How Is Adhd Diagnosed From Icd
ADHD is typically diagnosed by a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. To be diagnosed with ADHD, a person must have symptoms that are present for at least six months and that interfere with their daily life. A diagnosis can also be made if a person has symptoms that are present for at least 12 months, but they may not meet the full criteria for ADHD.
Coding Spotlight: Providers Guide To Coding Behavioral And Emotional Disorders
Dec 1, 2019State & Federal / Medicaid
Category: Medicaid
ICD-10-CM coding
Codes within categories F90 through F98 represent behavioral and emotional disorders with onset usually occurring in childhood and adolescence and may be used regardless of the age of the patient.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is among these common childhood disorders. While ADHD is not a learning disability, it can impact the ability to learn. This disorder is characterized by classic symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity.
Three subtypes of ADHD have been identified:
- Hyperactive/impulsive type The patient does not show significant inattention.
- Inattentive type The patient does not show significant hyperactive-impulsive behavior.
- Combined type Patient displays both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
Other disorders that sometimes accompany ADHD include Tourettes syndrome, oppositional defiant disorder, conduct disorder, anxiety, depression and bipolar disorder. ADHD continues into adulthood in about 50% of people with childhood ADHD. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders are coded based on a behavior type:
- Attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity
- Attention deficit syndrome with hyperactivity
ICD-10-CM lists the following conditions as special exclusions to ADHD:
- Anxiety disorders
Note: Excludes2 means not included here.
HEDIS® quality measures for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Two rates are reported:
Helpful tips:
Where To Go From Here
If you think you have ADHD, a diagnosis is a vital first step to help you better understand your challenges and find ways forward to overcome them. Frida offers a free ADHD screening tool to help you determine if you might have ADHD as well as the option to connect with a qualified clinician who can offer you a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Related readings:
Read Also: Can A Traumatic Event Cause Autism
Is Adhd Considered A Mental Illness By The Dsm
The category of mental illness is broad. The American Psychiatric Association defines mental illness as health conditions involving significant changes in emotion, thinking, or behavior that cause significant distress in social, work, or family activities.
ADHD does fall within the definition of mental illness but is most often referred to as a disorder or mental disorder. Mental illness and disorder are often used interchangeably.
What Are The Best Treatments For Adhd
There are countless ways to alleviate the symptoms of ADHD, but experts tend to agree that the most effective ADHD treatment is a combination of medication and multimodal therapy.
The first step in ADHD treatment is planning. What are your or your childs needs? More success at school? Increased productivity? Fewer behavioral issues and disruptions? Higher confidence? Better social skills? All your interventions should be person-centered and strength-based. They should also respect and enhance those things that bring happiness and joy. So think about your or your childs goals, and go from there.
Well cover ADHD medications at more length below, but lets start with multimodal therapy. The National Institutes of Health lists seven types of ADHD therapy and psychosocial interventions:
- Neurotypical self-control strategies
Read Also: What Is The Main Cause Of Autism
Diagnosing Adhd In Adults
ADHD often lasts into adulthood. To diagnose ADHD in adults and adolescents age 17 years or older, only 5 symptoms are needed instead of the 6 needed for younger children. Symptoms might look different at older ages. For example, in adults, hyperactivity may appear as extreme restlessness or wearing others out with their activity.
Adhd Myths Vs Adhd Facts
Misconceptions about ADHD can drive stigma and discrimination, and cause lasting damage. In 2021 the World Federation of ADHD published an International Consensus Statement that made 208 conclusions about the disorder. The statement was ratified by 80 authors who hailed from 27 different countries and 6 different continents. And it stated the following:
Stigmatizing attitudes toward ADHD are common and may play a role in socially and clinically important outcomes. These negative attitudes affect patients at all stages of their life. Such attitudes have been documented among individuals at all ages and in all groups, including family, peers, teachers, clinicians, and even individuals with ADHD themselves.
Like all humans, people with ADHD need to be part of a community, and feel a sense of belonging and acceptance, in order to achieve optimal well-being.
Here are a few of the more enduring myths about ADHD:
Recommended Reading: Why Do People Make Fun Of Autism
Symptoms And Diagnosis Of Adhd
If you are concerned about whether a child might have ADHD, the first step is to talk with a healthcare provider to find out if the symptoms fit the diagnosis. The diagnosis can be made by a mental health professional, like a psychologist or psychiatrist, or by a primary care provider, like a pediatrician.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that healthcare providers ask parents, teachers, and other adults who care for the child about the childs behavior in different settings, like at home, school, or with peers. Read more about the recommendations.
The healthcare provider should also determine whether the child has another condition that can either explain the symptoms better, or that occurs at the same time as ADHD. Read more about other concerns and conditions.
Criteria For Predominantly Inattentive Adhd
In order to be diagnosed with ADHD predominantly inattentive type you must meet five or more of the following symptoms if you are an adult and six or more symptoms if you are a child :
Carelessness/poor attention to detail: Often fails to give close attention to details or makes careless mistakes in schoolwork, at work, or during other activities
Diminished attention span: Often has difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play activities
Poor listening skills: Often does not seem to listen when spoken to directly
Lacks follow-through: Often does not follow through on instructions and fails to finish schoolwork, chores, or duties in the workplace
Disorganized: Often has difficulty organizing tasks and activities
Avoids tasks requiring concentration: Often avoids, dislikes, or is reluctant to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort
Loses things: Often loses things necessary for tasks or activities
Easily distracted: Is often easily distracted by things in the environment or unrelated thoughts.
Forgetful: Is often forgetful in daily activities
Don’t Miss: Can Autism Be Detected In The Womb
Adhd Differential Diagnoses And Co
A 2016 parent survey from the Centers for Disease Control determined that 6 in 10 children with ADHD had at least one additional mental disorder. In adults, its more like 8 in 10. When one diagnosis overlaps with another diagnosis, we call those conditions comorbid. And ADHD has one of the highest comorbidity rates of any psychiatric disorder.
According to the DSM-5, ADHD often overlaps with externalizing disorders. These disorders include oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder , both characterized by problematic behaviors. Adults with ADHD are sometimes diagnosed with borderline personality disorder and antisocial personality disorder , both characterized by emotional instability and difficulty in top-down regulation.
Other mental disorders associated with ADHD include the following:
- Learning and language disabilities
- Binge eating disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
Some of these comorbid conditions may share underlying mechanisms, based in cortical wiring, motor/coordination difficulties, or emotional dysregulation. Other mental health issues, like low self-esteem, may be secondary conditions brought on by the ADHD experience. In any event, comorbidities can make it harder to diagnose ADHD accurately, and can complicate treatment.
Tests Used To Diagnose Adhd
It is important to note that there is no single test that can diagnose ADHD. Instead, a diagnosis is made based on a comprehensive evaluation that includes a medical history, physical exam, and psychological testing.
There are several different rating scales and questionnaires that can be used to diagnose ADHD, such as the Conners Rating Scales and the Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Parent Rating Scale. A diagnosis of ADHD is usually made after taking into account information from multiple sources, such as parents, teachers, and medical professionals.
ICD 10 also states that ADHD can only be diagnosed in children aged six years or older. This is because the symptoms of ADHD can vary significantly over time and may not be present in all situations. For example, a child with ADHD may be able to focus on a favorite activity but have difficulty paying attention in school.
You May Like: What Does It Mean To Have Autism
What Section Of The Dsm Is Adhd In
As in DSM-IV, symptoms will be divided into two categories of inattention and hyperactivity and impulsivity that include behav- iors like failure to pay close attention to details, difficulty organizing tasks and activities, excessive talk- ing, fidgeting, or an inability to remain seated in appropriate situations.
What is a diagnosis of R41 840?
Coding Guidelines for R41. 840. R41. 840 is a valid ICD-10-CM diagnosis code meaning Attention and concentration deficit.
Why Do People With Adhd Talk So Much
The world is full of people who ramble on, dont pick up on your subtle cues that youd like to escape the conversation, and frequently interrupt you when youre speaking. This could be due to simple rudeness, but it might also be due to ADHD. Neurotypical people can quickly see warning signs that someone isnt listening or responding positively to what theyre saying. Then they make a split-second decision to stop talking. But it takes the ADHD brain longer to switch gears. Someone with ADHD might also be excited, or seek verbal reassurance, which keeps them talking. Self-regulation issues and impulsivity could also lead to a person with ADHD blurting out something they shouldnt.
Also Check: Is Autism A Mental Illness
Adhd In Women Vs Adhd In Men
Data from the CDC shows that boys are far more likely to be diagnosed with ADHD than their girl counterparts. But between 2003 and 2015, the number of women aged 15-44 who filled a prescription for an ADHD medication increased 344%.
Adult women with ADHD are often misdiagnosed with mood disorders. This is because ADHD can cause heightened emotionality. And other interesting things show up in research, like a study that showed women with higher levels of baseline irritability were likely to have more hyperactive and impulsive symptoms of ADHD after 18 months. This wasnt the case for men.
How Does Adhd Present Across The Lifespan
ADHD is a lifespan disorder, meaning it affects both kids and adults. But its symptoms can change drastically over the course of a lifetime. Some people even go into complete remission. Longitudinal studies show that 40-60% of children with ADHD will experience partial remission. They might be less impulsive or hyperactive, for example, but still have attention issues. Only 15% of children with ADHD will still meet all diagnostic criteria as adults.
So how does ADHD look across the lifespan? Well break it down in the sections below.
Read Also: Is Autism A Mental Illness Nhs
Are There Any Benefits To Having Adhd
Everyone with ADHD should know that their condition can be an asset. Its especially helpful to kids to be given a positive framework in which to see themselves and their ADHD brains. Parents and caregivers can help children find a metaphor that feels good to them. For example, having a neurodevelopmental disorder is boring, but having a race car brain is awesome! Especially when you can help write the owners manual.
People with ADHD can be incredibly creative, especially when they find an outlet that really engages them. They can be great problem-solvers. They can be hyperfocused and energetic, bright and clever, spontaneous and adaptable. Everyone who has ADHD is unique, with their own personal strengths that arent always traditionally valued in society. Parents of kids with ADHD can help their children find those strengths and amplify them.
Tabular List Of Diseases And Injuries
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized “head to toe” into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code F90.9:
Inclusion Terms
- Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder of childhood or adolescence NOS
- Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder NOS
Recommended Reading: How To Make Friends When You Have Autism
Behavioral And Emotional Disorders With Onset Usually Occurring In Childhood And Adolescencenote
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Includes
- Adhd
- Articulation disorder due to hyperkinesis
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- Developmental articulation disorder due to hyperkinesis
- Developmental speech disorder due to hyperkinesis
- Hyperkinetic conduct disorder
- Long term current use of medication for add and or adhd
- Long term current use of medication for attention deficit disorder or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- 886 Behavioral and developmental disorders
- : New code
- 2017
A Breakdown Of Adhd Medications: Benefits And Side Effects
Doctors who specialize in ADHD treatment typically recommend that people respect medication, but not fear it. There are two types of ADHD medication:
- Stimulants: methylphenidate and amphetamine
- Non-stimulants: atomoxetine, extended release guanfacine, and extended release clonidine
While working closely with a physician or psychiatrist, it may take some trial and error to get the right prescription and dosage of ADHD medication. Until you find the ideal formulation, possible side effects may include sleep issues, abdominal pain, and changes in appetite. Some medications are also associated with small delays in height gains in children. Too much medication may cause Zombie syndrome or Starbucks syndrome.
Though ADHD medications are proven to be safe and effective for people with the disorder, controversy still stems from overprescription and misuse of stimulant medication. Drug shopping and drug diversion is particularly problematic among college students.
Also Check: When Do You Find Out If Your Baby Has Autism
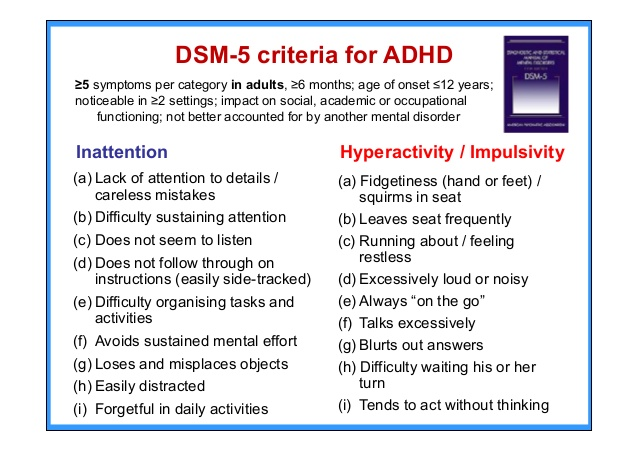
Dsm Criteria For Adhd
People with ADHD show a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development:
Why Was Adhd Added To Icd
The main reason why ADHD was added to ICD-10 was due to its high prevalence rate. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , about 11% of children aged four to 17 have been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States. This is a significant increase from previous years, which suggests that more people are becoming aware of the condition and seeking treatment.
Also Check: Can You Have Sensory Processing Disorder Without Autism
What Are The Risks Of Not Treating Adhd
- They may never gain a full understanding of who they are.
- They might lose faith in themselves. Untreated ADHD can lead to a negative feedback loop, where someone doesnt try because they feel that they cant succeed. They might become ashamed, frustrated, demoralized, depressed, anxious, or develop chronic self-esteem issues.
- People with undiagnosed ADHD or untreated ADHD might find ways to cope with their symptoms through self-medication. Some of those coping mechanisms arent necessarily unhealthy, like using intense exercise to achieve hours of focus. But other people might turn to drugs or alcohol.
- ADHD is associated with more frequent accidents, risky behaviors, and a reduction in life expectancy.
- Untreated ADHD can cause problems at school, at work, and in relationships.
Is Adhd A Learning Disorder
ADHD is more of a self-regulation disorder than a learning disorder, though it can cause learning challenges. ADHD and learning disorders/disabilities have a 45% comorbidity rate .
The DSM-5 describes three subtypes of specific learning disorder:
- Dyslexia
- Dysgraphia
- Dyscalculia
In the US, the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act defines a specific learning disability as a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding or in using language, spoken or written, that may manifest itself in the imperfect ability to listen, think, speak, read, write, spell, or to do mathematical calculations, including conditions such as perceptual disabilities, brain injury, minimal brain dysfunction, dyslexia, and developmental aphasia.
In American classrooms, children with SLDs and children with ADHD can be given special services and accommodations through individualized education programs and 504 plans. Through IEPs, parents and teachers can align about the best ways to help children succeed at school, whether that be through letting them sit on a balance ball rather than a chair when theyre at their desk, or giving them extra time for exams.
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Autism Behavior