Why Is Autism Partnership Different
What makes Autism Partnership different from other agencies is that we focus on building strong learning foundations. If children have disruptive and interfering behaviors it is extremely difficult for them to learn. Therefore we must concentrate our efforts on teaching them essential skills so that we can truly build upon their abilities to learn. Teaching children how to learn is essential. Tragically, building a strong foundation is often neglected.
However, without a strong behavioral foundation it is extremely difficult to teach critical skills such as communication, social and play skills. Of course, it takes hard work on everyones part. Skilled professionals conducting effective intervention, schools providing appropriate education and well-trained teachers, and parents providing love and support to become experts in their own right, are all important players in the partnership. Our approach to intervention applies sound teaching principles of learning to help children succeed. Improvement is simply not enough. Our children and their families deserve the highest quality of life.
Limitations Of The Current Review
The limitations of the current scoping review are: the broadness of the outcome measures investigated the potential confounding measure of generalization independently versus within a standardized scale the definition of ABA itself versus its many treatment derivatives and the continual development of the diagnostic tools used to assess ASD. Each of these will be described in turn below.
Many of the study records investigated specific tasks, responses, or skills. Thus, improvements in areas such as cognition may be misleading, because both improvements on specific tasks and improvements on full-scale cognitive assessments were scored as improvements in the cognitive outcome category . In addition, some of the outcome measures had considerable overlap in definitions, such as the cognition, language, social/communication, and adaptive behavior categories, thus potentially resulting in the coding of multiple outcome measures for a similar task. For example, receptive labeling tasks were coded under both cognitive and language outcome measures .
Autism: Aetiology Diagnosis And Prevalence
The term autism has been attributed to the Austrian-American psychiatrist Kanner in the early 1940s, although individual cases had been described well before that time. While Kanners work was written in English and has been recognised widely, his predecessor, the Swiss psychiatrist Bleuler, who coined the term autism, and his contemporary, the Austrian paediatrician Asperger, both writing in German, were virtually ignored. Asperger was eventually recognised when his writings were translated into English posthumously. Subsequently, the body of research grew until the diagnostic classification was formalised for the first time in 1980 in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders .
The diagnostic category changed over time, from Pervasive Developmental Disorders that including autistic disorder, Rhetts disorder, childhood disintegrative disorder, Aspergers disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified in the DSM-IV-TR to the single category Autism Spectrum Disorders in the DSM-5 . The diagnosis of ASD is based on two symptom domains, i.e., impaired social/communication and restricted, repetitive behaviours, and three levels of support needs. Autism was recognised as a heterogeneous condition with many presentations, i.e., each person with autism affected in different ways.
Recommended Reading: Can Autism Worsen Over Time
Impact Of Applied Behavior Analysis On Health
Applied behavior analysis helps children on the autism spectrum to adapt to social scenarios they may not understand.
Positive reinforcement. When a child in ABA therapy completes a task correctly or reaches a goal behavior, there is a reward. Studies show that when a person receives something of personal value following a behavior, they are more likely to repeat the behavior. Over time, applied behavior analysis helps to instill those desired behaviors in your child.â
Behavior and consequence. Just as good behaviors are rewarded, negative behaviors are discouraged. Applied behavior analysis helps your child make the connection between what happens before and after a behavior.
For example, if the teacher asks your student to clean up toys, your child responds in one of two ways. If they begin cleaning up the toys, the behavior is rewarded . If they yell, throw a tantrum, or refuse, the behavior is met with a negative consequence.â
Negative behaviors are often met by the teacher not responding to your childâs negative behavior. Until your child stops or indicates a willingness to cooperate with the command, there is no reward.
When your child first begins ABA therapy, the practitioner sets benchmarks for behavior. They will talk to you about what you want out of therapy for your child and establish a treatment plan. Over time, as your child progresses or regresses, new goals are set.
Treatment And Intervention Services For Autism Spectrum Disorder
Current treatments for autism spectrum disorder seek to reduce symptoms that interfere with daily functioning and quality of life.1 ASD affects each person differently, meaning that people with ASD have unique strengths and challenges and different treatment needs.1 Therefore, treatment plans usually involve multiple professionals and are catered toward the individual.
Treatments can be given in education, health, community, or home settings, or a combination of settings. It is important that providers communicate with each other and the person with ASD and their family to ensure that treatment goals and progress are meeting expectations.
As individuals with ASD exit from high school and grow into adulthood, additional services can help improve health and daily functioning, and facilitate social and community engagement. For some, supports to continue education, complete job training, find employment, and secure housing and transportation may be needed.
You May Like: Adhd Medication Wall Street Journal
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder is characterized by meaningful differences in language, social, and cognitive domains. Taking a proactive approach instead of overlooking issues can make a world of difference in your childs life. Many children who struggle with receptive language skills will eventually develop them on their own, but its easier if they can develop these skills at the same time as the children around them. ABA offers a structured, nurturing, one-on-one environment to help children with autism spectrum disorder acquire receptive language skills. If you have been looking for an autism app for a tablet or computer, the aba|tools Verbal Matrix® can help improve learners with autism with their communication skills.
What Is Applied Behaviour Analysis Used For
The Applied Behaviour Analysis approach and its techniques can help autistic children improve their social skills, self-care skills, communication skills, play skills and ability to manage their own behaviour. It can also help to reduce behaviour like inattention, aggression and screaming.
ABA can help autistic children develop independence, but it shouldnt be used to make children mask their autism or fit in with social norms.
Read Also: Free Lesson Plans For Autistic Students
What Is The Idea Behind Applied Behaviour Analysis For Autistic Children
These are the key ideas behind Applied Behaviour Analysis :
- Human behaviour is influenced by events or stimuli in the environment.
- Behaviour thats followed by positive consequences is more likely to happen again.
ABA uses these ideas to help autistic children learn new behaviour. It does this by giving children positive consequences for new behaviour. For example, if a child points to a teddy they want, the childs parents might follow this up with a positive consequence like giving the child the teddy. This makes it more likely that the child will repeat the behaviour in the future.
Eligibility Criteria And Study Selection
Studies were included if they met the following criteria: 1) the study should be a randomized controlled trial 2) participants were between the ages of 0 and 18 years old 3) participants were diagnosed with ASD 4) the treatment used in experimental group was based on / derived from applied behavior analysis 5) the treatment used in control group was conventional intervention 6) the study included at least one standardized continuous outcome measure related to autistic symptom. The final selection of studies was performed using tools provided in the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook .
Read Also: How To Refer To An Autistic Person
Pros Of Applied Behavior Analysis
Personalized plan. Applied behavior analysis looks different for each person. Individual goals are set based on what your child struggles with the most. During individual therapy sessions, the practitioner can adapt to your childâs needs that day.
Broad application. Applied behavior analysis is designed to help with many concerns, including:
- Severe anxiety â
ABA therapy can also be helpful for adults with autism and other behavioral disorders.
Proven results. Studies show that children who participate in applied behavior analysis therapy have good outcomes. In one study that reviewed intensive, long-term therapy, the participants showed gains in:
- Language development
- Skills for day-to-day living
- Social abilities
The participants in this study went to therapy for 25 to 40 hours per week for between one and three years.â
Applied Behavior Analysis Programs
- Can be very structured for work time, but also include play time and group activities
- Work best when they are used every day for enough time to show progress
- Are very tailored to individual needs
- Include family members to help choose goals and to continue teaching at home
Some ABA teaching programs include:
- Discrete Trial Training
- Incidental Teaching
Read Also: Is Adhd Mental Illness
Additional Resources For Applied Behavior Analysis In Autism
Association for Science in Autism Treatment A nonprofit organization focused on finding and encouraging scientifically effective methods for treating autism spectrum disorders.
Volunteer Match An organization that lists volunteer opportunities in a variety of fields, including autism treatment organizations.
Autism Speaks A research and advocacy group focused on finding the causes for, and treatments of, autism spectrum disorder.
The Autism Society of America A national non-profit that exists to improve the lives of all autism sufferers through advocacy, lobbying, and research efforts.
Behavior Analyst Certification Board A national certification and standards body governing ABA practices.
Association of Behavior Analysts International An international association that performs ABA advocacy and has many resources for job-seekers and active behavior analysts.
What Does Applied Behaviour Analysis For Autistic Children Involve
Programs based on Applied Behaviour Analysis generally involve:
- assessing a childs current skills and difficulties
- setting goals and objectives for example, learning how to say hello
- designing and implementing a program that teaches the target skill
- measuring the target skill to see whether the program is working
- evaluating the program itself and making changes as needed.
ABA can focus on a specific behaviour, like repeatedly taking off seatbelts in the car, or it can work more broadly on a range of developmental areas at the same time, like communication, self-care and play skills.
ABA programs use a range of teaching techniques to help autistic children learn new skills. These techniques might include Discrete Trial Training and incidental teaching. Programs might also use everyday interactions as opportunities for children to learn.
Children are given plenty of opportunities to practise new skills. As they learn skills, more skills are added to their programs. Over time, skills are combined into complex behaviour, like having conversations, playing cooperatively with others, or learning by watching others.
Depending on their needs, children can do ABA programs in a one-to-one or small group format at a centre, at home or in the community.
ABA programs for young autistic children usually involve more than 20 hours of therapy per week. Research has shown that this intensity is how ABA programs achieve outcomes.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Spell Autism
What Is Aba Therapy
In ABA therapy, a therapist reinforces desired behaviors and discourages unwanted behavior in a patient. Therapists use rewards to encourage a patient to develop communication, language, and other skills.
There are several different types of ABA. Which type is used depends on the patients age and goals.
Recommendations For Future Research
Recommendations for the further advancement in the field of ABA interventions for children and youth with ASD often include increasing the duration of the study, investigating comparisons to other non-ABA interventions, conducting follow-up studies for adults who participated in ABA interventions as children, and increasing the overall sample sizes. There has been an ongoing recommendation for larger scale studies over the last 20 years with respect to children and youth with ASD , as well as for long-term outcomes for adults with ASD . With respect to EIBI in particular, there is increasing importance for large-scale studies comparing the effectiveness of EIBI against other non-ABA interventions, including developmental social pragmatic interventions , which was also evident in the current review, as most comparison records that measured the effectiveness of EIBI compared their results to those of TAU or eclectic treatment approaches . Overall, although there are merits to both SCEDs and larger-scale group study designs there is a greater need for the latter when evaluating ABA. Our findings are in line with the perspective that ABA literature already has a wealth of SCEDs and is overdue for large scale studies such as RCTs to assess existing practices and, perhaps more importantly, to reevaluate and revise evolving ABA practices in the rapidly developing field of intervention for ASD .
Recommended Reading: How Early Can You Diagnose Autism
This Process Includes The Following Components:
- Selection of interfering behavior or behavioral skill deficit
- Identification of goals and objectives
- Establishment of a method of measuring target behaviors
- Evaluation of the current levels of performance
- Design and implementation of the interventions that teach new skills and/or reduce interfering behaviors
- Continuous measurement of target behaviors to determine the effectiveness of the intervention and
- Ongoing evaluation of the effectiveness of the intervention, with modifications made as necessary to maintain and/or increase both the effectiveness and the efficiency of the intervention .
As the MADSEC report describes above, treatment approaches grounded in ABA are now considered to be the gold standard of therapeutic and educational interventions for individuals with autism. The large amount of scientific evidence supporting ABA treatments for individuals with autism has led a number of other independent bodies to endorse the effectiveness of ABA, including the U.S. Surgeon General, the New York State Department of Health, the National Academy of Sciences, and the American Academy of Pediatrics .
What Distinguishes Aba From Other Disciplines
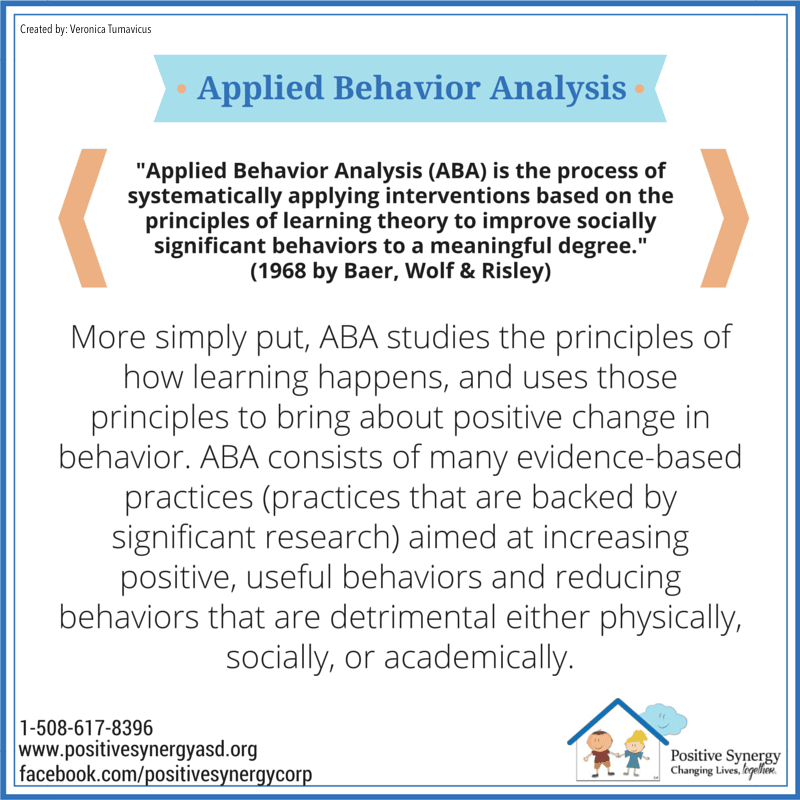
Applied Behavior Analysis focuses on behavior . It uses laws of behavior that have been experimentally demonstrated, and it uses clearly defined procedures to specify how to change behavior. The primary focus of ABA is on behavior that is important to individuals, in terms of enabling them to lead more fulfilling lives.
ABA employs teaching where the objectives of intervention are to teach your child those skills that will facilitate his development and help him achieve the greatest degree of independence and the highest quality of life possible. Although many different techniques comprise ABA the primary instructional method is called Discrete Trial Teaching . DTT involves breaking a skill into smaller parts, teaching one sub-skill at a time until mastery, allowing repeated practice in a concentrated period of time, providing prompting and fading as necessary and using reinforcement procedures.
Also Check: Is Dr Temperance Brennan Autistic
Where Does Applied Behaviour Analysis Come From
Applied Behaviour Analysis is based on learning theory, which comes from the field of behavioural psychology. The first study that looked at the use of ABA techniques with young autistic children was published by Dr Ivar Lovaas at the University of California at Los Angeles in 1987. There was a long-term follow-up study by Dr John McEachin at UCLA, which was published in 1993.
Licensure Or Certification For Behavioral Analysts
When you complete the Applied Behavior Analysis masters degree, youll meet all the coursework requirements needed to take the NYSED LBA and BCBA exams.
Russell Sage College graduates have exceeded the BACB pass rate for this exam, with a pass rate of 72% versus the national average of 65%.
The result? After completing our program, youll have met the coursework requirement for the BACB and the New York State Education Department requirements for licensure or certification as a Behavioral Analyst.
Don’t Miss: Does Max Burkholder Have Autism
Protocol Registration And Prisma Guidelines
The procedures for this meta-analysis have been registered in the PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews , which published protocols from systematic reviews prior to the initiation of data extraction in an effort to reduce reporting bias . The methods used to conduct this study were in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews . This study was designed in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines .
Outcome Of Expressive Language

Four studies reported the outcome of expressive language and we rated the overall quality of evidence as moderate . These studies reported 150 participants . Among the four studies, two used ABA-based intervention , one used ESDM33 and one used PECS . Thus, we did not have adequate studies to carry out a subgroup analysis. Significant improvement was shown in the overall synthesis . The heterogeneity was significant . Since Gordon et al.s study had significant baseline imbalance , we performed sensitivity analysis by removing it. The sensitivity analysis altered the result of heterogeneity . A forest plot illustrating these results was included in Figure 3.
Also Check: Swing For Adults With Autism
Using Applied Behavior Analysis In Addressing Biting Behavior Of A Child With Autism: A Case Study
2022, International Journal of Behavioral Sciences
Abstract
Introduction: This study focuses on a boy with autism spectrum disorder presenting with biting behaviors that interfere significantly with functioning. Method: This was a single-case study design examining how techniques of applied behavior analysis can be utilized to decrease the frequency of the child’s biting behavior and increase more adaptive behaviors. Results: The findings of the functional analysis indicated that other-inflicted biting behaviors were maintained by contingent escape from task demands and access to preferred objects and activities . Moreover, the self-inflicted biting behavior was found to be maintained by sensory stimulation . Given these, a structured behavioral intervention, consisting of differential reinforcement of alternative behaviors, coupled with extinction targeted to each function of the behavior, was effective in reducing other-inflicted biting behavior in the demand conditions and in the tangible conditions as well as reducing self-inflicted behaviors in the alone conditions . More appropriate, adaptive behaviors like compliance, picture-assisted requests, and oral sensory activities also increased significantly. Conclusion: These findings indicate that assessment and treatment based on the principles of applied behavior analysis can reduce not only problematic behaviors but also improve adaptive functioning.