How Is Ts Treated
Because tic symptoms often are mild and do not cause impairment, some people with TS require no treatment. There are effective medications and other treatments for people whose symptoms interfere with daily functioning.
Medications
- Medications that block dopamine are the most consistently useful medications to suppress tics . These drugs may have or cause side effects and should be carefully managed by a physician or healthcare provider
- Alpha-adrenergic agonists such as clonidine and guanfacine. These medications are used primarily for hypertension but are also used in the treatment of tics. These drugs may have or cause side effects and should be carefully managed by a physician or healthcare provider.
- Stimulant medications such as methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine can lessen ADHD symptoms in people with TS without causing tics to become more severe. Previously, these drugs were not recommended for children with tics or TS and those with a family history of tics. Some studies show the short-term use of these drugs can help children with TS who also have ADHD.
- Antidepressants, specifically,serotonin reuptake inhibitors have been proven effective in some people to control symptoms of depression, OCD, and anxiety.
Unfortunately, there is no one medication that is helpful to all people with TS, nor does any medication completely eliminate symptoms.
Other therapies and treatments can include:
Aspergers Syndrome/asds And Ocd
Obsessive-Compulsive Behaviors are typically associated with Aspergers syndrome and are often a major obstacle to making improvements. Whether or not AS will be folded into a new Autistic Spectrum Disorders category in the upcoming version of the American Psychiatric Associations Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, DSM-5, the importance of early identification and finding effective ways to address OCBs in this population will remain undiminished.
Because they inter-mingle and cross boundary markers with rigidities, perfectionisms, perseverations, stereotyped behaviors, habits, impulsivities, and some kinds of tics, arriving at an exact definition of OCBs can challenge even experts in the field. However, sometimes OCBs are so prevalent, systematized, and time consuming that Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is diagnosed as a separate condition co-occurring with AS. Like Aspergers and related ASDs, OCD is often associated with problems in social functioning however, in primary OCD, social deficits tend to be much less severe and pervasive and are not embedded in the context of distinctive autistic spectrum problems like mind-blindness, idiosyncratic mannerisms and communication style, or being extremely literal.
Associations Between Asd And Other Disorders
Significant correlations were observed between the SRS total raw score and tic severity and TS diagnosis , but not OCD or ADHD . We also examined differences in gender, OCD, and ADHD rates between those who did and did not meet the cut-off for probable ASD among individuals with TS. Chi-square analyses indicated no significant differences in gender . However, rates of comorbid OCD and ADHD were significantly higher among individuals with TS who also met criteria for ASD than among those who did not. In comparison, among participants with TS, 7.5% of individuals without OCD and 7.4% of individuals without ADHD met cut-off criteria for probable ASD.
Also Check: Is Freddie Highmore Actually Autistic
A Little Bit More About Autism
The problems that are associated with Autism relate to social skills, speech and language restrictions and restricted views towards activities and routines that make the person happy. Although there are often common themes that run through the Autistic Spectrum, how the condition affects individuals can vary greatly from individual to individual. Have you ever heard of the saying Im a little bit OCD about this? or Im a little Autistic about that? The fact is, parts of both disorders can arise in every one, and this can be a reminder that even if someone close to you may display some autism like behaviours doesnt necessarily mean that the are on the spectrum. Normally a diagnosis will be based on the presence of multiple autistic symptoms such as communication, forming positive relationships, exploring, speech, independence and the ability to learn.
The three main types of Autism:
A Parent Wonders: Are New Repetitive Behaviors Ocd Or Just Autism
May 16, 2014
Our 25-year-old son, diagnosed with PDD-NOS, has always had some repetitive behaviors. Lately, though, hes wanting to redo things such as getting undressed or showering right after hes done. Hell insist we backtrack if we drive through the neighborhood a different way because we didnt go the right way. Can you offer guidance on whether these behaviors are obsessive compulsive disorder or just part of his autism? What might help?
This weeks Got Questions? answer comes from clinical psychologist and associate professor Judy Reaven, of The Childrens Hospital and the University of Colorado School of Medicine, in Denver. Both institutions are part of the Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network.
Great question. A number of psychological disorders including obsessive compulsive disorder, or OCD frequently co-occur with autism. But its also true that some symptoms of autism overlap with those of other disorders such as OCD. So it can be difficult to distinguish those that are related to an individuals autism from those that are part of another condition.
Obsessions vs Special InterestsOCD is often confused with the special interests or preoccupations characteristic of autism. However, OCD is less about obsessive interests, which can be quite enjoyable. Its more about behaviors that an individual feels driven to perform to reduce great distress or anxiety.
Read Also: Who Killed Maddox Ritch
Is Ocd On The Autism Spectrum
Are you autistic If you have OCD?
Studies indicate that up to 84 percent of autistic people have some form of anxiety as much as 17 percent may specifically have OCD. And an even larger proportion of people with OCD may also have undiagnosed autism, according to one 2017 study.
Is OCD similar to autism?
Autistic symptoms and OCD can look similar
Autism Spectrum Disorder and OCD are two different conditions, however, it is true that some symptoms of autism overlap with those of other disorders, such as OCD, and can look similar .
Is OCD part of Aspergers?
Asperger’s syndrome is one of subcategories of pervasive developmental disorder defined by behavioral symptoms. These symptoms include repetitive and stereotyped patterns similar to the behavior of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
What Is The Cause Of Dyspraxia
Whilst the exact cause of dyspraxia is unknown, research suggests that it is more than likely a result of a delayed or impaired development of neurones in the brain, rather than brain damage.
Dyspraxia is not hereditary, but members of the same family sometimes display similar dyspraxic symptoms.
Can you have dyslexia and dyspraxia?
Learning difficulties which affect the way information is processed are known as Specific Learning Difficulties and include:
Dyspraxia Attention Deficit Disorder Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
It is fairly common for someone with dyspraxia to also have other learning difficulties such as dyslexia and ADD . These are known as co-occurring difficulties and symptoms can vary in severity from person to person.
Also Check: Will My 4 Year Old Autistic Son Ever Talk
Also Check: Outgrow Autism
Assessment Of Autism Spectrum Disorder And Other Mental Illness
For cohort members and their parents, data were extracted for diagnoses of autism spectrum disorders , OCD , anxiety disorders , depression , attention deficit hyperactivity disorder , and mental disabilities assigned by adult or child psychiatrists. Additionally, we assessed their psychiatric history, whether they had ever been admitted to a psychiatric hospital or been in outpatient care for a diagnosis of a psychiatric disorder . Date of diagnosis was defined as the first contact that led to the diagnosis of interest, irrespective of other previous psychiatric diagnoses in the case history. Parental diagnoses were classed hierarchically as non-mutually exclusive events. Information about parental age and place of residence at time of birth was obtained from the Danish Civil Registration System. For research purposes all personal information from the registers are anonymized. The Danish Data Protection Agency fully approved the study.
How Ocd Symptoms Are Different From Autism Symptoms
People with ASD frequently have intensely repetitive thoughts and behaviors, much like those seen in persons with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder . But people with OCD usually feel uncomfortable with their symptoms and would like to be rid of them, whereas people with ASD usually are not bothered by their obsessions, and in fact may embrace them. People with autism spectrum disorders also have a range of other social, language, and cognitive differences not seen in people with OCD.
Read Also: Do People With Autism Die Early
Helping Autistic Adults With Ocd
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is typically diagnosed in late adolescence, although it can be recognized in children before then. Adults and teenagers with autism are more prone to OCD than their peers without autism.
OCD-related thoughts and behaviors can get in the way of social interactions and make friendships difficult. The disorders symptoms can also make it hard to keep up with schoolwork or hold down a job.
Adults with comorbid OCD and autism can benefit from various treatment approaches.
- Support groups: These peer support groups provide structured social interactions in a safe and secure environment, helping individuals to feel more connected and less isolated.
- Social skills groups: These groups teach real-life skills that help members to function in everyday life. These skills can help with obtaining and maintaining a job as well as with self-care to foster independence.
- Medications: These can be helpful to manage anxiety symptoms, but they can also come with side effects that may be enhanced in people with autism. Talk to your doctor about the potential benefits versus the risks.
- Therapy: Group and individual therapy aims to work on specific symptoms of both OCD and autism. In therapy, clients can develop coping skills and tools for everyday life.
Understanding The Relationship Between Autism Ocd And Repetitive Behaviors
- anxiety, compulsion, DSM5, obsession, OCD, repetitive behavior, spring 2018 issue
- 4661 1
One of the long-standing challenges in supporting individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders is the high rate of repetitive behavior they demonstrate. In addition to these individuals demonstrating high rates of repetitive behavior, many caregivers and support providers find it difficult to reduce the frequency or severity of impact these behaviors have on adaptive functioning and participation in community-based programs and activities. Part of this difficulty could potentially be related to complications that derive from the fact that repetitive behavior also is a central symptom of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder and a variety of other neurodevelopmental disorders. This might be resulting in many treatment and support teams being confused about the nature of the repetitive behavior, and as a result, failing to use the most appropriate strategies to address those concerns. Our focus for this article will be to provide an outline of these initial concerns and offer some general insights into better understanding the relationship between ASD and OCD.
Philip Smith, PhD
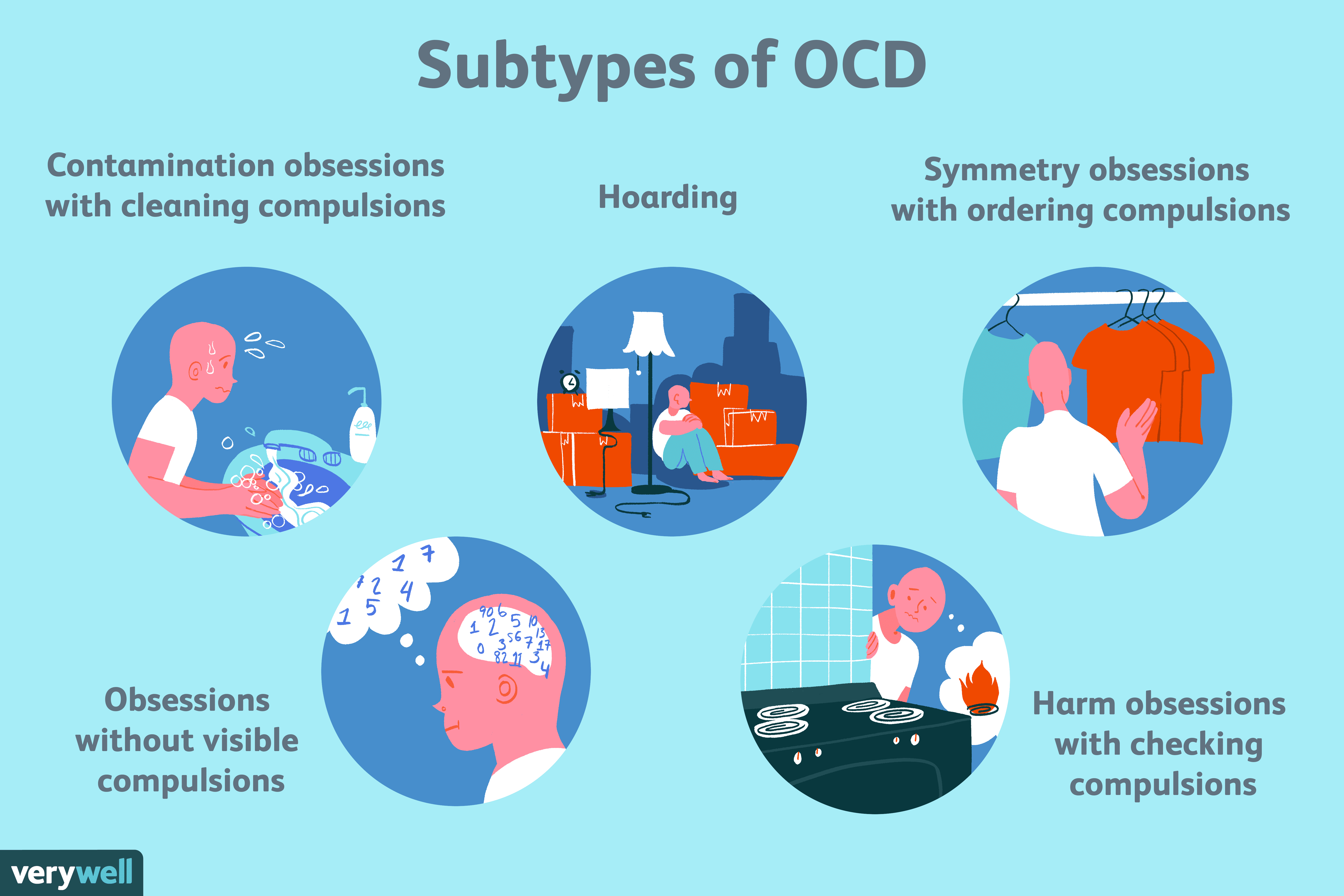
Some common examples of OCD symptoms include obsessions such as:
- Contamination
- Doubting ones memory or perception
- Scrupulosity
- Need for order or symmetry
- Unwanted, intrusive sexual/aggressive thought
- Checking
- Counting/repeating actions a certain number of times
- Arranging objects
Also Check: Kid Safe Lava Lamp
Treating These Mental Health Conditions
Professionals may treat the repetitive behaviors in both OCD and ASD similarly. For example, medication and behavioral therapy with a clinical psychologist can be treatment options after an initial diagnosis. As part of a treatment plan, the medicines most often given are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRIs.
There isnt a cure for either condition, but treatment can get symptoms under control. So the question comes up again, is OCD some form of Autism? Typically OCD is more treatable than autism. Depending on the severity of OCD, you might need long-term or intensive treatment.
For OCD, psychotherapy tends to be very effective. Exposure and response prevention or ERP is a subset of CBT often used for OCD. In ERP, you work with a therapist, and during that time, you are exposed gradually to an object you fear or an obsession. You then learn ways to avoid compulsive rituals in response to that exposure.
You could treat OCD with a plan that includes intensive outpatient and residential treatment, depending on the severity of symptoms or the impairment of functionality.
Fixations Or Intense Interests
Most common in high-functioning people with autism, fixations often manifest as intense focus surrounding a certain topic or area of interest. For example, a person with autism may obsessively practice a particular skill, or may read every book and article written about a certain subject.
Fixations may be harmful when they interfere with a persons life, but they can also be a positive feature of autism. Many high-functioning individuals with autism have turned their fixations into successful careers and made notable impacts in their fields.
Read Also: Best Toys For Toddler With Autism
How Should I Act Around Someone Who Has It
Kids who have Tourette syndrome want to be treated like everybody else. They can do regular stuff, just like other kids.
Many kids with Tourette syndrome get better as they get older. But, some people will always live with Tourette syndrome. The good news is that it wont make them less intelligent, and adults with Tourette syndrome can lead normal, happy lives.
Why Is Ocd So Common In Children With Autism
Somewhere in America, two children in separate homes wake up in the morning and began their day with a ritual. Proceeding immediately to their closets, they check to see that their collection of toys are there, aligned precisely as they were left the night before counting them carefully to make sure they are all there and in the proper order
This pattern might occur several times throughout the day, with such a degree of obsession that the child will throw a tantrum if anything gets in the way of their obsessive stock-taking ritual. If anything goes wronga toy goes missing, the storage space changes, anything disrupts the processthe results can be devastating to the child.
One of these children has been diagnosed with obsessive compulsive disorder and the other with autism spectrum disorder but their outward repetition of a compulsive behavior in this instance is nearly identical.
Autism and OCD are separate conditions, even though many of the behavioral symptoms overlap. Both ASD and OCD patients engage in repetitive behaviors that appear compulsive, and both can become agitated or even combative if someone attempts to stand in the way of those behaviors.
Also Check: Printable Visual Cards For Autism
Fragile X And Other X
The most prevalent chromosomal abnormality associated with ASD is Fragile X syndrome . Molecular testing for the FMR1 gene is recommended in individuals diagnosed with ASD and probands identified with FXS are excluded from most genetics studies of ASD. The behavioral phenotype of FXS includes OC behaviors as well as stereotypic behavior, gaze aversion, inattention, impulsivity, hyperactivity, hyperarousal, social anxiety, withdrawal, social decits with peers, abnormalities in communication, and unusual responses to sensory stimuli. The full mutation is described as having more than 200 CGG repeats in the 5 untranslated region of the FMR1 located at Xq27.3 and typically involves an altered pattern of methylation. There is transcriptional silencing of the FMR1 gene and lack of the FMR1 protein called FMRP. Recent studies suggest that some males with the premutation also have social, emotional, and cognitive decits, although sample sizes are small or clinically referred .
also recently reported on the results of a questionnaire study of 351 males with Duchenne muscular dystrophy . DMD is characterized by progressive proximal muscular dystrophy and is the result of mutations in a very large gene that encodes dystrophin and is located at Xp21.2. In this study, 11 of the subjects were reported to have ASD and of this number 3 also had OCD . Unfortunately, no details were provided concerning either the nature of the ASD or OCD symptomatology.
Ocd Symptoms Are Different
While most children with autism have repetitive movements or vocal tics that show us when they are feeling anxious or excited, the source of the obsessive habits of someone with OCD is different. When someone with OCD feels driven to fill their life with repetitive patterns this is part of a mental process. Their compulsive behaviors have complicated motives which are not reasonable and which, in themselves, are part of the diagnosis.
A child with OCD will explain why she needs something to be done exactly as she demands and will not be able to move from this rigid behavior. For example, she may be unable to eat her yogurt if there is a small piece of metal foil stuck to the rim of the container. No amount of coaxing or patient reasoning from the parent will make any difference or be able to reduce the childs anxiety.
You May Like: Writing An Autistic Character
How Do I Beat Ocd On My Own
25 Tips for Succeeding in Your OCD TreatmentAlways expect the unexpected. Be willing to accept risk. Never seek reassurance from yourself or others. Always try hard to agree with all obsessive thoughts never analyze, question, or argue with them. Dont waste time trying to prevent or not think your thoughts.More items
The Neurobiology Of Obssessive
To have a clear understanding of OCD, and how the disorder affects behaviour, one must first recognize that obsessions and compulsions are two separate manifestations of an illness that have similar biological roots. The DSM-5 defines obsessions as recurrent and persistent thoughts, urges, or images that are experienced as intrusive or unwanted, and compulsions are repetitive behaviours or mental acts that an individual feel driven to perform in response to an obsession or according to rules that must be applied rigidly . Compulsions are the outward manifestations of the hidden obsessive thoughts. They could be likened to the tip of an iceberg, whereas obsessions are the part of the ice berg that is hidden beneath from the surface. Hence, when an individual is not acting out the compulsion, it does not necessarily mean the obsessions are also gone. Per research, obsessions are more resistant to treatment than compulsions and are the source of profound distress in patients.
You May Like: What Is Low Functioning Autism