What Are The 5 Types Of Autism
Autism refers to a wide range of neurodevelopmental disorders. If your child is living with autism, it is important for you to understand the various types of autism and the symptoms presented by each.
Understanding the unique challenges presented by each type of autism will guide you in helping your child cope with the disorder. There are five major types of autism which include Aspergers syndrome, Rett syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, Kanners syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified.
Signs Of Autism In Teenagers And Adults
The characteristics of autism can affect you differently as you get older you may also recognise some of the signs of autism in children in yourself as an adult. Many people are diagnosed with autism as teenagers or adults based on noticing that they think and behave differently from most other people.
Signs of autism in teenagers
As you age and experience different environments, you might notice different signs of autism.
As an autistic teenager, you might:
As an autistic teenager, you might:
- find eye contact uncomfortable, or struggle to know how much eye contact to use
- do well when youre in your routine, but find it difficult when routines change changes might make you feel anxious, make it hard to concentrate, or mean you have to work harder on things itd normally be easy to do
- struggle to imagine things that you havent experienced before for example, if youre going to a party for the first time, it might be hard for you to imagine what will happen and what youll be expected to do
- find yourself making social mistakes without realising why for example, during conversations you might not realise there are things other people would rather not talk about, or dont think are important to talk about
As an autistic teenager, you might:
As an autistic teenager, you might:
As an autistic teenager, you might:
Signs of autism in adults
As an autistic adult, you might:
As an autistic adult, you might:
As an autistic adult, you might:
As an autistic adult, you might:
What Is The Prevalence Of Autism
The exact prevalence of autism in Australia and internationally is unknown.
The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that there were 205,200 Australians with autism in 2018, which is around 1% of the population or 1 in 100.
Internationally this rate varies significantly, from 1 person in every 59 people in the USA, to the average prevalence across Asia, Europe, and North America is between one and two percent.
Statistics also show that:
- the number of Australians diagnosed with autism increased by 42% between 2012 and 2015
- three out of four people diagnosed with autism are young people, aged between 5 and 24 years and
- 1-2 out of 4 Australians diagnosed with autism are female.
While the reported prevalence of autism varies around the world, there has been a clear increase in the number of people diagnosed on the autism spectrum in recent years, but this doesnt necessarily suggest that there are more autistic people in the world than there were ten or twenty years ago.
Evidence suggests that the increase is the result of a number of cultural and clinical factors, including social influences driving greater awareness of autism, and improved diagnostic procedures and changes in diagnostic criteria allowing more people to access a diagnosis.
According to Professor Whitehouse, from Australias Autism CRC, research shows the majority of the increase in autism prevalence over this period was due to an increase in diagnosing children with less severe behaviours.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Mutation Causes Autism
Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Symptoms of autism spectrum disorders may appear in the first 2 years of life, but in milder forms symptoms may not be detected until school age.
Children with an autism spectrum disorder develop symptoms in the following areas:
-
Social communications and interactions
-
Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior
Symptoms of an autism spectrum disorder range from mild to severe, but most people require some level of support in both areas. People with an ASD vary widely in their ability to function independently in school or society and in their need for supports. In addition, about 20 to 40% of children with an ASD, particularly those with an IQ less than 50, develop seizures Seizure Disorders In seizure disorders, the brains electrical activity is periodically disturbed, resulting in some degree of temporary brain dysfunction. Many people have unusual sensations just before a seizure read more before reaching adolescence. In about 25% of affected children, a loss of previously acquired skills occurs around the time of diagnosis and may be the initial indicator of a disorder.
You May Like: Autism Biting And Pinching
What’s It Like To Have Autism Spectrum Disorder

A kid with autism might have trouble:
- talking and learning the meaning of words
- making friends or fitting in
- dealing with changes
- dealing with loud noises, bright lights, or crowds
Kids also might move in an unusual way or do the same thing over and over .
A kid with autism may have a little trouble with these things, or a lot. Some kids need only a little bit of help, and others might need a lot of help with learning and doing everyday stuff.
Don’t Miss: Will My Son Ever Talk
Highly Focused Interests Or Hobbies
Many autistic people have intense and highly focused interests, often from a fairly young age. These can change over time or be lifelong. Autistic people can become experts in their special interests and often like to share their knowledge. A stereotypical example is trains but that is one of many. Greta Thunberg’s intense interest, for example, is protecting the environment.
Like all people, autistic people gain huge amounts of pleasure from pursuing their interests and see them as fundamental to their wellbeing and happiness.
Being highly focused helps many autistic people do well academically and in the workplace but they can also become so engrossed in particular topics or activities that they neglect other aspects of their lives.
Take a look at the Spectrum magazine, written for and by autistic people
Autism And Your Environment
Sometimes, when a situation is too much to cope with due to sensory input , or being asked to do things that cause stress or distress, an autistic person can become overwhelmed.
Meltdowns and shutdowns
When an autistic person becomes overwhelmed and isnt able to use or benefit from their coping strategies, they might have meltdowns or shutdowns.
Its important, for parents of autistic children in particular, to be aware that a meltdown isnt a tantrum. A tantrum is something that a child can control, and tantrums often happen because a child wants something. A meltdown or shutdown isnt something an autistic person can control, and its caused by being overwhelmed.
During a meltdown, an autistic person might try to make themselves feel less overwhelmed. This can include doing things like:
- trying to get away from people for example by running away or hiding
- trying to get people away from them for example by shouting, screaming, hitting, or acting aggressively
During a shutdown, an autistic person might try to block everything out for example by not responding to anything or anyone around them.
Challenging behaviour
Like everyone else, autistic people can display challenging behaviour if theyre in the wrong environment. While it can be challenging for the people around them, this behaviour is often a result of distress or frustration, particularly if an autistic person has difficulty with communicating.
Recommended Reading: Puzzle Piece Symbol For Autism
Research On Autism Spectrum Disorder
Study to Explore Early Development
SEED is a multi-year study funded by CDC. It is currently the largest study in the United States to help identify factors that may put children at risk for ASD and other developmental disabilities. Understanding the risk factors that make a person more likely to develop an ASD will help us learn more about the causes.
The six SEED study sites and a data coordinating center are part of the Centers for Autism and Developmental Disabilities Research and Epidemiology network.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
You May Like: Is Nonny From Bubble Guppies Autistic
Diagnosis Of Autism In Adults
It is not unusual for autistic people to have reached adulthood without a diagnosis.
Sometimes people will discover some information about autism that makes them think That sounds like me. They may then choose to talk to a health professional for a diagnosis, or they may not.
You may choose to seek a diagnosis for suspected autism if:
- you have been diagnosed with a mental health condition and/or intellectual disability during childhood or adolescence, but think that you may have autism
- you have struggled with feeling socially isolated and different
- your child or another family member has been diagnosed with autism and some of the characteristics of autism sound familiar to you.
If you wish to seek an assessment for autism, you can:
- talk to your GP who may refer you to a psychologist or psychiatrist with experience in the assessment and diagnosis of autism
- talk to a psychologist or psychiatrist with experience in the assessment and diagnosis of autism .
A psychologist or psychiatrist with experience in the assessment and diagnosis of autism will ask you about your childhood, and experiences at school and as an adult. They may also do some psychological or psychiatric testing. A speech therapist may also be consulted to assess your social communication skills. All of this information will be used to help make a diagnosis.
Is Rett Syndrome An Asd
Children with Rett syndrome often have behaviors similar to autism, and experts used to group it among spectrum disorders. But now that itâs known to be caused by a genetic mutation, itâs no longer considered an ASD.
National Institute of Mental Health: “Autism Spectrum Disorders.”
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: “Asperger Syndrome Fact Sheet.”
Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry: âSpecifying PDD-NOS: A Comparison of PDD-NOS, Asperger Syndrome, and Autism.â
Psychiatric Clinics of North America: âThe autistic spectrum: subgroups, boundaries, and treatment.â
Spectrum: âReclassification of Rett syndrome diagnosis stirs concerns.â
Rettsyndrome.org: âWhat is Rett Syndrome?â
Autism Speaks: âAsperger Syndrome,â âAbout Autism: Why Was My Child Diagnosed with Autism? And What Does It Mean?â
Centers for Disease Control: âFacts About ASD.â
Read Also: What Is The Symbol For Autism
What Is Aspergers Syndrome
In 1994 Aspergers Syndrome appeared as a separate presentation of a pervasive developmental disorder in standard diagnostic manuals, characterised by many as a milder type of autism.
The key characteristics of Asperger syndrome identified at the time were:
- Difficulties with social interaction and social communication
- Restricted and repetitive behaviours
- No intellectual disability
- No delay in verbal speech development
However, the idea that Aspergers is milder than autism has proven to be problematic, because it implies that living with Aspergers is less challenging than living with autism.
In May 2013, the diagnostic criteria for autism changed with the release of the latest diagnostic manual .
Since then Autistic Disorder and Aspergers syndrome are no longer differentiated as separate presentation of pervasive developmental disorders, but are now included under the single diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder or referred to as autism or the autism spectrum.
Autistic Traits And Diagnosis
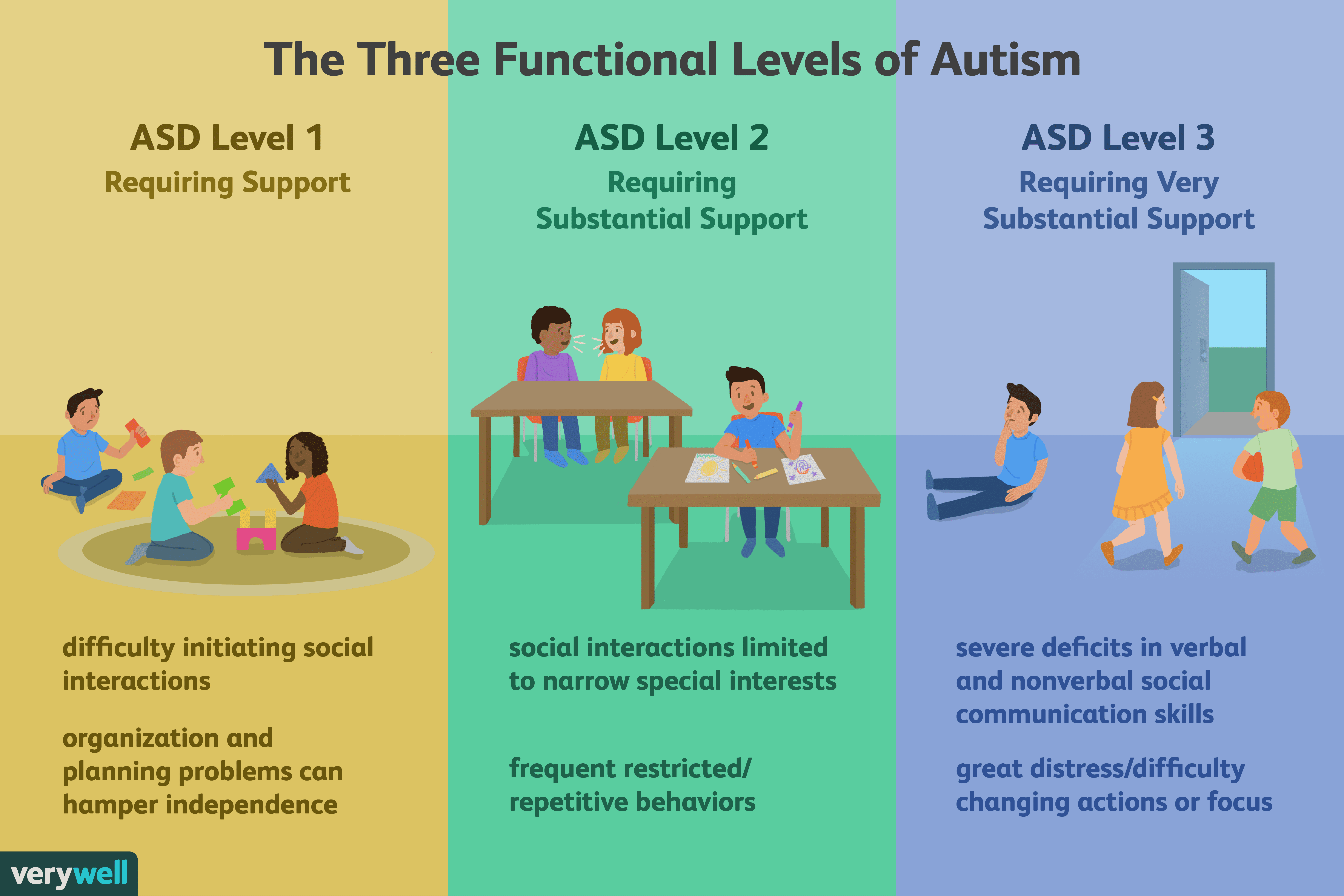
Autistic traits meaning things that autistic people often do, think, and feel are often shared by people who dont have autism too. This doesnt mean that everyone is a little bit autistic, or that autistic people dont need support.
To be diagnosed with autism, a person has to have a lot of autistic traits from birth, and those traits need to have a big effect on their life. In order to be diagnosed with autism, those traits must cause what a healthcare professional would call clinically significant difficulties in their day-to-day life. This means that they have difficulties with day-to-day life due to their autistic traits and need to use their own ways of overcoming those difficulties, or the people in their life need to help them to overcome them, or both.
Being in a supportive environment makes a big difference to an autistic persons wellbeing and quality of life.
Psychological therapies like cognitive behavioural therapy are often used to treat depression, anxiety, and sleep problems, both in people who have autism and people who dont.
Psychological therapies can help to manage conditions linked with autism, like anxiety, but psychological therapies arent a treatment for autism itself. Therapy techniques might need to be adapted to work for an autistic person.
Challenges in daily living
Possible therapies include:
Finding the right therapies
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
How Can Parents Find The Right Program
Parents should look for programs that:
- Involve direct consultation by senior clinicians
- Include staff who can clearly describe the design and implementation of an intervention
- Integrate research findings with professional judgment and data-based clinical decision making, the values and preferences of families, and capacity to effectively implement interventions address the comprehensive needs of individuals on the autism spectrum with sufficient intensity so children and adolescents can make meaningful progress
Restricted Or Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior Or Activities
These can include:
- an increase or decrease in sensitivity to specific sensory information from their surroundings, such as a negative reaction to a specific sound
- fixated interests or preoccupations
Autistic people are evaluated within each category, and the intensity of their symptoms is noted.
To receive an autism diagnosis, a person must display all three symptoms in the first category and at least two symptoms in the second category. Get more information on symptoms and how they may manifest in kids.
The exact cause of ASD is unknown. The most current research demonstrates theres no single cause.
Some suspected risk factors for ASD include:
- having an immediate family member whos autistic
- genetic mutations
An ASD diagnosis involves several screenings, genetic tests, and evaluations.
Also Check: Difference Between Fragile X And Autism
Getting Evaluated For Autism Spectrum Disorder
Parent interview In the first phase of the diagnostic evaluation, you will give your doctor background information about your childs medical, developmental, and behavioral history. If you have been keeping a journal or taking notes on anything thats concerned you, share that information. The doctor will also want to know about your familys medical and mental health history.
Medical exam The medical evaluation includes a general physical, a neurological exam, lab tests, and genetic testing. Your child will undergo this full screening to determine the cause of their developmental problems and to identify any co-existing conditions.
Hearing test Since hearing problems can result in social and language delays, they need to be excluded before an Autism Spectrum Disorder can be diagnosed. Your child will undergo a formal audiological assessment where they are tested for any hearing impairments, as well as any other hearing issues or sound sensitivities that sometimes co-occur with autism.
Observation Developmental specialists will observe your child in a variety of settings to look for unusual behavior associated with the Autism Spectrum Disorder. They may watch your child playing or interacting with other people.
Lead screening Because lead poisoning can cause autistic-like symptoms, the National Center for Environmental Health recommends that all children with developmental delays be screened for lead poisoning.
What Challenges Are Associated With Autism
Autism is often linked with physical, developmental or mental health conditions such as intellectual disability, epilepsy, gastro-intestinal issues, ADHD, dyspraxia, anxiety or depression.
However, many of the disabling challenges associated with autism come about when individuals dont have the respect, understanding and supports that allow them to be comfortable in a non-autistic world.
Read Also: Life Expectancy For Autism
What Are The Different Types Of Autism
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition is published by the American Psychiatric Association . Clinicians use it to diagnose a variety of psychiatric disorders.
The most recent fifth edition of the DSM was released in 2013. The DSM-5 currently recognizes five different ASD subtypes, or specifiers. They are:
- with or without accompanying intellectual impairment
- with or without accompanying language impairment
- associated with a known medical or genetic condition or environmental factor
- associated with another neurodevelopmental, mental, or behavioral disorder
Someone can receive a diagnosis of one or more specifiers.
Before the DSM-5, autistic people may have received a diagnosis of:
- autistic disorder
- pervasive development disorder-not otherwise specified
- childhood disintegrative disorder
Its important to note that a person who received one of these earlier diagnoses hasnt lost their diagnosis and wont need to be reevaluated.
Symptoms of ASD typically become clearly evident during early childhood, between 12 and 24 months of age. However, symptoms may also appear earlier or later.
Early symptoms may include a marked delay in language or social development.
The DSM-5 divides symptoms of ASD into two categories: problems with communication and social interaction, and restricted or repetitive patterns of behavior or activities.