What Does Triad Of Impairments Mean
Autism is also known as Autistic Spectrum Disorder because the symptoms of autism vary a great deal along a spectrum from mild to severe. The ‘Triad of Impairment‘ is used to describe the main features all people with autism have difficulty with to some degree.
Simply so, what are the triad of impairments?
These are known as ‘the triad of impairments‘, or ‘the three impairments‘: 1. Social Interaction. Difficulty understanding social ‘rules’, behaviour and relationships, for example, appearing indifferent to other people or not understanding how to take turns.
who created the triad of impairments? It was Wing who, with her lifelong collaborator and friend Judith Gould, established in the 1970s the ‘triad of impairments’ that came to define autism.
Furthermore, what is meant by the triad of impairments in autism?
Traditionally the Triad of Impairments in autism are seen as. Difficulty with communication. Difficulty with behaviour or social interaction. Difficulty with social skills.
What are the 3 main characteristics of autism?
These are some of the characteristics of ASD:
- problems with social interaction with others.
- unusual interest in objects.
- need for sameness.
- great variation in abilities.
- under or over reaction to one or more of the five senses: sight, touch, taste, smell, or hearing.
- repeated actions or body movements.
You May Like Also
Understanding Impairment In Autism
There are many adults with autism, and many children. Whilst they can appear to be worlds apart in some aspects, they are very similar in others. It must be remembered that the world can be a very unpredictable and frightening place to be, to someone with Autism.
This may explain why one common characteristic is a resistance to change. There are atypical autism traits, and inflexibility can for many ASD people. They may appear simply as a person who is very set in their ways and enjoys a fixed routine. Part of the behaviour in autism is an aversion to anything new, and any bending of or changes to the rules can result in angry outbursts or emotional distress.
Common habits that will have a fixed routine can be travelling the same route to and from school/work, wearing the same clothes, eating the exact the same food for all meals.
Change to this routine can be very distressing and cause a great deal of anxiousness. Big events can also trigger anxiety, such as holidays, christmas, changing schools/jobs, or having to attend a large social engagement.
Do Musicians With Perfect Pitch Have More Autism Traits Than Musicians Without Perfect Pitch An Empirical Study
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience , University of Aarhus, Aarhus, Denmark, The Royal Academy of Music, Aarhus/Aalborg, Denmark
- Eduardo A. Garza-Villarreal,
Affiliations Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience , University of Aarhus, Aarhus, Denmark, The Royal Academy of Music, Aarhus/Aalborg, Denmark, Department of Neurology, University Hospital, and Neuroscience Unit, Center for Research and Development in Health Sciences , Universidad Autonoma de Nuevo Leon, Nuevo Leon, Mexico
-
Affiliation Department of Psychology, Goldsmiths University of London, London, United Kingdom
Read Also: Level 2 Asd
Molecular Readouts Of Growth
Mounting evidence has highlighted key growth signaling pathways that are frequently perturbed in patients with ASD as well as mouse models of autism. This section will cover these key molecular readouts of growth in autism, including dysregulated growth factor, mammalian target of rapamycin , and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling. Characterizing how the regulators and downstream correlates of these growth pathways are dysregulated in ASD will allow us to better classify forms of autism into broad, but more homogeneous subtypes. This knowledge will be valuable for diagnosis of under- or over-growth phenotypic subtypes of ASD, selection of homogeneous patient populations for more rigorously controlled studies, and a potential biomarker that can be used to potentially assess efficacy of clinical trials. We propose that broadly stratifying patient populations in terms of under- or over-growth phenotypes based on the following signaling pathways would facilitate mechanistic and therapeutic insights into ASD, without necessitating an impractical fine categorization by precise genetic etiology.
Improved Methods For Subtyping
The emphasis on specificity in the DSM-5 improves researchers ability to identify samples of interest. In addition, DSM-5 introduces a dimensional approach that allows researchers to capture variability within samples in two important ways. First, although DSM-5 requires that symptoms from both the RRB and social-communication domains are present, it allows individual variation in the quality and quantity of specific RRBs and social-communication deficits. Second, DSM-5 formally recognizes many features that are not specific to ASD by which researchers can qualify ASD diagnoses.
Some individuals with ASD have unique patterns of social-communication deficits and RRBs, suggesting a possible avenue by which ASD subgroups might be defined. For example, results from a longitudinal study suggested that RRB quantity at 2 years of age is inversely related to language skills at 9 years. With respect to the quality of symptoms, there is some evidence to suggest that insistence on sameness behaviors are distinct from other core ASD features and from symptoms of anxiety. Insistence on sameness behaviors also seem to be independent of autism symptom severity, age, and intelligence quotient , suggesting that it may be a useful qualitative characteristic by which to identify ASD subtypes.
Figure 1
You May Like: Creating A Visual Schedule Autism
Using Social Skills Stories As A Strategy That Will Help Teach Social And Communication Skills To Children With Autism
A diagnosis of autism spectrum can be upsetting for many parents all of a sudden your world is upside down. However a diagnosis of autism spectrum need not be met with fear. Autism spectrum is more common than you probably thought with 1 in every 150 babies born being given a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
As with typically developing children, all children with autism will also develop at varying rates, with no two kids on the spectrum having the same autism characteristics.
Some children with Low functioning autism may have other problems such as little or no speech, seizures and will normally have educational difficulties.
Those children with autism characteristics such as asperger syndrome will have average or above intelligence, however their speech may still develop slowly but will develop. This set of individuals are often referred to as the little professor or geeks!
However typical to all children with autism ARE The Triad of Autistic Impairments or social skills deficits.
Each individuals deficits will vary,some kids on the spectrum may display severe social deficits whilst others may display less severe social deficits and be able to function quite well socially.
There is no cure for autism spectrum but there are various treatments for autism that will help teach social and communication skills to children with autism
Terminology And Distinction From Schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism while in 2007 it was believed to be one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed, parents continue to feel social stigma in situations where their child’s autistic behavior is perceived negatively, and many primary care physicians and medical specialists express some beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely.Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
Read Also: What Does Low Functioning Autism Mean
Autism Susceptibility Candidate 2
The autism susceptibility candidate 2 was initially suspected to be associated with ASD found in a pair of monozygotic twins which had a de novo balanced translocation which disrupted the AUTS2 locus . It has been reported that a subset of patients harboring deletions within exonic regions of AUTS2 present with a short stature, facial dysmorphism, and microcephaly . Given these phenotypes, AUTS2 mutations are thought to lead to predominately âundergrowthâ phenotypes. Since the initial identification of the AUTS2 locus, there have been over 30 additional individuals with cognitive disorders ranging from ASD to epilepsy, attention deficit disorder, intellectual disability and developmental delay harboring disruptions in both the coding and noncoding regions of the AUTS2 locus . Given that alteration of AUTS2 levels results in a myriad of neuronal deficits, it is not surprising that AUTS2 is highly expressed in developing brain regions important for higher order cognitive functions.
Quantitative Variation In Autistic Symptomatology In Affected Families
Numerous studies, using various methods of measurement, have documented the aggregation of autistic syndromes, symptoms, or traits in the close relatives of children with autism. Such observations of familial aggregation have ranged from a full diagnosis of autistic disorder , to milder autistic syndromes , to subclinical behavioral features of the autistic syndrome , to the broader autism phenotype, including personality traits that are akin to autistic symptoms , and to developmental impairments or delays that more specifically involve language .
Lauritsen et al. additionally observed that the siblings of children with Asperger Syndrome in the Danish National Register had a 13 times higher than general population risk for the development of full-blown autism, which constitutes some of the strongest evidence to date that the two disorders share common underlying genetic susceptibility factors. Studies that have carefully differentiated simplex autism from multiplex autism have suggested that familial aggregation of subclinical autistic traits may occur only in multiplex autism , providing further evidence for differentiation of mechanisms of genetic transmission for sporadic versus familial forms of the disorder.
Figure 1
Distribution of teacher-report SRS scores for male siblings of children with autism in single-incidence and multiple-incidence families.
You May Like: Nick Eh 30 Hide And Seek
Relevance For Future Research Efforts
Many large-scale ASD studies have now been conducted, which have included mixed patient populations, with variations in multiple critical factors including age, diagnosis, and symptom severity. However, it has remained difficult to extract meaningful conclusions from these studies, in part, since molecular changes are likely to be different among forms of ASD with differing underlying etiologies. Identifying common molecular pathways that are dysregulated among various genetic causes of ASD is an important step in effectively stratifying ASD into endophenotypes from which therapeutic responses can be more readily anticipated. Shrinking the heterogeneity of the disorder would also make the study of ASD more tractable, allowing investigations in monogenic mouse models to be more appropriately applied to other genetic forms of ASD. Utilizing overgrowth and undergrowth phenotypes as a basis for this stratification is useful since these phenotypes are present across multiple genetic causes of ASD and occur early in the development of disease.
Autism Brain Development How It Affects Learning
According to a neurosurgeon, ASD is a pervasive developmental disorder in the brain that affects four times more males than females. Some research suggests autism is caused by genetic factors that interfere with normal brain development, or environmental factors, such as the effects of pollution or the damage caused by viruses. However how autism is caused is still under research. Autism Spectrum Disorder is normally detected in children before the age of three and is a life long condition.
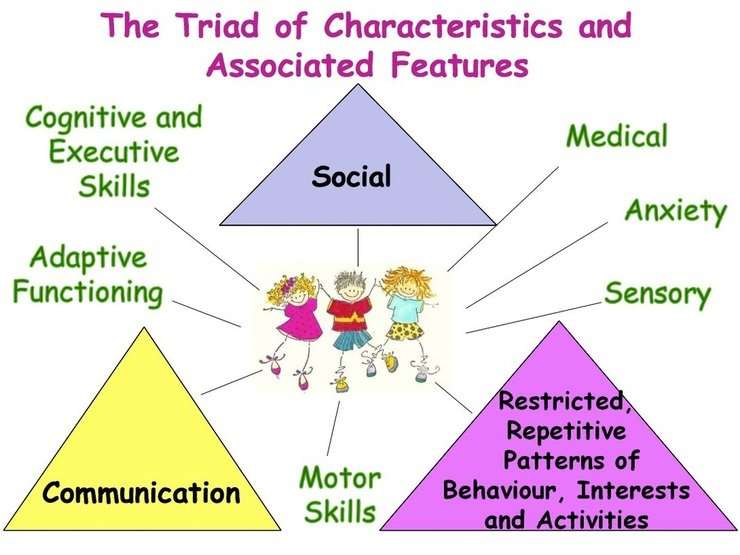
No two people are ever the same and this runs true with Autism Spectrum Disorder which affects individuals in various ways. The traits of autism are called the triad of autistic impairments. Every child with ASD will have to varying degrees the triad of autistic impairments.
The triad of autistic impairments means difficulties with three factors social communication, social interaction and imagination skills and behaviours. Probably the most obvious of the traits of autism is the persons ability to communicate both verbally and non-verbally.
So when considering autism brain development how it affects learning its good to remember all kids with autism will have marked difficulties with communication both verbal and non-verbal skills.
A child with ASD will have difficulties understanding things that we probably take for granted like jokes, metaphors wit and slang, this form of communication may be incomprehensible to a child with ASD.
Read Also: Is It Okay To Self Diagnose Autism
Cognitive And Adaptive Functioning
In addition to assessing whether or not a comorbid classification of ID is warranted, an individuals abilities within cognitive domains should also be assessed . Another key consideration may be patterns of discrepancy between cognitive and adaptive abilities, as some individuals with ASD have difficulty with daily living skills despite having adequate cognitive skills.
Three Areas Of Difficulty
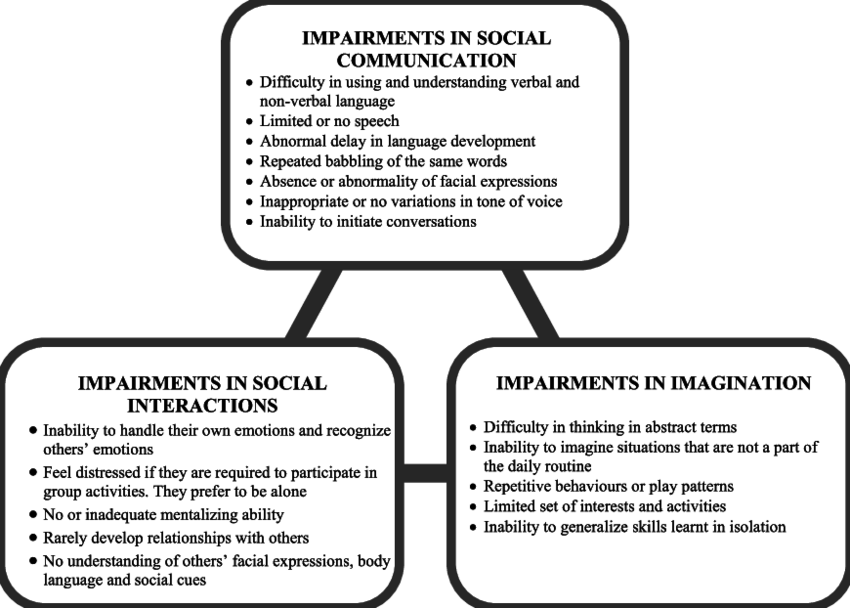
Autism is experienced differently by individuals, but there are three areas of difficulty which are commonly used to describe the condition, and are also used in the criteria when diagnosing autism. These are known as the triad of impairments. While people may experience different degrees of impairment for each part of the triad, people with autism experience the following:
- difficulties with social interaction finding it hard to understand, communicate and recognise how other people are feeling.
- difficulties with social communication struggling with verbal and non-verbal language
- difficulties with social imagination finding it hard to imagine what others are thinking or alternatives to their own routines.
As a result, people with autism typically struggle with the rules of social engagement, such as when to speak, when to laugh and when to empathise. While many people with autism have good language skills, others will speak little or not at all, though this does not mean they cannot communicate in other ways. Autistic people typically prefer communication to be simple and clear.
Many autistic people also have the following.
- PRINT:
You May Like: Asd Level 2 Symptoms
P112 Copy Number Variation
CNV at the human chromosome 16p11.2 locus is among the most common risk variants associated with ASD, accounting for approximately 0.5â1% of all cases . In fact, duplications and deletions in this ~600 kB region of 16p11.2 have been linked to a number of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric conditions, including intellectual disability, schizophrenia, epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and obesity . Several reports indicate that reciprocal phenotypes occur as a result of deletion or duplication of the approximately 27 protein-coding genes found in the affected region. Therefore, 16p11.2 CNVs present a unique model to explore the effects of altered dosage of genes within this region on underlying growth pathway correlates.
CNVs at 16p11.2 also confer highly penetrant and opposing effects on body mass index . Parallel to the effects observed with head size, deletion of this region often results in early-onset obesity, while duplication is associated with significantly reduced postnatal body weight and BMI . Importantly, a study that analyzed the co-occurrence of head size and BMI phenotypes observed a higher incidence of the 16p11.2 deletion among cohorts ascertained for both developmental delay and obesity , as opposed to cohorts assessed for either outcome alone . A potential avenue for future investigation in mouse model systems is to test the involvement of common molecular pathways in both neuronal and somatic growth defects in 16p11.2 CNVs.
Triad Of Impairment Social Communication
There are many difficulties that people with autism and asperger syndrome share. These are difficulties in understanding and translating body language, sarcasm, and metaphors. Of course, not all people displaying these charactistics have autism or aspergers.
Common difficulties for people with ASD include:
- Difficulties in engage in the flow of social conversation. Individuals with autism may shy away from social situations to avoid engaging with others. The worries of engagement, coupled with the loneliness, can lead to anxiety or depression.
- Social communication problems can arise by the unusual use of gestures, facial expressions, and gazes. This is different to the avoidance of eye contact or gaze that shy or depressed people show.
- Difficulties with interpreting body language, facial expressions and tones of voice from other people. Peopl with autism can struggle to understand the contect of what is being said, and this can lead to mi-understandings. This can affect releationship, school life and working life.
- Perception of an event from another persons point of view can be a real struggle for people with autism.
These difficulties are just some of the issues that people with autism face, and issues that can have a detrimental affect on their life andmental wellbeing.
Don’t Miss: Examples Of Restricted Repetitive Behaviors In Autism
Autism Hygiene And Self
Having deficits with social skills like hygiene and self-help skills is problematic.
For many individuals with autism spectrum disorder learning social skills can be confusing and at times even painful!
This is due to autistic sensory processing issues and the Triad of autistic impairments or social skills deficits, which are common symptoms for most individuals with autism spectrum disorder.
Having autistic sensory processing issues can mean your child is hyper or hypo sensitive to stimuli touch, sound, taste, smell and visual sensations. For example even a simple hygiene skill like brushing your teeth can cause discomfort even actual pain.
The triad of autistic impairments or social skills deficits means your child WILL struggle with social, communication and imagination skills like hygiene and self-help skills.
Therefore Autism hygiene and self-help skills will need direct teaching. This can be achieved using visual supports such as social stories, visual social story cards, flash cards and PECS
For example Jason is a fourteen year old autistic teen, he is of average intelligence and has good verbal skills.
Jason is going through puberty and has started to sweat, which can be quite unpleasant for those around Jason.
Jasons lack of personal hygiene has become an issue in class with his peers. But for Jason a lack of personal hygiene is NOT an issue and he is oblivious to the need for better hygiene he appears NOT TO NOTICE the name calling.