Disclaimers Faqs And Basic Information On The Dsm
Why am I creating this series: I am creating this series to increase the accessibility and transparency of the DSM-5 and the clinical tools people like me use when we are giving you a diagnosis. I find the mental health world can be overly mysterious, increasing anxiety and stress for many. I believe this process should be as understandable and transparent as possible. I am using visuals to break down the DSM-5 because, like many neurodivergent people, unless a thing is visual, I have a hard time understanding it!
Disclaimers: This is for educational purposes only and isnt intended as a substitute for medical advice or to be used as a primary diagnostic tool.
A word on language: I use direct language from the DSM. This is for educational purposes. Much of the language used is deficit-based and pathological in nature. It doesn’t mean I agree with all the wording . I have made this choice to increase the transparency of what is actually in the DSM.
What do A, B, and C mean? TheDSM is broken into different criteria buckets. While a person doesn’t need to have all symptoms of each criterion, they typically need to have all criteria met to be diagnosed.
What about international people? The DSM-5 is based in the United States . However, the criteria are very similar to the ICD, which is used globally and broadly in medical settings.
Okay, now that weve gone over the purpose, intent, and limits of this post. Lets dive in!
What Are The Risks Of Not Treating Adhd
- They may never gain a full understanding of who they are.
- They might lose faith in themselves. Untreated ADHD can lead to a negative feedback loop, where someone doesnt try because they feel that they cant succeed. They might become ashamed, frustrated, demoralized, depressed, anxious, or develop chronic self-esteem issues.
- People with undiagnosed ADHD or untreated ADHD might find ways to cope with their symptoms through self-medication. Some of those coping mechanisms arent necessarily unhealthy, like using intense exercise to achieve hours of focus. But other people might turn to drugs or alcohol.
- ADHD is associated with more frequent accidents, risky behaviors, and a reduction in life expectancy.
- Untreated ADHD can cause problems at school, at work, and in relationships.
Symptoms And Diagnosis Of Adhd
If you are concerned about whether a child might have ADHD, the first step is to talk with a healthcare provider to find out if the symptoms fit the diagnosis. The diagnosis can be made by a mental health professional, like a psychologist or psychiatrist, or by a primary care provider, like a pediatrician.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that healthcare providers ask parents, teachers, and other adults who care for the child about the childs behavior in different settings, like at home, school, or with peers. Read more about the recommendations.
The healthcare provider should also determine whether the child has another condition that can either explain the symptoms better, or that occurs at the same time as ADHD. Read more about other concerns and conditions.
Why Family Health History is Important if Your Child has Attention and Learning Problems
Also Check: Clothes For Autistic Adults
Adhd Criteria Subcategory B
The second subcategory of criteria A refers to hyperactivity and impulsivity. There are nine symptoms outlined in the DSM. Six symptoms need to be present and cause difficulties at work, school, or in relationships .
The following is direct text and language of the DSM-5).
Often fidgets with or taps hands or feet or squirms in seat.
Often leaves seat in situations when remaining seated is expected .
Often runs about or climbs in situations where it is inappropriate.
Often unable to play or engage in leisure activities quietly.
Is often on the go, acting as if driven by a motor .
Often talks excessively.
Often blurts out an answer before a question has been completed .
Often has difficulty waiting their turn .
Often interrupts or intrudes on others .
One critique of the DSM criteria for hyperactivity is that it overly focuses on external behavior and doesnt consider hyperactivity turned inward.
Hyperactivity can also be turned inward and internalized. This is more difficult to assess and capture. Particularly given the DSM criteria for ADHD is behavior-based, it can be more challenging to detect hyperactivity that has been turned inward . Inward-facing hyperactivity often results in anxiety, intense rumination, and a sense of internal agitation/restlessness.
Sign #: Easily Distracted

People with ADHD inattentive type are often pulled away to think about something other than the task at hand their brains just naturally stray. I call it Going to Bermuda. You could be sitting in class or at your computer working. Suddenly, you drift maybe you think about lunch, or something captures your attention, like the snowfall outside.
Many people with inattentive ADHD judge themselves negatively for this freewheeling thinking. The problem isnt that you gaze off, but rather that, when you come back from drifting, you feel disorganized, lost, and confused. Then panic sets in, and you wonder what you missed and how to catch up.
Inattentive ADHD Strategy
If you get easily distracted and space out, identify an ally to come to your aid. Do you have someone who can share their notes or take notes for you in a class or meeting so you can just listen and not worry that you missed writing down something important? Many students with ADHD are legally entitled to a notetaker, so inquire about this for your child. If you are an adult student with this challenge, talk to the student disabilities office about possible support.
In work or social situations, identify a colleague or friend who understands ADHD and doesnt judge you for it. Create a plan for communicating with them when youve gotten distracted or missed something. How can they quietly bring you up to speed? Help your child find a similar person who can help at recess or the lunch table.
Recommended Reading: What Percentage Of People Are Autistic
How Adhd Is Treated
ADHD has no cure but the symptoms can be managed. Treatment options can be found along several different avenues, each of which focus on improving ones quality of life on a personal, professional and or academic level.
Treatment options for ADHD include:
- Behavior therapy
- Stimulant medications, such as central nervous system stimulants to help with concentration and focus, including Concerta, Adderall, Dyanavel, Vyvanse, etc.)
- Non-stimulant medications, such as Strattera, Clonidine, Guanfacine and Atomoxetine
Factor Structure Of Dsm
displays the factor structure of DSM-5 proposed criteria. For the list of 18 DSM-IV ADHD symptoms only, a three-factor solution provided a trend for a better fit for the data than a two-factor solution. For the list of 22 proposed DSM-5 ADHD symptoms, a three-factor solution provided a significantly better fit for the data than a two-factor solution. Nonetheless, both a two-factor solution and a three-factor solution yielded a satisfactory fit for the 18 DSM-IV ADHD symptoms as well as for the 22 DSM-5 ADHD symptoms.
TABLE 2. Confirmatory Factor Analyses for DSM-IV and DSM-5 ADHD Criteria
| Analysis |
|---|
You May Like: Can A Child Get Autism After Birth
Other Concerns And Conditions With Adhd
The combination of ADHD with other disorders often presents extra challenges for children, parents, educators, and healthcare providers. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to screen every child with ADHD for other disorders and problems. This page provides an overview of the more common conditions and concerns that can occur with ADHD. Talk with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your childs symptoms.
Every child with ADHD should be screened for other disorders and problems.
In Addition The Following Conditions Must Be Met:
- Several inattentive or hyperactive-impulsive symptoms were present before age 12 years.
- Several symptoms are present in two or more setting, .
- There is clear evidence that the symptoms interfere with, or reduce the quality of, social, school, or work functioning.
- The symptoms do not happen only during the course of schizophrenia or another psychotic disorder. The symptoms are not better explained by another mental disorder .
You May Like: What Does Hypersensitivity Mean In Autism
How Are The 3 Types Of Adhd Diagnosed
Physicians use the symptoms described in the DSM-V to identify ADHD. The DSM-V lists nine symptoms that suggest ADHD Primarily Hyperactive and Impulsive, and nine that suggest ADHD Primarily Inattentive.2
A clinician may diagnose a child with ADHD only if they exhibit at least six of nine symptoms from one of the lists below, and if the symptoms have been noticeable for at least six months in two or more settings for example, at home and at school.
Whats more, the symptoms must interfere with the childs functioning or development, and at least some of the symptoms must have been apparent before age 12. Older teens and adults may need to demonstrate just five of these symptoms in multiple settings.
What Are The 3 Types Of Adhd
- Primarily Hyperactive and Impulsive ADHD
- Primarily Inattentive ADHD
- Combined Type ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder was once diagnosed as ADD or ADHD. Previously, hyperactive and impulsive symptoms were associated with the term ADHD, while inattentive symptoms like trouble listening or managing time were diagnosed as ADD. Today, the condition is simply called ADHD according to changes in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 1 and patients are diagnosed with one of three presentations.
You May Like: What Was Your Autistic Child Like In The Womb
University Of California Practices For The Documentation And Academic Accommodation Of Students With Attention
Federal and State law2 and University of California policies3 require the University to provide reasonable accommodation in its academic programs to qualified4 students with disabilities, including students with psychological disabilities.
The University is committed to providing reasonable accommodations appropriate to the nature and severity of the individual’s documented psychological disability in all academic programs, services, and activities. In defining a disability as primarily psychological in nature, these practices consider the definition of mental disorders as described in the most current edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders .5
What Is Inattentive Adhd
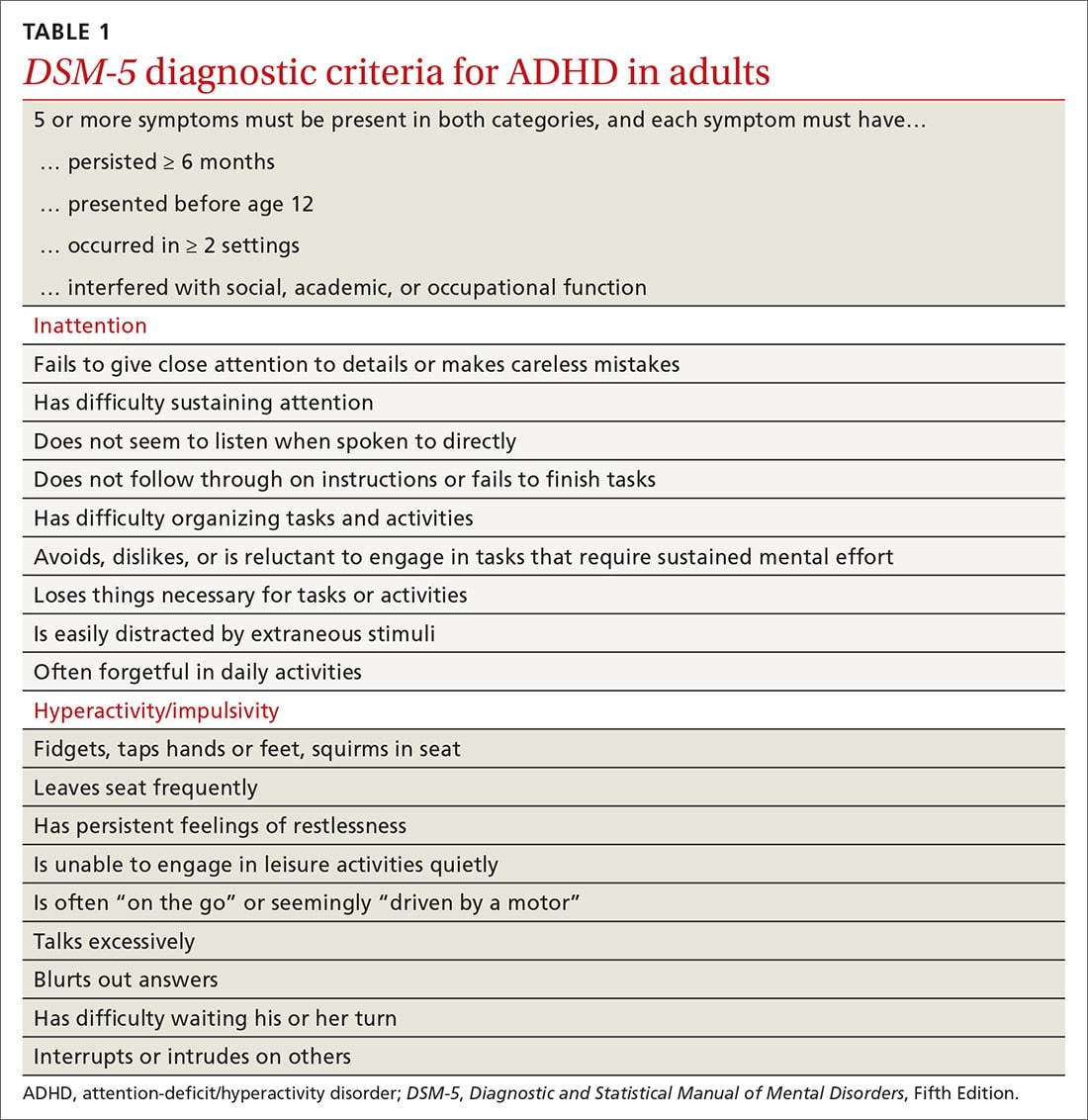
ADHD is a disorder that is neurodevelopmental, which refers to the nervous system as it develops across the lifespan. It can cause inattention, hyperactivity, and/or impulsivity.
ADHD typically appears between the ages of 3 and 6 years old, with an average age of diagnosis at 7 years old.
Approximately 11% of children between the ages of 4 and 17 have ADHD. While often thought of as a childhood disorder, ADHD persists into adulthood. About 4% of Americans over the age of 18 have ADHD.
While not separate disorders, ADHD is divided into three presentations, including:
- Predominantly inattentive presentation
- Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation
- Combined presentation
People with inattentive ADHD have a high occurrence of inattentive symptoms, such as disorganization and distractibility, but do not often show hyperactive-impulsive behaviors.
Also Check: Institutions For Severely Autistic Adults
Add Vs Adhd And The Different Types Of Adhd
ADD vs ADHD do the two terms mean the same thing or not? The short answer is yes and no.
In one way, the two are the same. ADD, or attention deficit disorder, was the term people used to define a persons inability to focus for a long time.
The DSM-5, or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , was updated in 2013, updating the diagnostic criteria for determining someone has ADHD, while the term ADD disappeared. ADHD is currently characterized by an ongoing struggle with inattentiveness and hyperactivity as well as impulsivity, which interferes with daily functioning and/or normal development. Some mental health professionals still use the names interchangeably.
On the other hand, ADD isnt the same because the term was used to describe a person who struggled with focus but was did not battle hyperactivity.
The name of this type of condition changed before as well:
One major difference with the DSM-5s change in 2013 was the criteria for diagnosing ADHD. According to the APA, how and when symptoms manifest make a difference because ADHD presents itself differently in kids and adults.
Additionally, it was previously considered that for a diagnosis of ADHD to be made, a clinically significant severity must be present but now symptoms are considered if the quality of life is reduced at home, work, school or in social settings.
Dsm Criteria For Adhd
People with ADHD show a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development:
You May Like: Does Weed Help With Adhd
Where To Go From Here
If you think you have ADHD, a diagnosis is a vital first step to help you better understand your challenges and find ways forward to overcome them. Frida offers a free ADHD screening tool to help you determine if you might have ADHD as well as the option to connect with a qualified clinician who can offer you a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Related readings:
Sign #: Difficulty Completing Tasks
The first overlooked sign of inattentive ADHD is difficulty completing tasks. People with inattentive ADHD are not lazy, stupid, unwilling, or oppositional. They are creative, outside-the-box thinkers whose minds stray from uninteresting tasks. They have a biologically based challenge with attending to an uninteresting task, maintaining their focus, and sticking with it until finished. All too often, their brains tire more quickly.
Sometimes a lack of focus doesnt indicate a lack of interest, but it could reflect a learning disorder, a lack of clarity on what to do, or a preoccupation with something else. Sadly, its commonly confused with lower intelligence and general capabilities when it really reflects challenges with working memory or how someone processes information.
Inattentive ADHD Strategy
Break each task into smaller chunks to help you sustain focus. The aim is to make a task seem approachable and manageable. So, the smaller the task, the better. Before sitting down to do something whether its homework, work, or chores consider how long you can concentrate before losing focus. Set that amount of time as your goal. Then decide how many work periods are reasonable to expect in one period. Add five-minute body, bathroom, water, or snack breaks between these work blocks. Decide on a pre-planned incentive you can earn after completing the period.
You May Like: Autism Service Dogs For Adults
What Are The Dsm
International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification is a globally used diagnostic tool that provides codes for classifying diseases. Clinicians often use these codes for insurance and billing purposes. The ICD-10-CM does not formally recognize ADHD and instead includes it in the diagnostic criteria for hyperkinetic disorder , which is primarily defined as inattention and overactivity.
ICD-10-CM codes used for ADHD include:
-
F90.0, Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, predominantly inattentive type
-
F90.1, Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, predominantly hyperactive type
-
F90.2, Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, combined type
-
F90.8, Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, other type
-
F90.9, Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, unspecified type
In the most recently released version of the ICD, known as the ICD-11-CM, ADHD has now replaced HKD and is moved to the grouping of neurodevelopmental disorders. The ICD-11-CM also recognizes ADHD subtypes including predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, or combined type. This current version of the ICD is being adopted into clinical use in 2022.
ICD-11-CM codes for ADHD include:
Importance Of An Accurate Adhd Diagnosis
A thorough evaluation and accurate diagnosis allows you to get the right treatment for your particular situation. If you dont seek an evaluation, the problems will just continueand you might figure its just stress or fatigue, Solanto says.
An accurate diagnosis will determine whether you need help for depression, anxiety, another mental health condition, or a medical problem like thyroid problems or , instead of or along with your ADHD treatment. The treatments for anxiety and depression are quite different from the treatments for ADHD, she notes. Without clarification on this, youre not going to get the help you need.
Recommended Reading: Autism Spectrum Disorder Dsm
Change In Clinical And Demographic Profiles With Dsm
presents the clinical and demographic profile of the 68 ADHD cases according to DSM-IV and the 12 additional cases using DSM-5 criteria. Both groups had generally a similar demographic profile. However, additional DSM-5derived cases had lower ADHD severity and disability scores. As expected, the 12 additional DSM-5 ADHD cases had a higher proportion of hyperactive/impulsive presentation and a lower proportion of inattentive presentation . The comorbidity pattern was generally similar between the two groups, except for conduct disorder, which was absent in the additional DSM-5 cases.
TABLE 3. Clinical Profile of Cases According to DSM-IV and Additional Cases Using DSM-5
| Characteristic |
|---|
After documenting lower symptom severity and clinical impairment scores for DSM-5 additional ADHD cases, we performed secondary analyses addressing whether these cases are more severe and impaired than the controls. Mean SNAP scores were 1.51 , 0.99 , and 0.28 for DSM-IV ADHD cases , DSM-5 additional ADHD cases , and control subjects , respectively. For the same groups, mean Sheehan Disability scores were 5.85 , 2.58 , and 0.86 , respectively. In analyses of variance, there were significant differences among the groups in both ADHD severity and clinical impairment . In post hoc analyses with Bonferroni tests, means for all three groups remained significantly different from each other for both severity and impairment.