Challenges And Future Perspectives
The field of imaging genetics has exponentially grown in recent decades from its candidate gene studies to large-scale longitudinal studies, cross-modal investigations, and translational animal models of various psychiatric disorders. In addition, imaging genetics has begun integrating transcriptomic data and analytical methods for assessing pathway enrichment, such as the score system for pathway regulation. Of addition to translational animal research and pharmacological intervention in vitro and in vivo, imaging genetics can also provide an insight into various behavioral and genetic factors that contribute to the risk of ASDs.
One of the challenges facing imaging genetics is the conceptualization of endophenotypes, which states that endophenotypes are heritable and associated with psychiatric disorders and may impede research on brain-based associations by limiting imaging genetic research to genes previously associated with a psychiatric disorder. It is important to properly replicate the studies, particularly those with false-positive results, to address the impact of a genetic variation in a disease, and this problem can be solved by correcting genome-wide associations with large sample size imaging phenotypes.
Read Also: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
What Is The Treatment For Autism
There is currently no cure for autism. However, autism can be managed and shaped at a young age, even as early as pre-school. Early intensive therapy can have a positive effect on development later in life.
Treatment of autism involves medical and behavioral therapies to help children with conversational language and social interactions. Treatment also involves helping children decrease their repetitive, self-stimulatory behaviors, tantrums and self-injurious behavior.
Medications can help treat specific symptoms such as aggressive or self-injurious behavior, inattention, poor sleep and repetitive behaviors. However, no medications are autism specific and medications should be used in conjunction with a family-centered, behavioral and educational program.
Do Symptoms Of Autism Change Over Time
For many children, symptoms improve with age and behavioral treatment. During adolescence, some children with ASD may become depressed or experience behavioral problems, and their treatment may need some modification as they transition to adulthood. People with ASD usually continue to need services and supports as they get older, but depending on severity of the disorder, people with ASD may be able to work successfully and live independently or within a supportive environment.
Don’t Miss: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Endophenotypes Common Variants And Domain Specificity In Asd
The relationship of specific genetic variants with specific cognitive processes, such as language, highlight the notion that the broad syndrome of ASD can be broken down into many component, or intermediate phenotypes, referred to as endophenotypes. The familial segregation of endophenotypes provides a genetic basis for the broader phenotype described earlier. A logical extension of this concept is that these endophenotypes represent one end of the continuum of the normal spectrum of behavior and cognition . Several groups have demonstrated that this is indeed the case with respect to CNTNAP2 , as the same allele that increases risk for language delay in ASD, increases risk for specific language impairment and modifies language ability in the general population. Similarly, common variation in different ASD-associated CNTNAP2 single nucleotide polymorphism , has been shown to modulate brain morphology in several ASD related cortical regions in normal controls .
The Molecular Diversity Of Asd
Several recent reviews summarize the growing list of dozens of common and rare genetic variants that have been associated with ASD at varying levels of statistical evidence , so I refer the reader to these reviews for comprehensive gene lists. Here, instead, I will try to synthesize what these findings may be telling us about ASD pathophysiology at what is still an early juncture in the search for ASD susceptibility genes.
The most obvious general conclusion from all of the published genetic studies is the extraordinary etiological heterogeneity of ASD. No specific gene accounts for the majority of ASD, rather, even the most common genetic forms account for not more than 12% of cases . Further, these genes, including those mentioned earlier, represent a diversity of specific molecular mechanisms, ranging from cell adhesion, synaptic vesicle release and neurotransmission, synaptic structure, RNA processing/splicing, and activity-dependent protein translation. On one hand, this should not be surprising, as autism is defined based on observation of cognition and behavior, not etiology. On the other hand, the diversity of potential mechanisms and the apparent lack of specificity of mutations for ASD begs the question as to whether ASD should even be viewed as a unitary disorder. Therefore, asking whether the diverse genes implicated in autism might converge on common pathways becomes an important question for understanding autism and developing new therapeutics.
Recommended Reading: Does Jerry Seinfeld Have Autism
A Complex & Evolving Relationship
The relationship between FXS and autism is complex and constantly evolving, and despite the frequency and severity of autism in FXS, there are still important gaps in knowledge due to limited research, samples, and surveys.
For further reading on the relationship between autism and Fragile X syndrome, see Fragile X Syndrome Related Concerns on the CDC website, and related consensus documents and articles below.
Learn More
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
Read Also: Autism Level 2 Meaning
Direct Evidence For The Contribution Of Environmental Factors
There has been much discussion about the initial suggestion that MMR vaccine. However there is now a scientific consensus that the evidence favors rejection of a causal relationship between thimerosal-containing vaccines and autism, based on multiple epidemiologic studies which did not support a link between thimerosal-containing vaccines and ASD . However, other environmental factors are likely to contribute to a significant proportion of ASD risk.
Prenatal and perinatal factors
In another meta-analysis focusing on the perinatal and neonatal period, the same authors identified several potential risk factors, the main being fetal presentation, umbilieal-cord complications, fetal distress, birth injury or trauma, multiple birth, maternal hemorrhage, summer birth, low birth weight, small for gestational age, low 5minute Apgar score, meconium aspiration, neonatal anemia, ABO or Rh incompatibility, and hyperbilirubinemia. Feeding difficulties and congenital malformation that are also mentioned should rather be considered as symptoms of an underlying cause of autism. The identification of summer birth as a risk factor is consistent with the results of a recent study showing that maternal infection in the first trimester increases autism risk.
Socioeconomic status
Drugs and toxic exposure
Twin And Pedigree Studies
In 1944, Kanner noted that parents shared common traits with their autistic children, introducing the broader autism phenotype and recognizing the importance of genetics . Thirty years later, twin studies revolutionized the field of autism research .
Twin studies were the first to demonstrate the heritability of autism. In 1977, the first twin-heritability estimate was published, based on a study of 10 dizygotic and 11 monozygotic pairs . Four out of the 11 MZ pairs but none of the DZ pairs were concordant for autism. Subsequently, over 30 twin studies have been published, further supporting the high heritability of autism . A meta-analysis of seven primary twin studies reported that the heritability estimates ranged from 64% to 93% . The correlations for MZ twins were at 0.98 , while the correlations for DZ twins were at 0.53 when the autism prevalence rate was assumed to be 5% and increased to 0.67 when the prevalence was 1% . Additionally, family studies have found that the relative risk of a child having autism relates to the amount of shared genome with affected relatives .
Fig. 1. Relative risk of autism by degree of relatedness with a person with autism. Relative risk for full and half siblings, and full cousins was provided in Hansen et al. . Relative risk for half first cousins was estimated based on Xie et al. . GS, genome shared.
Read Also: The Good Doctor Actor Autistic
Asd Is Diagnosed By Behavior
According to Frazier, theres no biological test available for autism.
The condition is clinically diagnosed using behavioral observation such as the ADOS , or for older children and adults, the ADI-R that was used in this study, he said.
Frazier pointed out that in either case, its important for children diagnosed with autism to have genetic testing, as recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics , to identify underlying genetic conditions.
On the other hand, children with genetic conditions can be evaluated for autism and related challenges, he said.
Even if a child doesnt meet the criteria for a diagnosis of ASD, a developmental evaluation for children with a genetic disorder can lead to identifying other conditions like social communication disorders, behavioral conditions or learning disabilities, and getting necessary supports and services in place that the child needs, Frazier said.
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Autism Largely Caused By Genetics Not Environment: Study
HealthDay Reporter
WEDNESDAY, July 17, 2019 — The largest study of its kind, involving more than 2 million people across five countries, finds that autism spectrum disorders are 80% reliant on inherited genes.
That means that environmental causes are responsible for just 20% of the risk.
The findings could open new doors to research into the genetic causes of autism, which the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention now says affects 1 in every 59 U.S. children.
It might also help ease fears that autism is caused by maternal factors — a mother’s weight, mode or timing of delivery, or nutrient intake, for example. The new study found the role of maternal factors to be “nonexistent or minimal.”
Instead, “the current study results provide the strongest evidence to our knowledge to date that the majority of risk for autism spectrum disorders is from genetic factors,” said a team led by Sven Sandin, an epidemiological researcher at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, Sweden.
The new study might help dampen public interest in supposed — but unproven — “environmental” causes of autism, such as vaccines. Long-discredited, fraudulent data linking childhood vaccination with autism is still widely cited by the “anti-vaxxer” movement.
They noted the new numbers are roughly in line with those from prior, smaller studies on the issue, further bolstering their validity.
JAMA Psychiatry
Also Check: Can A Child Outgrow Autism
Current Research On Autism
Autism is an active area of research with over 6,000 articles and over 700 reviews catalogued in PubMed in 2020.
In 2017, Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder provided an overview of the relationship between sleep and children with ASD.
Association of Genetic and Environmental Factors With Autism in a 5-Country Cohort is a study published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry in July 2019 that discovered that autism spectrum disorders are 80% caused by inherited genes. This is the largest study of its kind to date.
Researchers are also investigating conditions that tend to be comorbid with the disorder. In 2020, there is some evidence to suggest CRISP technology may lessen symptoms of Angelman syndrome and that a type of gene therapy may curb deadly seizures in certain forms of epilepsy.
Spectrum, a division of the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative, continues to highlight new research, such as this recent study from April 2021 suggesting that progress in treatment shows a strong tendency to level off in many children at age 6.
For more recent research, you can also check out Autism Speaks top 10 studies of 2020. Here, scientific staff and advisors summarize what they believe to be the most impactful autism studies of the year, including those that focus on interventions and health disparities. The United States Department of Health and Human Services also shares recent research and resources.
Genetic Causes And Modifiers Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Department of Physiology, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States
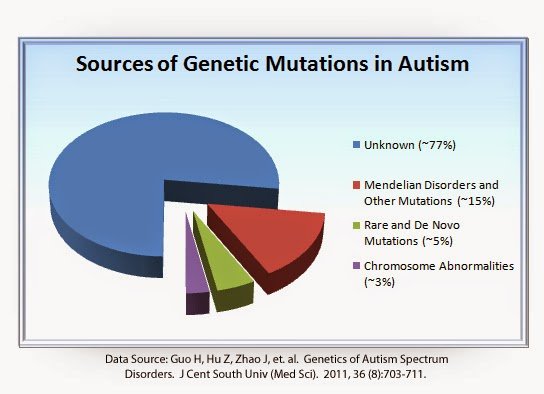
Autism Spectrum Disorder is one of the most prevalent neurodevelopmental disorders, affecting an estimated 1 in 59 children. ASD is highly genetically heterogeneous and may be caused by both inheritable and de novo gene variations. In the past decade, hundreds of genes have been identified that contribute to the serious deficits in communication, social cognition, and behavior that patients often experience. However, these only account for 1020% of ASD cases, and patients with similar pathogenic variants may be diagnosed on very different levels of the spectrum. In this review, we will describe the genetic landscape of ASD and discuss how genetic modifiers such as copy number variation, single nucleotide polymorphisms, and epigenetic alterations likely play a key role in modulating the phenotypic spectrum of ASD patients. We also consider how genetic modifiers can alter convergent signaling pathways and lead to impaired neural circuitry formation. Lastly, we review sex-linked modifiers and clinical implications. Further understanding of these mechanisms is crucial for both comprehending ASD and for developing novel therapies.
Recommended Reading: Comorbid Asd And Adhd
Scientists Identify New Gene Involved In Autism Spectrum Disorder
Forward genetics pinpoints gene linked to ASD involving severe speech impairment and opens door to search for more mutations, future treatments
eLifeKDM5AKDM5A
DALLAS Dec. 23, 2020 UT Southwestern scientists have adapted a classic research technique called forward genetics to identify new genes involved in autism spectrum disorder . In a study published this week in eLife, the researchers used this approach in mice to find one such gene called KDM5A.
Approximately 1 in 54 children in the U.S. is diagnosed with ASD, a neurodevelopmental disorder that causes disrupted communication, difficulties with social skills, and repetitive behaviors. As a disease with a strong genetic component, it is hypothesized that thousands of genetic mutations may contribute to ASD. But to date, only about 30 percent of cases can be explained by known genetic mutations.
For decades, forward genetics has been used to find mutations that cause disease. It involves inducing genetic mutations in mice, screening for certain phenotypes, and then identifying the causative mutation through sequencing of all genetic material of an organism, or its genome.
Beutler won the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery of a family of receptors that allow mammals to sense infections when they occur, triggering a powerful inflammatory response.
The study was supported by The Welch Foundation and the Walter and Lillian Cantor Foundation.
The Role Of Rare Mutations Versus Common Polymorphisms In Asd
A series of important findings over the last four years clearly challenges the notion that autism is mainly caused by combinations of common variants by identifying a large number of rare, recurrent, and non-recurrent mutations that lead to ASD. At the same time, whole genome association studies with common variants, while identifying a few loci with very small effect sizes, have not yielded independently replicated results . These rare mutations, mostly in the form of sub-microscopic chromosomal structural variation, called copy number variants , are now known to account for up to 10% of cases of idiopathic autism . Since many of these CNV have large effect sizes and thus are thought sufficient to cause ASD, they are predicted to significantly reduce reproductive fitness. Consistent with this, these causal CNV are often not transmitted from the parent, but instead occur de novo in the germline . However, in some cases, such as CNV at 16p11 and 15q11-13, the CNV are transmitted from an unaffected parent to cause the disorder in an offspring . The genetic or epigenetic mechanism for the reduced penetrance for ASD in the mutation-carrying parent is not known. However, it is also very likely that the parent carriers of such CNV have more subtle neuropsychiatric or cognitive phenotypes that have not yet been systematically identified.
Also Check: Symmetra Autistic Comic
What Causes Autism During Pregnancy
Studies are still looking into the factors that may contribute to the occurrence of autism.
Recent studies indicate that mutation and changes during conception and pregnancy, and even after delivery could increase risk of developing autism in children who are genetically predisposed to the disorder.
A study showed that the differences in the brains of the children could be detected as early as the second trimester of the pregnancy.
Although we do not have a definitive cause for autism, we know that it is developed through a combination of factors, including genetic and environmental factors.
It is not possible to change genetics. However, there are ways to limit exposure to certain environmental factors that have been shown to contribute to development of autism.
Although these are worth trying, it is not certain that lowering exposure will lower the childs risk for developing ASD.
The evidence we have about the environmental risk during pregnancy is still at its infancy. There are many ways to go.
A study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology in 2014 found that children who were born to mothers with iron deficiency are five times more likely to have autism.
This risk also increases if the mother is aged 35 or older. Metabolic conditions like obesity, high blood pressure or diabetes also contribute to the increase of the risk.
Various studies have shown connection between pregnancy exposure to air pollution and risk of developing autism.
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism
Autism usually develops before 3 years of age and affects each individual differently and to varying degrees. It ranges in severity from relatively mild social and communicative impairments to a severe disability requiring lifelong parental, school and societal support.
The hallmark symptom of autism is impaired social interaction. Children with autism may fail to respond to their name and often avoid eye contact with other people. They have difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling because they don’t understand social cues provided by tone of voice or facial expressions and they don’t watch other people’s faces to pick up on these cues.
Many children with autism engage in repetitive movements such as rocking, spinning, twirling or jumping, or in self-abusive behavior such as hand biting or head-banging.
Of children being diagnosed now with an autism spectrum disorder, about half will have intellectual disabilities defined by nonverbal IQ testing, and 25 percent will also develop seizures. Though most children show signs of autism in the first year of life, about 30 percent will seem fine and then regress in both their language and social interactions at around 18 months of age.
About 30 percent of children with autism have physical signs of some alteration in early development such as physical features that differ from their parents , small head size or structural brain malformations.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Symbol For Autism