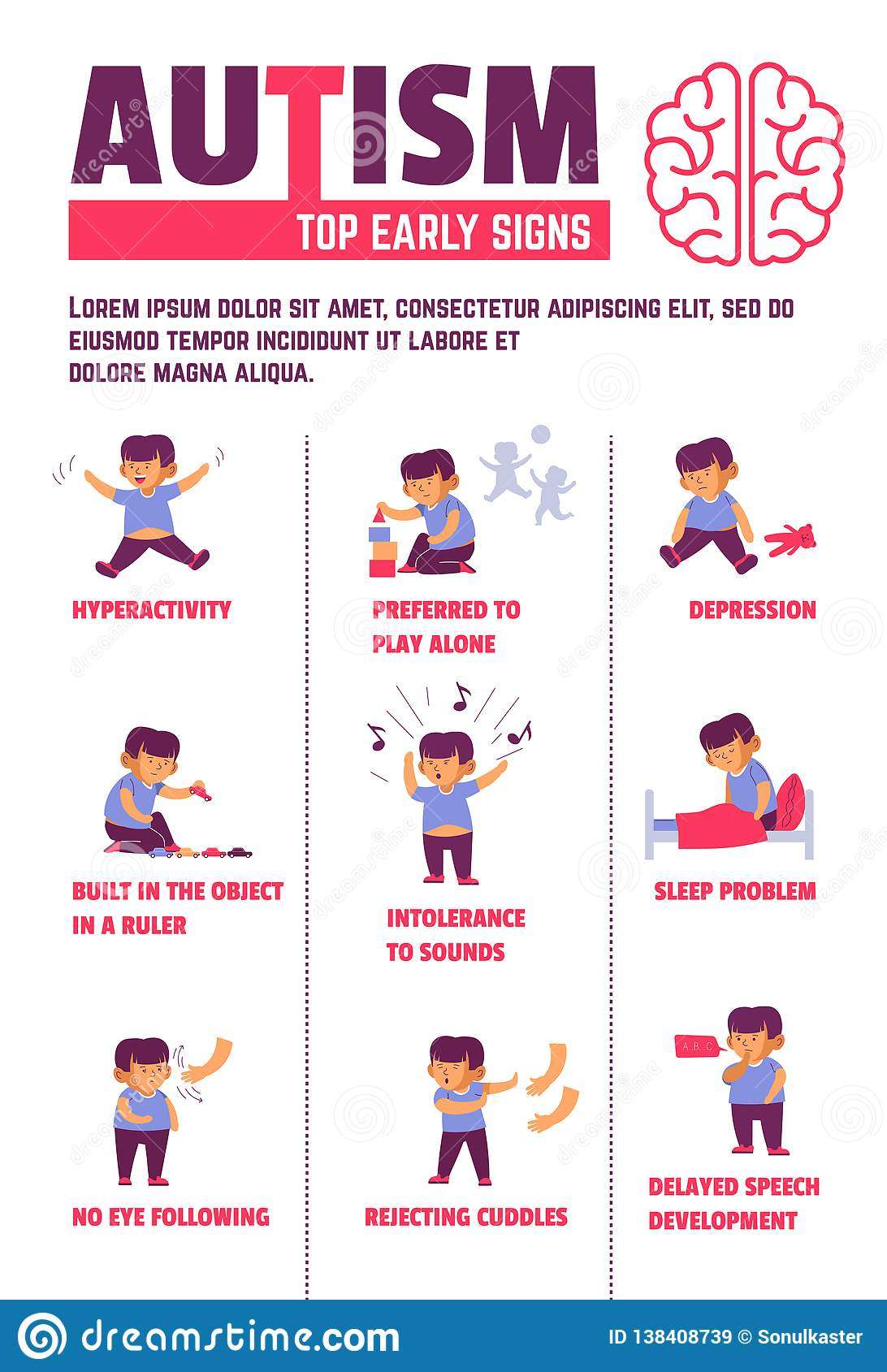
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism
The behaviours associated with autism fall into two broad areas: impaired social interaction and communication, and restricted and repetitive behaviours and interests.
The common signs and symptoms of autism are:
- lack of social or emotional exchanges like pointing, smiling, showing you things
- lack of non-verbal communication such as nodding and shaking head, using hand gestures
- difficulty developing and maintaining relationships appropriate to the age, such as peer play, lack of close friends
- delayed expressed speech and understanding of speech
- lack of eye contact when speaking
- loss of language skills at any age
- excessively following routines, patterns or behaviour, and becoming distressed at changes
- stereotyped or repetitive speech, movements or use of objects, such as rolling wheels before eyes, flapping hands, toe walking
- strongly reacting to sensory input such as sound, pain or textures
- restricted or fixated interests such as only playing with certain toys or discussing certain topics
- being aggressive toward other people or toward self
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school are often first recognized by parents and teachers and then evaluated by the schools special education team. The schools team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend these children visit their primary health care doctor or doctors who specialize in ASD for additional testing.
Parents may talk with these specialists about their childs social difficulties including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication issues may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. Parents may also find that their child has trouble forming friendships with peers.
Autism And Mental Health Conditions
Current evidence reports that around 5070% of autistic people also experience mental health conditions. There is also emerging evidence to suggest that autistic women and girls experience higher rates of mental illness than autistic men and boys.
The most common mental health conditions experienced by autistic people are depression, anxiety disorders and/or obsessive compulsive disorder.
These facts highlight the urgent need for mental health services and resources that are designed for and with autistic people.
You May Like: Dyslexia Vs Autism
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder refers to a group of complex neurodevelopment disorders characterized by repetitive and characteristic patterns of behavior and difficulties with social communication and interaction. The symptoms are present from early childhood and affect daily functioning.
The term spectrum refers to the wide range of symptoms, skills, and levels of disability in functioning that can occur in people with ASD. Some children and adults with ASD are fully able to perform all activities of daily living while others require substantial support to perform basic activities. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders includes Asperger syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorders not otherwise specified as part of ASD rather than as separate disorders. A diagnosis of ASD includes an assessment of intellectual disability and language impairment.
ASD occurs in every racial and ethnic group, and across all socioeconomic levels. However, boys are significantly more likely to develop ASD than girls. The latest analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1 in 68 children has ASD.
Diagnosis In Young Children
Diagnosis in young children is often a two-stage process.
Stage 1: General Developmental Screening During Well-Child Checkups
Every child should receive well-child check-ups with a pediatrician or an early childhood health care provider. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children be screened for developmental delays at their 9-, 18-, and 24- or 30-month well-child visits and specifically for autism at their 18- and 24-month well-child visits. Additional screening might be needed if a child is at high risk for ASD or developmental problems. Those at high risk include children who have a family member with ASD, have some ASD behaviors, have older parents, have certain genetic conditions, or who were born at a very low birth weight.
Parents experiences and concerns are very important in the screening process for young children. Sometimes the doctor will ask parents questions about the childs behaviors and combine those answers with information from ASD screening tools, and with his or her observations of the child. Read more about screening instruments on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website.
Children who show developmental problems during this screening process will be referred for a second stage of evaluation.
Stage 2: Additional Evaluation
This second evaluation is with a team of doctors and other health professionals who are experienced in diagnosing ASD.
This team may include:
The evaluation may assess:
- Blood tests
Don’t Miss: Difference Between Sensory Processing Disorder Aspergers
Common Traits Autistic People Experience
Some common traits many autistic people experience include:
- difficulty recognising or understanding other people’s emotions and expressing their own
- being over- or under-sensitive to things like loud noises and bright lights, and finding crowded noisy spaces challenging
- preferring familiar routines and finding unexpected changes to those routines challenging or distressing
- having intense and specific interests in things
- difficulties reading body language, understanding sarcasm and facial expressions
All of these traits can be experienced to lesser or greater degrees. Experiencing one or more of these traits doesnt necessarily mean you are autistic. But if these kinds of things are consistently present and are impacting upon your life, you may consider talking to your GP to discuss how you can seek a formal diagnosis.
-
As part of my autism, I tend to take things very literally.
Rosie
-
For those on the spectrum anxious about the future, I want to instill a sense of belief that I know many of us lack. The truth is every day we overcome our condition in so many different ways.
Sam
Useful Things To Consider When Seeking Support For Co
When seeking support for a co-occurring mental health condition, it would be advisable for Autistic adults and youth to keep a few things in mind. First, it is important to find a professional who is willing to make accommodations at the request of their clients. Second, a common problem many adults on the spectrum experience is running into mental health professionals who see their role as treating autism instead of assisting a person with the co-occurring mental health challenges that are the cause of more significant problems in their life. It is valuable to look for a professional who accepts that their new client is Autistic and will remain so, and that they are looking for help on improving their quality of life as an Autistic person, not as someone trying to be normal. Finally, keep in mind that when seeking mental health supports, peer support options are an important and valid way of improving quality of life. Much of the best support systems in the mental health world come from people with similar functional challenges supporting each other. These types of supports are exceedingly valuable.
You May Like: Autism And Mental Retardation Comorbidity
Causes And Risk Factors
While scientists dont know the exact causes of ASD, research suggests that genes can act together with influences from the environment to affect development in ways that lead to ASD. Although scientists are still trying to understand why some people develop ASD and others dont, some risk factors include:
- Having a sibling with ASD
- Having older parents
- Having certain genetic conditionspeople with conditions such as Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, and Rett syndrome are more likely than others to have ASD
- Very low birth weight
Why Children Are Misdiagnosed
Autism is not always a child’s first diagnosis, particularly if he or she is verbal and of average intelligence. Not infrequently, children who wind up with an autism diagnosis receive a range of other diagnoses firstincluding, in some cases, other types of mental disorders.
There is a simple reason for these misdiagnoses: a child who is bright and verbal may not be evaluated for autism. As a result, the child’s symptoms are viewed not as a set of related challenges, but as individual issues that could potentially be signs of another mental illness. There are a number of behaviors in autism and other mental illnesses that may share characteristics and lead to an erroneous diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Ian Ritch Girlfriend
How Autism Spectrum Disorder Is Diagnosed And Treated
Diagnosis
Autism spectrum disorder is diagnosed based on a childs development and behavior, according to the National Institute of Mental Health.3 It can be detected as early as 18 months, although most children arent diagnosed until after the age of four. The sooner its diagnosed, the better the developmental outcomes.
While theres no cure for ASD, early intervention services available under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act can dramatically improve a childs development, including walking, talking, and interacting socially.
Treatment
Treatment for autism spectrum disorder is highly individualized and involves a combination of therapies, services, and support. Although there are no medications that can treat the core symptoms of autism, medication may be used to improve functioning by helping individuals manage issues like seizures, depression, high energy levels, or difficulty focusing.
For the most part, treating ASD involves non-pharmaceutical interventions, such as:
Speech Therapy
Offers emotional support and resources to people with autism and their families
Other interventions may include intensive parent training programs, social skills groups, and play-based skills groups.
Is Autism A Mental Health Condition What Is The Difference
Every so often we progress past the need for something but get too stuck in our ways to change it. Take for example that old atlas you keep in your car, the CD collection you cant bring yourself to throw away or, more importantly, the misconception that autism is a mental health condition. At some point these all served a purpose in life yet, in the present day, they are now outdated and obsolete.
Nevertheless, while something like a compulsory home phone number request on an official form is a slight irritation, autisms mental health categorisation isnt so easy to dismiss due to the danger and damage it can cause. So, what is the difference between autism and a mental health condition, and why is it so important that these misunderstandings go the way of Microsofts Clippy?
Read Also: Autism Hypnosis
Cookie And Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refuseing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
These cookies collect information that is used either in aggregate form to help us understand how our website is being used or how effective our marketing campaigns are, or to help us customize our website and application for you in order to enhance your experience.
How Is Autism Managed
If your child is diagnosed with autism, you will be guided through the various treatment options. There are education programs and support services available for children with autism and their parents or caregivers from a number of organisations such as Autism Spectrum Australia.
Treatments used to manage autism are best started as early in a persons life as possible. Specific symptoms and social skills can be improved with the right support and programs. Because everyone with autism is different, the best results are obtained from a treatment program specifically tailored to their individual needs.
Language and social skills are taught through intensive educational programs and behavioural therapies. Speech pathology focuses on developing communication and social skills. Occupational therapy concentrates on sensory motor development, such as learning play and fine motor skills, as well as how to cope in social situations.
Public and private schooling options are available for children with autism. Find out more about schooling options on the Autism Awareness website.
Sometimes claims are made about treatments that are misleading. Avoid treatments that offer a cure or recovery as there is no evidence to support these claims. Ensure that the treatments and supports you choose are informed by evidence.
Autism Awareness Australia provides self-care tips and helpful links and resources.
Don’t Miss: Do Autistic People Die Early
Performance Cost And Respondent Burden
This dimension describes the effectiveness, efficiency and economy of the statistical output.
As a âsecondary usesâ data set, the MHSDS does not require the collection of new data items by autism service providers. It re-uses existing clinical and operational data for purposes other than direct patient care.
Providers are not required to submit data held only on paper records as no provision has been made in the MHSDS for the cost of transcribing these records to an electronic format.
Only two of the data tables are mandated to flow each time any activity is reported within the MHSDS , completion of the remaining tables is only required when activity has occurred that is captured within these tables.
Read Also: Schedules For Autism
Comparisons Of Positive And Negative Symptoms
ADOS
For both analyses, tests for homogeneity of variances were violated. Therefore, we ran BrownForsythe tests to examine equality of means and GamesHowell post hoc comparisons, which are more robust to homogeneity of variance violations. Diagnosis had a statistically significant effect on both positive symptoms, F = 57.69 p< .001 and negative symptoms, F = 11.83 p< .001. For positive symptoms, post hoc comparisons revealed that the ASD group displayed more positive symptoms than both the SZ and TD groups , and the SZ group scored marginally higher on this scale than the TD group . For negative symptoms, the ASD group scored significantly higher than the TD group , and group differences between the SZ and TD groups approached significance as the SZ group scored marginally higher . However, there were no statistically significant differences between the ASD and SZ groups for negative ASD symptoms .
We next examined ROC curves to see if ADOS-2 positive symptoms better discriminate ASD and SZ than ADOS-2 negative symptoms. By Metzs standards, negative items poorly discriminated ASD and SZ , AUC = .64, p = .03. In contrast, positive items did a good job discriminating the ASD and SZ samples, AUC = .81, p< .001.
PANSS
Figure 2*p< .05, ***p< .001 . Error bars represent standard error of the means. + and symbols refer to positive and negative symptoms, respectively. ASD, Autism Spectrum Disorder SZ. Schizophrenia TD, Typical Development.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Mild Autism
Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
Not all people with ASD will have all of the signs and symptoms of the disorder, although most will experience several. Signs and symptoms of autism spectrum disorder include:
- Making little or no eye contact
- Not looking at or listening to people
- Failure to respond to someone trying to get their attention
- Having problems having back-and-forth conversations
- Having facial expressions, gestures, and movements that don’t match what’s being said
- An unusual tone of voice
- Trouble understanding others’ points of view or predicting others’ actions
- Unusual behaviors or repeating certain behaviors
- Intense, lasting interest in certain topics
- Overly focused interests
- Inability to cope with changes in routine
- Greater or lesser sensitivity than neurotypical people to sensory input, such as noise or temperature
People with autism also have marked strengths, which may include:
The ability to remember information for a long time
Being a strong visual and auditory learner
Excelling in a particular subject, such as math, art, or music
Myths & Misconceptions About Autism
Researchers are learning more and more about autism every year. While it was virtually unheard of just a few decades ago, autism is now a well-known disorder. Its prevalence has risen from one in 1,500 children in 1975 to one in 59 children today, according to the CDC, making autism a very common disorder.4 Still, myths and misconceptions about autism spectrum disorder abound. Here, we debunk the most common of these.
Don’t Miss: Writing An Autistic Character
How Is Autism Treated
There is no cure for ASD. Therapies and behavioral interventions are designed to remedy specific symptoms and can substantially improve those symptoms. The ideal treatment plan coordinates therapies and interventions that meet the specific needs of the individual. Most health care professionals agree that the earlier the intervention, the better.
Educational/behavioral interventions: Early behavioral/educational interventions have been very successful in many children with ASD. In these interventions therapists use highly structured and intensive skill-oriented training sessions to help children develop social and language skills, such as applied behavioral analysis, which encourages positive behaviors and discourages negative ones. In addition, family counseling for the parents and siblings of children with ASD often helps families cope with the particular challenges of living with a child with ASD.
Mental Health And Autism
Those of us with autism are more likely to experience mental health problems than the general population. This can be because there are fewer resources and support to help develop coping skills. Also, we can experience more negative life events, face stigma and discrimination from people and services. Its really important that services are able to properly identify mental health problems, so people can get the right support at the right time.
Recommended Reading: Setting Up An Autistic Classroom