The Brain Of An Autistic Person Simply Works Differently
Autistic people can find communicating and engaging with others hard. But a typical autistic person does not exist, and autistic traits may be in all of us.
Pi: Some autistic people can memorize numbers very well
A whole range of different conditions belong to the autism spectrum disorder or autism, a life-long neurodevelopmental disorder that affects how people communicate and interact with the world.
One in 160 children has autism but several recent studies have reported rates that are substantially higher, according to the World Health Organization .
ASD is considered a developmental disorder because although it can be diagnosed later in life it begins in early childhood and tends to persist into adolescence and adulthood.
The level of intellectual functioning in autistic people varies hugely, ranging from profound impairment to superior non-verbal cognitive skills. It is estimated that around 50% of people with autism also suffer from an intellectual disability, according to the WHO.
There is a wide range of symptoms in autistic people. Some of the main symptoms include communication problems like delayed speech development, and difficulty in social interactions, such as making friends, maintaining eye contact, reading people’s body language or facial expressions, and expressing how they feel. Repetitive behaviors and strict routines may also be noticed, like repetitive body movements or finding it difficult to adjust even to small changes.
How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Treated
There is no cure for autism, but treatment can make a big difference. The younger kids are when they start treatment, the better.
Doctors, therapists, and special education teachers can help kids learn to talk, play, and learn. Therapists also help kids learn about making friends, taking turns, and getting along.
Tms Treatment For Autism: What Is It And Does It Work
Talk about transcranial magnetic stimulation, or TMS therapy, is raising hopes of parents who wonder if the treatment could work for their child with autism spectrum disorder .
Parents with children on the spectrum are wary of the term cure. For some, its because theyve been disappointed by snakeoil and false hope more than they care to remember for others, the term cure seems more fitting to a disease. When you talk with parents of kids on the spectrum, most are willing to do anything to help their children thrive while firmly embracing who he/she is.
Read Also: Can You Be Slightly Autistic
Can Someone With Autism Have A Normal Child
Can an adult with autism be a successful parent? The answer is absolutely yes, under the right circumstances. While a person with moderate or severe autism is unlikely to have the skills to parent a child, many people with high-functioning autism are ready, willing, and able to take on the challenges of raising kids.
How Does An Autistic Brain Develop
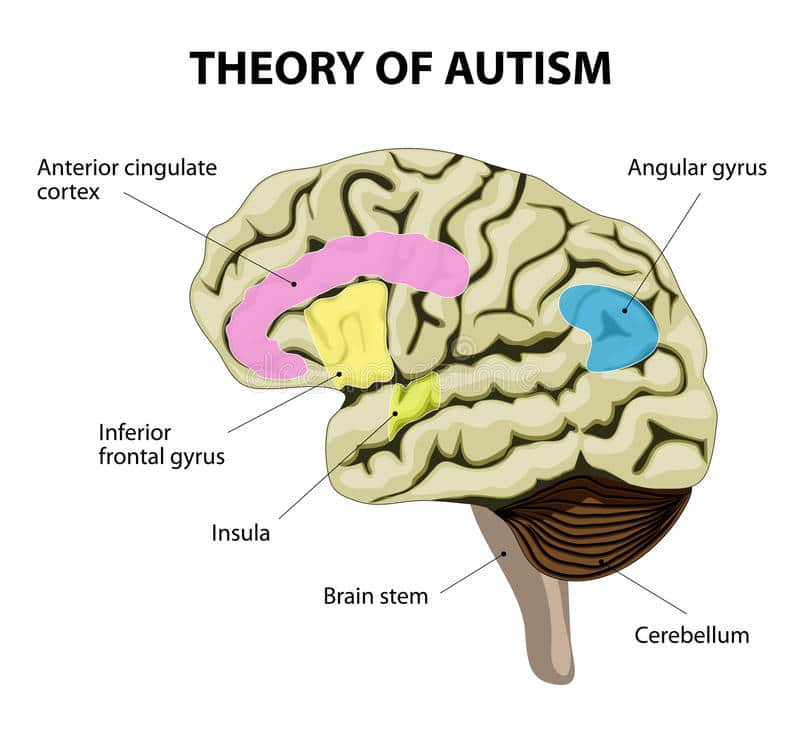
Deviant brain growth in autism occurs at the very time when the formation of cerebral circuitry is at its most exuberant and vulnerable stage, and it may signal disruption of this process of circuit formation. The resulting aberrant connectivity and dysfunction may lead to the development of autistic behaviors.
Recommended Reading: Dsm 5 Criteria Autism
What Happens As The Autistic Brain Ages
ASD starts in early childhood and continues into adulthood. Many of the symptoms and the brain patterns normalize with age but, along the way, a lot of complex development takes place.
For instance, 20 to 30 percent of people living with autism develop seizure disorders. But the reason isnt really understood. It may just be that there’s this chicken and egg issue, or sometimes the seizure disorder can predispose them to autism, and sometimes it might be the other way around, and we really understand that link yet, Dr. Anderson says.
Then, there are other mental health conditions that come into play. It is common for people living with ASD to also experience anxiety, depression and OCDmore so than in the general population.
One thing is for sure, society can benefit from the autistic brain. Many people with autism don’t see it as a disorder. They may see it as a gift, Dr. Anderson says. Society generates enormous benefits from individuals with autism. They’re so good at tasks that are really important to society. And I think it’s important to always emphasize that it’s in society’s best interest to help create environments where people with different brain structures and ways of behaving can thrive.
Breaking Down Current Theories About Autism And The Brain
For my first few posts on Psychology Today, I wanted to give an overview of the most popular theories about the brain basis of autism. Over the first two blog posts, I’ll discuss four theoriesbut keep in mind there are others as well.
In this first post, I will review the social motivation hypothesis and overly intense world hypothesis.
Social Motivation Hypothesis
One of the core symptoms of autism is a lack of social interaction, especially for young children. Parents often notice that their child with autism is less likely to show them toys or to spontaneously interact with other children or adults compared to neurotypical children.
The social motivation hypothesis proposes that this might be due to the brains reward system. We know that for neurotypical individuals, social interactions are rewarding. For example, research has shown that eye contact with attractive faces activates the reward centers of the brain . The idea behind the social motivation hypothesis is that maybe children with autism do not find social interactions as rewarding as their neurotypical peerswhich would explain why children with autism are less likely to initiate social interaction.
Neuroscience research from my lab , and others have provided evidence for the social motivation hypothesis. We found that children with autism have less reward-related brain activity than their neurotypical peers when they are anticipating social information .
Recommended Reading: What Do Autistic People Look Like
Brains Of Teens With Autism Spectrum Disorder Work Differently
Understanding the developing mind and brain of a teenager with all of the changes they are going through can be extremely difficult. This difficulty can be compounded when you have a teen with Autism Spectrum Disorder as their brain works differently from neurotypical teenagers. To assist your teen as they journey through adolescence, it can be helpful to understand how teenagers brains work differently if they are on the spectrum.
Brain Functions In Asd
At a neuroimaging level, functional MRI and magnetoencephalography enable the exploration of atypical brain functions of ASD. Many studies have shown that structural differences between ASD and TD are different depend on age. As structural differences are related to different functions of brain domain, it is necessary to observe the brain functions across the human lifespan. According to the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria, social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behaviors, we will review recent studies about the atypical brain functions of ASD based on two core features in age-dependent manner.
Also Check: Can You Join The Police With Autism
Is There A Defective Gene Associated With Autism
In the universitys study, titled In autism, too many brain connections may be at root of condition, it was suggested that some diverse autistic symptoms may point to miscommunication among cells in the brain of the person with autism.
Senior author Azad Bonni, who is Edison Professor of Neuroscience at Washington University School of Medicine, stated: This study raises the possibility that there may be too many synapses in the brains of patients with autism.
You might think that having more synapses would make the brain work better, but that doesnt seem to be the case. An increased number of synapses creates miscommunication among neurons in the developing brain that correlates with impairments like learning, although we dont know how, he continued.
Do These Differences Impact Symptoms
Most likely the result of these connections manifest into the signs and the symptoms that we see. However, Dr. Anderson cautions that it is hard to know exactly what brain connection correlates to what sign. Ultimately, there’s still an awful lot that we need to know, he says. Just looking at that brain imaging, we aren’t really able to explain all of the behaviors that we see.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Different Levels Of Autism
A Neuroscientific View Of How Autism Affects The Brain
How autism affects the brain is a topic that plays on peoples minds if they are coming to terms with a diagnosis or have limited understanding of neurodivergence. The good news is there are scientific studies that can help answer some questionsalthough more research is needed.
Since autism is considered a neurodivergent diagnosis, it is important to ask how it impacts brain development, brain activity, and how does someone with autism processing information differently affect daily functioning?
Scans of a neurotypical and neurodivergent brain could hold some answers, as well show how the brain is shaped, how it grows, and how activity in the brain hemispheres differs and is similar to neurotypical individuals.
Does Autism Come From The Mother Or Father
The team found that mothers passed only half of their structural variants on to their autistic childrena frequency that would be expected by chance alonesuggesting that variants inherited from mothers were not associated with autism. But surprisingly, fathers did pass on substantially more than 50% of their variants.
Recommended Reading: How To Help Autistic Child With Social Skills
What Characteristics Do People With Autism Have
No two individuals in this world are ever the same! However, there are some characteristics of autism spectrum disorder that are common across every ethnic and socioeconomic group. These characteristics can affect how an autistic person is able to communicate, interact with others, and whether they have learning abilities/differences, and different behaviors.
Some traits in autistic children can be detected as early as infancy. These include if the infant hyper-focuses on objects for extended periods, doesnt make eye contact, and doesnt really babble or meet some other recommended developmental milestones.
Autism is a spectrum disorder, and how it presents can vary depending on the severity of autism symptoms. Those symptoms can include, but not be limited to, social/emotional responses, difficulty in social interaction, preferred routines and environments, and repetitive behaviors.
People With Autism Have More Symmetrical Brains Heres What That Could Mean
In spite of how they appear, the left and right hemispheres of the human brain tend to be far from perfect reflections of each other. Some neurological disorders can affect that imbalance, causing the two halves to appear strikingly alike.
So far, studies on whether autism is among those conditions have been less than convincing. To get a more definitive answer, researchers analysed thousands of brains and showed there is slightly more symmetry for those on the spectrum.
But what does that really mean?
To get this answer, scientists from the Enhancing Neuro-Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis consortium collected decades of brain scans from more than 1,700 individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder and more than 1,800 with no diagnosis.
The consortium were hardly strangers to analysing huge banks of data, having only recently conducted a similar study on ASD brain anatomy involving more than 3,000 subjects.
The condition covers a spectrum of characteristics that can make life a little more challenging for some, affecting their ability to socialise, communicate, and process stimuli.
With such variation in behaviours, sensations, and impact, tracing the traits making up ASD down to simple neurological differences is no easy task.
Doing so could help make the disorder easier to diagnose and lead to novel therapies, opening the way to providing better methods of assistance for those who need it.
This research was published in Nature Communications.
Don’t Miss: Video Games And Adhd
Brain Connectivity In Asd
The brain is a structural and functional system that has features of complex networks . Early brain imaging studies have focused on region specific differences in activity however, accumulated data implicate an important role of brain network activity in the brain function . Brain connectivity can be divided into functional and structural connectivity: temporal similarities of brain activity in multiple regions and physical connections between the brain regions. A number of studies using the brain imaging techniques such as fMRI and diffusion tensor image identified abnormal brain connectivity in individuals with ASD. Long-range cortical hypo-connectivity theory has been largely supported by many investigators , even there are some opposite reports to show hyper-connectivity in ASD . Other investigators also demonstrated that local-range hyper-connectivity , however, these results are controversial and the agreement on terminology, local- and long-range, is still lacking.
Thus, below we mainly focused on the global connectivity depending on the developmental stage.
White Matter: Connecting The Clinical Dots
The second study, also published in Biological Psychiatry, linked changes in the brains white matter growth with autism traits in some children.
The researchers used a type of MRI scan called diffusion-weighted imaging, which allowed them to look at white matter regions, or tracts, in the brain. White matter provides the structural connections in the brain, allowing different regions to communicate with each other.
The study included 125 children with autism and 69 typically developing children who served as controls, between the ages of 2.5 and 7.
The researchers found that the development of the white matter tracts in the brain was linked to changes in autism symptom severity. They observed slower development in children whose symptom severity increased over time, and faster development in those with decreased severity over time.
From a biological standpoint, this emphasizes the role of white matter development in autism and autism symptoms, said Derek Sayre Andrews, postdoctoral scholar at the MIND Institute and lead author on the paper. We hope that in the future, measurements like this can identify children who would benefit from more intensive intervention and serve as a marker to determine the effectiveness of an intervention for a particular child, he said.
Also Check: Colleges With Autism Programs
So Can Brain Imaging Be Used To Diagnose Autism
There is evidence that using technologies like MRI and DTI can help with the diagnosis of autism. However, it is not conclusive that using only these imaging tools will give concrete diagnosis of autism.
There are so many aspects to consider that this technology would not be able to detect in the way that assessments do. Things like language production and use, social interactions, the ability to read body language and facial expressions, among other social/emotional cues.
There are other complex neurodevelopmental disorders that these imaging techniques may be able to better detect, like schizophrenia. The thought that autism affects brain activity and that autistic brain ages can alter brain regions can also affect how these images are read and perceived.
With those points, and the fact that there are still plenty of autism related studies being done, it is hard to say if imaging alone can detect and diagnose autism. There are plenty of assessments and therapies currently used that have helped move the study of autism spectrum disorder forward, and help those affected learn necessary skills to interact and communicate with their environment.
References
Cheon, K., Ha, S., Kim, N., Sim, H., & Sohn, I. . Characteristics of Brains in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Structure, Function and Connectivity across the Lifespan. US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health.
Support Autism Parenting Magazine
Autism & The Lobes Of The Brain
Additionally, within each hemisphere of the brain, there are four lobes: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Within these lobes are structures that control everything the body does, from movement to thinking. On top of the lobes is the cerebral cortex, where information processing takes place.
The greater the surface area of the cerebral cortex, the more information the brain is capable of processing. The brain has folds, to add to the surface area of the cerebral cortex. Researchers at San Diego State University have found evidence that suggests that the folds develop differently in people with autism. In autistic brains, there is much more folding in some of both the left and right lobes.
The changes have been connected to modifications in network connectivity in neurons. The weaker a connection, the deeper the folds are. Other research has indicated that language production and processing are altered.
Yet, says PsyCom, the neurobiology of an autistic brain is still hidden. Some experts have said that the more they study brains affected by autism, the more they realize that it may not be so much about the hardware as the software. It may be that the timing of the brain activity is different, affecting how the signals from one region of the brain being sent to another get distorted. It might be that as the autistic brain ages, the aging process brings about more changes that impact the development of autistic symptoms.
You May Like: How To Prevent Having A Child With Autism
What Part Does The Cerebellum Play In Autism
The study found there may be more involvement of the cerebellum in the brain of people with autism than originally thought. It found that, although the cerebellum was known for motor skills, it may also be involved in other functions of people with autism, like attention to detail, for example.
Professor Bonni and his colleagues have continued research on this protein and the connection to autism. He believes that excessive communication and connections between neurons could be a contributing factor, but feels more studies need to be done.
He states that if this connection does turn out to be true, there may be ways to control the number of synapses in the brain. This could help those with this gene mutation and other people with autism also.
Autistic Brains Organised Differently Say Scientists
People with autism use their brains differently from other people, which may explain why some have extraordinary abilities to remember and draw objects in detail, according to new research.
University of Montreal scientists say in autistic people, the brain areas that deal with visual information are highly developed.
Other brain areas are less active.
The National Autistic Society says the findings significantly increase understanding of the condition.
The research, published in the journal Human Brain Mapping, pulls together 15 years of data on the way the autistic brain works.
Better at visual tasks
It suggests that the brains of autistic people are organised differently from those of other people the area at the back of the brain, which processes visual information, is more highly developed.
That leaves less brain capacity in areas which deal with decision-making and planning.
That may be why people with autism can be better than others at carrying out some types of visual tasks.
For example, some are able to draw highly accurate and detailed images from memory.
However, they can find it difficult to interpret things like facial expressions.
The condition varies in severity, with some people functioning well, but others completely unable to take part in normal society.
The researchers believe their findings may lead towards new ways of helping people to live with the condition.
Understanding autism
Autism experts regard the research findings as significant.
Read Also: Inattentive Adhd Symptoms Adults