hemispheres of ASD brains have slightly more symmetry than those of a regular brain. This small difference in asymmetry isnt enough to diagnosis ASD, according to a report in Nature Communications. And, exactly how the symmetry may play into autisms traits is still be researched.
Now, were going to get a little technical. Grey matter ripples into peaks and troughs called gyri and sulci, respectively. According to researchers from San Diego State University, these deep folds and wrinkles may develop differently in ASD. Specifically, in autistic brains there is significantly more folding in the left parietal and temporal lobes as well as in the right frontal and temporal regions.
Apparent Reversal Of Neurobiological Defects In The Adult
A remarkable finding in some recently studied animal models of autistic symptoms has been the surprising degree to which autistic symptoms have been apparently reversed or ameliorated by replacing or modulating gene function after birth or even in the adult. The first example of this came with a Drosophila model of Fragile × syndrome . Normally, the mutant flies have a defect in social/courtship learning and also have defects in the axons of neurons clustered in a brain region known as the mushroom body. The Fragile × disease pathway was modulated by administration of several drugs including metabotropic glutamate antagonists that can decrease the excessive protein translation caused by mutations in FMR or even using lithium carbonate, which modulates downstream signaling of the Fragile × pathway through the kinase GSK-3. Remarkably, in flies born with fixed defects in social behavior the phenotype could be rescued almost completely in adulthood by administration of metabotropic glutamate antagonists or even lithium .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Autism Spectrum
What Makes Us More Prone To Ptsd
In simple terms, our brain is designed to hold onto trauma.
There are 2 reasons:
Stay with meI promise you will get this. Lets first take a journey through our brains 3 levels based on the evolution of the brain. Fortunately, nature did not get too complicatedit just plopped one brain on top of the other, thus expanding its functionality over time.
Level 1
The Reptile Flight or Fight
The reptilian brain is the most primitive part of our brain, and its main function is to protect us. Our meltdowns & shutdowns occur because of this part of our brain. The reptilian brain gives us four options:
Level 2
Early Mammal Emotions, Emotions, Emotions!
This is the middle part of our brain. Everythingeverythingcomes through this door first.
Think about it like a bouncer at the door at a bar. The bouncer lets everyone in that seems like they are not going to cause havoci.e. they are seen as a safe bet.
The amygdala then sends input in the right direction.
If the person is considered potentially dangerous then the amygdala sends the signal down to the reptile part of our brain to execute survival and avoidance strategies.
Can Someone With Autism Have A Normal Child
Can an adult with autism be a successful parent? The answer is absolutely yes, under the right circumstances. While a person with moderate or severe autism is unlikely to have the skills to parent a child, many people with high-functioning autism are ready, willing, and able to take on the challenges of raising kids.
Recommended Reading: Who Discovered Autism Asperger Syndrome
How Does Autism Affect The Brain
- Open annotations. The current annotation count on this page is being calculated.
Image credit: CC0
Autism is a brain disorder that affects how people interact with others. It occupies a spectrum, with severe autism at one end and high-functioning autism at the other. People with severe autism usually have intellectual impairments and little spoken language. Those with high-functioning autism have average or above average IQ, but struggle with more subtle aspects of communication, such as body language. As well as social difficulties, many individuals with autism show repetitive behaviors and have narrow interests.
The brains of people with autism process information differently to those of people without autism. The brain as a whole shows less coordinated activity in autism, for example. But whether individual brain regions themselves also work differently in autism is unclear. Watanabe et al. set out to answer this question by using a brain scanner to compare the resting brain activity of high-functioning people with autism to that of people without autism.
Also Check: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Understanding Adhd And Autistic Burnout Within The Workplace
The amygdala is an almond-shaped brain structure that is critical for interpreting and tagging emotionally significant things in our environment. For example, if you see a snake and feel a rush of fear, you can thank your amygdala. The amygdala has tagged snakes as something important . Similarly, if you hear a song that brings you back to a highly emotional time in your life , thats also your amygdala.
As you might imagine, the amygdala sometimes tags things as scary that we wish it didntwhich is why this brain area has been important to our understanding of anxiety disorders and fear . In autism, over-activation in the amygdala is potentially related to why these individuals find social situations unpleasant, or even aversive .
According to the IWH, it might be over-activity of both the prefrontal cortex and amygdala that explains the hyper-sensitivity of individuals on the spectrum. Interestingly, this theory could also explain the exceptional talents of some individuals on the spectrum. For example, individuals with autism may have amazing memories, be able to notice extremely small and important details, or perfect pitch .
Wrap up
I hope it was helpful to review and break down these two theories. Stay tuned for the next two in the next post!
References
Kampe, K.K.W., Frith, C.D., Dolan, R.J., Frith, U. . Reward value of attractiveness and gaze. Nature, 413, 589.
Pring, L. . Savant talent. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 47, 500503.
Recommended Reading: Adult Autism In Women
The Brains Of High Functioning Autistic Individuals Do Not Synchronize With Those Of Others
We studied brain function in autism during free viewing of social interactions.
-
The brains of individuals with autism do not tick together with others.
-
Long-range functional connectivity is altered in individuals with autism.
-
Link between autistic traits and social brain synchrony extends to normal population.
Breaking Down Current Theories About Autism And The Brain
For my first few posts on Psychology Today, I wanted to give an overview of the most popular theories about the brain basis of autism. Over the first two blog posts, I’ll discuss four theoriesbut keep in mind there are others as well.
In this first post, I will review the social motivation hypothesis and overly intense world hypothesis.
Social Motivation Hypothesis
One of the core symptoms of autism is a lack of social interaction, especially for young children. Parents often notice that their child with autism is less likely to show them toys or to spontaneously interact with other children or adults compared to neurotypical children.
The social motivation hypothesis proposes that this might be due to the brains reward system. We know that for neurotypical individuals, social interactions are rewarding. For example, research has shown that eye contact with attractive faces activates the reward centers of the brain . The idea behind the social motivation hypothesis is that maybe children with autism do not find social interactions as rewarding as their neurotypical peerswhich would explain why children with autism are less likely to initiate social interaction.
Neuroscience research from my lab , and others have provided evidence for the social motivation hypothesis. We found that children with autism have less reward-related brain activity than their neurotypical peers when they are anticipating social information .
Also Check: Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis
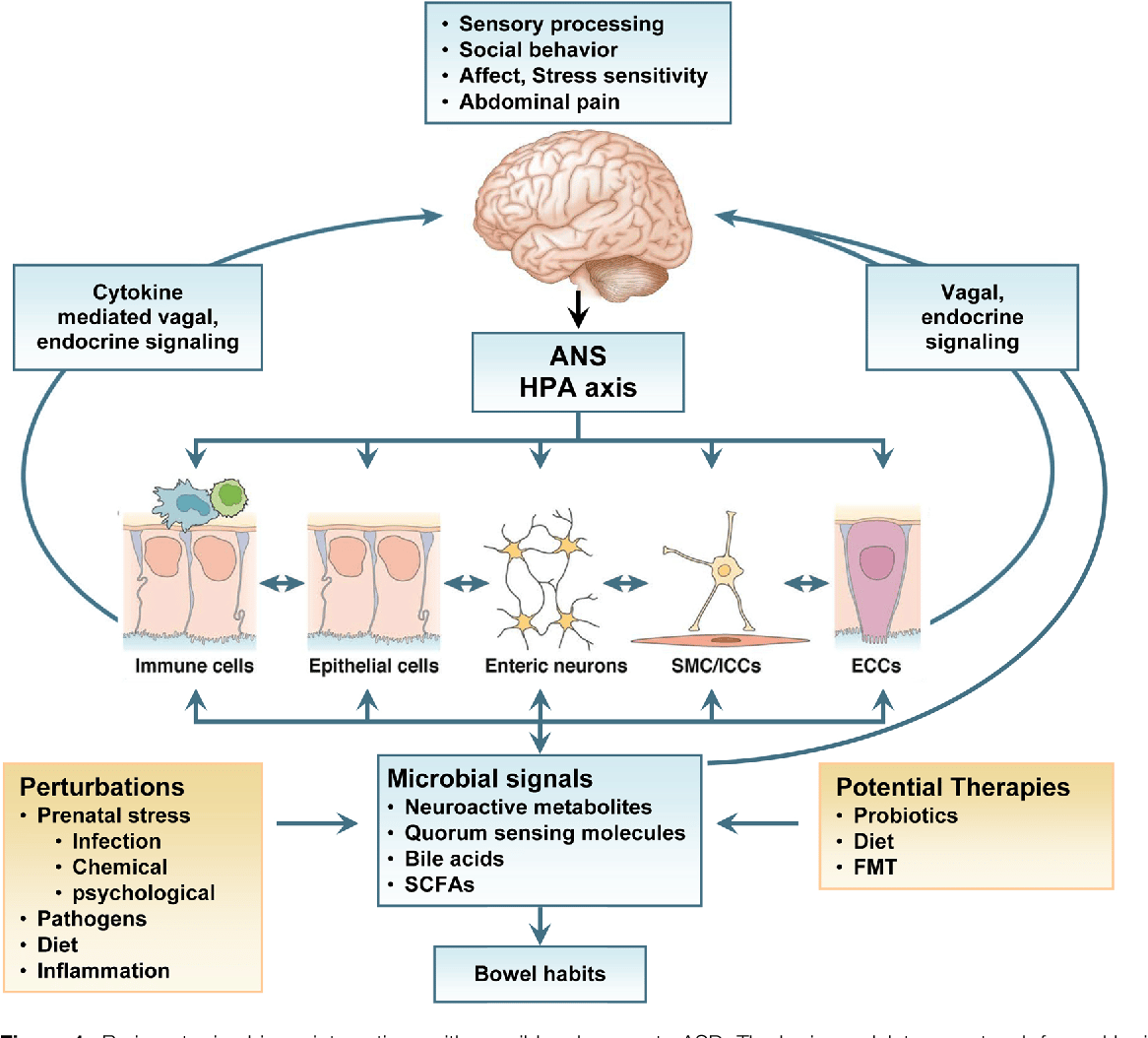
How Does An Autistic Brain Develop
Deviant brain growth in autism occurs at the very time when the formation of cerebral circuitry is at its most exuberant and vulnerable stage, and it may signal disruption of this process of circuit formation. The resulting aberrant connectivity and dysfunction may lead to the development of autistic behaviors.
Brain Structure Changes In Autism Explained
Angie Voyles AskhamSpectrum
Listen to this story:
Autism is a neurodevelopmental condition. Although it is diagnosed based on the presence of two core behaviors restricted interests and repetitive behaviors, as well as difficulties with social interactions and communication those traits are thought to arise because of alterations in how different parts of the brain form and connect to one another.
No research has uncovered a characteristic brain structure for autism, meaning that no single pattern of changes appears in every autistic person. Studies of brain structure often turn up dissimilar results there is great variety across individuals in general. But some trends have begun to emerge for subsets of autistic people. These differences might one day provide some insight into how some autistic peoples brains function. They may also point to bespoke treatments for particular subtypes of autism.
Here is what we know about how brain structure differs between people with and without autism.
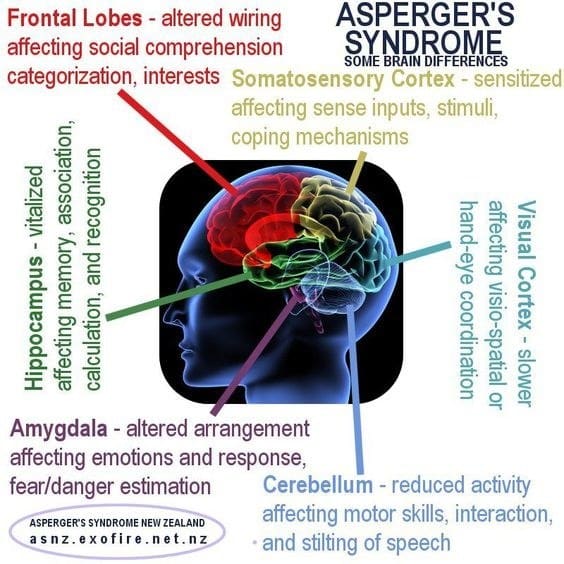
Which brain regions are known to be structurally different betweenautistic and non-autistic people?Studies that make use of a brain-scanning technique called magnetic resonance imaging have highlighted a few brain regions that are structurally distinct in people with autism.
Other structural differences, such as the rate of brain growth and amount of cerebrospinal fluid, appear similar between the sexes6,9.
Read Also: How To Get Tested For Autism As An Adults
What Part Does The Cerebellum Play In Autism
The study found there may be more involvement of the cerebellum in the brain of people with autism than originally thought. It found that, although the cerebellum was known for motor skills, it may also be involved in other functions of people with autism, like attention to detail, for example.
Professor Bonni and his colleagues have continued research on this protein and the connection to autism. He believes that excessive communication and connections between neurons could be a contributing factor, but feels more studies need to be done.
He states that if this connection does turn out to be true, there may be ways to control the number of synapses in the brain. This could help those with this gene mutation and other people with autism also.
What If My Friend Has Autism Spectrum Disorder
Some people with ASD do not feel that they have a disorder and dont want to change. Theyre proud of who they are and they want to be accepted, even though they may have different strengths and weaknesses than most other people.
All people deserve respect. But kids with ASD may be teased, bullied, or left out because theyre different. Bullying and teasing are never the right way to treat other people, but it may be hard to be a friend with someone who has ASD.
Kids with ASD often dont understand playful jokes. You may need to be very clear when you communicate with someone who has ASD.
Try to be patient and kind. Remember how hard it might be for the person with ASD to understand how to be a friend. Stand up for classmates who are bullied. Tell adults, so they can help protect kids who are bullied.
Also Check: Causes Of Autism During Pregnancy
Social Brain Network In Autism
Neuropsychiatric and neuropsychological evaluations in Autism have revealed selective dysfunction of social cognition, with sparing of motor, perceptual and basic cognitive skills. Social cognition includes a range of skills and functions required for successful interpersonal interaction, mediated by a Social Brain Network, consisting brain regions that are dysfunctional in autism: Fusiform face area , inferior frontal gyrus , posterior superior temporal sulcus , superior frontal gyrus and the amygdala .3–5
People With Autism Have More Symmetrical Brains Heres What That Could Mean
In spite of how they appear, the left and right hemispheres of the human brain tend to be far from perfect reflections of each other. Some neurological disorders can affect that imbalance, causing the two halves to appear strikingly alike.
So far, studies on whether autism is among those conditions have been less than convincing. To get a more definitive answer, researchers analysed thousands of brains and showed there is slightly more symmetry for those on the spectrum.
But what does that really mean?
To get this answer, scientists from the Enhancing Neuro-Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis consortium collected decades of brain scans from more than 1,700 individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder and more than 1,800 with no diagnosis.
The consortium were hardly strangers to analysing huge banks of data, having only recently conducted a similar study on ASD brain anatomy involving more than 3,000 subjects.
The condition covers a spectrum of characteristics that can make life a little more challenging for some, affecting their ability to socialise, communicate, and process stimuli.
With such variation in behaviours, sensations, and impact, tracing the traits making up ASD down to simple neurological differences is no easy task.
Doing so could help make the disorder easier to diagnose and lead to novel therapies, opening the way to providing better methods of assistance for those who need it.
This research was published in Nature Communications.
Read Also: How To Assess Autism In Adults
How Does The Brain Function With Autism
Others have found that autistic children have enlarged amygdalae early in development and that the difference levels off over time2,4. Autistic people have decreased amounts of brain tissue in parts of the cerebellum, the brain structure at the base of the skull, according to a meta-analysis of 17 imaging studies5.
How Autistic Brain Works
21.5K Likes, 370 Comments. TikTok video from squishiesophie : “i am nOT saying this is how all autistic brains work this is just how mine does #squishiesophie”. Lol BGM that matches the large moss scene.
116.4Kviews|
TikTok video from Chels : “I dont own this content but posted its for autism awareness. #JDSTREET #WonderWaterDrip #blogger #mumlife #parents #mumsanddaughters #film #shortmovie #shortfilm #autism #autismawareness #autismacceptance #autismoftiktok #fyp #TKMaxxTalentShow #parenting #mummy #mother #beyourself #filmclip #filmclips #movieclips #animation”. How an Autistic brain works | 7 different areas are effected . Jingle Bells.
270views|
Don’t Miss: Is It Hard To Potty Train A Child With Autism
Is There A Defective Gene Associated With Autism
In the universitys study, titled In autism, too many brain connections may be at root of condition, it was suggested that some diverse autistic symptoms may point to miscommunication among cells in the brain of the person with autism.
Senior author Azad Bonni, who is Edison Professor of Neuroscience at Washington University School of Medicine, stated: This study raises the possibility that there may be too many synapses in the brains of patients with autism.
You might think that having more synapses would make the brain work better, but that doesnt seem to be the case. An increased number of synapses creates miscommunication among neurons in the developing brain that correlates with impairments like learning, although we dont know how, he continued.
Brain Study Finds Evidence That Autism Involves Too Many Synapses
Researchers propose that someday it may be possible treat autism with drugs that restore normal pruning of brain-cell connections
A newly published brain-tissue study suggests that children affected by autism have a surplus of synapses, or connections between brain cells. The excess is due to a slowdown in the normal pruning process that occurs during brain development, the researchers say.
The study team also found that the medication rapamycin both restores normal synaptic pruning and reduces autism-like behaviors in a mouse model of autism. They propose that someday a similar medication might be used to treat autism after a child or even adult has been diagnosed.
The report, by neuroscientists at Columbia University Medical Center, appears in the journal Neuron.
Autism Speaks is currently funding several studies on rapamycin. It is also supporting a treatment study using a medication with a very similar action for treatment of autism associated with tuberous sclerosis complex . This rare syndrome often, but not always, involves autism. Indeed, the laboratory mice used in the new Columbia study were developed as an animal model of this syndrome.
The insights from the new study also underscore the vital importance of post-mortem brain donations in advancing research on autism treatments, Dr. Wang adds.
Autism Speaks actively supports autism brain banking through Autism BrainNet.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Main Difference Between Autism And Aspergers