What Are The 5 Different Types Of Autism
The different kinds of autism include:
- Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder , previously called Aspergers Syndrome;
- Rhett Syndrome, although this has been removed from the spectrum;
- Childhood Disintegrative Disorder ;
- Kanners Syndrome or Classic Autistic Disorder; and
- Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified .
Autism Spectrum Disorder Level : Requiring Substantial Support
According to DSM-5, individuals with level 2 autism require substantial support. Generally, they need more support than individuals with level 1 autism. Even with support, they might have a hard time adjusting to changes in the environment around them.
There are a variety of therapies can help them. For example, sensory integration therapyhelps individuals learn how to deal with sensory input. In other respect, individuals with level 2 autism tend to benefit from occupational therapy. This type of therapy helps them develop the skills that they need to complete daily tasks in order to make easier their daily routines, such as decision-making or job-related skills.
A person with level 2 autism, meaning that with moderate autism, may exhibit normal or below normal mental functioning. They may have some degree of mental retardation or they may have a normal IQ of about 100. This person with level 2 autism might find self-care tasks difficult and challenging.
The symptoms which are associated with level 2 autism include more severe lack of both verbal and nonverbal communication skills compared to level 1 autism. To put it in a different way, they have a significant lack of verbal and nonverbal communication skills. They might have an unusual or reduced response to social cues, communication or interactions. They mostly use overly simple sentences during the conversation.
Challenges In Severe Autism
According to some researchers, the extreme behaviors seen in severe autism are very often the result of either frustration, sensory overload, or physical pain. Because people with severe autism have such a hard time communicating their needs verbally, they may find expression in behaviors that can be frightening to their caregivers and others.
If the behaviors can’t be addressed or managed, they can actually be dangerous; in many cases, it becomes impossible for parents or siblings to live safely with a severely autistic teen or adult.
Also Check: Is The Good Doctor Actor Really Autistic
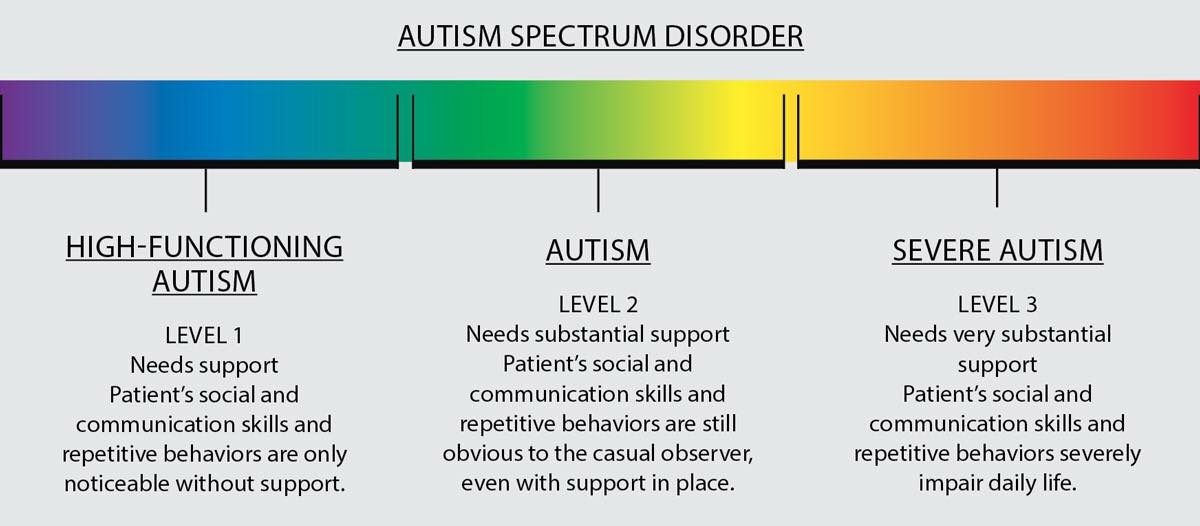
What Are The 3 Levels Of Autism
Pipkin said the most recent edition of the “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders” has provided three levels of severity in order to better individualize autism diagnoses and communicate a persons need for support.
She provided helpful markers in better understanding the levels of autism:
At Level One, an individual is expected to need some degree of support based on their degree of impairment related to social communication and restricted or repetitive behaviors, Pipkin said. They may be someone who, with the appropriate supports, can function fairly well in most settings. However, upon closer inspection they may be seen to struggle in the back-and-forth aspects of conversation or lack close friends due to their lack of interest or inability to initiate friendships.
At Level Two, an individual is likely to require substantial support based on their social communication abilities and their restricted or repetitive behaviors, Pipkin explained.
Related: Parents and loved ones of children with autism tell what they wish they’d known earlier.
Variations In The Level Of Impairments
Each person with autism spectrum disorder is different from each other. Thats why there are variations in the level of each functional impairment in the same person. In addition, even among individuals who get diagnosed with the same level of autism, it can vary. Some dysfunctions or impairments might be more prominent in some individuals than in others.
Also, the functioning level which is assigned to a child or adult with autism spectrum disorder serves as a guide for what treatments, what interventions, and what kind of support the person needs in order to achieve the best functional outcome.
Due to the variations, even individuals with severe symptoms of autism may have extraordinary talents and skills. Nonverbal does not mean the same thing as incapable. Moreover, there are some individuals with mild symptoms who have also severe symptoms.
In addition, many individuals with autism have splinter skills, which means that they are able to do a specific task that does not generalize to other tasks. Splinter skills are the abilities that are completely real and legitimate, but very limited in scope.
Read Also: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Other Terminology You May Have Heard For Types Of Autism
Terms like mild or high functioning arent official diagnoses. Some people find these terms useful, but many in the autistic community havent found them to be helpful or accurate, largely due to the range of abilities that can be present in an autistic person.
You may also have heard about three levels of autism, with level 1 being the mildest and level 3 the most severe.
Terms For Types Of Autism That Are No Longer Used Today
When autism was categorized by types, the lines between the different types of autism could be blurry. Diagnosis was, and still is, complicated and often stressful for families.
If you or your child received a diagnosis before the DSM-5 changed, you may still be using the older terminology . Thats OK. Your doctor may continue to use those terms if they help.
You May Like: How To Tell If My Baby Is Autistic
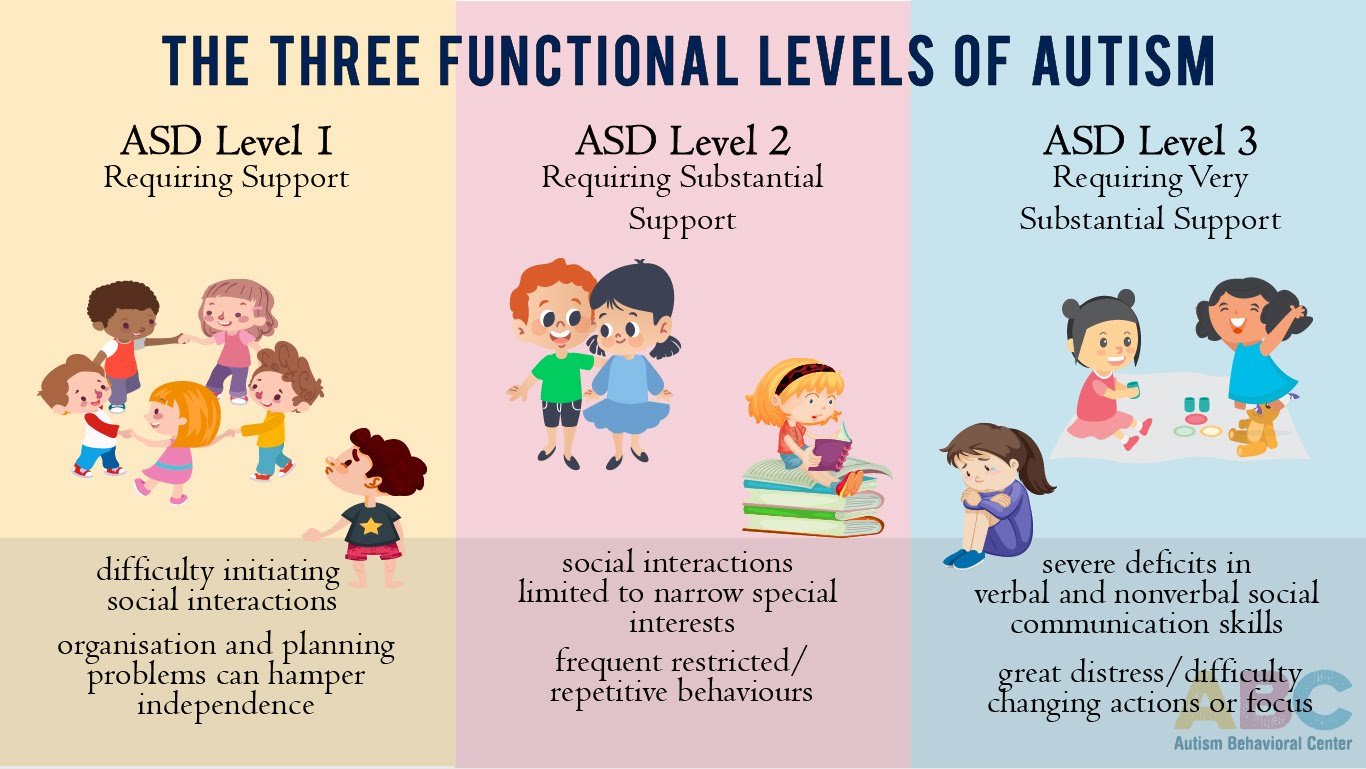
Level 3 Asd: Requiring Very Substantial Support
This level is the most severe form of autism spectrum disorder. People at Level 3 exhibit significant difficulties with social communication as well as social skills.
People with Level 3 ASD also have restricted and repetitive behaviors to the extent that they get in the way of functioning independently in their daily lives and activities. They have extreme difficulty coping with changes. Changes cause great stress and difficulty.
Some people with Level 3 ASD can communicate with words. However, many of them do not communicate verbally or do not use many words in communication. They may be over- or under-sensitive to certain sensory inputs.
Individuals with Level 3 ASD speak with few words, they rarely initiate interaction. When they do initiate interaction, it is limited to meeting needs only. They engage in restricted and repetitive behaviors like echolalia, rocking back and forth, or spinning things.
Those at Level 3 ASD require very substantial support in order to acquire skills to help them in their daily lives.
Level : Requires Support
- Social communication has noticeable impairments! Under this level, a patient may be able to talk in proper/meaningful sentences. However, interactions are missed.
- Trouble to initiate social interactions.
- There is a lack of to and fro flow of conversation between people.
- Inability to socialise and make friends.
- Inability to organise and strategies themselves.
Also Check: Can You Outgrow Autism
Why The Types Of Autism Shifted To One Diagnosis
The current diagnosis autism spectrum disorder debuted in the latest edition of the DSM , published in 2013. Prior to that, they were categorized as five different types of autism: autistic disorder, pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified , Asperger syndrome, Childhood Disintegrative Disorder and Rett Syndrome .;
But research found that these categories were not reliably diagnosed, according to Thomas W. Frazier, a doctor of clinical psychology and Autism Speaks chief science officer. The diagnosis would shift over time and was partly dependent on the provider who made the diagnosis, he says.
Therefore, experts landed on a single diagnosis, which allows for a more nuanced understanding of the disorder. While people on the autism spectrum share common characteristics related to social communication, repetitive, restricted behaviors, sensory issues, etc., there is great diversity within the autism spectrum, says Stephen Shore, a doctor of education and clinical assistant professor at Adelphi Universitys College of Education and Health Sciences in New York. When youve met one person on the autism spectrum, youve met one person on the autism spectrum.;
How Diagnosis Of Autism Changed With Dsm
The DSM is the official publication of the American Psychiatric Association which defines psychiatric and developmental disorders.;While it has no legal status, the DSM does have an enormous impact on the way insurers, schools, and other service providers think about and treat autism.
Until 2013, the DSM described the autism spectrum as a disorder that included five distinct diagnoses. Asperger syndrome was, essentially, a synonym for “high functioning autism,” while autistic disorder meant almost the same thing as “severe autism.” People with PDD-NOS had some but not all of the symptoms of autism . Rett syndrome and Fragile X syndrome, rare genetic disorders, were also considered to be part of the autism spectrum.
Then, in May 2013, the DSM-5 was published. The DSM-5, unlike the DSM-IV, defines autism as;a single spectrum disorder,;with a set of criteria describing symptoms in the areas of;social communication,;behavior, flexibility, and;sensory sensitivity; Anyone who had already been diagnosed with one of those disorders was “grandfathered” into the new autism spectrum disorder. A new diagnosis, social communication disorder, was created to classify people with very mild versions of autism-like symptoms.
The Three Levels of Support
The autism spectrum is incredibly wide and varied. Some people with autism are brilliant;while others are intellectually disabled. Some have severe communication problems while others are authors and public speakers.
Read Also: Are Stuttering And Autism Related
Level : Requiring Very Substantial Support
Level 3 is the most severe form of autism. Children in this category will manifest many of the same behaviors as those with levels 1 and 2, but to a more extreme degree.
Problems expressing themselves both verbally and nonverbally can make it very hard to function, interact socially, and deal with a change in focus or location. Engaging in repetitive behaviors is another symptom of level 3 ASD.
A person with ASD level 3 will have a very limited ability to speak intelligibly and will rarely initiate interactions. When they do initiate an interaction, they will do so awkwardly. Someone with level 3 will also respond only to very direct social approaches from other people.
Limitations Of Asd Levels
Although the ASD levels are useful for indicating autism severity and support needs, the categories aren’t comprehensive. They can be subjective and lacking in nuance, and the DSM-5 offers little specificity regarding the types of support indicated or situations in which support is needed. For example, some autistic people need support at school but are fine at home, while others may do well at school but struggle in social situations.
What’s more, the level a person is assigned when they’re first diagnosed can shift as they develop and refine social skills and as the severity of issues such as anxiety or depression, common among people with autism, fluctuates.
The bottom line: Being assigned one of the three levels of autism can be useful for understanding how high- or low-functioning someone is likely to be and determining what types of services and supports would serve them best. It won’t, however, predict or account for nuances in their personality and behavior, which means the support and services they receive will need to be highly individualized.
You May Like: What Is The Best Pet For An Autistic Child
Check For Physical Issues
Few people with severe autism have the ability to describe physical symptoms or problems. Thus, it’s a good idea to start by checking whether a child with severe autism has physical symptoms that may be exacerbating problem behaviors.
It’s not uncommon, for example, to discover that a child’s apparently aggressive behavior is actually a response to severe gastrointestinal painpain which can be treated through dietary changes. Once the pain is gone, the person finds it much easier to relax, engage, learn, and behave appropriately.
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
Also Check: Types Of Empathy Autism
Level 1 Asd: Requiring Support
Level 1 ASD is the least severe. This could be viewed as mild autism.
People who qualify as having Level 1 ASD may struggle in social situations and have some concerns with restrictive or repetitive behaviors but they only require minimal support to help them function in their day to day activities.
People with Level 1 ASD are likely able to communicate verbally. They may be able to have some relationships. However, they may struggle maintaining a conversation and making and keeping friends may not come easily or naturally to them.
People with Level 1 ASD may prefer to stick to established routines and feel uncomfortable with changes or unexpected events. They may want to do certain things in their own way.
About Aspiro Wilderness Adventure Therapy
The Aspiro Adventure programs are uniquely crafted to assist students and their families in creating lasting, life-long emotional changes through compassionate, intentional, research-backed, and safe outdoor adventure therapy programs. The professionals at all of the Aspiro group programs understand individuals dont come with instructions, and every student is unique, capable, and amazing in their own right.
All of our programs focus on helping adolescents, young adults, and their families through difficulties that occur when various behavioral, cognitive, or developmental issues are present. Research shows that engaging individuals on a personal level with strategic and intentional activities will aid in developing the tools and skills necessary to engage life in a healthy and positive way. Aspiro group programs include Aspiro Adventure, Daniels Academy, Vantage Point, Pure Life, ;Black mountain Academy, and Outback.
Recommended Reading: Does Jerry Seinfeld Have Autism
Current Classifications Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
While the old system of classification may seem a little more cut-and-dried, the subtle differences that often distinguished one from the other left room for a lot of confusion and much was open to interpretation. To address this, ASD is now categorized into three different levels, indicating what level of support a patient may need.
- ASD Level 1 Level 1 ASD is currently the lowest classification. Those on this level will require some support to help with issues like inhibited social interaction and lack of organization and planning skills.
- ASD Level 2 In the mid-range of ASD is Level 2. In this level, individuals require substantial support and have problems that are more readily obvious to others. These issues may be trouble with verbal communication, having very restricted interests, and exhibiting frequent, repetitive behaviors.
- ASD Level 3 On the most severe end of the spectrum is Level 3 which requires very substantial support. Signs associated with both Level 1 and Level 2 are still present but are far more severe and accompanied by other complications as well. Individuals at this level will have limited ability to communicate and interact socially with others.
Severe Versions Of Autism Symptoms
To qualify for an autism spectrum diagnosis, a person must have symptoms significant enough to impair daily life. Every autistic person must have social, communication, and sensory challenges that make life more difficult/
Even so-called “high functioning” autism can be very challenging. But those challenges rise to a very different level for people with “severe” autism.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Autism
Levels Of Autism From A Less Neurotypical Perspective
I’d like to share something I came across a good while ago. Though I’ve been able to locate it on the web, I’m not quite sure of its original source. It goes something like this :
“I know an autistic person who can typically make eye contact, understand body language, and understand sarcasm, while not having a lot of meltdowns and keeping their ‘stims’ to themselves. This person would be considered high-functioning. I also know an autistic person who gets overloaded in public places, often can’t stand to be touched, go to the store alone, or switch from one activity to another. They might also forget to shower or eat. This person would be considered low-functioning. Guess what? They’re both me.”
Autistic people aren’t the only ones who suggest that this classification system is no good, mind you; some researchers argue against it as well.;
- American Psychiatric Association. . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders . Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association.
What Are The 3 Levels Of Autism Everything You Need To Know
Last year the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that 1 in 54 U.S. children aged 8 and up was diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder a 10% increase from the CDCs last study in 2000. What exactly is autism spectrum disorder, and what can it be like to live with it?
Also Check: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Level 2 Asd: Requiring Substantial Support
Level 2 ASD is the middle-range of autism in terms of severity of symptoms and needs for supports.
People who qualify as having Level 2 ASD need more support than people with Level 1 ASD. They have more difficulty with social skills. Their challenges in social situations may be more noticeable to other people around them as compared to those with Level 1 ASD.
People with Level 2 ASD may or may not communicate verbally. If they do, their conversations may be very short or only on specific topics or they may need extensive support in order to participate in social activities.
The nonverbal behavior of people with Level 2 ASD may be more atypical from the majority of their peers. They may not look at someone who is talking to them. They may not make much eye contact. They may not express emotions through tone of voice or through facial expressions in the same way that most other people do.
People with Level 2 ASD struggle more than those with Level 1 ASD regarding their restrictive or repetitive behaviors. They may have routines or habits that they feel they must do and, if these get interrupted, they become very uncomfortable or upset.