Hundreds Of Autistic People Are Detained In Hospitals With Numbers Doubling Since 2015
Find your bookmarks in your Independent Premium section, under my profile
Desperate to know how her autistic son Ryan was coping after being detained for years in an NHS mental health hospital, Sharon Clarke dialled the telephone number for the ward again, struggling to understand why she couldnt get through she had no idea then that both her and her husbands telephone numbers had been deliberately blocked by NHS staff.
Whoever was responsible has never been identified but the intentional act in October 2019 was yet further proof for Sharon that her son was in the wrong place and needed help to get out.
The Humber Centre, in Hull, is a secure forensic psychiatry unit, more commonly used for treating those who have committed crimes because of a serious mental illness. Ryan Addison has been locked up by the NHS having never committed a crime.
For the last four years he has been isolated in long-term segregation and monitored at all times by at least three staff. Over the years, he has been so heavily medicated with powerful drugs he has had to have 14 teeth removed. He was fitted with dentures but they were lost 18 months ago and have yet to be replaced, his mother says.
Hospital reports seen by The Independent show he has also suffered bruises after being restrained by nine staff, as well as a broken arm and a broken foot. There have also been suggestions by staff in reports that he shows signs of sexual abuse.
How Did You Implement The Project
Firstly, we re-worked the environment tool endorsed by NICE. We did so by researching other tools, trialling their use and making it more specific using colour coding to facilitate quick win recommendations that we could hand out on the spot. It also made it easier to transfer the information to a spreadsheet and track trends.
It was difficult to engage busy ward managers at first and unfortunately our project dove-tailed with the end of a different project using urgent care lounges for the same purpose as The Haven. We implemented information sessions and flyers with heads of departments to get our foot in the door and soon enough people were on board with autism awareness-raising then with looking at the environment in acute settings. We did not go over budget. It was a case of engaging key people in the right way.
Introducing The Mental Health Support Team In Sen Schools: Hertfordshire And West Essex
The MHST is an early intervention service, working with mild to moderate mental health difficulties and challenging behaviours. This is part of a national programme to offer early interventions in school settings. PALMS is hosting the MHST.
The MHST supports mental wellbeing in the following SEN schools in Herts and West Essex: The Collett, Colnbrook, Garston Manor, Middleton, Southfield, The Valley, Woolgrove, Oakview, and Wells Park. We are only able to offer support to parents/ carers of children who attend schools that have signed up to support from the MHST for SEN schools.
This support will be delivered by an Educational Mental Health Practitioner . The MHST is currently offering virtual support due to covid-19, therefore you will need access to a computer or smartphone.
What support does the MHST offer?
The MHST helps to support mental health in schools in several ways:
- Workshops with young people or parent/carers
- Group based work with young people or parent/carers
- Guided 1:1 self-help sessions with young people, parent/carers around proactive prevention and support for mild to moderate mental health difficulties and challenging behaviour
- A whole school approach to understanding and improving mental health, which may include supporting the schools mental health lead, supporting with the wellbeing curriculum, identifying mental health resources, creating posters and displays etc
Read Also: Symbol For Autism Awareness
Autistic Traits And Diagnosis
Autistic traits meaning things that autistic people often do, think, and feel are often shared by people who dont have autism too. This doesnt mean that everyone is a little bit autistic, or that autistic people dont need support.
To be diagnosed with autism, a person has to have a lot of autistic traits from birth, and those traits need to have a big effect on their life. In order to be diagnosed with autism, those traits must cause what a healthcare professional would call clinically significant difficulties in their day-to-day life. This means that they have difficulties with day-to-day life due to their autistic traits and need to use their own ways of overcoming those difficulties, or the people in their life need to help them to overcome them, or both.
Being in a supportive environment makes a big difference to an autistic persons wellbeing and quality of life.
Psychological therapies like cognitive behavioural therapy are often used to treat depression, anxiety, and sleep problems, both in people who have autism and people who dont.
Psychological therapies can help to manage conditions linked with autism, like anxiety, but psychological therapies arent a treatment for autism itself. Therapy techniques might need to be adapted to work for an autistic person.
Challenges in daily living
Possible therapies include:
Finding the right therapies
Performance Cost And Respondent Burden

This dimension describes the effectiveness, efficiency and economy of the statistical output.
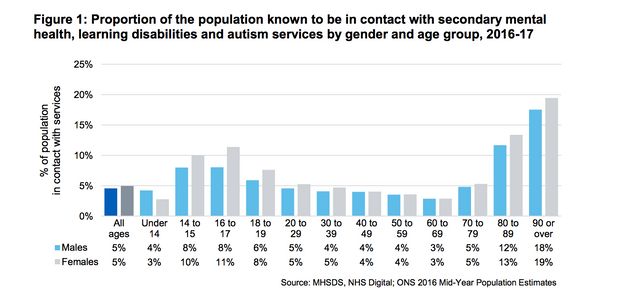
As a ‘secondary uses’ data set, the MHSDS does not require the collection of new data items by autism service providers. It re-uses existing clinical and operational data for purposes other than direct patient care.
Providers are not required to submit data held only on paper records as no provision has been made in the MHSDS for the cost of transcribing these records to an electronic format.
Only two of the data tables are mandated to flow each time any activity is reported within the MHSDS , completion of the remaining tables is only required when activity has occurred that is captured within these tables.
Read Also: Schedules For Autism
Cookie And Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refuseing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
These cookies collect information that is used either in aggregate form to help us understand how our website is being used or how effective our marketing campaigns are, or to help us customize our website and application for you in order to enhance your experience.
How Is Autism Normally Diagnosed
Getting a diagnosis for a child can be helpful, as it enables parents, as well as others, to understand and support the child better.
Diagnostic assessment can also help to clarify if a child requires any extra support or resources for their special needs. Support from voluntary organization and opportunities to meet parents of children with similar difficulties can also be a source of great support.
The assessment of autism tends to be conducted at child developmental centres or by child and adolescent mental health services by professionals such as paediatricians, psychologists, speech and language therapists or psychiatrists.
It usually involves detailed interviews with the childs parents/carers concentrating on the childs early development and current behaviour, direct play assessment with the child as well as collecting information from the childs nursery or school.
The childs GP can refer them to an appropriate specialist.
You May Like: Outgrow Autism
Common Conditions Among People With Autism
While many people with autism are misdiagnosed with other types of mental illness, many are also appropriately diagnosed with both autism and mental illness. In fact, mental illness is more common among people with autism than it is among the general population.
The most common co-occurring mental illnesses for people with autism include depression and anxiety.
It’s not completely clear why this may be the case. One theory suggests that there is a genetic link between autism and mental illness. Another theory points to the extreme challenges of living in the modern world with autism. The fact is that for many people with autism, it is anxiety-provoking and depressing to attempt to overcome social, sensory, and/or intellectual challenges that are simply part of who they are.
In addition to mental illness, many children and adults with autism receive additional developmental diagnoses. While it can be argued in many cases that the symptoms are associated with autism, it is sometimes helpful to know that a child is both autistic and, for example, diagnosable with ADHD, learning disabilities, hyperlexia, Savant Syndrome, or another disorder.
A secondary diagnosis, while it may or may not be completely appropriate, can sometimes provide direction for therapy, academic support, and services. Hopefully, in doing so, this could correct any potential misdiagnoses moving forward.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Autism
The onset of autism is usually apparent prior to or around three years of age.
However, for children who might have more subtle difficulties or are very able, the symptoms may be recognised only when they are older.
This is because some children are very well supported in their home and nurseries and their difficulties are not so apparent until they are expected to be more independent.
People also sometimes think that children will grow out of it, or their difficulties tend to be attributed to their personality or other issues, such as shyness or being naughty.
There are a range of early signs that parents tend to report. These include a childs avoidance of eye contact, a childs different way of communication, for example the child may not be sharing their interest or curiosity with others, although they may be able to request what they want.
Young children with autism spectrum may also have reduced non-verbal communication, and may not point or gesture. Some parents notice that their childs play may be different to that of their peers, for example lacking in creativity and imagination.
Many children with suspected autism may have difficulty in joining with other children and may prefer to play alone or with adults. Children with autism have delayed development of language, which tends to be one of the most frequent causes for concern.
However, it is also important to recognise specific strengths that children with autism often present with.
Read Also: Modern Treatment Programs For Autism Generally Involve
How Mental Illness Is Diagnosed And Treated
Diagnosis
Because of the wide range of mental illnesses in the books, along with the fact that many people have one or more co-occurring mental illnesses, diagnosing mental health problems can be challenging. Diagnosis of mental illnesses is made using specific criteria found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders. In general, mental illness can be classified as mild, moderate or severe. If more than one mental illness is present, mental health professionals will try to determine whether one led to or influenced another. For example, someone with social anxiety may also experience depression as a result of feeling isolated.
Treatment
For someone who is on the autism spectrum and also has a mental illness, treating the mental illness in the context of the developmental disorder is essential for success. People with autism should find a mental health provider who is experienced in treating people who are on the spectrum.
Treating mental illness, like treating autism, requires a highly individualized treatment plan. Ideally, treatment will include both medication and therapy, along with lifestyle changes that support good mental health.
Medication
Therapy
Some of the therapies used to treat mental illness include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Helps individuals identify and change dysfunctional thought patterns and develop skills for coping with negative thoughts and emotions
Interpersonal Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Interview Procedure And Data Analysis
Study participants chose to be interviewed either at home or at facilities at a university campus that they were familiar with while visiting through their participation in the cohort study. Interviews lasted about one and a half hours and were supported using a semi-structured interview guide. To elicit rich data, the interviews started with a card-sorting exercise that involved selecting phrases relating to autism, for example, anxiety, communication problems, introverted, nervous exhaustion and mental health, for example, anxiety, depression, inability to cope, stress levels, which interviewees believed described their experiences, and then allocated to either autism or mental health. The cards were developed with the projectâs two advisory panels, who guided the approach and provided words to include relating to autism and mental health. The selected cards were then used as prompts for the young adult to talk about their experiences and understandings of autism and mental health, and how they responded to, or managed, mental health issues. Participants were then asked to describe a time when they had experienced significant emotional distress or mental health difficulty. The interview then explored participantsâ perceptions and understanding of this experience, how they responded, and what support they received at the time.
Don’t Miss: What Are Good Toys For Autistic Toddlers
Signs Of Autism In Children
The signs of autism can change as children grow babies and toddlers show different signs of autism than children aged 4 and older.
Babies and toddlers
Signs of autism in babies and toddlers can include a number of things that affect different parts of their life and behaviour.
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- start talking later than most children
- seem less aware of others around them for example, they might not respond to their name being called
- make repetitive movements when excited or upset – for example flapping their hands, rocking back and forth, or making the same noise repeatedly
Autistic babies and toddlers might not:
- smile back when you smile at them
- point to show when they want something
- point to show you something they find interesting
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- spend a long time setting up toys in a certain way, and set them up the same way every time
- enjoy lining toys up in order, or watching parts of them move
Autistic babies and toddlers might not:
- seem interested in playing with other children their age
- seem to use their toys to make up stories or pretend they might also start pretend play at a later age than most children
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- react strongly to sounds, smells, touch, tastes, or things they can see for example, if they like the way a stuffed toy feels, they want to spend a lot of time stroking the toy
- become upset if given something to eat or drink thats new to them
- eat a limited range of foods
For Parents And Carers
If you look after someone who’s autistic, ask your council for a carer’s assessment.
This is an assessment to find out what support or financial benefits you might be able to get to help you care for an autistic person.
If you think you or your child needs help from a health professional, speak to a GP or the assessment team that diagnosed you.
They may be able to refer you to a specialist who can help, such as:
- an occupational therapist
- a speech and language therapist
- a mental health specialist
- problems with reading, writing and spelling
- clumsy movements and problems with organisation and following instructions
Extra support at school can often help.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Mental Health In Young Autistic People
What does “normal” mental health mean for autistic people? A new study, co-designed by academic researchers from the Centre for Research in Autism and Education and young autistic people from Ambitious about Autism, examines what “normal” mental health looks like in young autistic people and what happens if/when this changes.
More and more is being done to raise awareness of mental health problems at a public and a policy level, and understandably so. One in six adults has a common mental health condition and a fifth of adults have thought of taking their own life at some point . Young people are a particularly vulnerable group, given that most mental health conditions develop between childhood and adulthood and may be at their peak between the ages of 16-25 years. But what about mental health in young autistic people?
Although autism is not a mental health condition, around 70-80% of children and autistic adults have experienced mental health problems. This isnt an issue that has gone unnoticed, with autistic people, their families, and the people who work with them highlighting mental health as a priority area for research. Despite efforts to address this gap in knowledge, little work has explored the mental health needs of young autistic people.
When To See Your Gp
You may find the video on this page useful for understanding autism a bit more.
If you think that you may have Autism Spectrum Disorder, it is important that you meet with your GP to discuss your concerns. Your GP will refer you to the Primary Care Mental Health Service and they will complete an initial assessment with you. This information is used to make a referral to the CLASS clinic.
We understand that making appointments and visiting the GP can be difficult for some people. For additional support around vising your GP, please see this guide for adults who think they might be autistic.
Recommended Reading: What Are Good Toys For Autistic Toddlers