Depression And Adhd: Chicken And Egg
For many individuals, depression and ADHD go hand in hand. Their dual symptoms include a persistent, sad, or irritable mood, loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities, changes in appetite or weight, sleep problems , low energy, feelings of worthlessness, or inappropriate guilt. Some clients experience thoughts or acts of self-harm.
As with anxiety, there are three ways ADHD-depression present together. Most commonly, depression follows the ADHD. Managing ADHD symptoms is tough, so a person with ADHD may feel hopeless and ineffective, leading to diagnosable depression. Even with a good evaluation, the only way to test this is to address the ADHD with stimulants and cognitive behavioral therapy, and see if the depressive symptoms lessen. Frequently, they will.
In other cases, clients respond favorably to stimulants at first, only to have a quick drop-off in their impact. Stimulants raise energy and alertness, and increase productivity, which helps people feel better. However, that improvement may mask underlying depressive symptoms that exist in tandem with ADHD, and may last only as long as the stimulant is working, usually eight to 12 hours. Fortunately, these clients tend to be good candidates for adding an SNRI. Treating co-occurring depression and ADHD in this way allows the prescriber to try lower stimulant doses while maintaining treatment satisfaction.
Donât Miss: Is Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Make Time For Your Enjoyment
Both children and adults with ADHD or autism may benefit from having some downtime each day to do something they enjoy, such as reading, playing a musical instrument, or spending time with a pet. This can help to relieve stress and improve overall mood and focus. Also, when you choose to make time for yourself it directly impacts your ability to be more patient, present, and understanding with your loved ones who have ADHD or autism.
Compliance With Ethical Standards
All procedures performed in this study were approved by the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Helsinki committee of the medical center waived the need for informed consent, as the study was retrospective and all the data were derived from the clinical charts.
Donât Miss: Does Autism Affect Lifespan
Also Check: What Does An Autistic Shutdown Feel Like
Intervention Options And Distinctions
Some parents may prefer to start with non-medicinal therapies to manage behaviors asso- ciated with autism that hinder academic and interpersonal success. One mainstay ASD intervention is behavioral therapy administered by a psychologist who specializes in ASD or a professional trained in Applied Behavioral Analysis. Behavioral therapy reinforces an individuals strengths and discourages inhibiting behaviors. Posting lists, rules, and schedules to keep ASD kids organized can be helpful. Checking off items on a checklist can give autistic kids a sense of accomplishment when they complete tasks.
Physical exercise is a useful intervention for children with ADHD and/or autism, all of whom seem to have boundless energy. Channeling excess energy into physical activity, such as swimming or karate which dont require a lot of interaction with other kids allows them to burn it off without the pressures of socializing.
Medication can also form part of an individuals care plan. Because children with ASD have more unpredictable reactions to stimulants compared to children with ADHD, they are less likely to be prescribed. Most pediatricians, and virtually all child psychiatrists, feel competent in prescribing stimulants for ADHD, but might refer a child with ASD to a psychiatrist or a psycho-pharmacologist before trying different types of medications or increasing the dosage of current ones.
- quetiapine fumarate
- risperidone
FREE EBOOK
Impact Of Comorbid Adhd And Asd: A Continuum
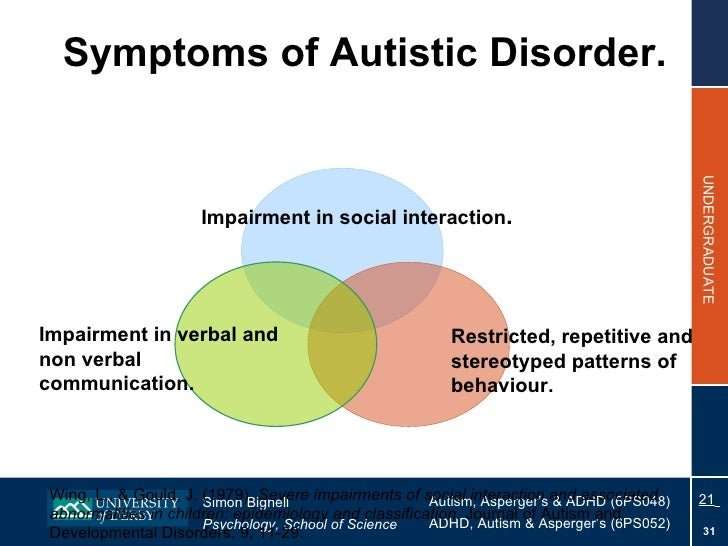
Research on co-occurring ADHD and ASD has been limited by diagnostic restraints, since according to DSM-IV, many works have excluded subjects with more than one developmental or psychiatric disorder . The study conducted by Sinzig et al. , reveals a large phenotypic overlay between ADHD and ASD. The two identified subtypes, hyperactive-communication impaired and inattentive-stereotyped, follow the DSM classification and could be the manifestation of two distinct neurochemical circuitsdopaminergic and serotonergicinvolved in the disorders. In view of this, the division of ASD into two-dimensional scales of social-communication and RRB dimensions, and of ADHD into inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms has high significance for the classification of developmental conditions.
Also Check: Autism Resources For Parents
Beyond Meds: Treating Add And Asd
Before or after a child gets a definitive diagnosis, behavioral therapies can help. If a child has ongoing social challenges, for example, many of the interventions are similar such as behavioral therapy to help develop skills, Bertin says.
After Clarks ADHD diagnosis, he received counseling and assistance with organizational skills. Later, when he was identified as autistic, the focus of treatment changed. Treatment now involves helping Clark intellectually grasp the gaps between him and the rest of society why hygiene matters, what kind of things he does that other people might find odd or insensitive, his mother says.
Several other interventions, including speech therapy, occupational therapy, educational interventions, and parent training, can be explored.
How Is Autism Diagnosed
Like ADHD, Autism cant be diagnosed with a medical test like a blood test or physical exam. Instead, its diagnosed with psychological exams and other observational signs. The DSM-5 changed the way autism is diagnosed significantly. Before the revisions, autism was broken up into different categories based on severity and specific symptoms. However, autism is so variable many clinicians believed the categories werent able to accurately describe autism as a whole. Instead, its now defined as an autism spectrum disorder, which encompasses the full range of possible symptoms and severities.
Its important to note, the criteria for an autism diagnosis looks at deficiencies and uses words like deficit. This language is debated because of the way it may impact people to learn they have a chronic condition that causes deficits. However, being diagnosed with a disorder doesnt mean you are doomed to be deficient, and you may learn to cope with autism on your own or with help in a way that allows you to live a productive and meaningful life.
Heres a breakdown of the diagnostic criteria in the DSM-5:
You must experience persistent deficits in three areas of social communication and interaction. These issues arent just specific to one context, like school or home. Instead, you will struggle with social norms in multiple settings. Social communication and social interaction include:
You must also experience two of the four types of restricted, repetitive behaviors.
Also Check: How To Teach An Autistic Child Potty Training
How Does Treatment For Adhd And Autism Differ
Treatments for both ADHD and autism can vary depending on the severity of the condition and how much the symptoms affect everyday life.
Behaviour therapy and medication can help with both these conditions. With autism, however, extra therapy may be recommended such as counselling, education support, speech therapy and occupational therapy.
With both, an early diagnosis can help children and their families to manage the condition. If you are at all concerned that your child has either ADHD or autism, its a good idea to speak to your doctor or paediatrician as soon as possible.
Dont Miss: How To Tell If A Child Is Autistic
Conclusion: Implications For Future Research
In light of the new DSM-5 criteria, which allow a dual diagnosis of ASD and ADHD behaviors, further investigation into clinical overlap of these two conditions will possibly enhance our understanding of the etiology/genetics factors and common metabolic pathways of these disorders, and of the appropriate sequence of therapeutic interventions and pharmacological treatment for their co-occurrence, particularly in early preschoolers. It remains to be seen whether early intervention could change the course of ASD in statu nascendi, interpreted as a continuum with other NDDs such as ADHD or SCD of less than severe character.
Recommended Reading: Adhd Delayed Sleep Phase
Autism In Women: Diagnostic Considerations
If you are seeking a diagnosis, prepare yourself to face skepticism possibly even from your clinician. Unfortunately, anyone without a nuanced understanding of the spectrum may be doubtful of a seemingly normal adult female requesting an evaluation.
Thats why it is essential to work with clinicians who have experience diagnosing autism in adults. It is especially helpful if they have knowledge of any existing diagnoses, like ADHD, and have previously evaluated or counseled other women. While the research on autism in women is sparse, first-hand experience can equip these clinicians to accurately assess the possibility of autism.
The good news is that experienced, knowledgeable psychologists and psychiatrists do exist, and one of those individuals will take your concerns and questions seriously. The clinician will likely evaluate you using a combination of diagnostic surveys and interviews with you and someone who knew you as a child. Generally, this is a parent, but it could be any person who observed you consistently before age four or five. After your doctor gathers this information, it will inform your diagnosis.
You can decide to be evaluated at any point in your life. Receiving my diagnosis, at age 19, improved my relationships with family and friends. I didnt become a different person, but afterward I could articulate my ways of thinking and perception.
Parents And Teachers Reports
Differences in informant reports of clinically elevated ADHD and anxiety symptoms were also of interest. Parents reported more severe ADHD symptoms, while teachers reported more severe anxiety symptoms. This can be explained as almost one third of the study participants received medication for ADHD, which decreased symptom severity in the structured school setting. In contrast, the school environment provides more stressful social situations, which may lead to more noticeable anxiety symptoms. Therefore, we chose to use only the parental reports for the assessment of comorbidities .
Llanes et al. compared parentsâ and teachersâ reports on ADHD and anxiety symptoms in preschool and school-aged children, and found a low concordance between these informers, with teachers reporting fewer problems overall.
Don’t Miss: Is Autism A Severe Disability
Differences Between Adhd And Asd
Despite both conditions sharing similar symptoms, they are two different disorders.
Ability to focus
While those with autism may lose concentration when doing tasks they dont particularly like, they can show intense focus and fixate on special interests they have. Those with ADHD are easily distracted and generally dislike any task that requires attention to detail.
Communication
Autistic individuals tend to be socially awkward with the inability to put thoughts and feelings together to communicate effectively and rarely make eye contact. Though on occasion, some with ASD can talk in great lengths but only about their particular interests.
In contrast, those with ADHD may have the gift of the gab, disrupting others mid-conversation and leading their own confidently.
Repetition
Individuals with ASD generally prefer order, doing the same things repeatedly and dislike unpredictable changes. They find comfort in having the same daily routine, eating the same food or being severely attached to only one particular favorite toy. In comparison, those with ADHD can be disorganized, dislike repetition and often get bored fairly quickly.
Read Also: How Long Do Autistic Live
Differential Diagnosis Of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
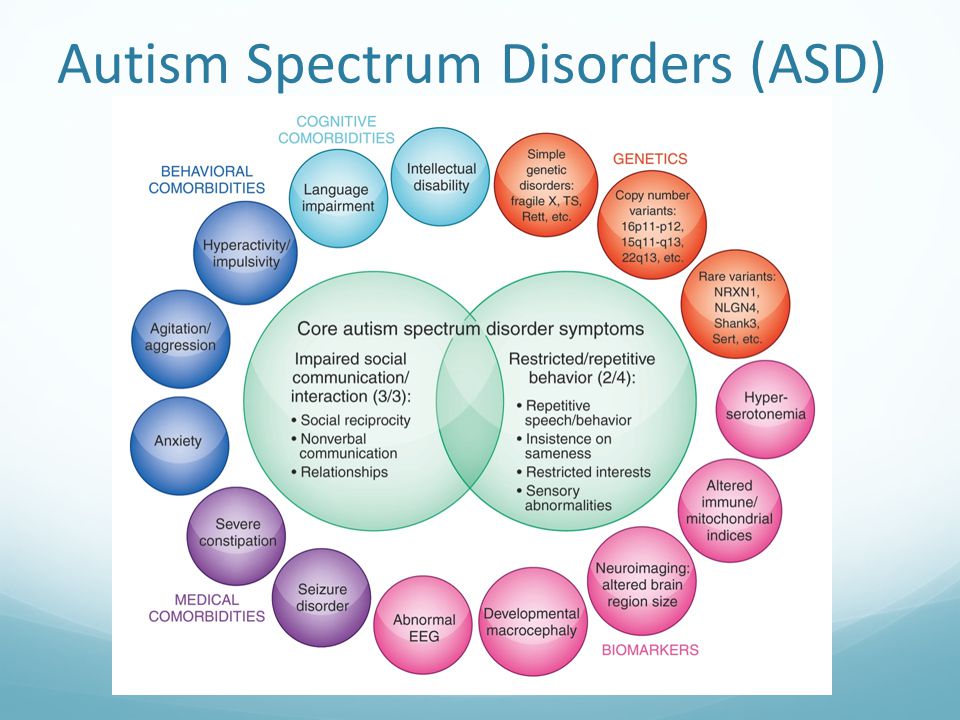
Neurodevelopmental disorders are impairments in the growth, development, and function of the brain that affect emotion, learning ability, and memory, and that unfold as the individual grows. This disorder is highlighted by characteristic deficiencies: cognitive impairment, delays in maturationally-influenced psychological features, overlap among NDDs, and genetic predisposition,
In DSM-IV, the chapter that includes Diagnoses usually first made in infancy, childhood, or adolescence has been deleted and substituted in DSM-5 by the referred Neurodevelopmental Disorders , which includes six categories:
-
Specific Learning Disorder
-
Motor Disorders
-
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
The recognition of the prevalence of comorbidities in NDD, particularly during the preschool years, is important in order to obtain a more complete and comprehensive vision of the range of abilities and deficits of a child without being limited by the possibilities of exclusion obsolete diagnostic criteria of DSM-IV. Especially since these conditions often overlap, an accurate differential diagnosis is needed to provide appropriate services. Where once our diagnostic manual prevented comorbid diagnoses of disorders such as autism and ADHD, this exclusion is no longer present in DSM-5. This is the recognition that although symptoms can overlap, a child with autism and ADHD is clearly different from a child with autism alone and therefore, may require different intervention services .
Recommended Reading: Are People Born With Autism
Intellectual Disability And Adhd
The diagnosis of intellectual disability , also to be known as intellectual developmental disorder in the WHOs most current International Classification of Diseases , was also revised in the DSM-5 to replace the DSM-IV diagnosis of mental retardation. ID is a chronic condition diagnosed in 2% to 3% of children > 5 years of age that often co-occurs withand affects prognosis forother neurodevelopmental and mental health disorders. ID is characterized by developmental deficits in cognitive function or in adaptive functioning, such that individuals may be unable to meet developmental and sociocultural standards for personal independence and social responsibility . In ID, intelligence quotient scores are 2 standard deviations below the population mean . Based on DSM-5 criteria, adaptive function rather than an IQ score is used to define the level of severity , because support requirements depend largely on the level of adaptive function .
ADHD is the most common neurodevelopmental disorder comorbid with ID. Prevalence rates are three to four times higher in children or youth with ID than in the general population . However, diagnosing ADHD in individuals with ID is particularly difficult because lower intellectual functioning can affect attention and behaviour , leading to diagnostic overshadowing. ADHD-like symptoms may also mask a coexisting organic or psychiatric illness .
Autism Spectrum Disorder And Adhd In Adults
Autism Spectrum Disorder and ADHD are two neurodevelopmental disorders with a high co-occurrence rate. This rate does not change in the adulthood phase, and it is observed as two conditions accompanying each other at high rates. They face similar but unique problems and challenges. It can be said that there are similarities in symptoms in order to get a clinical evaluation and diagnosis. Research on autism and ADHD in adults is very limited. As such, clinicians and professionals generally agree on the diagnosis of these disorders and the initiation of treatment for these individuals.
As mentioned above, there is not enough and sufficient data and research in the literature on autism and ADHD in adults. Despite this, the probability of co-occurrence of these disorders is estimated to be between 20% and 40%.
Although ADHD and autism symptoms are largely similar, they have characteristic symptoms at some points. Inadequate social communication and certain restricted behaviors are symptoms of both, but ADHD also includes inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
Adults with autism have more ADHD symptoms than children with autism. Therefore, functional impairments are more disturbing in adults with autism. Their lives become more challenging. This conclusion was reached as a result of a study conducted on the frequency and severity of autism and ADHD-related behaviors.
You May Like: When Do Symptoms Of Autism Appear
Autism In Women: Accommodations And Treatment
There is no universally prescribed medication for people on the autism spectrum. Prescription treatments more often address a comorbid condition, such as anxiety, mood disorders, ADHD, or seizures.
However, almost all autistic people are encouraged to try cognitive behavioral therapy . This talk-based counseling can help autistic adults identify and process the ways they experience the world differently. A therapist can help an autistic patient develop an understanding of social rules or learn how to advocate for themselves in a work setting.
It is important to note that an adult with autism can determine which new skills they want to learn and which personal differences they want to keep or change. By contrast, many young children placed in Applied Behavior Analysis therapy are trained to behave less autistic while still too young to parse out how being on the spectrum affects their sense of self.
Accommodations for people with autism include creating sensory-friendly spaces, establishing clearly defined social rules, and holding neurodiversity-based autism education in the community. In a work-place, there might be the provision of a job mentor or the flexibility to work from home.
Autism And Comorbid Conditions
This article offers a brief overview of autism and comorbid conditions.
Autism is often linked with other conditions. Where one or more conditions co-exist, they are called comorbid conditions.
The characteristics of autism, according to DSM 5, are as follows
Autism is most often, but not exclusively, linked with intellectual disabilities, ADHD, OCD, epilepsy and childhood-onset schizophrenia.
Research continues to establish more exact comorbid figures however, below are the numbers at the time of writing
- Number of people with autism and OCD around 17% with individuals who have a diagnosis of autism showing a 2-fold higher risk of a later diagnosis of OCD
- Number of people with autism and an intellectual disability 56%
- Number of people with autism and ADHD around 30% 50%
- Number of people with autism and epilepsy around 20%
A substantial number of children with autism can also display gastrointestinal symptoms 79.3% .
According to Autistica, 79% of autistic adults are also affected by mental health issues such as depression.
You May Like: Is The Actor In The Good Doctor Autistic