Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Symptoms of autism spectrum disorders may appear in the first 2 years of life, but in milder forms symptoms may not be detected until school age.
Children with an autism spectrum disorder develop symptoms in the following areas:
-
Social communications and interactions
-
Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior
Symptoms of an autism spectrum disorder range from mild to severe, but most people require some level of support in both areas. People with an ASD vary widely in their ability to function independently in school or society and in their need for supports. In addition, about 20 to 40% of children with an ASD, particularly those with an IQ less than 50, develop seizures Seizure Disorders In seizure disorders, the brain’s electrical activity is periodically disturbed, resulting in some degree of temporary brain dysfunction. Many people have unusual sensations just before a seizure… read more before reaching adolescence. In about 25% of affected children, a loss of previously acquired skills occurs around the time of diagnosis and may be the initial indicator of a disorder.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
No two kids with ASD have the same signs and symptoms. Many things can play a role, such as language delays, thinking and learning problems and behavioral challenges. For this reason, autism is described as a spectrum.
Children with ASD often have problems with:
- Body language and eye contact.
- Social interactions.
In toddlers, parents might notice the following behaviors from their child:
- Delayed speech.
- Using only a few gestures .
- Not responding when someone calls their name.
- Avoiding eye contact.
- Not sharing enjoyment or interests with others.
- Unusual ways of moving the hands, fingers, or whole body.
- Being very focused or attached to unusual objects.
- Little to no imitating of others or pretending.
- Unusual sensory interests.
- Rituals such as repeating things over and over or lining up objects.
Milder symptoms may not be recognized until a child is older and has problems with:
- Forming friendships.
- Knowing how to act in different social situations.
- Unusual, intense interests in specific topics or activities.
Symptoms Of Autism In Children
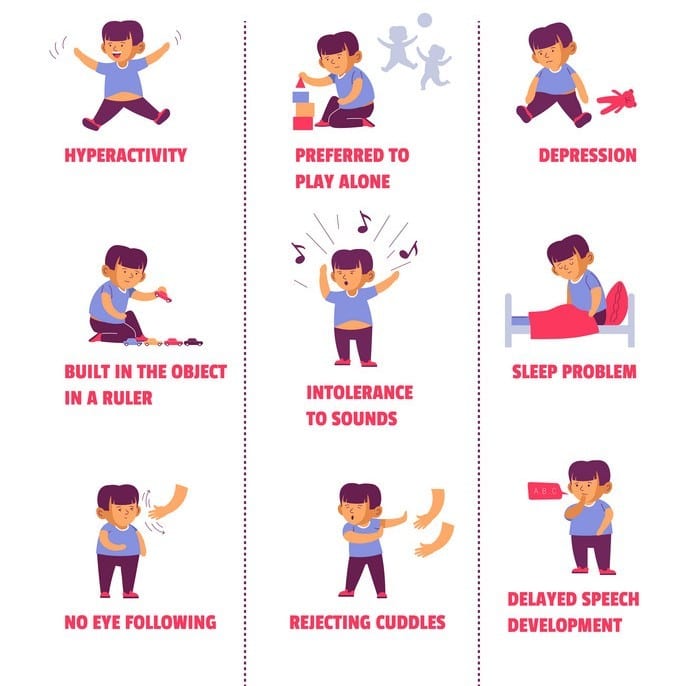
Symptoms of autism in children fall into two major categories: communication challenges and restricted and repetitive behaviors. Children may also experience sensory issues and might find themselves overstimulated or understimulated by sounds, light, smells, or pain.
Communication Challenges
This is a symptom that is common in children and adults. For example, autistic people might struggle to speak, maintain eye contact, control their facial expressions, or repeat gestures.
These are some of the other ways communication challenges might reveal themselves in people with this condition:
- They may not respect peoples personal space.
- They don’t respond to their name when its called, especially at a really young age.
- They have a hard time playing with children of the same age.
- They find it difficult to understand other peoples emotions and, in some cases, don’t know theyve hurt someone elses feelings.
- They often get distracted in between conversations.
- They might sometimes speak in a tone that is different from their regular tone of voice and keep this going for a while.
- They may find it difficult to understand non-verbal cues.
Restricted and Repetitive Behaviors
Autistic children might engage in certain behaviors that might seem atypical if you arent familiar with them. They could also repeat these behaviors very often.
Some restricted and repetitive behaviors autistic children exhibit include:
You May Like: Do Autistic Toddlers Like To Climb
Diagnostic Criteria For 29900 Autism Spectrum Disorder
To meet diagnostic criteria for ASD according to DSM-5, a child must have persistent deficits in each of three areas of social communication and interaction plus at least two of four types of restricted, repetitive behaviors .
Specify current severity:
Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior.
Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder
In order to determine whether your child has autism spectrum disorder or another developmental condition, clinicians look carefully at the way your child interacts with others, communicates, and behaves. Diagnosis is based on the patterns of behavior that are revealed.
If you are concerned that your child has autism spectrum disorder and developmental screening confirms the risk, ask your family doctor or pediatrician to refer you immediately to an autism specialist or team of specialists for a comprehensive evaluation. Since the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder is complicated, it is essential that you meet with experts who have training and experience in this highly specialized area.
The team of specialists involved in diagnosing your child may include:
Need urgent help? .
Recommended Reading: How Might Development Differ If A Child Is Autistic
Behavior Interests And Activities
People with an autism spectrum disorder are often very resistant to changes, such as new food, toys, furniture arrangement, and clothing. They may become excessively attached to particular inanimate objects. They often do things repetitively. Younger and/or more severely affected children often repeat certain acts, such as rocking, hand flapping, or spinning objects. Some may injure themselves through repetitive behaviors such as head banging or biting themselves. Less severely affected people may watch the same video multiple times or insist on eating the same food every meal. People with an ASD often have very specialized, often unusual interests. For instance, a child may be preoccupied with vacuum cleaners.
People with an autism spectrum disorder often have over-reactions or under-reactions to sensations. They may be extremely repelled by certain odors, tastes, or textures, or react unusually to painful, hot, or cold sensations that other people find distressing. They may ignore some sounds and be extremely bothered by others.
Diagnosis Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Early signs of this disorder can be noticed by parents/caregivers or pediatricians before a child reaches one year of age. However, symptoms typically become more consistently visible by the time a child is 2 or 3 years old. In some cases, the functional impairment related to autism may be mild and not apparent until the child starts school, after which their deficits may be pronounced when amongst their peers.
Social communication deficits may include1:
- Difficulty appreciating their own & others’ emotions
- Aversion to maintaining eye contact
- Lack of proficiency with use of non-verbal gestures
- Stilted or scripted speech
- Difficulty making friends or keeping them
Restricted interests and repetitive behaviors may include1:
- Inflexibility of behavior, extreme difficulty coping with change
- Being overly focused on niche subjects to the exclusion of others
- Expecting others to be equally interested in those subjects
- Difficulty tolerating changes in routine and new experiences
- Sensory hypersensitivity, e.g., aversion to loud noises
- Stereotypical movements such as hand flapping, rocking, spinning
- Arranging things, often toys, in a very particular manner
You May Like: Autism Symptoms In Adults Checklist
Autism Symptoms In Adults At Home
Other peoples feelings baffle you. You have a collection of figurines on your desk that must be in the same order at all times. These, and other common manifestations of ASD, may be apparent in adults at home:
- Your family members lovingly refer to you as the eccentric professor of the family, even though you dont work in academia.
- Youve always wanted a best friend, but never found one.
- You often invent your own words and expressions to describe things.
- Even when youre in a quiet place, like the library, you find yourself making involuntary noises like clearing your throat over and over.
- You follow the same schedule every day of the week, and dont like unexpected events.
- Expressions like, Curiosity killed the cat or Dont count your chickens before they hatch are confusing to you.
- You are always bumping into things and tripping over your own feet.
- In your leisure time, you prefer to play individual games and sports, like golf, where everyone works for themselves instead of working toward a common goal on a team.
When Should I See My Doctor
If you think your child has ASD, see your doctor. Early intervention offers the best outcomes for children with ASD, whether their traits are obvious or subtle.
There may be different signs of autism at different ages.
- In the first year, your baby with ASD might not be interested in other people. They may not make eye contact with you. They may not smile or gesture like other babies.
- As toddlers, children with ASD might not respond to their name. They might focus on one or 2 activities repetitively, like lining up toys. They may not be interested in playing with other children. They might develop unusual ways of speaking.
- Older children with ASD might have difficulties in social situations, following instructions or making friends.
You might receive an autism diagnosis as an adult. You may spend your life feeling like you dont quite fit in. You may have difficulties with relationships, work and social situations. You may also have mental health conditions like anxiety or depression.
Autism Awareness Australia provides information about signs of autism in people at different ages.
Recommended Reading: Do Babies With Autism Babble
What Are The Causes Of Autism
Experts donât fully understand all of the causes of autism spectrum disorder. It seems to be genetic, but things such as parental age and prescription medications taken during pregnancy may be involved.
For instance:
- A person is more likely to be on the spectrum if a brother, sister, or parent is. But it doesnât always run in families.
- About 10% of kids with ASD have a form of genetic disorder such as Down syndrome and fragile X syndrome.
- A large Danish study found a link between ASD and advanced parental age of either parent.
- Women prescribed opioids just before pregnancy are likelier to have a child with ASD.
Some children who are on the spectrum start showing signs as young as a few months old. Others seem to have normal development for the first few months or years of their lives and then they start showing symptoms.
But up to half of parents of children with ASD noticed issues by the time their child reached 12 months, and between 80% and 90% noticed problems by 2 years. Children with ASD will have symptoms throughout their lives, but itâs possible for them to get better as they get older.
The autism spectrum is very wide. Some people might have very noticeable issues, others might not. The common thread is differences in social skills, communication, and behavior compared with people who arenât on the spectrum.
How Does Autism Affect Kids
Autistic children may not reach the same developmental milestones as their peers, or they may demonstrate the loss of previously developed social or language skills.
For instance, a 2-year-old without autism may show interest in simple games of make-believe. A 4-year-old without autism may enjoy engaging in activities with other children. An autistic child may have trouble interacting with others or dislike it altogether.
Autistic children may also engage in repetitive behaviors, have difficulty sleeping, or compulsively eat nonfood items. They may find it hard to thrive without a structured environment or consistent routine.
If your child is autistic, you may have to work closely with their teachers to ensure they succeed in the classroom.
Many resources are available to help autistic children as well as their loved ones. Local support groups can be found through the national nonprofit the Autism Society of America.
Also Check: Why Is Autism Speaks Harmful
What Role Do Genes Play
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
Universal Symptoms Of Autism

Everyone with an appropriate autism spectrum diagnosis has certain symptoms, described in the American Psychiatric Association “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition” . These include:
- Deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts
- Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction
- Deficits in developing, maintaining, and understand relationships
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities
- Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior
- Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus
- Hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input or unusual interest in sensory aspects of the environment
All of these symptoms, of course, can occur in someone who is not autistic. To qualify for an autism diagnosis, therefore, all of the symptoms must be present. In addition, the symptoms must not be explainable by another diagnosis.
For example, a person with deficits in communicative behaviors may be hard of hearing or have low vision, either of which would impair typical communicative skills. Finally, the symptoms must be significant enough to have a real impact on activities of daily life.
Recommended Reading: Non Pharmacological Treatment For Adhd
Autism In Young Children
Signs of autism in young children include:
- not responding to their name
- avoiding eye contact
- not smiling when you smile at them
- getting very upset if they do not like a certain taste, smell or sound
- repetitive movements, such as flapping their hands, flicking their fingers or rocking their body
- not talking as much as other children
- repeating the same phrases
Signs of autism in older children include:
- not seeming to understand what others are thinking or feeling
- finding it hard to say how they feel
- liking a strict daily routine and getting very upset if it changes
- having a very keen interest in certain subjects or activities
- getting very upset if you ask them to do something
- finding it hard to make friends or preferring to be on their own
- taking things very literally for example, they may not understand phrases like “break a leg”
New Jerseys High Rate Of Autism
When people have autism, their social interaction and communication are disrupted. The Centers for Disease Control and Preventions autism monitoring network found that New Jersey had the highest rate of autism in nearly every biannual study since 2000. It is likely that the high prevalence of autism in New Jersey is due to the excellent services the state provides for ASD. This states care system is based on solid records, making it easier to identify cases and provide the best possible care for children with autism.
You May Like: Services For Autistic Adults In North Carolina
How To Help Your Child Aged Birth To 5 Years With Autism
Following an ASD diagnosis for your baby, toddler or preschooler, use the following steps to ensure your childs care:
1. Learn about your childs needs.
Kids with autism might have language delays or trouble communicating with others. They may have unusual or repetitive behaviors or trouble with learning. However, no two kids with autism are alike and, as the parent, youre the expert on your child.
So, when talking to doctors or therapists, ask lots of questions. Tell them your concerns. If youre not happy with the answers, consider getting a second opinion.
Some kids with autism may have other conditions likeseizures, gastrointestinal problems and trouble sleeping. If you have any health concerns, tell your doctor. Your child may need to see a specialist and have tests.
When you feel comfortable with your childs autism diagnosis, learn about treatment options that may include therapy and education services.
2. Learn about education services.
Inearly intervention, children learn with the help of therapists at home, at daycare, or at another facility. Parents and caregivers learn how to help improve their childs language and communication.
Kids with autism age 3 or older may get anindividualized education program from their local school district. This plan will outline the need for things likespeech therapy,occupational therapy or a classroom aide to help with positive behavior choices. To learn more, call your school districts office of special education.
Diagnosis In Young Children
Diagnosis in young children is often a two-stage process.
Stage 1: General Developmental Screening During Well-Child Checkups
Every child should receive well-child check-ups with a pediatrician or an early childhood health care provider. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children receive screening for developmental delays at their 9-, 18-, and 24- or 30-month well-child visits, with specific autism screenings at their 18- and 24-month well-child visits. A child may receive additional screening if they are at high risk for ASD or developmental problems. Children at high risk include those who have a family member with ASD, show some behaviors that are typical of ASD, have older parents, have certain genetic conditions, or who had a very low birth weight.
Considering caregivers experiences and concerns is an important part of the screening process for young children. The health care provider may ask questions about the childs behaviors and evaluate those answers in combination with information from ASD screening tools and clinical observations of the child. Read more about screening instruments on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website.
If a child shows developmental differences in behavior or functioning during this screening process, the health care provider may refer the child for additional evaluation.
Stage 2: Additional Diagnostic Evaluation
The diagnostic evaluation is likely to include:
Also Check: How To Teach Yes No Questions Autism