Restricted And Repetitive Behaviors
ASD includes a wide variety of characteristics. Some of these include behavioral characteristics which widely range from slow development of social and learning skills to difficulties creating connections with other people. They may develop these difficulties of creating connections due to anxiety or depression, which autistic people are more likely to experience, and as a result isolate themselves.
Other behavioral characteristics include abnormal responses to sensations including sights, sounds, touch, taste and smell, and problems keeping a consistent speech rhythm. The latter problem influences an individual’s social skills, leading to potential problems in how they are understood by communication partners. Behavioral characteristics displayed by autistic people typically influence development, language, and social competence. Behavioral characteristics of autistic people can be observed as perceptual disturbances, disturbances of development rate, relating, speech and language, and motility.
The second core symptom of autism spectrum is a pattern of restricted and repetitive behaviors, activities, and interests. In order to be diagnosed with ASD under DSM-5 or DSM-5-TR, a person must have at least two of the following behaviors:
Autistic individuals can display many forms of repetitive or restricted behavior, which the Repetitive Behavior Scale-Revised categorizes as follows.
Self-injury
Theories And Empirical Research
Confucianism
is a study and theory of relationships especially within hierarchies. Social harmonyâthe central goal of Confucianismâresults in part from every individual knowing his or her place in the social order, and playing his or her part well. Particular duties arise from each personâs particular situation in relation to others. The individual stands simultaneously in several different relationships with different people: as a junior in relation to parents and elders and as a senior in relation to younger siblings, students, and others. Juniors are considered in Confucianism to owe their seniors reverence and seniors have duties of benevolence and concern toward juniors. A focus on mutuality is prevalent in East Asian cultures to this day.
Minding relationships
The mindfulness theory of relationships shows how closeness in relationships may be enhanced. Minding is the âreciprocal knowing process involving the nonstop, interrelated thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of persons in a relationship.â Five components of âmindingâ include:
Different Levels Of Asd
The levels of support in DSM-5 indicate the individuals ability to communicate, manage their daily life, and their restricted interests. While those at level 1 can lead a life with little support, people at level 3 may need a lot of support.
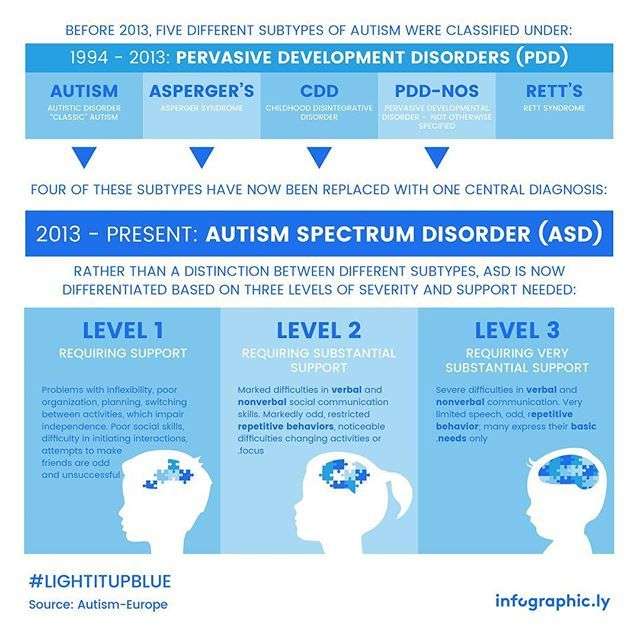
Diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in the DSM has changed over the years. With these changes also came the support levels of ASD.
Different levels of ASD describe different levels of severity of social skills and behaviors.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Autism Diagnosis
Autism Aspergers Advocacy Australia
Autism is a spectrum disorder that causes social and behavioral problems. There are three different levels of autism, which range from mild to severe.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , about one in 59 children have autism. Signs of the condition are usually present at a young age, but occasionally people do not receive a diagnosis until adulthood.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 , doctors categorize autism by assigning level 1, 2, or 3 to two of the domains of symptoms.
One severity score is for impairment in social function, while a second severity score is for restrictive, repetitive behaviors. The levels the doctor assigns depend on the severity of the symptoms.
A correct autism diagnosis that includes the levels of severity can help doctors and other specialists work with the individual to provide the right treatment and support. In this article, learn more about the levels of autism.
What Are The 3 Levels Of Autism
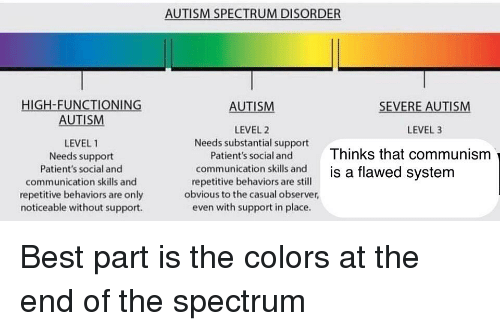
There are three levels noted for ASD as defined by the DSM 5 . Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects behavior, social skills, and communication skills. While there is a separation between social communication and restricted and repetitive behaviors, more often than not, both areas are typically within the same category. This discussion focuses more on the social dynamic and functional challenges as being similar. More nuanced understanding is best done by a psychological or neuropsychological evaluation that will include an assessment of cognitive abilities, which can present as atypical.
Also Check: What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Autism
Diagnosis And Early Recognition
ASD is a developmental disorder, with symptoms present before the age of 3 years. Speech delay, or the loss of previously acquired speech, is often the first developmental milestone alerting parents and professionals to possible difficulties related to ASD. Deviances from typical development can sometimes be apparent by 812 months of age however, a diagnosis of ASD cannot be reliably made until the age of 2 years. Because there is currently no known biological test for ASD , a diagnosis is based on developmental history and observed behaviors. Structured diagnostic measures, such as the Autism Diagnostic Interview and the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, are administered by highly trained clinicians, and are considered gold standards for diagnosing ASD. Clinicians use information from these measures as well as information collected through any other observation to help determine whether an individual meets criteria for ASD based on symptoms outlined in the DSM-IV. Because a significant proportion of children presenting with ASD have an identifiable genetic disorder, such as Fragile X syndrome, karyotyping and other biomedical tests are often conducted to define the cause of the symptoms for a given child better.
Rachel Kent, Emily Simonoff, in, 2017
Ways Low Functioning Autism Differs From High
No two children with ASD will experience the same symptoms. Rather, doctors place children on a spectrum according to severity.
Aspergers syndrome is now considered related to by distinct from autism. Children with Aspergers syndrome are the highest functioning on the spectrum. Children with limited communication skills and behavioral regulation have low functioning autism.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If My Baby Has Autism
What Are The Indicators Of Asd
The main characteristics related to ASD fall into 2 broad areas:
- difficulty with social interactions and communication
- restricted and repetitive behaviours and interests
The common signs and traits of ASD in children include the following:
- lack of social or emotional exchanges like pointing, smiling, showing you things
- lack of non-verbal communication such as nodding and shaking head, using hand gestures
- difficulty developing and maintaining relationships appropriate to their age, such as peer play, lack of close friends
- delayed expressed speech and understanding of speech
- lack of eye contact when speaking
- loss of language skills at any age
- excessively following routines, patterns or behaviour, and becoming distressed at changes
- stereotyped or repetitive speech
- using objects in unusual ways, such as rolling wheels before eyes
- movements, such as flapping hands, toe walking
- strongly reacting to sensory input such as sound, pain or textures
- restricted or fixated interests. This might be only playing with certain toys or talking about certain topics
- having difficulty managing emotions, such as frequent and long tantrums
In adults, ASD traits may include the following:
- struggling with time management
- your cultural or social surroundings
How Common Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Based on most recent CDC report, ASD is estimated to affect about 1 in 54 children, with boys being more likely to have ASD than girls. There were more than 5 million adults in the US, or 2.21% of the population, with ASD as of 2017. Government statistics suggest that the prevalence of ASD has risen 10% to 17% in recent years.
Also Check: Can Autism Be Passed Down
Read Also: Is Autism And Schizophrenia Linked
Social Communication / Interaction Behaviors May Include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Appearing not to look at or listen to people who are talking
- Infrequently sharing interest, emotion, or enjoyment of objects or activities
- Not responding or being slow to respond to ones name or to other verbal bids for attention
- Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Displaying facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions
- Difficulties adjusting behaviors to social situations
- Difficulties sharing in imaginative play or in making friends
Normal Verbal Skills But Difficult Communication
High-functioning autistic people have normal verbal skills but find it difficult to have normal back-and-forth conversations with others. Their tone of voice can also appear robotic or odd.
Individuals might also struggle with functional use of language. For example, he or she might know several synonyms for “beverage” but find it challenging to ask for a drink.
Read Also: How Young Can You Detect Autism
Autism Symptoms In Adults At Home
Other peoples feelings baffle you. You have a collection of figurines on your desk that must be in the same order at all times. These, and other common manifestations of ASD, may be apparent in adults at home:
- Your family members lovingly refer to you as the eccentric professor of the family, even though you dont work in academia.
- Youve always wanted a best friend, but never found one.
- You often invent your own words and expressions to describe things.
- Even when youre in a quiet place, like the library, you find yourself making involuntary noises like clearing your throat over and over.
- You follow the same schedule every day of the week, and dont like unexpected events.
- Expressions like, Curiosity killed the cat or Dont count your chickens before they hatch are confusing to you.
- You are always bumping into things and tripping over your own feet.
- In your leisure time, you prefer to play individual games and sports, like golf, where everyone works for themselves instead of working toward a common goal on a team.
Level 3 Asd: Requiring Very Substantial Support

This level is the most severe form of autism spectrum disorder. People at Level 3 exhibit significant difficulties with social communication as well as social skills.
People with Level 3 ASD also have restricted and repetitive behaviors to the extent that they get in the way of functioning independently in their daily lives and activities. They have extreme difficulty coping with changes. Changes cause great stress and difficulty.
Some people with Level 3 ASD can communicate with words. However, many of them do not communicate verbally or do not use many words in communication. They may be over- or under-sensitive to certain sensory inputs.
Individuals with Level 3 ASD speak with few words, they rarely initiate interaction. When they do initiate interaction, it is limited to meeting needs only. They engage in restricted and repetitive behaviors like echolalia, rocking back and forth, or spinning things.
Those at Level 3 ASD require very substantial support in order to acquire skills to help them in their daily lives.
Recommended Reading: Is Autism Speaks A Hate Group
In The 2010s And Through Today
A new version of The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders was published in 2013. This is the manual doctors use today.
Asperger’s syndrome is no longer a diagnosis in the DSM-5. Instead, the manual provides just one diagnosis for all people with autism symptoms: autism spectrum disorder .
People with ASD have problems with social communication. They may resist changes in routine and be hypersensitive to noise, smell, touch, and other types of sensory experiences. These problems can range from mild to extreme.
People with mild symptoms and those with severe speech delays or sensory issues are all diagnosed with ASD.
The DSM-5 does identify the “level of support” a person with autism might need. These functional levels range from 1 to 3 based on the severity of one’s autism, with 1 describing people who need the least support because their symptoms are mild.
However, few people outside of the medical community refer to someone as having level 1 autism. Often, the terms Asperger’s syndrome or mild autism are still used.
Current Classifications Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
While the old system of classification may seem a little more cut-and-dried, the subtle differences that often distinguished one from the other left room for a lot of confusion and much was open to interpretation. To address this, ASD is now categorized into three different levels, indicating what level of support a patient may need.
- ASD Level 1 Level 1 ASD is currently the lowest classification. Those on this level will require some support to help with issues like inhibited social interaction and lack of organization and planning skills.
- ASD Level 2 In the mid-range of ASD is Level 2. In this level, individuals require substantial support and have problems that are more readily obvious to others. These issues may be trouble with verbal communication, having very restricted interests, and exhibiting frequent, repetitive behaviors.
- ASD Level 3 On the most severe end of the spectrum is Level 3 which requires very substantial support. Signs associated with both Level 1 and Level 2 are still present but are far more severe and accompanied by other complications as well. Individuals at this level will have limited ability to communicate and interact socially with others.
You May Like: Is Aba Therapy Only For Autism
Not Classic Autism Symptoms
The biggest problem with high functioning autism is that many parents and even some doctors are not sure what to look for. This is mostly because high functioning autistics can often blend in and adapt to situations.
As I said, when you think of Autism you often picture a child who is nonverbal and rocking back and forth in a corner. However, there are definitely clear signs of high functioning autism. They are just not necessarily the classic autism symptoms that you hear about.
Different Levels Of Autism
Dr. Vilma received her M.D. in Obstetrics, Gynecology, Infertility and Reproductive Endocrinology from Harvard. With twenty years of practical experience, she combined her passion for women’s health advocacy and writing into a blisteringly successful career.
Learn about our Editorial Policy.
The functioning level of a person with an autism spectrum disorder diagnosis depends on the severity of his/her symptoms, dysfunctions and impairments in communication, and behavioral and social skills. Learning how psychologists and other medical specialists evaluate an individual to diagnose autism and assign a level of function can help you understand and manage this complex disorder.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Autistic People Not Like Being Touched
Why Book With Endeavour Care Training
Leading Nurse led healthcare training provider with genuine delegate reviews on Skillsplatform
Who Will Benefit?
This 3 hour course is ideal for all healthcare and social care staff who are involved in supporting individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Course Description:
This theory based course will explain that Autism spectrum disorder is a condition related to brain development that impacts how a person perceives and socialises with others, causing problems in social interaction and communication.
The disorder also includes limited and repetitive patterns of behaviour. The term “spectrum” in autism spectrum disorder refers to the wide range of symptoms and severity
Course Aims and Intended Learning Outcomes
- Explanation of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- How ASD affects the way a person communicates and relates to people around them
- Behaviours exhibited by some people with Autism Spectrum Disorder Methods of supporting a person with ASD
What is it mapped to?
- Level 2 award enables learners to achieve the standard required, knowledge and understanding of a subject relevant to their own work setting.
Assessment and Certification
- a short Q& A session which will assess understanding of the theoretical component.
Course Length
Severe Deficits In Verbal Communication
Many of the people diagnosed with low-functioning autism are non-verbal. Those who are verbal have great difficulty using words to communicate. The CDC factsheet cited above notes that about 40 percent of children on the autism spectrum are non-verbal. These children cannot use spoken words in their interactions with others. They can mis-interpret verbal and non-verbal cues.
Also Check: Group Homes For Autistic Adults In Utah
Can Mild Autism Go Away
It is a straightforward no. There is no cure for autism, and it is a lifelong condition. There are several types of autism spectrum disorders and their levels of disability vary greatly. Some children who have mild symptoms may benefit from learning how to manage the disorder more effectively than others.
Level 2 Autism: Requiring Substantial Support
The diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder Level 2 includes more significant challenges that impair day-to-day functioning. The deficits with communication are usually greater and the social skills gaps are often wider especially as they move into middle school where social dynamics are more nuanced and complex. The deficits noted above become more prominent and persistent. The people in this category are more notably awkward, and nonverbal communication is especially difficult. Eye contact, spatial awareness, sensory sensitivity, awkward interpersonal interactions are often notable in this population. Adolescents who have level two autism often have difficulties moving from one activity to the next , difficulty when plans change or being placed in new situations , and have notable prominent patterns of rigid thinking processes or perseverations on the same topic . Additionally, it is common to have intense fixated interests and repetitive behavior movements .
Don’t Miss: Do Autistic Adults Live Independently
Level : Needs Substantial Support
Level 2 ASD is associated with more noticeable social and verbal communication challenges than level 1 ASD. Even with proper support, difficulties in communicating efficiently and responding inappropriately may occur.
Patients suffering from level 2 autism may:
- Have difficulty decoding non-verbal cues such as facial expressions
- Communicate in short sentences
- Only engage in specific discussions
Due to the inability to cope with change, level 2 ASD may cause struggles with daily functioning. Changes may often cause feelings of distress.