How Common Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Based on most recent CDC report, ASD is estimated to affect about 1 in 54 children, with boys being more likely to have ASD than girls. There were more than 5 million adults in the US, or 2.21% of the population, with ASD as of 2017. Government statistics suggest that the prevalence of ASD has risen 10% to 17% in recent years.
Level : Requiring Substantial Support
The communication issues that a person with Level 2 ASD may face include:
- noticeable issues with verbal and nonverbal social communication skills
- social issues being apparent despite supports in place
- limited initiation of social interaction
- reduced response to social interactions from others
- interactions that are limited to narrow special interests
- more significant differences in nonverbal communication
The repetitive behavioral issues a person with Level 2 ASD may face include:
- inflexible behavior
- struggling to cope with change
- restricted or repetitive behaviors that are obvious to a casual observer and interfere with functioning in several contexts
- difficulty changing focus or action
Autism Subtypes: Understanding The Spectrum
May 19, 2022
Your autistic childs behavior may not conform to classic characteristics described by doctors and research. Does the spectrum have subtypes meaning autism may manifest uniquely according to differing categories? This used to be the case, until an umbrella term, autism spectrum disorders, was introduced.
The spectrum nature of autism makes it difficult to diagnose it also means it is difficult to categorize. Perhaps realizing this, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders merged the subtypes into a single diagnosis called autism spectrum disorders . While some feel the subtypes were flawed, others feel a single diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders may exclude borderline cases of autism.
Before the DSM-5 replaced the subcategories with a single diagnosis, a patient could be diagnosed with five independent disorders according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . The subtypes listed under Pervasive Developmental Disorders were: autistic disorder, aspergers disorder, childhood disintegrative disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified, and Rett syndrome.
Also Check: Infant Shudder Syndrome And Autism
What Conditions Are Considered Spectrum Disorders
Until recently, experts talked about different types of autism, such as autistic disorder, Aspergerâs syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified . But now they are all called âautism spectrum disorders.â
If you still hear people use some of the older terms, youâll want to know what they mean:
Asperger’s syndrome. This is on the milder end of the autism spectrum. A person with Asperger’s may be very intelligent and able to handle their daily life. They may be really focused on topics that interest them and discuss them nonstop. But they have a much harder time socially.
Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified . This mouthful of a diagnosis included most children whose autism was more severe than Asperger’s syndrome, but not as severe as autistic disorder.
Autistic disorder. This older term is further along the autism spectrum than Aspergerâs and PDD-NOS. It includes the same types of symptoms, but at a more intense level.
Childhood disintegrative disorder. This was the rarest and most severe part of the spectrum. It described children who develop normally and then quickly lose many social, language, and mental skills, usually between ages 2 and 4. Often, these children also developed a seizure disorder.
Signs Of Autism In Children

The signs of autism can change as children grow babies and toddlers show different signs of autism than children aged 4 and older.
Babies and toddlers
Signs of autism in babies and toddlers can include a number of things that affect different parts of their life and behaviour.
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- start talking later than most children
- seem less aware of others around them for example, they might not respond to their name being called
- make repetitive movements when excited or upset – for example flapping their hands, rocking back and forth, or making the same noise repeatedly
Autistic babies and toddlers might not:
- smile back when you smile at them
- point to show when they want something
- point to show you something they find interesting
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- spend a long time setting up toys in a certain way, and set them up the same way every time
- enjoy lining toys up in order, or watching parts of them move
Autistic babies and toddlers might not:
- seem interested in playing with other children their age
- seem to use their toys to make up stories or pretend they might also start pretend play at a later age than most children
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- react strongly to sounds, smells, touch, tastes, or things they can see for example, if they like the way a stuffed toy feels, they want to spend a lot of time stroking the toy
- become upset if given something to eat or drink thats new to them
- eat a limited range of foods
Don’t Miss: What Is The Stigma Of Autism
Are Siblings At Greater Risk For Autism Spectrum Disorder
The truth is that genetics do play a role in autism. When one child is diagnosed with ASD, the next child to come along has about a 20% greater risk of developing autism than normal. When the first two children in a family have both been diagnosed with ASD, the third child has about a 32% greater risk of developing ASD.
How Is Rett Syndrome Different From Autism
Both conditions can make it hard to communicate and socialize.
But there are key differences:
- Rett syndrome usually happens in girls, while autism spectrum disorder is much more common in boys.
- Some symptoms of Rett syndrome donât happen with autism spectrum disorder. These include slowed rate of head growth, loss of hand skills, less mobility, and irregular breathing.
- A child with Rett syndrome usually prefers people more than objects and likes when you show them affection. The opposite can be true in a child with autism spectrum disorder.
Don’t Miss: Can Autism Be Genetic
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS and several other NIH Institutes and Centers support research on autism spectrum disorder.
NIH participates in the Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee , a Federal advisory committee that is designed to coordinate Federal efforts and provide advice on issues related to ASD. The committee is composed of representatives from various U.S. Department of Health and Human Services agencies, the Department of Education, and other governmental organizations, as well as public members, including individuals with ASD and representatives of patient advocacy organizations. One responsibility of the IACC is to develop a strategic plan for ASD research, which guides research programs supported by NIH and other participating organizations.
More information about research on ASD supported by NINDS and other NIH Institutes and Centers can be found using NIH RePORTER , a searchable database of current and past research projects supported by NIH and other federal agencies. RePORTER also includes links to publications and resources from these projects.
Family Support For Autistic People
The family members of autistic individuals are also likely to need some support. Having an autistic child can have a significant effect on parents, who may react to the diagnosis in a variety of ways, including relief, shock, grief, anger and guilt.
Feelings of stress, confusion and anxiety are also common in parents who are caring for an autistic child. It can be valuable for parents to consider joining a support group or participating in counselling.
For more information visit the Better Health Channel page Autism spectrum disorder tips for parents.
You May Like: Is Autism A Mental Illness Nhs
How Is Asd Managed
Various treatment options will be explained to you if your child is diagnosed with ASD. A number of organisations offer education programs and support services, such as Autism Spectrum Australia. These services can support children with ASD, and their parents or caregivers.
Its best to start treatments early after diagnosis. The right support and programs will improve specific symptoms and social skills.
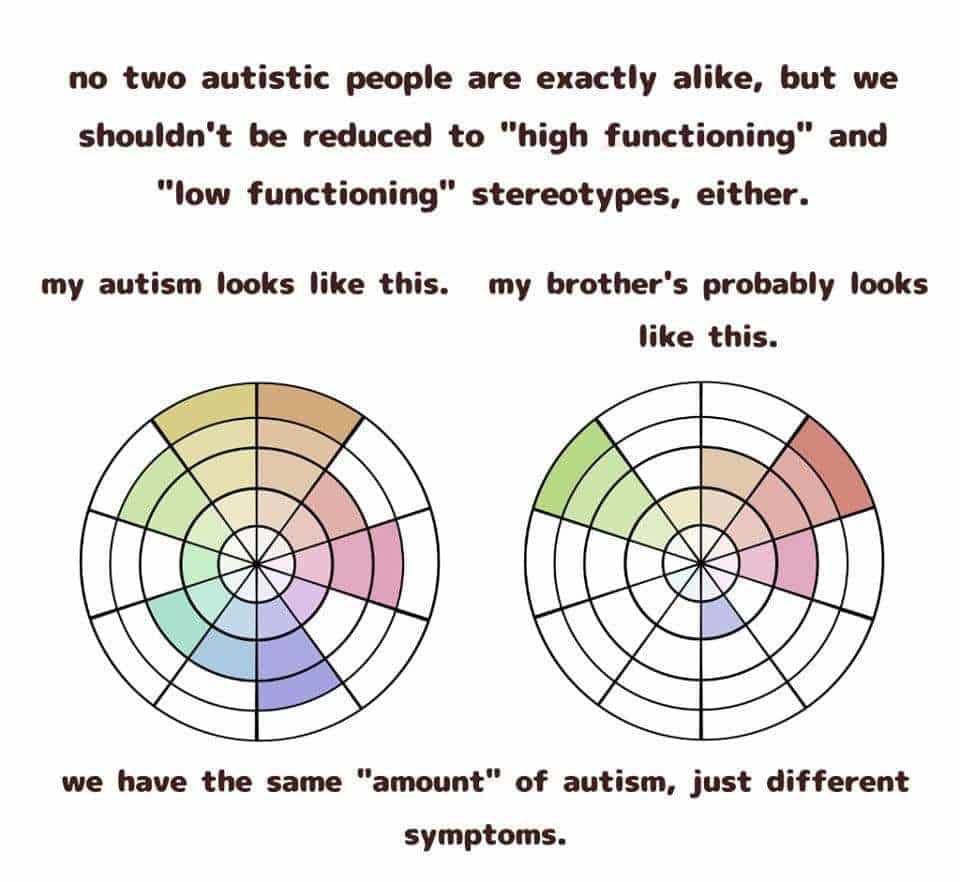
ASD is a dynamic disorder. Each person with ASD has a unique experience. which is influenced by many different factors. That is why autism is thought of as a spectrum. Treatment programs specifically tailored to individual needs often have the best results.
- Intensive educational programs and therapies can teach language and social skills.
- Speech pathology focuses on developing communication and social skills.
- Occupational therapy can support participation and independence as well as sensory motor development. For example, play skills, fine motor skills and learning how to cope in different environments.
Ensure that the therapies, treatments and supports you choose are informed by evidence. Avoid treatments that offer a cure or recovery. There is no evidence to support these claims.
People with ASD may also have a mental illness. Your doctor can help you to get treatment under the mental health care treatment plan. This provides you with 20 appointments with a mental health professional each year.
You can also attend an ASD support group.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know the primary causes of ASD, but studies suggest that a persons genes can act together with aspects of their environment to affect development in ways that lead to ASD. Some factors that are associated with an increased likelihood of developing ASD include:
- Having a sibling with ASD
- Having older parents
- Having certain genetic conditions
- Having a very low birth weight
Also Check: Adhd At Work Symptoms
How Can I Tell If Someone I Know Has Autism
Individuals with ASD interact with others differently. They often appear to have difficulty understanding and expressing emotion and may express attachment in a different manner.
Many individuals with ASD do not develop effective spoken language and rely upon other methods of communicating, such as pointing to pictures or using a tablet computer with special language applications. Others have echolalia, the repeating of words or phrases over and over. Individuals with ASD often have difficulty understanding the nonverbal aspect of language such as social cues, body language, and vocal qualities .
Individuals with ASD often have a great need for routine and order, which can make them upset if objects in their environment or time schedules change. Children with ASD may not play with toys in the same manner as their peers and may become fixated on specific objects. Persons with ASD have a different reaction to sensory stimuli by seeing, hearing, feeling, or tasting things with more or less intensity than others.
Children with ASD often have a different rate of development, especially in the areas of communication, social, and cognitive skills. In contrast, motor development may occur at a typical rate. Sometimes skills will appear in children with ASD at the expected rate or time and then disappear.
How Often Asd Occurs
CDCs Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network has been estimating the number of 8-year-old children with ASD in the United States since 2000.
ASD occurs in all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups. It is more than 4 times more common among boys than among girls.
Read Also: Am I Mildly Autistic
Level : Requires Support
Level 1 ASD is the mildest form of autism. Children with level 1 ASD have a hard time communicating appropriately with others. For example, they may not say the right thing at the right time or be able to read social cues and body language.
A person with ASD level 1 usually is able to speak in full sentences and communicate, but has trouble engaging in back-and-forth conversation with others. They may try to make friends, but not be very successful.
They may also have trouble moving from one activity to another or trying new things. Additionally, they may have problems with organization and planning, which may prevent them from being as independent as other people their age.
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
Caregivers and teachers are often the first to recognize ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school. The schools special education team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend that a child undergo additional evaluation with their primary health care provider or a health care provider who specialize in ASD.
A childs caregivers may talk with these health care providers about their childs social difficulties, including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication differences may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. They also may have trouble forming friendships with peers.
Don’t Miss: When Did Autism Become A Spectrum
Level : Requires Substantial Support
People with ASD level 2 will have more obvious problems with verbal and social communication than those diagnosed with level 1. Likewise, they will find it harder to change focus or move from one activity to the next.
Children with level 2 tend to have very narrow interests and engage in repetitive behaviors that can make it difficult for them to function in certain situations. For example, they may pace back and forth or say the same thing over and over again.
A person diagnosed with ASD level 2 tends to speak in simple sentences and also struggles with nonverbal forms of communication.
Autistic Traits And Diagnosis
Autistic traits meaning things that autistic people often do, think, and feel are often shared by people who dont have autism too. This doesnt mean that everyone is a little bit autistic, or that autistic people dont need support.
To be diagnosed with autism, a person has to have a lot of autistic traits from birth, and those traits need to have a big effect on their life. In order to be diagnosed with autism, those traits must cause what a healthcare professional would call clinically significant difficulties in their day-to-day life. This means that they have difficulties with day-to-day life due to their autistic traits and need to use their own ways of overcoming those difficulties, or the people in their life need to help them to overcome them, or both.
Being in a supportive environment makes a big difference to an autistic persons wellbeing and quality of life.
Psychological therapies like cognitive behavioural therapy are often used to treat depression, anxiety, and sleep problems, both in people who have autism and people who dont.
Psychological therapies can help to manage conditions linked with autism, like anxiety, but psychological therapies arent a treatment for autism itself. Therapy techniques might need to be adapted to work for an autistic person.
Challenges in daily living
Depending on whats offered by your NHS board and local organisations, there are therapies to help overcome the challenges that autistic people can experience.
Read Also: How To Tell If Your Child Is Autistic Or Adhd
What Are The Symptoms Of Rett Syndrome
The age when symptoms appear varies. But most babies with Rett syndrome seem to grow normally for the first 6 months before any signs of the disorder become obvious.
The most common changes usually show up when babies are between 12 and 18 months, and they can be sudden or progress slowly.
Some symptoms of Rett syndrome are:
Slowed growth. The brain doesnât grow properly, and the head is usually small — doctors call this microcephaly. This stunted growth becomes clearer as your child gets older.
Problems with hand movements. Most children with Rett syndrome lose the use of their hands. They tend to wring or rub their hands together.
No language skills. Between the ages of 1 to 4, social and language skills start to decline. Children with Rett syndrome stop talking and can have extreme social anxiety. They may stay away from or not be interested in other people, toys, and their surroundings.
Problems with muscles and coordination. This can make walking awkward.
Trouble with breathing. This can include very fast breathing , forceful exhaling of air or saliva, and swallowing air.
Seizures. Most people with Rett syndrome have seizures at some point in their lives.
Itâs also possible to have:
Behavior changes. Children with Rett syndrome tend to become tense and irritable as they get older. At times they may cry or scream for a while or have long fits of laughter.
Some kids with Rett syndrome also make unusual faces, lick their hands, or grasp at hair or clothes.
Diagnostic Criteria For 29900 Autism Spectrum Disorder
To meet diagnostic criteria for ASD according to DSM-5, a child must have persistent deficits in each of three areas of social communication and interaction plus at least two of four types of restricted, repetitive behaviors .
Specify current severity:
Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior.
Don’t Miss: Can An Autistic Person Drive