Looking At Brain Functions And Activity
The National Institute of Mental Health found that the certain sections of the brain in people with ADHD mature slower than those without ADHD. This delay occurs mostly in the frontal lobe, the part of the brain that is responsible for impulse control, concentration, attention, and planning.
Even though certain sections of the brain are associated with ADHD behaviors, how the parts of the brain communicate with each another may also be important in people with this condition. Someone with ADHD might show impairments related to cognitive, behavioral, and motivational functioning. This means that not only looking at brain structure but also at brain activity during a task may provide clues as to the causes of ADHD.
But many clinicians do not rely on brain imaging scans for an ADHD diagnosis. In fact, many of these tests are not reliable, valid, or approved.
Food and Drug Administration approved one biological test to help diagnose ADHD in children from 6 to 17 years old. Its called the Neuropsychiatric EEG-Based Assessment Aid System. It records the type and number of brain waves that nerve cells give off each second. It is shown that people with ADHD tend to have a higher brain wave ratio between the two common brain waves theta and beta compared to people without ADHD. But this test isnt meant to replace clinical evaluations. The results are meant to be used alongside a patients medical history and physical assessment.
What Are The Challenges Of Diagnosing Adhd
Diagnosing ADHD isnt as clear-cut as other medical procedures. Most mental health practitioners require you or your child to fill a survey about behavioral situations. Children may also undergo written or verbal tests.
One of the challenges of diagnosing ADHD is varying symptoms among sufferers. Some children dont display typical symptoms such as inattention, while others have unique tendencies such as obsessive-compulsive behavior.
Advances in medical technology mean an ADHD brain scan is the best technique for making a proper diagnosis. They evaluate brain wave activity and blood flow to determine whether one has a neurodevelopmental disorder or not.
Diagnosing Adhd And Outlook
A psychologist, or psychiatrist will diagnose ADHD based on symptoms as they relate to the criteria listed in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . Assessing symptoms typically includes a detailed patient/parent interview, medical history review, and tests to measure attention, distractibility, and memory recall.
Also Check: Can Autism Get Worse With Age
Brain Differences In Adhd
- Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre
- Summary:
- Largest imaging study of ADHD to date identifies differences in five regions of the brain, with greatest differences seen in children rather than adults.
Largest imaging study of ADHD to date identifies differences in five regions of the brain, with greatest differences seen in children rather than adults.
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder is associated with the delayed development of five brain regions and should be considered a brain disorder, according to a study published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
The study is the largest to look at the brain volumes of people with ADHD, involving more than 3,200 people. The authors say the findings could help improve understanding of the disorder, and might be important in challenging beliefs that ADHD is a label for difficult children or the result of poor parenting.
ADHD symptoms include inattention and/or hyperactivity and acting impulsively. The disorder affects more than one in 20 under-18 year olds, and two-thirds of those diagnosed continue to experience symptoms as adults.
The new international study measured differences in the brain structure of 1,713 people with a diagnosis of ADHD and 1,529 people without, all aged between four and 63 years old.
The study found that overall brain volume and five of the regional volumes were smaller in people with ADHD — the caudate nucleus, putamen, nucleus accumbens, amygdala and hippocampus.
Story Source:
Adhd Slows Brain Development
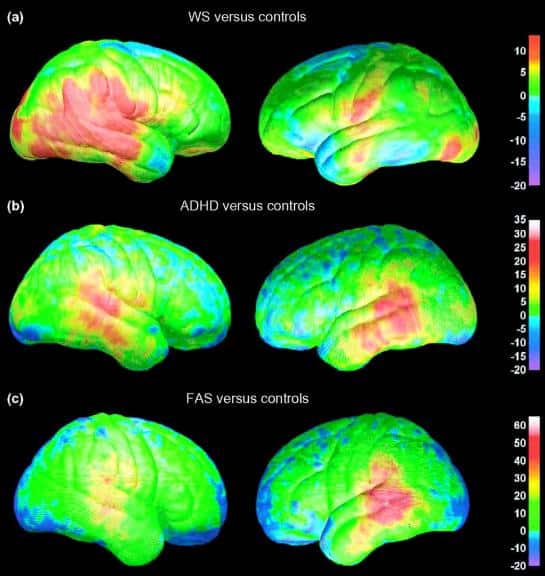
The brain develops the same way in the ADHD brain. However, brain development is slower, especially in the front parts that help control attention and impulsivity. Thus, ADHD is considered a neurodevelopmental disorder.
Over time, the ADHD brain does mature. However, depending on severity of symptoms, the brain might not reach the same level of maturity as the non-ADHD brain. Indeed, neuroscientists found that adults who were diagnosed with ADHD as children had a lower total brain volume than adults who were not diagnosed with ADHD. The cortical thickness of the outer layer of their brain was lower and they had more cortical thinning in the parts of the brain affected by ADHD.
Essentially, this means that these adults had fewer brain cells in these areas. A reason why may be because the non-ADHD brain develops brain cells faster than the ADHD brain. Thus, those individuals have more grey matter to start with in the first place before cortical thinning starts to happen.
Read Also: Can Autism Go Away With Age
Brain Structure And Function In Adhd
The brain is the most complex human organ. Therefore, it makes sense that understanding the connection between ADHD and both brain structure and function is also complex. Studies have researched whether there are structural differences between kids with ADHD and those without the disorder. Using MRIs, one study examined children with and without ADHD over a 10-year period. They found that brain size was different between the two groups. Children with ADHD had smaller brains by about 3 percent , although it is important to point out that intelligence is not affected by brain size. The researchers also reported that brain development was the same in children with or without ADHD.
The study also found that certain areas of the brain were smaller in children with more severe ADHD symptoms. These areas, such as the frontal lobes, are involved in:
- impulse control
Researchers also looked at the differences in white and grey matter in children with and without ADHD. White matter consists of axons, or nerve fibers. Grey matter is the outer layer of the brain. Researchers found that people with ADHD may have different neural pathways in areas of the brain involved in:
- impulsive behavior
These different pathways might partly explain why people with ADHD often have behavioral issues and learning difficulties.
What Can I Do
It is clear that kids with ADHD need our help. The best support is a multi-modal approach in which they receive a variety of interventions. We know that a combination of medications and behaviour therapy are the most effective approaches to managing ADHD.
ADHD affects the brain. Thus, medications are often part of treatment plans because they can improve the efficiency of dopamine and normalize the connections in the motivation and reward networks of the brain, even when kids are doing boring tasks. Medications can protect and promote brain development and help kids with ADHD pay attention better, think about the consequences of their actions, and keep their cool.
With regards to behaviour strategies, focused intervention on developing the executive skills of the brain is important. Structuring the environment and providing the necessary supports for areas of difficulty, such as using pictures to help support the working memory, are also helpful.
To maximize support for your child and optimize your childs treatment plan, it is important to have your team of professionals to support you and your child on your journey to success.
Finally, highlight your childs interests, efforts, and accomplishments their strengths are the foundation from which success is built from. When kids feel confident and are interested, their brain can work much like others without ADHD.
You May Like: Does Autism Worsen With Age
Looking Inside The Brain
Some researchers believe that clinical ratings and measures are unreliable. Results can often vary based on clinicians, cultures, and countries. Looking at images of brain waves and patterns is a more objective way of evaluating ADHD.
A functional magnetic resonance image can help scientists compare the brain function of people with and without ADHD. Just as an electrocardiogram shows the hearts electrical activity, a functional MRI shows the brain in action. Since ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder, it makes sense to look at brain activity. Abnormalities in the structural and functional connectivity of the brains networks are consistently linked to ADHD.
But there arent many studies looking at brain activity and ADHD. Scientists are still trying to figure out the best activity or pattern to look for in these scans.
There are many different brain scan machines and methods that researchers use to study brains with ADHD. Some of these include:
- single-photon emission computed tomography
- positron emission tomography
- functional magnetic resonance imaging
One pilot compared the brain MRIs of adolescents with ADHD to those without. The patterns from grey matter accurately classified about 79.3 percent of the participants who had been previously diagnosed with ADHD.
Brains With Adhd Look Different
It’s easy to think we all have attention problems, whether you’re glued to your smartphone, can’t seem to sit still, or drift off while someone’s telling us a boring story. A new study published in The Lancet Psychology, however, has found that the brain of someone with real attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is physically different from a normal brain.
In a massive coordinated effort at universities across several continents, more than six dozen scientists analyzed magnetic resonance imaging brain scans of 1,713 patients diagnosed with ADHD and 1,529 patients without the condition. The researchers determined that five brain regionsthe accumbens, amygdala, caudate, hippocampus, and putamenare all slightly smaller in people with ADHD. In children younger than 15 years old, the size differential was even more pronounced than in adults over the age of 21.
Of those regions, only the caudate and putamen had already been shown to be smaller in ADHD patients. Previous studies that peered into the structure of the brain for clues about the causes of ADHD often involved too few patients to be able to detect the miniscule size variations that were shown in the new report. A previous MRI scan study by Hoogman had also found a correlation between a smaller total brain volume and more severe ADHD symptoms.
Read Also: How To Explain High Functioning Autism
Adhd And Deficits In Pfc Function
Patients with ADHD have symptoms similar to those caused by lesions to the right PFC.44, 90â92 Imaging studies have shown reduced size and reduced functional activity of the right PFC in patients with ADHD.46, 93â97 Recent studies have also reported more disorganized white matter tracks emanating from the PFC in patients with ADHD, consistent with weaker prefrontal connectivity.98, 99 Other brain regions connected to the PFC, e.g., the caudate and cerebellum, have also been reported to be smaller in some studies of children with ADHD.100 There is also evidence of slower prefrontal maturation in some patients with ADHD.101 However, for many patients, ADHD is a lifelong disorder, as supported by results from imaging studies showing evidence of weakened PFC function and reduced right PFC volume in adults with ADHD symptoms.102, 103 Supporting the notion of ADHD as a highly heritable disorder are imaging studies showing disruptions in prefrontal white matter tracts in both parents and their children when both have ADHD.98
Neuronal Networks Representing Goals And Rules
The PFC regulates attention, actions, and emotion through networks of PFC neurons. These networks consist of pyramidal cells that use glutamate as their neurotransmitter and are able to excite each other to maintain firing even in the absence of environmental stimulation.55 These networks are able to âkeep in mindâ information to help guide attention and behavior in a thoughtful manner. For example, they can keep in mind information about where you just left a book you were reading or your reading glasses . Higher-order networks appear to be able to represent goals and plans for the future . The neurons in these networks interact with other pyramidal cells through synapses on dendritic spines.55 These spines contain NE alpha-2A receptors56 or DA D1 receptors,57 which dynamically alter the strength of incoming network connections and are essential to PFC function.
Read Also: What Dies Adhd Mean
No Two Children Or Teens With Adhd Are The Same
Diagnosing and treating ADHD is a complex process as sufferers may also have co-occuring conditions such social communication difficulties, sensory processing issues, dyslexia, dyspraxia, Tourettes syndrome and oppositional defiant disorder to mention some. The diagnosis needs to be carried out by an expert and for a diagnosis of ADHD to be considered, the person must exhibit core symptoms , demonstrate significant problems with daily life in several life areas and have had the symptoms for a minimum of six months.
There is an excellent guide to ADHD here.
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others

Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
18 September 2021
Sungkean Kim, Ji Hyun Baek, Ji Sun Kim
18 January 2021
Max M. Owens, Nicholas Allgaier, Hugh Garavan
Graeme Fairchild, David J. Hawes, Stephane A. De Brito
volume 25, pages 30203033
Also Check: Arts And Crafts For Autistic Adults
Differences In The Adhd Brain
ADHD is a condition that comes under a lot of scrutiny. Naysayers question if it is real or say it is caused by lack of motivation, willpower, or bad parentingnone of which is true. However, if you or your child has ADHD, you can feel vulnerable to these comments.
Knowing that there are biological differences in the ADHD braincompared to the brain of a person who does not have ADHDfeels validating. The difference can be divided into three areas: structure, function, and chemistry.
Management And Lifestyle Modifications:
Treatment is required to enhance the quality of life in people with ADHD brain. The medical sources suggest behavioral treatment initially for children under the age of five. Early intervention can help to:
- Reduce behavioral issues
- Assistance with social skills
- Avoid task completion failures
Medication is usually regarded as the first step of ADHD brain therapy for children ages five. Some lifestyle changes may also be beneficial. According to research, in individuals with ADHD brain, certain brain areas become hyperactive, while others become hypoactive. This shows that there may be an issue with the brains computational capacity to satisfy the cognitive requirement of the task correctly.
Medications for ADHD:
Prescription drugs remain the primary line therapy for most children with respect to appropriate ADHD control. While it may appear that prescribing stimulants to somebody who is habitually hyperactive is counterproductive, these medicines really have the opposite impact on ADHD patients.
The issue of stimulants is that theyll have adverse consequences in some people, including:
According to the scientific sources, over 60% of people respond well to the first stimulant recommended to them. If a stimulant drug does not work for you, a non-stimulant medicine is another alternative for the ADHD brain.
Lifestyle Modifications:
See Also: What Could Cause Rapid ADHD Mood Swings In Adults
Complete The Form Below And Well Get Back To You Immediately.
Read Also: Can A Brain Scan Diagnose Autism
Brain Chemicals May Struggle To Get The Message Across
Brain networks are made up of brain cells that pass information along from neuron to neuron. To do this, the tail end of one neuron releases tiny amounts of chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals have to cross a small gap called a synapse to get to the tip of the next neuron.
ADHD can affect this process in a few ways:
- The sending neuron may not release enough neurotransmitters.
- The receiving neuron may have trouble catching the neurotransmitters.
- The neurotransmitters may get sucked back up by the sending neuron too fast, before a good connection is made with the receiving neuron.
For many people with ADHD, treatment can improve these connections. Tapping into peoples interests can help too.
Brain researchers are learning more and more about ADHD. But keep in mind we havent yet reached the point where brain scans can be used to diagnose people with ADHD. Learn how kids are evaluated for ADHD, and how its diagnosed in adults.
How To Really Deal With An Adhd Brain
Now that we have a brief background on the different brain networks, brain chemistry, and brain structures of an ADHD brain, let’s talk about what we can do to support those with an ADHD diagnosis.
Firstly, you might ask: what does understanding the ADHD vs Neurotypical brain differences bring? How can it really help me manage my conditionð¤?
Well, it can help you accept that ADHD is NOT your fault. Because you gained the knowledge on the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder brain, you can now rest easy that your symptoms, such as your lack of impulse control and difficulty sustaining attention, are NEVER intentionalð. With this awareness, you can become ready to accept your condition and fully work with it.
So, how do you deal with an ADHD brain?
Aside from having the official ADHD diagnosis from a mental health professional ð©ââï¸ , you might want to look into the little, daily things you can do to manage your symptoms. Some people with ADHD may overlook things like reward systems and motivations, which is sad because they can help you make peace with your struggles with ADHD.
Work Harmoniously with our Brain
Compared to neurotypicals, the brain of a person with ADHD needs a more stimulating environment. We can do much more when we are interested in what we have on our platesð.
Emotion Regulation and Having Deep Breathes
Impulse Control and All Types of Pressure
The Uniqueness and Creativity We Have
Recommended Reading: How To Get A Child With Autism To Stop Hitting