What Are Add And Adhd
Attention problems are among the most common mental health issues in the United States that affect children and adults. People with attention disorders may find it difficult to concentrate, sit still, or complete tasks. Children with ADHD begin life in a world thats not designed for them, requiring calmness, focus, and attention. Children are often challenged by these tasks as they develop, but children with ADHD may struggle even more. However, treatment learning ways to cope with attention problems can help.
Attention deficit disorder was the term used to describe disorders that cause attention problems. But today, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder is the official medical term. In some cases, ADD may be used to describe an attention disorder that does not cause significant hyperactivity symptoms. It may seem inaccurate to use ADHD to describe someone who does not appear to have a problem with hyperactivity, but if you receive an official diagnosis from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , you will be diagnosed with ADHD. However, there are multiple types of ADHD, and learning the type that you or your child has can help you better understand the disorder.
Do More Women Have Inattentive Type Adhd Than Have Hyperactive
ADHD isnt gender-biased, but it often goes undiagnosed in girls. More women and girls have Inattentive ADHD than have Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD. Young girls and women who struggle with inattentive ADHD symptoms are overshadowed by hyperactive boys, who demonstrate more stereotypical hyperactive ADHD behavior. Instead of detecting their symptoms as ADHD, medical professionals frequently mistake them for mood disorders. If you think you or your daughter may have ADHD symptoms, take our ADHD test for women and girls and share your results with a medical professional.
That said, Inattentive Type ADHD is not exclusive to girls. Many boys have this subtype of ADHD, though their symptoms may be similarly overlooked or misdiagnosed due to gender stereotypes.
Effective Treatments For Adhd
To properly treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, a diagnosis is needed. Diagnosing the condition can be challenging because theres not one single test to rely on. Instead, a health care provider or counselor may first work to rule out any other conditions causing the symptoms. Theyll then gather information and use psychological tests or ADHD rating scales to diagnose the mental health condition.
Criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual are essential in making a diagnosis.
- Other psychiatric disorders resemble ADHD.
- For example, many other mental health disorders can have similar symptoms, such as anxiety and depression, bipolar disorder, learning disability and language disorders, defiant disorder, or conduct disorder.
- A medical condition can affect behavior and thinking, like thyroid problems, low blood sugar, or a neurological condition like brain injuries.
- Certain drugs and medications can also cause similar symptoms.
Once theres an elimination of other potential issues, a treatment plan can begin.
You May Like: Signs My Daughter Is Autistic
Symptoms Of Autism And Adhd
Both autism and ADHD are described as neurodevelopmental disorders in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders .
The descriptions of the two disorders don’t overlap at any point, so it would be reasonable to conclude that they are entirely different from one another. In fact, until 2013, it was not permissible to diagnose both autism and ADHD in the same person.
In 2013, however, dual diagnoses became an accepted practiceand the number of people with dual diagnoses grew. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes that about 14% of children with ADHD also have autism diagnoses . More than half of children with autism may have symptoms of ADHD.
Verywell / Michela Buttignol
While the symptoms of ADHD and autism may not look the same on paper, they can look very similar in person.
Traits like distractibility and impulsivity, for example, are part of the ADHD diagnosis. While they’re not part of the autism diagnosis, they appear in most people with autism. Speech delays and idiosyncrasies are part of the autism spectrum disorder diagnosis and not the ADHD diagnosis. Yet, people with ADHD often have speech delays.
Both ADHD and autism are usually diagnosed in childhood, and symptoms are likely to continue throughout patients’ lives.
Add Vs Adhd: What’s The Difference
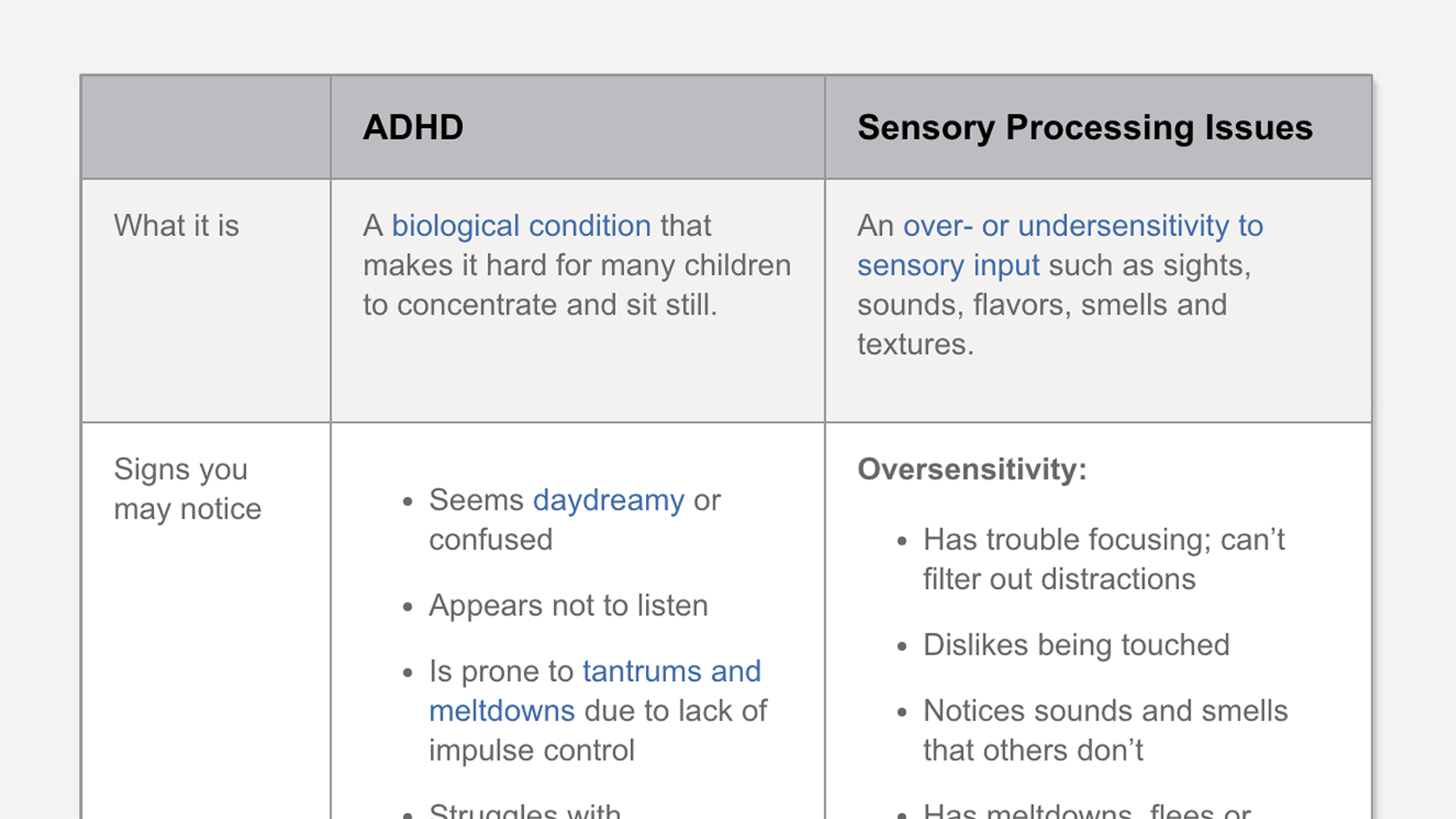
While many people continue to use the terms ADD and ADHD interchangeably, it’s important to recognize that they are not the same. Here are some key points to be aware of:
- ADD is an older term for what is now known as the inattentive type of ADHD.
- The term ADHD has been used to describe both inattentive and hyperactive types since the mid-1990s.
- However, some people continue to use the term ADD as a way to indicate that the condition does not include hyperactivity as a symptom.
- The DSM-5 currently recognizes three subtypes of ADHD: inattentive type , hyperactive-impulsive type, and combined type.
ADD doesn’t manifest itself in the same way that predominantly hyperactive-impulsive or combined types do. Children with these presentations have different symptoms.
Children with the other two presentations of ADHD, for example, tend to act out or exhibit behavior problems in class. Children with inattentive type ADHD are generally not disruptive in school. They may even sit in class quietly, but that doesn’t mean their disorder isn’t a problem and that they’re not struggling to focus. In addition, not all children with inattentive type ADHD are alike.
Children with combined type ADHD display several symptoms of both hyperactive-impulsive type and inattentive type.
You May Like: Is Ocd A Form Of Autism
Adhd Is A Form Of Neurodivergence
In addition to the many name changes over the years, our understanding of what it means to have ADHD characteristics has also shifted as research has shed more light on different forms of neurodivergence.
ADHD is a disability, but this is primarily because society is neurotypically-centered. ADHD is not an “abnormality.” Instead, it represents a form of neurodivergence, which means differences in how a person’s brain functions. Neurodivergent people may behave, learn, and process information differently than what is regarded as “typical.”
While it can be helpful to understand how ADHD characteristics can influence a person’s ability to function in their environment, it is important to remember that it is a genetic neurotype and not a disorder that needs to be cured. Different approaches can help a person manage their ADHD traits, but each person is unique, and there is no single strategy that works for everyone.
If you or your child has ADHD, understanding traits and recognizing strengths can be helpful. It can also be beneficial to explore lifestyle adjustments and coping strategies that work best for you.
Can You Outgrow Adhd
Because the symptoms of ADHD change over time, some may assume you can outgrow the disorder. In fact, it was once common to think that ADHD was a disorder that only affected children, and adults would eventually stop struggling with ADHD symptoms. However, today we believe ADHD is a disorder that starts in childhood and lasts into adulthood. Still, some children experience fewer ADHD problems over time to the point that it no longer impairs their lives. This may be because they learn to cope with problems that would cause impairments in adult life. Children with mild or moderate ADHD may be able to adapt to the disorder over time.
Still, the majority of people with ADHD continue to struggle with it into adulthood. Since ADHD symptoms can appear in adults in a way that it doesnt in children, growing up with ADHD may mean coping with changing symptoms. With treatment, its possible to learn effective coping strategies that allow you to live a life that is not impaired by ADHD symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How Much Speech Therapy For Autism
Trying To Keep Tidy: Disorganization
The fact that an ADHD brain struggles with object permanence and therefore keeps lots of things out. Combined with its tendency to move on from a task when its only about 60-80% done, means that theres often a lot of stuff. All that stuff – starts to overstimulate the ADHD brain and it can make it so that its hard to recognize whats important- triggering anxiety onto the scene to trigger you to see whats important and protect you from the onslaught.
How Is Adhd Diagnosed In Adults
ADHD is a disorder that begins in childhood and continues into adulthood. Adults who are diagnosed with ADHD experienced several symptoms of ADHD before the age of 12. As adults, they currently experience at least five persistent symptoms of inattention and/or five persistent symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity. These symptoms must be present in two or more settings and interfere with, or reduce the quality of, social, school, or work functioning.
Adults who think they may have ADHD should talk to their health care provider. Primary care providers routinely diagnose and treat ADHD and may refer individuals to mental health professionals. If you need help starting the conversation, check out NIMHs Tips for Talking With Your Health Care Provider fact sheet.
Stress, other mental health conditions, and physical conditions or illnesses can cause similar symptoms to those of ADHD. Therefore, a thorough evaluation by a health care provider or mental health professional is necessary to determine the cause of the symptoms and identify effective treatments. During this evaluation, the health care provider or mental health professional will examine factors including the persons mood, medical history, and whether they struggle with other issues, such as alcohol or substance misuse.
Read Also: Can You Tell Someone Has Autism By Looking At Them
Adhd And Anxiety Similarities:
But even those similar experiences differ in quality for ADHD brains:
-
Restlessness tends to be more long-standing, not just when worried
-
Racing thoughts are not always only worried/ future-oriented
-
Insomnia isnt always tied to worry/ fear
-
ADHD brains get overwhelmed by lots of feelings- not just anxiety and panic.
Why Was The Name Changed From Add To Adhd
ADHD has had several different names in the past and theres an on-going debate about whether its current name should be changed as well. The name changes reflect the still-growing foundation of knowledge about the condition, which can have a variety of presentations.
How has the name evolved? Heres a brief history.
The condition that healthcare practitioners today call ADHD was first given a name by the American Psychiatric Association in 1968, when it was called Hyperkinetic Reaction of Childhood in the organizations Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, second edition, the manual mental health practitioners use to make a diagnosis.³
But that name captured only one form of ADHDthe type that comes with behaviors like and inability to focus, according to pediatric psychologists Jeffery N. Epstein and Richard E. A. Loren, both of Cincinnati Childrens Hospital, in a 2013 paper in the journal Neuropsychiatry.
Twelve years later, the name was changed to ADD. That was in 1980, when the disorder was markedly re-conceptualized with a focus on problems with attention, impulsivity and hyperactivity, Dr. Epstein and Dr. Loren note, and was renamed attention deficit disorder in the DSM-IIIan update of the organizations diagnostic manual.
So, from 1980 until 1987, healthcare practitioners and the general public called it ADD.
Don’t Miss: Dsm V Autism Spectrum Disorder
Are There Different Types Of Adhd
ADHD is an umbrella term, and there are three different subtypes:
-
Inattentive type ADHD : Can include struggling with attention to detail, getting/staying organized, listening, following instructions, sustaining attention on tasks, and distractibility.
-
Hyperactive-impulsive type ADHD: Can include restlessness, fidgeting, excessive talking, and interrupting.
-
Combined type ADHD: A combination of the above two subtypes.
What Are Symptoms Of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Inattentive Type In Adults

According to the American Psychiatric Associations diagnostic criteria, there are nine symptoms associated with inattention. Although nearly everyone experiences inattention problems at times, people with the predominantly inattentive presentation of ADHD frequently experience the following symptoms. These symptoms may intrude and interfere in their daily functioning at work, with family members or in social situations. The nine symptoms associated with the predominantly inattentive presentation of ADHD are:
- Often has trouble staying focused on tasks at work, home or play
- Frequently does not pay close attention to details or makes careless mistakes at work or while doing other tasks
- Often has trouble organizing tasks or activities
- Is easily distracted
- Frequently does not follow through on instructions or fails to complete work assignments, chores or other activities
- Often forgets doing routine chores
- Avoids tasks that require long periods of mental focus
- Often loses items needed to complete tasks or activities
- Does not appear to be listening even when spoken to directly
Adults may have predominantly inattentive presentation of ADHD if they:
- Experience serious or chronic problems due to five or more of these symptoms
- Have no other mental health disorder that could be the cause of these symptoms
- Have few-to-no symptoms of hyperactivity or impulsivity
Other psychological conditions, such as depression or anxiety, can also accompany ADHD in adults.
Also Check: How Many Children Are Diagnosed With Autism
Is There A Difference Between Add And Adhd In Behavioral Therapy Treatment
No matter what you call them, all three presentations of ADHD are treatable through the standard techniques of applied behavior analysis. Since ADD is just a subset of what we call ADHD today, theres no real difference in treatments between the two.
In fact, ABA therapy for ADD and ADHD is one of the few scientifically proven treatments available. According to the Clinical Psychology Review, behavioral therapy should be the first choice for treatment in mild cases or in preschool age children. Catching the disorder early and applying consistent and effective behavioral therapies can keep cases from getting to the point where medication becomes necessary.
There are plenty of tools in the ABA toolbox to handle ADHD, but some of the more common therapies used are:
- Discrete Trial Training DTT uses drills to model appropriate behaviors, breaking down troubling behaviors into a sequence of more manageable components and reinforcing them piece by piece.
- Self-management Training Typically used with older ADHD patients, this emphasizes using self-praise and other internal feedback techniques to calm the impulses they experience and even out behaviors.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy A hybrid of behavioral and psychotherapy techniques, this kind of treatment can be used one-on-one or in group settings to encourage patients to self-assess and self-regulate.
How Does Drake Help Treat Add
For 25 years, the Drake Institute of Neurophysical Medicine has provided families with a different approach to treating ADD or ADHD, using a non-invasive, drug-free treatment program capable of delivering long term results. Because the focus of our treatment is on healing the brain and not simply medicating away the symptoms of the disorder, the patient is able to retrain the brain to improve or overcome its own dysregulation or disorder.
In fact, because our process is individually tailored to each persons unique situation, our treatment is designed to deliver quality of life improvements for all types of ADD, including all 7 of the different types of ADD listed below. Our treatment process is anchored in research and clinical experience, and utilizes extensive brain map guided neurofeedback therapy which allows our patients to have an opportunity to live healthy, fulfilling lives long after treatment has ended.
Dr. David Velkoff, Medical Director and co-founder of the Drake Institute, ensures that we utilize the most advanced qEEG brain mapping technology to help identify and examine the different types of attention deficit disorder and their correlating brain functioning abnormalities. The results of brain mapping technology are then used to guide our neurofeedback treatment protocols for treating ADD, which helps mitigate the troubles associated with ADD while simultaneously providing each individual with a custom-tailored path to recovery.
You May Like: Adderall And Wellbutrin For Adhd
What Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Many people have heard of ADHD. It may make you think of kids who have trouble paying attention or who are hyperactive or impulsive. Adults can have ADHD, too. About 4% to 5% of U.S. adults have it. But few adults get diagnosed or treated for it.
Who gets adult ADHD? Every adult who has ADHD had it as a child. Some may have been diagnosed and known it. But some may have not been diagnosed when they were young and only find out later in life.
While many kids with ADHD outgrow it, about 60% still have it as adults. Adult ADHD seems to affect men and women equally.
Thereâs no cure for ADHD. If your doctor says you have it, youâll work together to make a treatment plan just for you.
Adhd Predominantly Inattentive Presentation
Kids with this condition aren’t hyperactive. They don’t have the high energy level seen in others with ADHD. In fact, children with this form may seem shy or “in their own world.”
ADD is diagnosed if a child under age 16 has 6 or more symptoms of inattention for at least 6 consecutive months but no signs of hyperactivity/impulsivity.
The symptoms include:
- Trouble paying attention
- Doesn’t like or avoids long mental tasks
- Trouble staying on task during school, at home, or even at play
- Disorganized and seems forgetful
- Doesn’t appear to listen when directly spoken to
- Doesn’t pay close attention to details
- Loses things often
Also Check: How Does A Child Get Autism
Additude Seems To Write Only About Adhd Why Is That
ADDitudeMag.com offers a wide range of articles about ADD and ADHD, which is the official, medical term used to describe attention deficit disorder regardless of whether a patient has symptoms of hyperactivity. Because ADD is considered an outdated term by medical practitioners, we use the term inattentive ADHD to describe the sub-type not associated with hyperactivity or impulsivity. We use the term ADHD to broadly mean both the inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive sub-types, and hyperactive/inattentive ADHD when appropriate as well.