What Are The Dsm
In 2013, the American Psychiatric Association released the fifth edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders .
The DSM-5 is now the standard reference that healthcare providers use to diagnose mental and behavioral conditions, including autism.
By special permission of the American Psychiatric Association, you can read the full-text of the new diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder and the related diagnosis of social communication disorder below.
Also see: Answers to frequently asked questions about DSM-5 criteria for autism
Associated Features Supporting Diagnosis
Many individuals with autism spectrum disorder also have intellectual impairment and/ or language impairment . Even those with average or high intelligence have an uneven profile of abilities. The gap between intellectual and adaptive functional skills is often large. Motor deficits are often present, including odd gait, clumsiness, and other abnormal motor signs . Self-injury may occur, and disruptive/challenging behaviors are more common in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder than other disorders, including intellectual disability. Adolescents and adults with autism spectrum disorder are prone to anxiety and depression. Some individuals develop catatonic-like motor behavior , but these are typically not of the magnitude of a catatonic episode. However, it is possible for individuals with autism spectrum disorder to experience a marked deterioration in motor symptoms and display a full catatonic episode with symptoms such as mutism, posturing, grimacing and waxy flexibility. The risk period for comorbid catatonia appears to be greatest in the adolescent years.
Restrictive / Repetitive Behaviors May Include:
- Repeating certain behaviors or having unusual behaviors, such as repeating words or phrases
- Having a lasting intense interest in specific topics, such as numbers, details, or facts
- Showing overly focused interests, such as with moving objects or parts of objects
- Becoming upset by slight changes in a routine and having difficulty with transitions
- Being more sensitive or less sensitive than other people to sensory input, such as light, sound, clothing, or temperature
People with ASD may also experience sleep problems and irritability.
People on the autism spectrum also may have many strengths, including:
- Being able to learn things in detail and remember information for long periods of time
- Being strong visual and auditory learners
- Excelling in math, science, music, or art
You May Like: Nyc Autism Charter Schools
Screening For Autism In Children
A timely diagnosis and intervention can benefit children on the autism spectrum and with other developmental disorders. Timely diagnosis is a necessary first step for identifying and beginning appropriate therapies and supports.
When assessing a child for autism spectrum disorder, a health professional or team of professionals will determine a child’s level of risk. They will use standardized questionnaires or tools as well as their clinical judgment.
Some more familiar screening tools in Canada include the:
- Infant Toddler Checklist
- Autism Observation Scale for Infants
- Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule Toddler Module
- Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers: Revised with Follow-Up
The first signs of autism spectrum disorder are usually present in very early childhood. Parents are often the first to note concerns about their child’s development. Autism can be detected through screening in children as young as 12 months old.
Children on the autism spectrum may show signs across many areas of development. Not all signs are necessary for a child to receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
Autism develops differently for each person. The term spectrum is used because symptoms can occur in combination or in degrees of intensity. Symptoms can also vary widely from person to person and across the lifespan.
Adapted from: Canadian Pediatric Society
Is Autism A Mental Illness Dsm
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , autism spectrum disorder is also classified as a mental illness. As a result, autism is classified as a neurodevelopmental disorder in the DSM-5.
The DSM-5 describes autism spectrum disorder as a mental disorder. The DSM-5 defines autism as a psychiatric disorder . Many characteristics of autism overlap with those of other mental illnesses, which is why it is frequently misdiagnosed. The obsession of children with autism with a particular field of study may be accompanied by an indifference to the interests and concerns of others. Self-obsession is a common feature of narcissistic personality disorder. Autism is more likely than other illnesses to result in mental illness. In addition to mental illness, the majority of children and adults with autism have developmental disabilities. It is possible for a secondary diagnosis to direct therapy, academic support, and mental health services. People with autism and those suffering from other mental illnesses may exhibit behaviors similar to one another.
Don’t Miss: Is Autism More Common In Boys
The Impact Of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Social Understanding
A few months shy but never too late to spread the awareness of Autism Spectrum Disorder . By detention, Autism is regarded as a disorder that affects how one perceives and socializes due to your brain development. This can often lead to having difficulty with social interaction and communication. The condition also displays restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior. In autism spectrum disorder, the term spectrum alludes to the vast range of symptoms and severity. This could mean that the range of development could relate to great intellectual abilities and talents or the exact opposite. Throughout the article we will touch base with this disorder along with the stereotypes, misconceptions and truths about the disorder as a whole.
The Purpose Of This Revision In The Dsm
A general overview of diagnostic criteria, per the DSM-5, is persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts . This can include problems with:
-
- Social-emotional reciprocity
- Developing, maintaining, and understanding social relationships.
Autism spectrum disorder also requires:
-
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities such as stereotyped or repetitive motor movements
-
- Ritualized patterns or inflexible adherence to routines
-
- Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus
- and/or hyper- or hypo reactivity to sensory input .
Other criteria also include that symptoms:
-
- Must be present in the individuals early developmental period
-
- Must cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of current functioning
- Are not better explained by intellectual disability or global developmental delay .
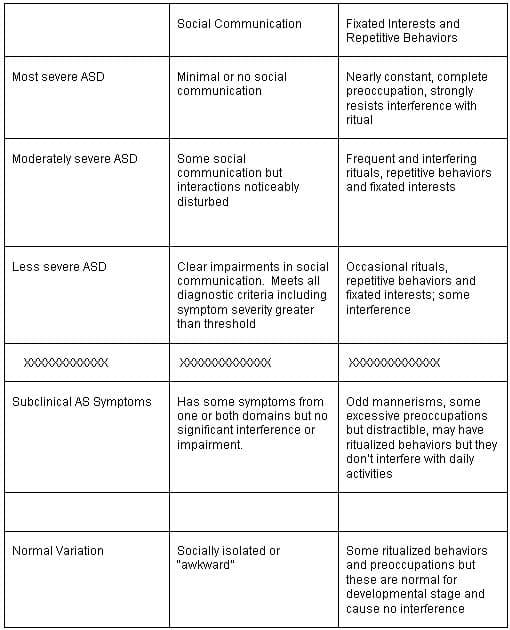
Severity specifiers are given for social communication impairments and restricted repetitive patterns of behavior . Severity for both criterion A and B are listed at three different levels:
-
- Level 1 requiring support
-
- Level 2 requiring substantial support
- Level 3 requiring very substantial support.
Don’t Miss: Is Stimming Only Related To Autism
Restricted Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior
This kind of behavior should be present and for a diagnosis at least two of these should be apparent:
Even if these symptoms are present, further requirements are still needed for an autism diagnosis. For example, the symptoms should be present from early onit is however possible that full manifestation only occurs later due to circumstances. These symptoms should cause significant problems in important areas of the childs life and should not be better explained by intellectual disability or global development delay.
What Are Acute Stress Disorders
Acute stress disorders are a type of mental illness. They can happen after you experience a traumatic event. A traumatic event is something horrible and scary that you see, hear about, or that happens to you. ASD can make it hard for you to go on with your life after the event.
ASD can happen to anyone. It is more common in women than men. It is also more common in people who have had other mental health problems in the past such as anxiety or depression. People who have post-traumatic stress disorder are also at risk for ASD.
If you have ASD, you may feel like youre in danger even when youre not. You may be constantly on guard and always alert. You may have trouble sleeping and concentrating. Sometimes You may feel numb, or you may not be able to feel anything at all. You may also have flashbacks of the event. These are called intrusive memories. They can happen at any time, even when youre doing something else.
Also Check: How To Feed An Autistic Child
What Are The New Criteria For Diagnosing Autism
The DSM-5 criteria for autism fall under two categories:
In addition, clinicians are asked to rate the severity of these problems, based on the level of daily support they require.
Read the full text of the DSM-5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder.
How will these DSM-5 changes affect people already diagnosed with Asperger syndrome, PDD-NOS or other previous autism categories?
The DSM-5 states, Individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnoses of autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
What if I or my child want to keep the diagnosis of Asperger syndrome?
Many people strongly identify with their diagnosis of Asperger syndrome. Healthcare providers can still indicate a diagnosis of Asperger syndrome in a patients medical record, alongside the current DSM-5 coding for autism spectrum disorder. Colleges and school districts may vary in their policies for educational records.
What is the new diagnosis of social communication disorder? Who will it affect?
This new diagnosis applies to people who have persistent problems with the social use of language, but dont have restricted interests or repetitive behaviors.
Also see: What is social communication disorder? How is it treated?
Is social communication disorder on the autism spectrum?
Have additional questions? Send them to
Diagnostic And Statistical Manual Fifth Edition
Although not the most commonly used manual in the UK, DSM-5 is likely to have a significant influence on the next edition of the ICD. This manual has recently been updated and is also used by diagnosticians.
The diagnostic criteria are clearer and simpler than in the previous version of the DSM, and sensory behaviours are now included. This is useful as many autistic people have sensory differences which affect them on a day-to-day basis. It now includes ‘specifiers’ to indicate support needs and other factors that impact on the diagnosis.
Also Check: How To Get Child Tested For Autism
Deficits Or Difficulty With Social Communication
According to the manual, a child should have ongoing difficulties in all three areas of social communication and interaction.
Research To Drive The Future Of Autism

Nevertheless, no matter how controversial these changes are, they were based on sound research, analysis and expert opinion. The aim of the changes to the DSM 5 for Autism Spectrum Disorder, were made in the hope that diagnosing Autistic disorders would be more reliable, more specific and hold more validity by standing the test of time.
There is apprehension as to how the changes will impact people who will no longer meet the stricter criteria for diagnosis, especially people at the higher end of the spectrum. Will they still be eligible for the support that they have had within education? This is concerning especially as it is likely that they also have additional learning difficulties.
Obviously, these changes will have an impact not just on the people who are diagnosed with Autism, but also their families.
Since the publication of the Autism Spectrum Disorder DSM 5, scientists have found that there is distinct brain connectivity difference between children with Autism in comparison with children who have other forms of Autism. A specific example is where that children with Aspergers do not have a speech delay but children with other forms of Autism do.
Recommended Reading: Why Does Autism Occur More In Males
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
Caregivers and teachers are often the first to recognize ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school. The schools special education team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend that a child undergo additional evaluation with their primary health care provider or a health care provider who specialize in ASD.
A childs caregivers may talk with these health care providers about their childs social difficulties, including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication differences may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. They also may have trouble forming friendships with peers.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know the primary causes of ASD, but studies suggest that a persons genes can act together with aspects of their environment to affect development in ways that lead to ASD. Some factors that are associated with an increased likelihood of developing ASD include:
- Having a sibling with ASD
- Having older parents
- Having certain genetic conditions
- Having a very low birth weight
Also Check: When Is National Autism Day
Where To Seek Help
If your child meets these requirements, it is necessary to get in touch with a professional at the earliest. Consult us at Continua Kids to get in touch with the best autism doctor in Delhi. At Continua Kids, we support specially-abled children to live the life that they deserve. We are a research-directed, holistic center, and aim to impart early intervention programs concerning your childs overall well-being. By providing guidance and support in your parenting experience, we strive to help your child reach their full potential in all aspects of life.
Free Brochures And Shareable Resources
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: This brochure provides information about the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of ASD. Also available en español.
- Digital Shareables on Autism Spectrum Disorder: Help support ASD awareness and education in your community. Use these digital resources, including graphics and messages, to spread the word about ASD.
Don’t Miss: Can Drugs And Alcohol Cause Autism
What Is The Dsm
Medical professionals and researchers often consult the DSM-5, a manual sometimes referred to as the bible of mental conditions. In this article the criteria for an autism diagnosis according to the DSM-5 will be examined.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is a manual often cited in scientific journals medical professionals like psychiatrists and pediatricians refer to it when diagnosingbut for some of us it appears to be a bit of a daunting read reserved for those with multiple abbreviations accompanying their name.
The name of the handbook, The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders contributes to the intimidation factor. While it was never intended as a beach read for the public, the DSM-5 contains a lot of diagnostic information that may be useful for educators and parents, in addition to its intended medical and research audience.
Most doctors in the US use the manual as the authoritative guide when diagnosing autism spectrum disorders . For medical professionals without a lot of autism related experience, the DSM-5 provides guidelines and criteria to facilitate consistent and reliable diagnoses.
It may be a valuable diagnostic tool, but its also been criticized by many cliniciansspecifically criticism regarding its validity, reliability and utility . Issues relating to overdiagnosis and the risk of pathologizing normal behavior or conditions are further areas of concern according to Young .
Does My Child Have Autism Note
. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Below plus at least two of four types of restricted repetitive behaviors see B1. For a full copy of this manual please visit the American Psychiatric Association website.
Autism Spectrum Disorder is diagnosed based on the presence of multiple symptoms that disrupt a persons ability to communicate form relationships explore play and learn. The effects of autism in such people may range from mild to very severe. Autism is a highly variable neurodevelopmental disorder and has long been thought to cover a wide spectrum ranging from individuals with high support needswho may be non-speaking developmentally delayed and more likely to present with other co-existing diagnoses including intellectual disabilityto individuals with low support needs.
To meet diagnostic criteria for ASD according to DSM-5 a child must have persistent deficits in each of three areas of social communication and interaction see A1. In North America medical professionals use the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5 revised May 2013 to evaluate autism spectrum disorder ASD. O Distinguish between behaviors that are clearly atypical and present.
The criteria for an autism diagnosis according to the DSM-5 includes signs and symptoms and it states how many of these need to be present. Read the full text of the DSM-5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder and social communication disorder. DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA DSM-5.
Also Check: Do Vaccines Cause Autism Articles