Parent Attitudes On Genetic Testing For Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder
Around one percent of the worlds population has been diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. Dr. Lei-Shih Chen, associate professor in the Department of Health and Kinesiology, conducted research focused on parent perception, knowledge and experience with autism genetic testing.
The idea is we want to know why. Why do kids have autism? Is that genetics? Is that inherited from one of the parents or both parents? Not every kid will be able to diagnose with an autism gene but as this is the starting point, we want to know why, Chen said.
The study conducted by Chen and her colleagues serves as an initial window to understand parental intention to pursue genetic testing for their child with autism spectrum disorder.
Chen uses international comparison research to understand what parents of children with ASD think about genetic testing.
Chen said through genetically testing a child with ASD, doctors will be able to create a better healthcare management plan that is tailored specifically to the child. Additionally, the genetic tests provide parents with valuable information.
ASD has a family history component, so if parents have a child with ASD, there is a high likelihood for them to have another child with ASD.
The benefit of genetically testing children with autism is what we are able to see from the tests, Chen said.
The research conducted by Chen helps to educate parents on the benefits and information that can come from genetic testing.
Pathogenic Yield Of Genetic Testing In Autism Spectrum Disorder
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Dr Harris is a coinvestigator on a study funded by Clinical Research Associates, LLC, an affiliate of the Simons Foundation. Dr Harris is also a coinvestigator on a study funded by Ionis Pharmaceuticals the other authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES: Dr Harris is a coinvestigator on a study funded by Clinical Research Associates , LLC, an affiliate of the Simons Foundation. Dr Harris is also a coinvestigator on a study funded by Ionis Pharmaceuticals the other authors have indicated they have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Pediatrics
Holly K. Harris, Georgios D. Sideridis, William J. Barbaresi, Elizabeth Harstad Pathogenic Yield of Genetic Testing in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatrics October 2020 146 : e20193211. 10.1542/peds.2019-3211
Video Abstract
Genetic testing is recommended for individuals with autism spectrum disorder . Pathogenic yield varies by clinician and/or patient characteristics. Our objectives were to determine the pathogenic yield of genetic testing, the variability in rate of pathogenic results based on subject characteristics, and the percentage of pathogenic findings resulting in further medical recommendations in toddlers with a Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition diagnosis of ASD.
What Is The Role Of Genetic Tests In The Workup Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Practice guidelines from the American Academy of Neurology and the Child Neurology Society recommend genetic testing for fragile X in autistic children who meet any of the following criteria :
-
The child has mental retardation
-
Mental retardation cannot be excluded
-
There is a family history of fragile X or undiagnosed mental retardation
-
Dysmorphic features are present
Recommended Reading: Does The Good Doctor Really Have Autism
All Diseases Have A Genetic Component But There Is Still A Lot To Be Learned About The Extent And Detail That Genes Play In Diseases
Understanding the genetics and the genetic disorders that can take place behind diseases is critical to developing early diagnostic testing, new treatments and possible interventions to either help or minimize the impacts of a disease or the depth of its severity.
Identifying genetic disorders and their causes helps to determine if a mutation was inherited or if it was developed due to external environmental causes such as viruses or toxins.
There are several types of genetic tests that can be performed as a way to identify genetic disorders:
Prenatal diagnostic testing can be used to detect changes in a fetuss genes or chromosomes and is performed when couples have an increased risk of having a baby with a genetic disorder. A tissue sample is taken through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
Newborn screening provides early detection of certain diseases that can help intervene to prevent the onset of symptoms or to minimize the severity of the disease.
Carrier testing helps prospective parents learn if they have recessive alleles for genetic diseases such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis and other related conditions. This type of testing is generally carried out for people who have a family history of a genetic disorder or in certain ethnic groups that have been identified as having a greater propensity for a genetic condition.
If both parents are tested, the test can provide information about a couples risk of having a child with a genetic condition.
What If The Genetic Testing Shows No Abnormalities Does That Mean My Childs Autism Is Not Associated With A Genetic Change Does It Mean My Child Does Not Have Autism

Surprisingly, the majority of patients with autism who undergo genetic testing have negative results . In these cases, we believe there is likely still is a genetic cause for the autism, but the tests available today just werent able to find it. It could also be that the autism was caused by many factors working together such as genetics AND environmental factors.
Negative genetic testing does not rule out a diagnosis of autism. Instead, it indicates that science and medicine simply have a lot more to learn about autism.
Genetic medicine is constantly changing and improving. It is important to check in with your genetics team at least once per year to ask if there are any updates to previous tests or if new tests have become available.
You May Like: Dr Millie Hinkle
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disorder. Someone with ASD may have difficulty with social interaction, communication, and behavior. For example, the earliest signs of ASD are that children may not make eye contact with their parents and may not be aware when someone is talking to them. About 30% of people external icon with ASD have an intellectual disability.
Other Developmental Disorders With Genetic Cause
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder that is characterized by intellectual disability. FMR1 is the human gene that codes for a protein called fragile X mental retardation protein or FMRP. When functioning properly, it is responsible for normal cognitive development and female reproductive functioning.
Boys suffering from FXS have an IQ under 55 and girls are intellectually disabled. Physical attributes may include a narrow, long face with flexible fingers. Boys may have abnormally large testicles.
Tuberous sclerosis is another genetic disorder that leads to developmental delays. It is caused by mutations in two genes – TSC1 and TSC2.
Rett syndrome is caused by the mutation of the MECP2 gene. This gene controls the functions of other genes, which means mutations can disrupt the normal development of a child. This is a neurological disorder marked by reduced mobility, curvature of the spine, muscle weakness, and abnormal posturing of the arms, legs, and top parts of the body.
The risks for the above developmental disorders can be assessed with genetic testing, which can be performed as early as infancy.
You May Like: Is Nonny Autistic
New Test Improves Diagnosis Of A Common Genetic Cause Of Autism
A new stand-alone test can more precisely diagnose people with a common genetic cause of autism than the current testing regime.
The international study, led by the Murdoch Childrens Research Institute in collaboration with Lineagen, Inc., an innovative diagnostic genetic testing and clinical information services company based in Utah, published in Scientific Reports, describes a trial of a more cost-effective, accurate and timely way to identify those with Fragile X syndrome, one of the most common genetic causes of intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder.
Fragile X associated costs to raise one affected child have been estimated at more than $2.5 million to the health system.*
Fragile X affects about 1 in 4,000 children with about 90,000 Australians and over one million Americans impacted in some way. A large proportion of these are women who themselves are not affected with Fragile X, but carry a DNA premutation in their FMR1 gene. This premutation predisposes these women to have children with Fragile X.
A major issue with Fragile X is that at a young age the syndrome is not clinically distinct, with an average age of diagnosis in Australia about five years, and, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, over three 3 years in the US.
The impact of delayed diagnosis is significant and potentially preventable not only to the families but also for our health system, he said.
Recommended Reading: Is The Good Doctor Autistic
What Other Genetic Tests For Autism Are Available
As a part of our range of autism services, Cortica offers other biomedical tests for autism, but CMA is the only first-tier genetic test recommended for all individuals with autism, intellectual developmental disorder, or global developmental delay.
Other genetic tests that your practitioner may recommend are Whole Exome Sequencing, sequencing of specific individual genes or panels of genes, or SNP testing .
Read Also: Mild Autism Symptoms In Adults
What Does This Test Tell Me
A CNV is when a region of the chromosome is found to have either less than or more than two copies. On occasion, an individual may have an extra copy or a missing copy of an entire chromosome. More often, the extra piece or missing piece involves a small region or a chromosome, and not the entire chromosome. When this is the case, it is referred to as a copy number variant .
Why Would I Want Genetic Testing For My Child With Autism
Finding a genetic cause for autism can help the healthcare team make better and more specific recommendations for that particular patient. We want all of our patients to have the support and services that are best for them as individuals so they can meet their greatest potential.
Even if a genetic diagnosis doesnt change the patients medical management, many patients and families have reported benefit from simply having a name for something and better overall understanding.
Read Also: How Can I Tell If My Child Is Autistic
Genetic Tests For Autism Can Sometimes Change Lives
The assays don’t always yield results, but the information they offer can, at times, alter the course of treatment or prevention
Almost as soon as James was born in April 2003, it was clear that he was not well. When he failed a newborn screening test and was struggling to breathe, he was sent straight from the delivery room to the neonatal intensive care unit. Doctors there suspected he had a genetic condition, but genetic testing, such as it was 15 years ago, yielded no answers. So nine days later, James mother, Angela, took him home.
As an infant, James struggled to eat and never slept for more than 20 minutes at a time, but Angela attributed these things to his being a newborn and to the stress of their cross-country move. He didnt sit unassisted at 1 year or crawl until he was 18 months old, but doctors and friends reassured her he was fine. When James was 14 months old, a physical therapist acquaintance took one look at the child and told Angela he clearly had some sort of developmental delay. But even the specialists she then took her son to see dismissed his loud squeals, hand-flapping and tendency to ignore others as consequences of his poor hearing. He was finally diagnosed with autism at age 4.
Even so, most autistic people and their families never gain access to that information: In the United States, roughly one in three children with autism is offered genetic tests.
If I Am Interested How Do I Get My Child Tested
The best place to start is a baseline evaluation with your local geneticist. Your pediatrician, primary care doctor, neurologist or other healthcare provider can give you a referral to your local genetics doctor and genetic counselor. This initial visit usually lasts about 60-90 minutes and the team will discuss which genetic test they think is best to start with.
Many genetics providers now offer telemedicine visits or specialized environments that decrease sensory overload specifically for patients with autism.
Don’t Miss: What Does Mild Autism Look Like
Currently Genetic Testing Can Only Confirm That There Has Been A Genetic Mutation That Can Lead To Autism In A Person However Researchers Are Continuing To Make Progress In Linking Genetic Testing With A Diagnosis Of Autism
In 2012, a team of Australian scientists claimed that they had developed a genetic test that predicts a persons risk of developing ASD with 72 percent accuracy. At the time, this claim was challenged, but it did point to ongoing research trying to find a more accurate way to diagnose autism through genetic means.
In 2018, researchers announced the findings of a new blood test that predicts autism with 92 percent accuracy. The scientists found an association between ASD and damage to some proteins found in the blood’s plasma, or the fluid that carries white and red blood cells.
Of the several blood and urine tests that the scientists developed, the most accurate one found that children with ASD had higher levels of a compound called dityrosine and another class of compounds called advanced glycation end-products .
The overall control group was small, but the study points to the progress that is being made regarding genetic testing and autism. The goal is to achieve an earlier diagnosis so that earlier intervention strategies can be employed.
The Potential Benefits Of Genetic Testing
When a genetic abnormality is found, genetic testing may offer a health care team a unique perspective of an individual. This is often referred to as precision medicine – the ability to use precise individualized information for tailored clinical management.
There are many potential benefits that can be gained from genetic testing and identifying a genetic abnormality. They include:
- finding an explanation and underlying cause for the autism in a given family
- risk for other behavioral and medical conditions associated with a given genetic change, such as cardiac or renal abnormalities, which may in turn impact clinical management and medication selection
- obtaining genetic counseling and risk assessment for family planning for parents and siblings of someone with autism
- having a clearer picture of areas of strengths and vulnerabilities, based on information from other families with the same genetic abnormality and accessing specific medical resources
- connecting families with the same genetic abnormality through support groups
- being eligible for clinical trials targeting a specific genetic abnormality when available
Recommended Reading: Autism Doctor Show
Do Autistic Children Laugh
The researchers report that children with autism are more likely to produce unshared laughter laughing when others arent which jibes with the parent reports. In effect, children with autism seem to laugh when the urge strikes them, regardless of whether other people find a particular situation funny.
The Importance Of Early Diagnosis And Intervention For Autism
Early diagnosis and intervention are important for positive outcomes with autism. A quarter of children who are diagnosed by age 3 with autism and ASD are ready to enter school by age 7, while those who are not diagnosed by that age often require special care throughout their life.
Medications and therapies can help with the symptoms of autism spectrum disorder, but those treatments must be implemented early on in a childs life.
The only way for ASD treatment to start early is by seeking the help of a specialist as soon as developmental delay appears.
Unfortunately, most parents do not know what to look for and in some children, the symptoms arent so obvious. This can delay treatment leading to long-lasting effects.
You May Like: Level 1 High Functioning Autism
A Blood Test For Autism
Autism spectrum disorders can be a challenge to diagnose. A definitive diagnosis generally requires careful assessment on a series of performance tasks in a specialized clinic. Now, researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital have developed a potential blood test that can be performed in a standard diagnostic laboratory and appears to identify ASDs with 85 percent accuracy.
Using microarrays to analyze patterns of gene activity in blood samples from 258 patients and 158 people without ASDs, Louis Kunkel, PhD, director of the Genomics program at Children’s, and Isaac Kohane, MD, PhD, director of the Informatics program, have identified a genetic “signature” that consists of 245 genes uniquely switched on or off in people with ASDs.
“The signature we obtained supports the hypothesis that a number of mutations, rather than a single mutation, are responsible for ASDs,” says Kohane
Kunkel and Kohane hope that a test based on this signature would become a first-line diagnostic tool for ASDs. And, as they recruit more study subjects, they also hope to identify genetic signatures that discriminate between classic autism, Asperger’s syndrome and unspecified pervasive developmental disorders .
“We are now looking at the whole autism spectrum because our numbers are small,” says Kunkel. “What we want to do–once we have large enough numbers–is to start to subclassify those with ASDs.”
Can You Do Genetic Testing For Autism
Scientists who focus on autism research are increasingly making discoveries to determine whether ASD is a genetic condition . This is leading to more investigations into the potential use of genetic testing for diagnosis.
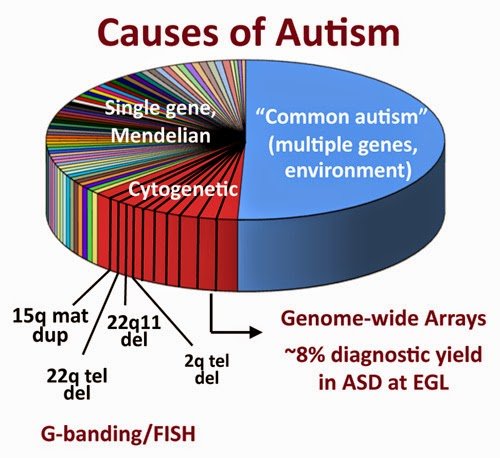
Genetic testing can be offered to individuals who are suspected of being autistic but these tests dont test for specific autism genes, but rather test syndromic forms of autism such as abnormalities in the chromosomesthere are certain deletions or duplications that occur in the chromosomes found to be related to the expression of autism symptoms .
Current genetic testing for autism diagnosis includes chromosomal microarray analysis, G-banded karyotyping, and fragile X testing. According to DeThorne & Ceman, , postnatal testing is the most common form of genetic testing associated with autism spectrum disorders .
According to Chen, et al. , genetic testing has become a useful tool for people with a history of autism or those showing possible symptoms. Unfortunately, despite the fact, a genetic cause of autism is identified in less than 25% of individuals on the spectrum. Schaefer, G. B. & Mendelsohn indicates a success rate of 6-15% but this includes the range of autism spectrum disorders i.e. pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified , atypical autism, and asperger syndrome.
Genetic testing for autism offers potential benefits such as:
Recommended Reading: Freddie Highmore Really Autistic