Pragmatic Impairments And Other Developmental Or Behavior Problems
Pragmatic language difficulties have been described in a variety of psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders, including schizophrenia , bipolar disorder , and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder , among others. With respect to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, it has been hypothesized that the primary symptoms of the disorder may cause impairments in social communication, which result in additional limitations on communication, social participation, and academic achievement . Pragmatic impairments have also been found frequently among children with neurologic conditions, such as epilepsy and among children with behavioral problems . Additional research is needed to understand the impact that SCD and pragmatic language impairments have on the acquisition of academic skills, problematic behaviors, and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder Vs Autism: How To Obtain An Accurate Diagnosis
Due to the differences in ASD and SCD, professional assessment is critical.
You certainly dont want to project anything onto your child that isnt there or spend precious time and resources treating something that doesnt exist.
However, if your child has a need, a diagnosis allows you to get her the help to learn important communication skills to succeed in school, at home, and in life.
To obtain an accurate diagnosis so you can get the proper treatment, therapy and help for your child, here are a few tips.
- Rule out ASD with an assessment performed by your childs doctor and other professionals.
- Gain a referral to a speech pathologist who understands how to diagnose and treat social pragmatic communication disorder.
- Ensure the speech therapist observes and evaluates your child in numerous settings, including home, the classroom and community interactions.
- Remind your childs teacher and caregivers to complete any questionnaires the therapist provides.
- Schedule formal one-on-one testing when the therapist assesses your childs specific communication and language capabilities, skills, and challenges.
- Remember that an accurate diagnosis is complicated further if a child also has a speech disorder, ADD/ADHD, other behavioral disorders or a learning disability, so ensure the therapist addresses these concerns, too.
After you receive a formal diagnosis, you can begin beneficial therapy. It could change your childs life.
Familial Aggregation And Genetics
While there is no published research regarding the heredity and/or genetics of SCD, there has been some research showing familial aggregation of social communication difficulties and a burgeoning literature of studies exploring genetic associations. With respect to familial aggregation, pragmatic language difficulties have been found to run in families of children with autism as well as in families of individuals with specific language impairment . Moreover, pragmatic language has been found to be more impaired among probands with ASD whose parents are categorized as broader autism phenotype, when compared to those whose parents are not . Further, studies have shown significant heritability of pragmatic skills in families that include individuals with both autism and specific language impairment, indicating nonadditive genetic effects .
Read Also: How Would You Know If You Have Autism
Differences Between Asd And Scd
| Traits | ||
| Plays with toys in the same way every time Repeats words and phrases Repetitive body gestures and movements i.e., hand flapping, rocking body | Restricted or repetitive interests arent linked to SCD | |
| Cognitive ability | Some children can have difficulty regulating and controlling their behavior and can also have an enhanced ability to perceive details. The cognitive strengths and weaknesses of a child with ASD differ across the spectrum. | Difficulty in understanding verbal and non-verbal communication is not linked to low cognitive ability |
In both cases, individuals diagnosed with autism or SCD experience difficulty with verbal and non-verbal communication.
Essentially, because both autism and social pragmatic communication disorder have similarities in terms of communication ability, in order to diagnose a child with SCD, a diagnosis of ASD needs to be ruled out. Based on the criteria of the DSM-5, to diagnose a child with ASD, the child needs to have traits of repetitive patterns of behavior, special interests or activities in addition to communication issues. I cannot emphasize enough that it is wrong to assume SCD is a milder form of ASD. Yes, there are similarities, just like any other communication disorder included in the DSM-5, but these two conditions are significantly different from each other in their criteria.
How Is Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder Diagnosed
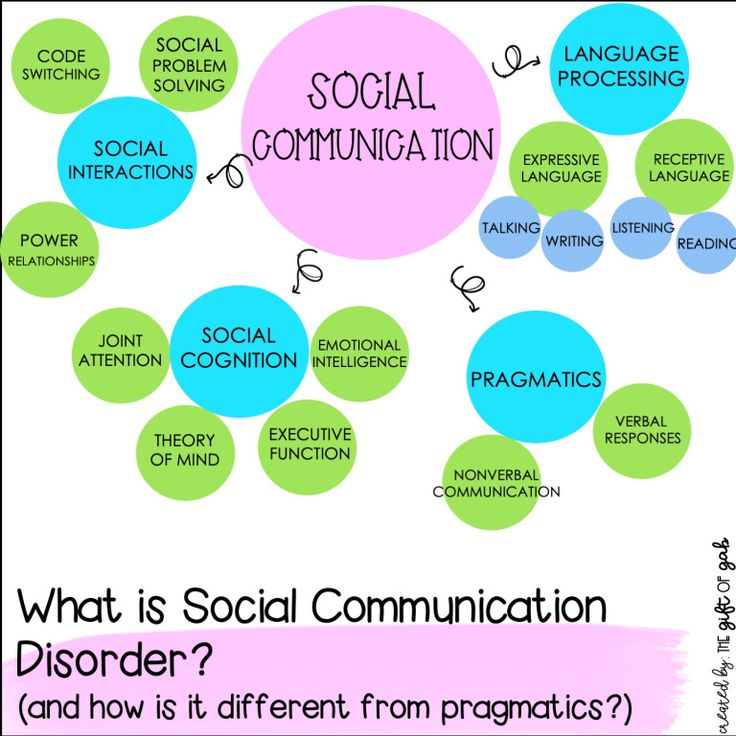
Social pragmatic communication disorder is diagnosed through a series of screenings, such as a hearing test and evaluations from a speech pathologist, as well as collected information from parents, teachers, doctors, and caregivers. Interviews, questionnaires, personal observations, and family medical history all offer valuable clues that can lead to a diagnosis of SCD.
When a child is being evaluated for SCD, it is important to tell the medical professionals conducting the evaluation if the child has a habit of repetitive behavior, extremely focused interests, and/or an unusual reaction to sensory input as they are common behaviors associated with autism spectrum disorder.
Read Also: Has Camels Milk Helped Anyone With Autism
What Are The Symptoms Of Social Communication Disorder
Poor pragmatics or changing speech and communication to fit the circumstances is one of the hallmark characteristics of SCD. People with SCD have trouble modifying their communication including tone of voice, pitch, and volume based on the specific situation.
According to Autism Speaks, people with SCD may also struggle with:
- Responding to others
Early signs in young children, according to the Child Mind Institute, might include:
- A delay in reaching language milestones
- A low interest in social interactions
Young children with SCD may rarely initiate social interactions or respond minimally when social overtures are made, according to the Child Mind Institute.
How Is Social Communication Diagnosed
Parents, grandparents, teachers, family friends, pediatricians, family doctors, and anyone else in the life of a child with the symptoms of social communication disorder is likely to first suspect the child is on the autism spectrum. A diagnosis of SCD can only be made after a thorough evaluation reveals that the patterns of repetitive and restricted behaviors and interests so characteristic of autism aren’t present.
Clinicians will also have to rule out other disorders that can present with similar symptoms, notably ADHD, social anxiety, and intellectual disability. If another disorder better explains the symptoms seen in a particular person, that diagnosis will be made instead.
The most important thing parents can do is communicate with their child’s primary healthcare provider about the concerns they have and the symptoms they have noticed. If they already suspect that social communication disorder may be at play because their child doesn’t have some of the defining features of autism, they can certainly communicate this, too.
Read Also: Autistic Behaviour In Adults
Finding A Therapist Who Specializes In Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder Or Autism
Regardless of whether or not your child has ASD or SCD, its important that he or she works with professionals who specialize in the specific condition.
For example, if your child has SCD, a speech-language pathologist who specializes in SCD may be available via your childs school. If not, speak with your healthcare provider or reach out to ASD resources who may be able to offer referrals.
Speech-language pathologists are trained to work with individuals who have non-verbal communications as well as social interactions.
In addition to providing individuals and their families with practice and training, they also offer interactive visual tools such as picture boards or tablets which can help to bridge the gap as the individual makes progress through therapy.
How Can Residential Treatment Improve Social Communication Difficulties
The best way to work on functional communication skills is through social skills training and real-world experiences. At New Focus Academy, our dedicated staff use recreation to teach and practice valuable social skills, get students out of their comfort zones, and expose them to new, positive leisure experiences. Students at New Focus attend daily groups focused on developing appropriate social skills. These skills are then practiced through experiential activities in the community and with peers. Students will participate in daily fitness and outdoor recreation activities to promote well-being.
Recognizing how social communication difficulties can impact academic performance has motivated us to create classroom curriculum designed to teach functional academics. For example, students take classes in social-emotional learning, life skills, community-based living, and function math and language arts. Social-emotional learning involves discussing and practicing emotional regulation, social & physical boundaries, internet safety, and job-specific social skills. This helps students become more engaged in the learning process, as they understand how course material relates to their everyday lives, not just abstract concepts, and fuels group discussions about how they relate to these topics. Residential treatment centers that offer academics help students apply social skills learned in different types of social settings, which helps them develop greater social-emotional fluency.
Read Also: Why Is Autism A Spectrum Condition
Diagnostic Criteria For Social Communication Disorder
The following criterion is from the 2013 Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition, DSM-5. See the DSM-5 for details and examples.
DSM 5 315.39
American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. Arlington, VA, American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
Social Communication Disorder Treatment Options
If you have concerns about your childs social communication, one good first step is speaking with their pediatrician or teacher. They can connect you with someone who can evaluate your child for SCD.
When you talk with your childs pediatrician, they might refer you to a speech-language pathologist for an evaluation. The goal of the evaluation is to understand your childs communication skills in different settings.
During the evaluation, the SLP will interact with your child and ask questions to determine how they use and understand language in social contexts. To evaluate your child, the SLP may:
- interview you and your childs teacher
- play with your child and engage in structured activities to assess communication and language skills
- observe your child at school or at home
Once your child has a diagnosis, their care professional might help you develop a treatment plan. Treatment plans often involve collaboration between parents, teachers, and SLPs. Your childs plan will likely be tailored to their specific needs and will focus on improving their communication skills, particularly in social situations.
One-on-one therapy sessions with SLPs can be helpful in teaching new communication skills. Kids can also apply these skills in group sessions, which allow them to practice what theyve learned in a social setting.
Treatment approaches for social communication disorder may include :
Read Also: How To Teach Kids With Autism
What Is Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder
Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder is characterized by difficulty with the use of social language and communication skills. Social pragmatics refers to the practical social understanding of things that are happening in a social context. With deficits in social pragmatics, a teen may miss many of the nuances of communication, key meaning of a conversation, and have trouble expressing themselves clearly and directly. These struggles may be common of teens on the spectrum, but they dont explain executive functioning deficits, sensory processing issues, and overdominant verbal abilities in those who continue to struggle with social communication.
Signs of Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder may include:
- Not responding to people in a way that is understandable
- Interrupting others during conversation
- Difficulties following rules for conversation and storytelling
- May not use gestures such as waving and pointing
- Difficulty expressing feelings and emotions
- Changing the topic or losing track of what is being discussed
- Difficulty using words as needed to make conversation
- Trouble making friends and maintaining friendships
- Delays in speech or language development which can even include disinterest in talking
What Therapies Would Help

Because SCD is a new diagnosis, we lack established guidelines for treatment. Therapies that focus on improving social communication should help. And many therapies for autism focus on improving social communication. So its likely that individuals with SCD would benefit from these programs. They include speech and language therapy, Applied Behavioral Analysis, Pivotal Response Training, Early Start Denver Model, social skills groups, and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy.
Most important of all: Treatment should address the unique needs of the individual, as established by a thorough evaluation.
Recommended Reading: How To Teach Empathy To Autistic Child
Distinguishing Pragmatic Impairments From Language Disorders
In the early 1980s, Rapin and Allen introduced the term semantic-pragmatic deficit syndrome to characterize children who are overly verbose, demonstrate word finding difficulty, and have difficulty with conversation including poor topic maintenance. Similarly, Bishop and Rosenbloom used the term semantic-pragmatic disorder to describe children who have difficulty understanding and following the rules of conversation and may use unusual language or word choice to communicate. However, it has been suggested that semantic deficits may not always co-occur with pragmatic deficits. To differentiate individuals with deficits in pragmatics , the term pragmatic language impairment was coined . Further research has confirmed that the clinical characteristics of pragmatic language impairment include difficulties understanding and using language in context and/or following the social rules of language, despite relative strengths in word knowledge and grammar . However, the boundaries of pragmatic impairments have not been consistently defined in the literature. Specifically, there has been considerable debate about whether pragmatic language impairment can be fully separated from the social and communication impairments of other language disorders .
Professional Help Is Crucial
As weve mentioned, children with SCD need professional intervention to develop their social interaction skills. Its not reasonable to expect them to simply pick up these skills by spending time with other children. In fact, placing a child with SCD into socially demanding environments without appropriate support can do more harm than good by leading to teasing and isolation.
At the same time, participating in social activities with proper support can be a wonderful learning experience. A therapist trained in social communication intervention can provide your child and you with the strategies needed to make these experiences rewarding and beneficial. We encourage you to work closely with your childs speech-language pathologists to reinforce the new skills hes learning in therapy.
More resources to explore:
Recommended Reading: Nyc Autism Charter Schools
Social Pragmatic Goals In Speech Therapy
Every one of the goals above corresponds to a need identified as part of the speech evaluations. Conversation skills, problem solving, nonverbal communication, and social cognition are all factored into these goals and how they impact a childs ability in conversational exchanges.
You can learn more about the impact of this type of intervention through the eyes of the child in this video.
Social Communication Disorder Comorbidity With Autism
Social communication disorder can co-occur alongside other developmental and learning disabilities. When it comes to ASD, however, the two conditions cannot be considered comorbid.
ASHA explains that because social communication problems are a primary feature of autism, social communication disorder is not given as a secondary or comorbid diagnosis. Someone with ASD already has social communication deficits, along with restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior.
Don’t Miss: How To Help Autistic Child Calm Down
Family Support & Involvement
Your family is your childs microcosm of society. Since communication doesnt happen in a vacuum, the therapist will train the whole family in techniques, strategies, games, tools, etc., to help you communicate with your child. This practice will pay off in your childs interactions with other social groups and communities, too.
Some Illustrative Examples That Individuals With Scd May Struggle With:
- Greeting and/or sharing information that is appropriate for the social context
- Speaking differently in a classroom than the playground
- Talking differently to children and adults
- Taking turns in conversations
- Knowing how to use verbal and nonverbal signal to guide interaction
- Recognizing nonliteral or ambiguous meaning of language
Other requirements for a diagnosis of SCD include that these deficits result in limitations of effective communication, social participation, academic achievement, and/or occupational performance. Also, the symptoms must be related to the early developmental period of a childs life and not related to other medical/neurological conditions or abilities.
Social communication is based on the development of basic speech and language skills.
Therefore, SCD is rarely seen in children younger than four years due to lack of development of speech and language abilities needed to diagnose it. Milder forms of this disorder, however, may not be seen until early adolescence when language and social interactions grow in complexity.
ASD and SCD differ by the presence of restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities in autism and their absence in SCD.
For parents seeking answers for their childs development, it is important to keep in mind that only if a developmental history fails to provide evidence of these past patterns, should a diagnosis of social communication disorder be considered.
What do you think about this diagnosis?
Don’t Miss: How To Get Tested For Adhd Adults
Treatment For Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder
As with all treatment strategies, it is important to make any form of intervention child-focused. Doing this allows the therapist, facilitator or parent to understand the weaknesses of the child so that the child improves on those areas specifically. When it comes to SCD, treatment should be within the frame of social interactions and work to eliminate factors that form barriers in order to facilitate communication and participation.
There are several forms of treatment that can help improve a childs social communication skills. Some treatment modalities include augmentative and alternative communication and video modeling. Typically, speech therapy is most common for social communication disorder, but another form of therapy parents can consider is drama therapy. Lets take a look.
What Is The Difference Between Social Communication Disorder And Autism Spectrum Disorder

The difference between Social communication disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder relates the presence or absence of restrictive, repetitive behaviours. For a diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder BOTH Social communication difficulties AND restrictive, repetitive behaviours must be present. The main difference with Social Communication Disorder is that the repetitive behaviours are NOT also occurring.
If your child has at least two repetitive behaviours, it could point to a diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder . If not, it could be given a diagnosis of Social Communication Disorder .
The DSM-V is the document that outlines the key criteria for both Social Communication Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder.
You May Like: How To Tell If My Baby Is Autistic