What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
Every person with ASD is unique, so the timing and severity of the first signs and symptoms can vary widely. Some children with ASD show signs within the first few months of life. In others, symptoms may not become obvious until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD appear to develop normally until around 18 to 24 months of age and then stop gaining new skills and/or start losing skills.
During infancy , a child may show symptoms that include:
- Limited or no eye contact
- No babbling
- Playing with toys in an unusual or limited manner
- Showing more interest in objects instead of people
- Starting language skills but then stopping or losing those skills
- Showing repetitive movements with their fingers, hands, arms or head
Up to 2 years of age, there may be continuing symptoms from infancy. A child may also:
- Focus only on certain interests
- Be unable to have reciprocal social interactions
- Move in unusual ways, such as tilting their head, flexing their fingers or hands, opening their mouth or sticking out their tongue
- Have no interest in playing with other children
- Repeat words or phrases without appearing to understand them
- Have behavioural issues, including self-injury
- Have trouble controlling their emotions
- Like to have things a certain way, such as always eating the same food
Possible signs of ASD at any age:
Recommended Reading: Can Autism Be Outgrown
How Many People Have Low
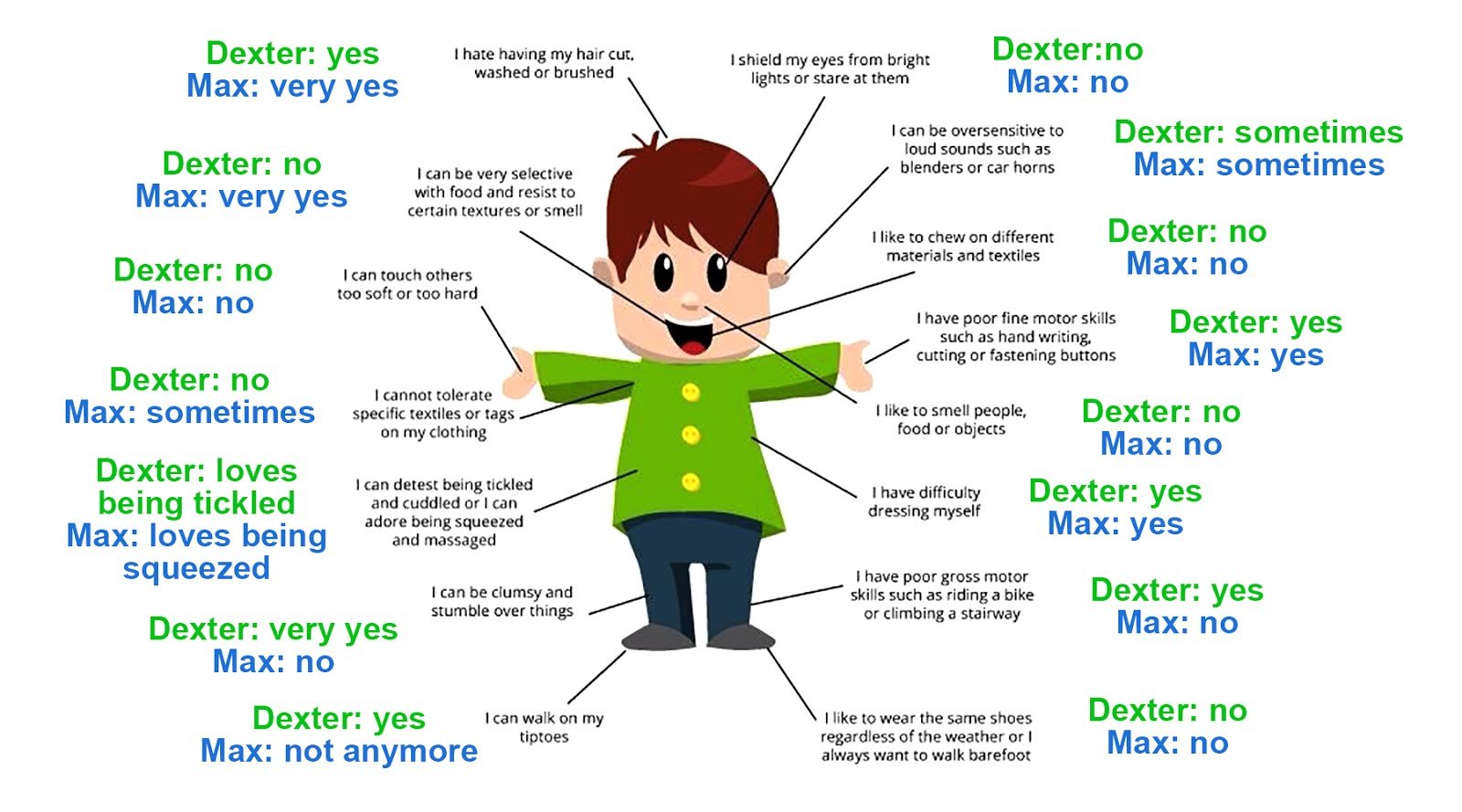
Autism spectrum disorder is associated with three severity levels. People with Level 3 autism need a significant amount of help with everyday activities, and they have very poor communication skills. Parsing data for those traits makes prevalence clear.
Autism Speaks says about a third of people with autism are nonverbal, and about 31% of kids with ASD also have an intellectual disability. At first glance, it seems obvious that a child with an inability to speak or problem solve would have low-functioning autism. But the reality is more complex.
Experts explain that people who appear nearly neurotypical are often considered high-functioning. By contrast, people thought of as low-functioning have disabilities that are visually and aurally obvious. Each person with autism spectrum disorder has strengths and challenges, and they are often location dependent.
A child with ASD might do just fine in:
- School. The child can complete assignments on time, sit quietly throughout the day, and avoid bullying.
- Church. The child can sit quietly through a sermon.
- Cars. The child can ride in the backseat of a car calmly.
But that same child could struggle with meltdowns at home. If an unexpected person appears or the routine changes, the child feels overwhelmed.
An assessment of high-functioning autism might make sense at school. At home, the term doesnt fit as well.
Top 10 Facts About Adult Autism
Steven Gans, MD, is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
People with autism, like everyone else, are adults for much longer than they are kids. Thats an easy fact to overlook when you search online for information about autism, because most articles and images focus on young children.
While its true that symptoms of autism appear first in early childhood, autism is not a pediatric disorder. Adults with autism face lifelong challenges.
So why is relatively little written about autism and adulthood? While theres no absolute answer, here are some educated guesses:
- Autism manifests before age 3, so most new diagnoses of autism are in children.
- Most people who actively read about autism are worried-but-hopeful parents of children who are or may be autistic.
- Because of the changes in how autism is defined, many adults now considered autistic never received an autism diagnosis.
- High-functioning adults with autism are often uninterested in reading about non-autistic perspectives on autism.
- Some adults with autism have intellectual disabilities that make it extremely difficult to read about autism.
Also Check: Collin Gosselin Autisum
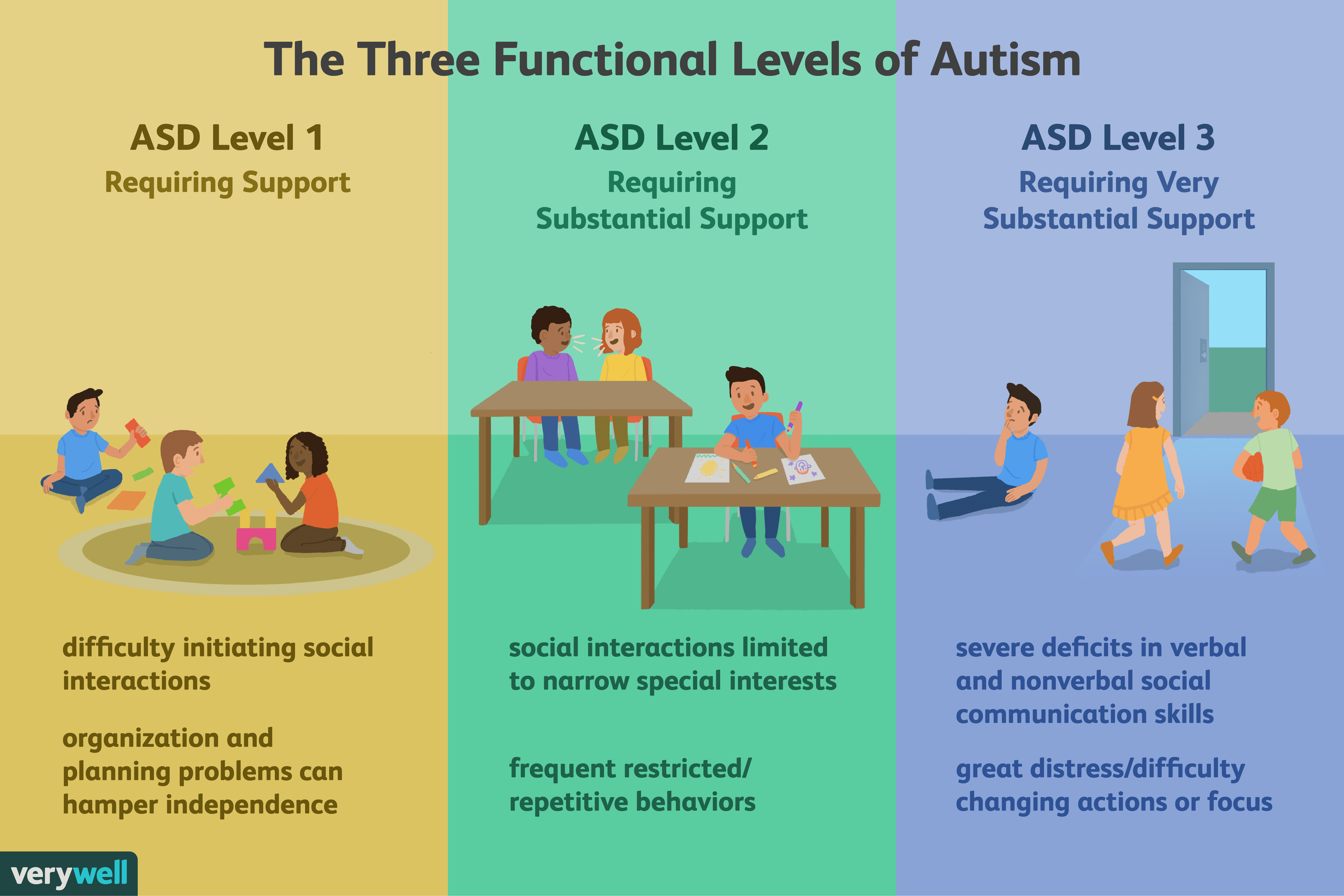
Level : Requiring Support
The communication issues that a person with Level 1 ASD may face include:
- difficulty initiating social interactions
The repetitive behavioral issues a person with Level 1 ASD may face include:
- inflexible behavior that interferes with general functioning in one or more contexts
- problems switching between activities
- issues with organization and planning, which can impact independence
Level : Requiring Very Substantial Support
The communication issues a person with Level 3 ASD may face include:
- severe issues in both verbal and nonverbal social communication, which severely impair functioning
- very limited initiation of social interactions
- minimal response to social interaction from others
- using few words of intelligible speech
- unusual methods of meeting social needs and responding to only very direct approaches
The repetitive behavioral issues a person with Level 3 ASD may face include:
- inflexible behavior
The levels of ASD correspond to the severity of the autism symptoms described above and the degree of support required.
In addition, it is important to keep in mind that the amount of support an autistic person needs can vary according to different ages or situations.
Read Also: Autism And Tuberous Sclerosis
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Previously Called Autism And Pervasive Developmental Disorders
Autism spectrum disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by the following:
- Difficulties in social communication differences, including verbal and nonverbal communication.
- Deficits in social interactions.
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests or activities and sensory problems
Many of those with ASD can have delayed or absence of language development, intellectual disabilities, poor motor coordination and attention weaknesses.
The Facts About Autism And Common Misconceptions
Are you finding that well-meaning family and friends, media commentators even some health professionals are making you more concerned and confused about your own or your childs autism or suspected autism?
Misinformation and mixed messages can lead to feelings of guilt and isolation and can work against a proactive diagnosis and support program. Although the global understanding of autism is constantly evolving, here are some of the commonly understood facts, to help you put some of these misconceptions about autism to bed.
Read Also: Level 2 Autism Symptoms
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS and several other NIH Institutes and Centers support research on autism spectrum disorder.
Read Also: What Kind Of Autism Does Symmetra Have
What If My Friend Has Autism Spectrum Disorder
Some people with ASD do not feel that they have a disorder and don’t want to change. They’re proud of who they are and they want to be accepted, even though they may have different strengths and weaknesses than most other people.
All people deserve respect. But kids with ASD may be teased, bullied, or left out because they’re different. Bullying and teasing are never the right way to treat other people, but it may be hard to be a friend with someone who has ASD.
Kids with ASD often don’t understand playful jokes. You may need to be very clear when you communicate with someone who has ASD.
Try to be patient and kind. Remember how hard it might be for the person with ASD to understand how to be a friend. Stand up for classmates who are bullied. Tell adults, so they can help protect kids who are bullied.
Also Check: Does Freddie Highmore Have Autism
A Spectrum Disorder Is Variant Enough For The Definition To Change Over Time
In the earliest years experts believed that autism was somehow directly linked to schizophrenia its now understood that this is not at all the case. Others may even wrongly assume that autism is an organic disease not a disease in the same sense we typically think of disease.
General consensus among practitioners today, however, is that its a neurological condition affecting a persons ability to develop normally, and is likely rooted in a combination of unknown genetic irregularities, and possibly even some environmental factors.
Taking all the research gathered over the last century, combined with all the clinical observations described to date, we arrive at our current understanding of autism as a spectrum disorder with a wide range of cognitive variations, behaviors and expressions.
Is that the end of the story? Not likely. As the field of genetic science continues to develop, and science unravels the mysteries of human development, its more than possible that the umbrella of what we call autism spectrum disorder today will one day be deconstructed into more refined categories and perhaps removed from the DSM-5 all together.
For now, this is where autism lies on the spectrum of human understanding.
Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
People with ASD have difficulty with social communication and interaction, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The list below gives some examples of the types of behaviors that are seen in people diagnosed with ASD. Not all people with ASD will show all behaviors, but most will show several.
Also Check: Autistic Friendly Movies
How Is Asd Diagnosed
ASD symptoms can vary greatly from person to person depending on the severity of the disorder. Symptoms may even go unrecognized for young children who have mild ASD or less debilitating handicaps.
Autism spectrum disorder is diagnosed by clinicians based on symptoms, signs, and testing according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-V, a guide created by the American Psychiatric Association used to diagnose mental disorders. Children should be screened for developmental delays during periodic checkups and specifically for autism at 18- and 24-month well-child visits.
Very early indicators that require evaluation by an expert include:
- no babbling or pointing by age 1
- no single words by age 16 months or two-word phrases by age 2
- no response to name
- excessive lining up of toys or objects
- no smiling or social responsiveness
Later indicators include:
- impaired ability to make friends with peers
- impaired ability to initiate or sustain a conversation with others
- absence or impairment of imaginative and social play
- repetitive or unusual use of language
- abnormally intense or focused interest
- preoccupation with certain objects or subjects
- inflexible adherence to specific routines or rituals
What Is The History Of Autism
The understanding of autism has developed over a number of decades. While the term autism was defined by Kanner, there is varying evidence that other professionals, including Grunya Efimovna Sukhareva and Paul Bleuler, had recognised the unique presentation of symptoms much earlier than this. Since the 1940s the diagnostic criteria has evolved and shifted as we learn more but now autism is widely understood as a spectrum of conditions with wide-ranging degrees of impairment
Dont Miss: What Causes Autism Exploring The Environmental Contribution
Also Check: Adhd Dyslexia Comorbidity
Functional Impact Of Autism On A Person
For some people autism can impact all areas of life significantly, while for others it can impact certain aspects of life to a lesser degree. Because of this, autism is referred to as a spectrum and diagnosed based on both signs and characteristics, and the impact that these differences may have on a persons life over time
If the signs or characteristics shown by a person are causing significant challenges in social, personal, family, occupational or other important areas of a persons life then it is likely that the person will be diagnosed as having autism, or being on the autism spectrum.
If the signs and characteristics are not having a major impact on a persons life or relationships, and they are able to function in all social and interpersonal settings, its unlikely that autism will be diagnosed.
The specific behaviours that capture the criteria listed above and the degree to which they affect daily life differ between individuals and can be influenced by factors such as age, learning and available supports. Due to this variability, the DSM5 provides severity levels 1 to 3 for each of the two domains to reflect the degree to which the behaviours they capture interfere in the individuals daily life requiring support.
NOTE: It is important to remember that these severity levels are a snapshot of functioning at the time of diagnosis and may change over time as skills develop and/or demands change.
Meaning Of Disorder In Asd
When considering what ASD means, it can also be helpful to understand that a disorder is not a term that is good or bad. It is simply an explanatory term that summarizes a set of characteristics or behaviors that a person may experience.
So, by using the term disorder in the phrase autism spectrum disorder, this is referring to how the diagnosis of ASD includes a set of characteristics or behaviors that typically make up a person who would qualify as having autism spectrum disorder. Generally, this means that a person with ASD has a cluster of certain behaviors related to social skills, communication skills, and restrictive or repetitive behaviors.
Read Also: Autism Gaze
What Role Do Genes Play
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
Modern Interpretation Of Types Of Autism
Fig 3
Each type of Autism demonstrates a degree of difficulty that a patient faces with verbal, social and communicative interactions. Just as a shade in rainbow overlaps and blends to the next one, so does the autism spectrum thus turning it into a challenging exercise for physicians to determine where one range in the spectrum starts and where it ends, comments Mary Alexa, autism therapy specialist.
Read Also: Are There Different Levels Of Autism
Level : Requires Support
Level 1 ASD is the mildest, or the most “high-functioning,” form of autism. Children with level 1 ASD have a hard time communicating appropriately with others. For example, they may not say the right thing at the right time or be able to read social cues and body language.
A person with ASD level 1 usually is able to speak in full sentences and communicate, but has trouble engaging in back-and-forth conversation with others. They may try to make friends, but not be very successful.
They may also have trouble moving from one activity to another or trying new things. Additionally, they may have problems with organization and planning, which may prevent them from being as independent as other people their age.
Some People Use Other Names For Autism
There are other names for autism used by some people, such as:
- autism spectrum disorder the medical name for autism
- autism spectrum condition used instead of ASD by some people
- Asperger’s used by some people to describe autistic people with average or above average intelligence
Unlike some people with autism, people with Asperger’s do not have a learning disability.
Some people call this “high-functioning” autism.
Doctors do not diagnose people with Asperger’s anymore.
But if you were diagnosed with it before, this will stay as your diagnosis.
Also Check: Recovery From Autism
Are Siblings At Greater Risk For Autism Spectrum Disorder
The truth is that genetics do play a role in autism. When one child is diagnosed with ASD, the next child to come along has about a 20% greater risk of developing autism than normal. When the first two children in a family have both been diagnosed with ASD, the third child has about a 32% greater risk of developing ASD.
Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder In Adults

Common symptoms of autism in adults include:
- Difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling
- Trouble interpreting facial expressions, body language, or social cues
- Difficulty regulating emotion
- Trouble keeping up a conversation
- Inflection that does not reflect feelings
- Difficulty maintaining the natural give-and-take of a conversation prone to monologues on a favorite subject
- Tendency to engage in repetitive or routine behaviors
- Only participates in a restricted range of activities
- Strict consistency to daily routines outbursts when changes occur
- Exhibiting strong, special interests
Autism spectrum disorder is typically a life-long condition, though early diagnosis and treatment can make a tremendous difference.
Read Also: Autism Symbol Colors
Signs In Developmental Period
- In order to be diagnosed with autism, symptoms must have been present in the early developmental period of a persons life. It can be difficult to pick up on signs and characteristics of autism for many parents, as raising a child in something that is very new to most people. For parents that already have a child diagnosed with autism, they may be more aware of the signs of autism so they pick up on these earlier. Or for other parents that have an older child that is typically developing, they also may pick up on the signs of autism earlier as they have a child to compare development with. See our signs and checklist for children with autism page for more information.
- For many adults, they many only become aware of the signs or characteristics of autism in relation to their own behaviours later in life. When they then think back over their life they may start to identify how autism may have impacted their life at different moments such as realising that others seemed to know what others were thinking when they found it difficult to read peoples emotions. Many adults with autism have learnt strategies to support their challenges throughout their lifetime. It is therefore important to think about what signs or characteristics were present at a young age when seeking a diagnosis as an adult. See our signs and checklist for adults with autism page for more information.