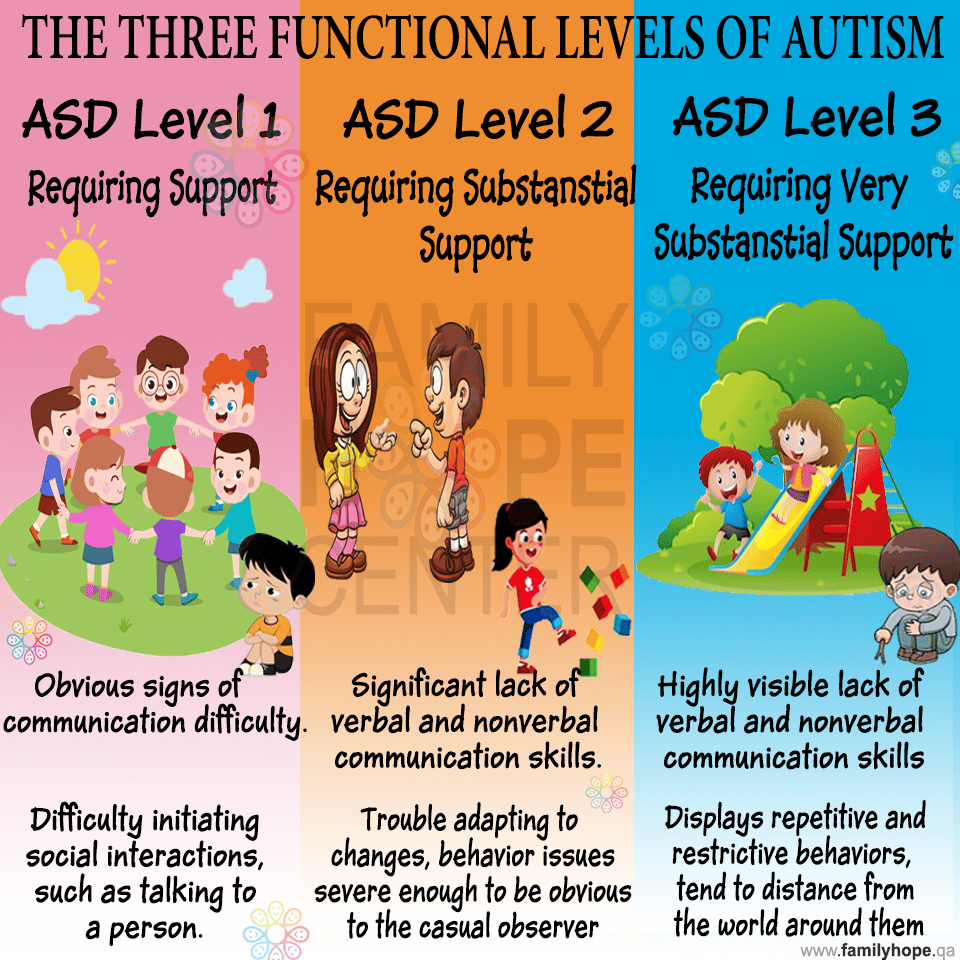
Level : Requires Support
Level 1 ASD is the mildest form of autism. Children with level 1 ASD have a hard time communicating appropriately with others. For example, they may not say the right thing at the right time or be able to read social cues and body language.
A person with ASD level 1 usually is able to speak in full sentences and communicate, but has trouble engaging in back-and-forth conversation with others. They may try to make friends, but not be very successful.
They may also have trouble moving from one activity to another or trying new things. Additionally, they may have problems with organization and planning, which may prevent them from being as independent as other people their age.
Is Aspergers A Type Of Autism
Aspergers syndrome was initially considered different from autism spectrum disorder. However, in 2013 the DSM-5 categorized Aspergers and all additional types of autism under autism spectrum disorders. All Aspergers symptoms currently fall under ASD.
Autism and Aspergers syndrome are no longer considered different diagnoses. A previous Aspergers diagnosis is now regarded as autistic.
The Different Levels Of Autism
Does the phrase if youve met one person with autism, youve met one person with autism ring a bell? It might seem like a no-brainer, but it is surprising how often we forget that autism spectrum disorder is exactly that: a range of symptoms on a spectrum.
Asking questions is an important part of the human journey, and we want to celebrate that journey of understanding each other. So weve gathered a few of those questions on this topic from people like YOU. Hopefully, we can shed some light on it!
You May Like: How Many Different Kinds Of Autism
Level 2 Requiring Substantial Support
People who qualify as Level 2 of ASD are known to require substantial support from the people around them. Yet, even that support may not be enough to help them take complete control over their life.
Communication for them is complicated given that carrying a coherent conversation is extremely difficult for level 2 patients.
Typically, such a patient may speak concise sentences and have difficulty understanding nonverbal cues and facial expressions.
While level 1 ASD patients feel uncomfortable at changing routines, level 2 patients get startled by even the most minute changes. This makes it extremely difficult for them to function during the day when several changes come up.
Levels Of Autism In Toddlers
There are four levels of autism in toddlers, according to the Autism Society. They are: 1. Severe: Toddlers with severe autism may not speak at all and may have very limited social interaction. They may also have repetitive behaviors and may be resistant to change. 2. Moderate: Toddlers with moderate autism may have some speech and social skills, but they may be limited. 3. Mild: Toddlers with mild autism may have good speech and social skills, but they may still have some repetitive behaviors. They may also be resistant to change. 4. High functioning: Toddlers with high-functioning autism may have excellent speech and social skills. They may still have some repetitive behaviors, but they are usually able to cope with change.
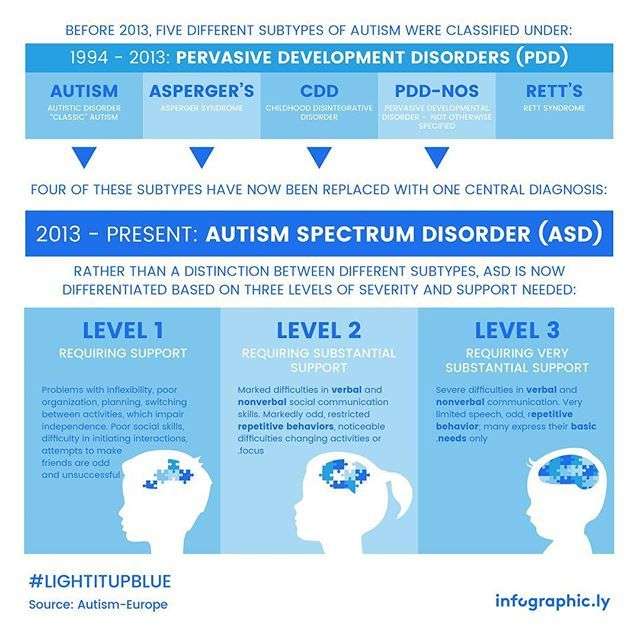
In 2013, DSM-5, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, added three new levels to the criteria for an ASD diagnosis. In general, individual support levels vary depending on the type of Autism. Well look at diagnoses and what level 1 autism in toddlers could look like today. A toddler with a level one Autism diagnosis has a moderate to mild case of the disease. A doctor will diagnose your child with ASD based on a diagnosis of the condition. Developing routines and habits to help reduce symptoms of autism spectrum disorder is a good idea for parents. Some parents seek behavioral therapy, whereas others seek nutritional intervention.
You May Like: Dsm-5 Autism Test
Level 1 Requiring Support
Classified as the least severe, level 1 ASD patients may be able to function without substantial support. They can communicate verbally and maintain relationships but often struggle to carry or initiate a conversation.
Level 1 ASD patients also struggle with maintaining friendships without light support. Deviating away from an established routine may make them uncomfortable. This is why they prefer to stick to strict schedules and specific ways of doing things their own way.
These people often require some minimal support to organize and plan their lives.
Restrictive/repetitive Behaviors May Include:
- Repeating certain behaviors or having unusual behaviors. For example, repeating words or phrases, a behavior called echolalia
- Having a lasting intense interest in certain topics, such as numbers, details, or facts
- Having overly focused interests, such as with moving objects or parts of objects
- Getting upset by slight changes in a routine
- Being more or less sensitive than other people to sensory input, such as light, noise, clothing, or temperature
Symptoms can typically be observed early in life, as young as two years old however, many individuals are not diagnosed until the school-age years or even high school. It all depends on the severity of symptoms and having someone notice that there is an issue.
Some individuals have mild to moderate autism symptoms, while some others may be impacted severely. Here is where the three types of spectrum disorders come into play. Each type of spectrum is defined by its varying degrees of symptoms.
What are the 3 types of autism?
Recommended Reading: Is Autism A Hereditary Disorder
Level 1 Requires Support
Level 1 is the mildest type of ASD, and is sometimes referred to as high-functioning autism. Children at level 1 typically have a more difficult time communicating with other people. They may also have difficulty interpreting social cues and body language.
In some cases, people at level 1 have trouble moving from one task to another or trying something altogether new. They can sometimes have trouble with organization and planning skills, too, making it more difficult for them to accomplish things.
Assigning A Functioning Level
At the completion of the childs in-depth testing and assessment, specialists assign one of three autism functioning levels from mild to severe based on DSM-5 criteria for this assignment. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention factsheet gives an example of rating various areas of function, such as intelligence and social and communication skills. The following sections summarize the DSM-5 three levels of autism as outlined by Autism Speaks.
Recommended Reading: How To Improve Joint Attention In Autism
How Are Levels Of Autism Diagnosed
The DSM-5 outlines the three functional levels of autism. It provides guidelines that providers use to determine how much support a person with ASD needs.
Autistic people who need the least amount of support to function in their daily lives receive a level 1 diagnosis.
Support needed for a person with level 1 autism might include:
- Building self-control
- Understanding non-verbal communication
- Reducing anxiety
How much support people with mild autism need depends on many factors and varies from person to person.
What Is Autistic Disorder
This type of spectrum is known as classic autism. The classic autistic disorder is what people typically think of when they hear the word autism. According to the Autism Support of West Shore, those with this type of spectrum disorder have significant language delays, social and communication challenges, and unusual behaviors and interests. These individuals are usually affected by intellectual disabilities. This type is considered the most severe form of autism. Its also the most common.
People who have autistic disorder may:
- have a hard time accepting touch by other people,
- perform restricted or repetitive behaviors like hand-flapping or fidgeting
- experience sensory overload,
- have issues communicating or limited social skills
Signs of autism may be different in children depending on their age. Young children may begin showing signs of autistic disorder within their first 12 months of life. They may avoid eye contact or fail to return a smile from their mother or father. Older children may find it difficult to communicate how they feel. They may have a hard time making friends or seem unable to understand how others are thinking and feeling.
Research shows that early diagnosis and intervention for autism have long-term positive effects on a childs life. Proper early intervention can help children with an autism diagnosis improve their language and behavioral skills.
Aspergers Syndrome is the mildest form of autism and is closely associated with level one of ASD.
Read Also: Stages Of Speech Development In Autism
The 3 Levels Of Autism Explained
Autism is a diagnosis that often carries a certain connotation. Those who are unfamiliar with the nuances of autism spectrum disorder may assume that all children on the spectrum participate in repetitive behaviors, dont make eye contact, and are largely non-verbal. While these signs can certainly be present, there are many children who fall within the spectrum whose symptoms are far milder and even those whose symptoms are more severe. Its a wide and diverse range of possible complications, and despite what some may think, children within the spectrum do not all fall into neat little categories. For that reason, the classifications of ASD have changed significantly over the years.
A Short History Of Autism

Researchers have been working on autism and autism-like disorders since the 1940s. At that time, autism studies tended to be small in scale and used varying definitions of the disorder. Autism was also sometimes lumped in with other conditions.
Focused research into ASD became more common in the 1980s when the DSM-III established autism as a distinct diagnosis. Since then, researchers have explored the causes, symptoms, comorbidities, efficacy of treatments, and many other issues related to autism.
Researchers have yet to discover a cause for autism. Many of the ideas put forth thus far have been disproven. Likely a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors are at work, which is the case with many psychiatric disorders and conditions.
Also Check: What’s The Difference Between Autism And Mental Retardation
Other Forms Of Autism
Not all forms of autism are reflected in the three levels. As a spectrum disorder, there are some presentations of the disability that dont fit into these set levels.
An example of this is Aspergers syndrome, which falls on the milder side of the spectrum. A person with Aspergers syndrome normally presents with high intelligence and daily functioning capabilities. They usually display hyper-focused obsession with certain topics, and they struggle in social situations. Aspergers syndrome is often undiagnosed because people do not recognize its symptoms as those of an autism spectrum disorder.
Another example is atypical autism, which used to be known as pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified , before that term was retired. This describes those who had autistic disorder that was more severe than standard Aspergers syndrome, but not as debilitating as classic autistic disorder.
Previous Autism Spectrum Disorder Terminology
Much of the misconception surrounding ASD comes from terminology that was used prior to 2013. In this prior classification system, children fell into one of the following three categories:
- Autistic Disorder More severe cases of ASD were previously classified as autistic disorder. The condition was often defined by communication troubles, repetitive behaviors, and social challenges among other symptoms.
- Aspergers Syndrome On the opposite end of the spectrum was Aspergers syndrome which was characterized by milder symptoms which may impact an individuals communication or social skills.
- Pervasive Development Disorder, Not Otherwise Specified For children who fell in the middle and didnt fully meet the requirements for either autistic disorder or Aspergers, a diagnosis of PDD-NOS was often given.
Read Also: How To Support A Child With Autism In Childcare
At What Age Does Autism Appear
Autism spectrum disorder typically develops during early childhood. Some infants may show symptoms of autism within the first 12 months, while other infants may not present with symptoms until after 2 years old. Some children diagnosed with autism may meet developmental milestones and new skills relative to their age until 18 to 24 months, and then stop development of skills or even lose the skills they once had.
The Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
An individual with Autism Spectrum Disorder often has behavioral challenges with how they act in social settings, challenges learning, and expressing themselves as well as understanding or empathizing with others. A lot of individuals with ASD share symptoms but can experience a wide range of severity in specific symptoms.
Each individual is different and so are their strengths and challenges when it comes to symptom severity.
Categorizing ASD into three different levels helps clinicians to diagnose ASD and develop appropriate therapies for the unique needs of the patient. These therapeutic approaches assist the person with ASD to make the most of their strengths and improve their social skills, language skills, and behaviors.
For parents, families, caregivers, and other members of the autistic individuals support team, knowing which level of ASD symptoms helps prepare them for the types of challenges their child might face in everyday life.
The Differences Between High & Low-Functioning Autism
The 2013 Publication of the updated DSM-5 breaks ASD down into three levels of severity, with level one being the mildest symptoms with high-functioning capability and level three being the most severe with low-functioning challenges.
Recommended Reading: Can Stress During Pregnancy Cause Autism
How Diagnosis Of Autism Changed With Dsm
The DSM is the official publication of the American Psychiatric Association which defines psychiatric and developmental disorders. While it has no legal status, the DSM does have an enormous impact on the way insurers, schools, and other service providers think about and treat autism.
Until 2013, the DSM described the autism spectrum as a disorder that included five distinct diagnoses. Asperger syndrome was, essentially, a synonym for “high functioning autism,” while autistic disorder meant almost the same thing as “severe autism.” People with PDD-NOS had some but not all of the symptoms of autism . Rett syndrome and Fragile X syndrome, rare genetic disorders, were also considered to be part of the autism spectrum.
Then, in May 2013, the DSM-5 was published. The DSM-5, unlike the DSM-IV, defines autism as a single spectrum disorder, with a set of criteria describing symptoms in the areas of social communication, behavior, flexibility, and sensory sensitivity Anyone who had already been diagnosed with one of those disorders was “grandfathered” into the new autism spectrum disorder. A new diagnosis, social communication disorder, was created to classify people with very mild versions of autism-like symptoms.
The Three Levels of Support
The autism spectrum is incredibly wide and varied. Some people with autism are brilliant while others are intellectually disabled. Some have severe communication problems while others are authors and public speakers.
Cognitive Abilities And Autism
In relation to function challenges, an important aspect to understand is the intersection between intellectual abilities/cognitive processes and ASD level. For example, a young person may have Level 2 ASD, but a strong stable cognitive profile with no major intellectual deficits can result in a great deal of strength and potential for success, whereas a student with ASD level 1, with lower cognitive abilities or large disparities in their cognitive abilities/intellectual scores on an IQ test may functionally have a lot of struggles. Thus, it is important to understand their Autism level in combination with their cognitive strengths and weaknesses. Additionally, there is growing evidence from NIMH that the WISC-IV FSIQ continues to underestimate the intellectual ability of Autism Children, requiring skilled clinicians who specialize in ASD to understand and better assess these students correctly.
Also Check: Autistic Meltdown In Adults
Level 3 Autism: Requiring Very Substantial Support
Autism Spectrum Disorder Level 3 is the most severe form of Autism. People in this category will have many of the same patterns of behaviors and sensory struggles as those with levels 1 and 2 yet this is typically more severe. People with ASD level 3 have problems expressing themselves both verbally and nonverbally, and may not verbally communicate with words. This more severe struggle can cause significant impairment in social connection, adapting to change, being flooded by sensory overload, and engaging in perpetual repetitive behaviors.
How Do I Know If I Have Level 2 Autism
The second level requires substantial assistance, and communicative problems in both verbal and nonverbal communication can be detected. Difficulty changing activities or focusing, odd behaviors that are restricted in repetitiveness, and restricted in repetitiveness are all indicators of this. Level 3 requires a significant amount of support because it involves severe communication difficulties in both verbal and nonverbal communication.
Also Check: How Does An Autistic Brain Work
What Does Level 3 Autism Look Like
There is no one answer to this question as every individual with autism is unique. However, there are some common behaviors and characteristics associated with level 3 autism, also known as severe autism. Individuals with severe autism may have little to no speech, may be nonverbal, and may be resistant to changes in routine or environment. They may also have significant sensory issues and may be easily overwhelmed by stimuli. In addition, they may exhibit repetitive behaviors, such as stimming, and may be fixated on certain objects or interests.
A diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder is classified according to DSM-5 in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. The fifth edition of the criteria for autism diagnosis provides three clear levels of support based on the patients needs. Level 1 in autism is the mildest or highest functioning form. Children with ASD level 2, as opposed to children with normal levels, are more likely to engage in social communication and repetitive behaviors. Autism spectrum disorder level 3 is characterized by severe challenges in social interaction and behavior. Level 3 autism symptoms manifest as inflexibility of behavior, as well as difficulty adapting to new situations. The DSM-IV included a number of subcategories of autism, including Rett syndrome and childhood disintegrative disorder.