Does Aspergers Syndrome Still Exist In Dsm 5
With the new model of Autism, it means that Aspergers Syndrome which was added to the DSM back in 1994 and has existed for a period of time, was removed in May 2013. Which begs the question does Aspergers still exist? In official terms no, because the diagnosis would be Autistic Spectrum Disorder Level I.
The reason for diagnosing what was Aspergers as Autistic Spectrum Disorder Level I is that in general terms the need is of a low level of support. On the face of it, that is correct, but the type of low-level support that is needed has to be of a different genre than for someone who is ASD Level III.
However, to just give a label of ASD Level I, is not sufficient. Autism, at different level, affects each child or adult differently. On a personal experience, I have encountered clients with similar autistic traits but how the traits impact on their lives will depend on their personality levels of sensitivity resilience and the effectiveness of their support. To counteract the impact of ASD labelling, there should be specific descriptors to highlight individual signs and symptoms.
Aspergers may not exist as a definitive within the DSM 5 Autism Spectrum Disorder, but clinicians will still carry on using the international coding system especially when they are dealing with medical insurance companies , as Aspergers is still included in that system. Groups and organisations that support their members that have Aspergers will continue to use the descriptor.
Classification Based On Dsm
The DSM-5 criteria for ASD differ from the DSM-IV-TR criteria in several respects. First, they do not distinguish subtypes of ASD, such as autistic disorder and Asperger disorder, instead classifying a single category of ASD. Second, the DSM-5 recognizes only 2 domains of impairment: social communication and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, and all 3 items in the social communication domain are required. Third, in contrast to the 12 distinct diagnostic criteria of the DSM-IV-TR, the DSM-5 specifies 7 criteria but some of the DSM-5 criteria describe more general principles and behaviors than in the DSM-IV-TR.34 Fourth, the DSM-5 ASD criteria allow for the consideration of historical behaviors in addition to current behaviors, instead of primarily focusing on current behavior as with the DSM-IV-TR ASD criteria.
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder is a complex developmental condition involving persistent challenges with social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behavior. While autism is considered a lifelong disorder, the degree of impairment in functioning because of these challenges varies between individuals with autism.
You May Like: How To Teach Kids With Autism
Risks And Benefits Of Adult Diagnosis
Many adults who meet diagnostic criteria for ASD do not carry formal medical diagnoses of ASD, either because they have never come to medical attention or because they have been misdiagnosed with a differential condition . When deciding whether to refer an adult patient for a diagnostic evaluation for ASD, one should consider potential risks and benefits of a diagnosis, and should discuss these possibilities with the patient and, if applicable, their supporters.
Potential benefits of a formal diagnosis are as follows.
- Would confer legal rights to accommodations in school, at work, in healthcare, or in other settings.
- May assist the individual in developing a better understanding of self.
- May provide peace of mind through the professional confirmation of life experiences.
- May provide means to experience better coping or quality of life by more directly helping in recognizing strengths and accommodating challenges.
- May provide others means to understand and support the individual.
- May qualify the individual for benefits and services for people who have an ASD diagnosis.
- May qualify the individual for programs for people with disabilities, such as scholarships or incentives that are meant to increase workplace diversity.
Potential risks associated with seeking an ASD diagnosis are as follows.
Potential Impact On Asd Prevalence Estimates

When ASD prevalence estimates are adjusted to include only children meeting DSM-5 ASD criteria, the prevalence of ASD is lower than previously reported ASD prevalence for both 2006 and 2008 . The adjusted prevalence estimates included 5339 children meeting both DSM-IV-TR ADDM Network criteria for ASD and DSM-5 ASD criteria and 304 children who did not meet ADDM Network ASD case status after clinician review but did have documented behaviors consistent with DSM-5 ASD criteria. For 2006, the prevalence estimate using DSM-5 criteria was 7.4 per 1000 compared with 9.0 based on the ADDM Network application of the DSM-IV-TR. For 2008, the DSM-5based estimate was 10.0 per 1000 compared with 11.3 based on the DSM-IV-TR .
Don’t Miss: Can Not Taking Prenatal Vitamins Cause Autism
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism is not a single disorder, but a spectrum of closely related disorders with a shared core of symptoms. Every individual on the autism spectrum has problems to some degree with social interaction, empathy, communication, and flexible behavior. But the level of disability and the combination of symptoms varies tremendously from person to person. In fact, two kids with the same diagnosis may look very different when it comes to their behaviors and abilities.
If youre a parent dealing with a child on the autism spectrum, you may hear many different terms including high-functioning autism, atypical autism, autism spectrum disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder. These terms can be confusing, not only because there are so many, but because doctors, therapists, and other parents may use them in dissimilar ways.
But no matter what doctors, teachers, and other specialists call the autism spectrum disorder, its your childs unique needs that are truly important. No diagnostic label can tell you exactly what challenges your child will have. Finding treatment that addresses your childs needs, rather than focusing on what to call the problem, is the most helpful thing you can do. You dont need a diagnosis to start getting help for your childs symptoms.
Whats in a name?
Dont Miss: What Is The Best Pet For An Autistic Child
Behavioral Psychological And Educational Interventions
People with ASD may be referred to a health care provider who specializes in providing behavioral, psychological, educational, or skill-building interventions. These programs are typically highly structured and intensive, and they may involve caregivers, siblings, and other family members. These programs may help people with ASD:
- Learn social, communication, and language skills
- Reduce behaviors that interfere with daily functioning
- Increase or build upon strengths
- Learn life skills necessary for living independently
Also Check: Is Junie B Jones Autistic
What Are The New Criteria For Diagnosing Autism
The DSM-5 criteria for autism fall under two categories:
In addition, clinicians are asked to rate the severity of these problems, based on the level of daily support they require.
Read the full text of the DSM-5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder.
How will these DSM-5 changes affect people already diagnosed with Asperger syndrome, PDD-NOS or other previous autism categories?
The DSM-5 states, Individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnoses of autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
What if I or my child want to keep the diagnosis of Asperger syndrome?
Many people strongly identify with their diagnosis of Asperger syndrome. Healthcare providers can still indicate a diagnosis of Asperger syndrome in a patients medical record, alongside the current DSM-5 coding for autism spectrum disorder. Colleges and school districts may vary in their policies for educational records.
What is the new diagnosis of social communication disorder? Who will it affect?
This new diagnosis applies to people who have persistent problems with the social use of language, but dont have restricted interests or repetitive behaviors.
Also see: What is social communication disorder? How is it treated?
Is social communication disorder on the autism spectrum?
Have additional questions? Send them to
Autism Spectrum Disorder: Whats Your Level Of Support
Since autism exists on a spectrum, the level of support needed in day-to-day life varies greatly from person to person.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders looks at three levels of needs, which are defined by how much support the autistic person requires.
In addition, many diagnoses tied to autism spectrum disorder are now outdated and seen as part of the autism spectrum. Some autistic people still identify with these diagnoses.
Some of these diagnoses and labels include:
- atypical autism
- pervasive developmental disorder
Every autistic person is unique. An autistic person wont always fit exactly into one of these levels or categories. For instance, some autistic people may be nonverbal but need only minimal support in day-to-day life.
Don’t Miss: What Is The New Definition Of Autism
Use Of Principles Versus Examples
DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria had included examples, derived from multiple levels of analyses, that described specific behaviors, such as shared enjoyment, general qualities, and important contexts , through which deficits in ASD could reliably be seen . Recognizing the myriad behavioral presentations among individuals with ASD of varying developmental levels, DSM-5 and ICD-11 introduced broad principles in place of specific examples to better define symptom subdomains. The new principles, each accompanied by a non-exhaustive list of similar examples, present deficits within each subdomain that are applicable across age ranges and developmental levels, thus providing greater systematic sensitivity and specificity. Notably, however, while conceptualized through clinical observation, the DSM-5 and ICD-11 criteria included within each domain are not empirically-defined dimensions .
How Does The Dsm
Six major changes include:
1. Four previously separate categories of autism consolidated into one umbrella diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
Previous categories:
- Pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified
2. Consolidation of three previous categories of autism symptoms into two categories of symptoms.
Previous categories:
- Persistent deficits in social communication/interaction and
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior
3. The addition of sensory issues as a symptom under the restricted/repetitive behavior category. This includes hyper- or hypo-reactivity to stimuli or unusual interests in stimuli
4. A severity assessment scale based on level of support needed for daily function.
5. Additional assessment for:
- Any known genetic causes of autism
- Language level
- Intellectual disability and
- The presence of autism-associated medical conditions
6. Creation of a new diagnosis of social communication disorder for disabilities in social communication without repetitive, restricted behaviors.
You May Like: Do I Have Adhd Teenager
Diagnosis Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Early signs of this disorder can be noticed by parents/caregivers or pediatricians before a child reaches one year of age. However, symptoms typically become more consistently visible by the time a child is 2 or 3 years old. In some cases, the functional impairment related to autism may be mild and not apparent until the child starts school, after which their deficits may be pronounced when amongst their peers.
Social communication deficits may include1:
- Difficulty appreciating their own & others’ emotions
- Aversion to maintaining eye contact
- Lack of proficiency with use of non-verbal gestures
- Stilted or scripted speech
- Difficulty making friends or keeping them
Restricted interests and repetitive behaviors may include1:
- Inflexibility of behavior, extreme difficulty coping with change
- Being overly focused on niche subjects to the exclusion of others
- Expecting others to be equally interested in those subjects
- Difficulty tolerating changes in routine and new experiences
- Sensory hypersensitivity, e.g., aversion to loud noises
- Stereotypical movements such as hand flapping, rocking, spinning
- Arranging things, often toys, in a very particular manner
What Are The Types Of Autism
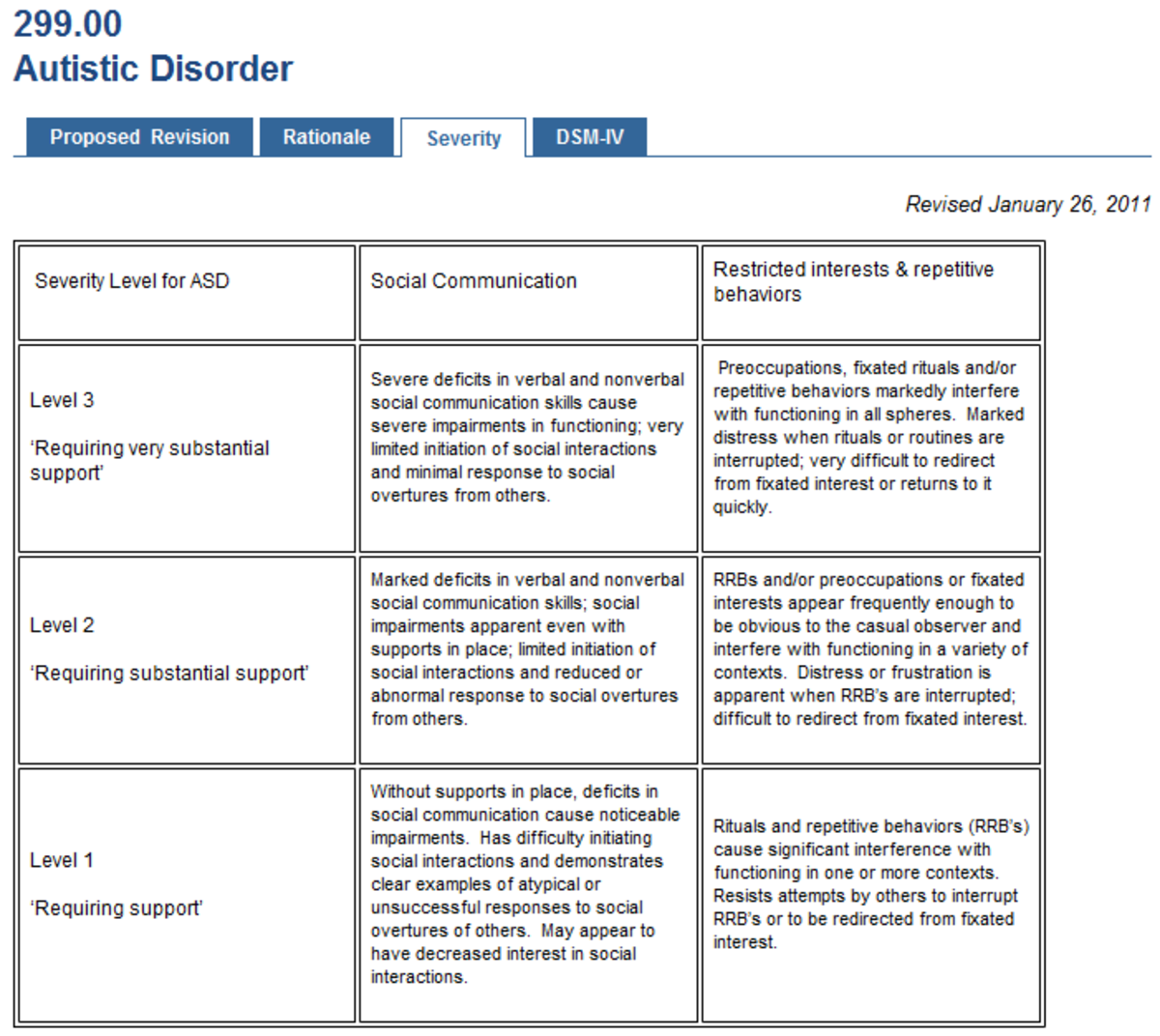
In the past, doctors diagnosed autism according to four different subtypes of the condition. However, healthcare professionals now classify autism spectrum disorder as one broad category with three different levels to specify the degree of support an autistic person needs.
Before 2013, healthcare professionals defined the four types of autism as:
- childhood disintegrative disorder
- pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified
However, the American Psychiatric Association revised their Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders in 2013, which did not include these four subtypes of autism. They now all fall under the one umbrella term of ASD.
Keep reading to learn more about how we categorize ASD, including the various levels, and how doctors diagnose the condition.
ASD is now the umbrella term for the group of complex neurodevelopmental disorders that make up autism. It is a condition that affects communication and behavior.
The autism spectrum refers to the variety of potential differences, skills, and levels of ability that are present in autistic people.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , around in the United States are on the autism spectrum.
The differences in autistic people are often present from early childhood and can impact daily functioning.
Autistic people can experience the following challenges:
According to the National Institute of Mental Health, early signs of ASD can include:
Don’t Miss: What Does Autism Do To The Brain
Diagnosis In Young Children
Diagnosis in young children is often a two-stage process.
Stage 1: General Developmental Screening During Well-Child Checkups
Every child should receive well-child check-ups with a pediatrician or an early childhood health care provider. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children receive screening for developmental delays at their 9-, 18-, and 24- or 30-month well-child visits, with specific autism screenings at their 18- and 24-month well-child visits. A child may receive additional screening if they are at high risk for ASD or developmental problems. Children at high risk include those who have a family member with ASD, show some behaviors that are typical of ASD, have older parents, have certain genetic conditions, or who had a very low birth weight.
Considering caregivers experiences and concerns is an important part of the screening process for young children. The health care provider may ask questions about the childs behaviors and evaluate those answers in combination with information from ASD screening tools and clinical observations of the child. Read more about screening instruments on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website.
If a child shows developmental differences in behavior or functioning during this screening process, the health care provider may refer the child for additional evaluation.
Stage 2: Additional Diagnostic Evaluation
The diagnostic evaluation is likely to include:
- Blood tests
What Is The New Diagnosis Of Social Communication Disorder Who Will It Affect
This new diagnosis applies to people who have persistent problems with the social use of language, but dont have restricted interests or repetitive behaviors.
Some people who would have previously received a diagnosis of PDD-NOS may now receive a diagnosis of social communication disorder. However, this should apply only to newly diagnosed people. It should not be applied retroactively to someone already diagnosed with PDD-NOS under the DSM-IV criteria.
Also Check: What Is Low Functioning Autism
Does Autism Run In Families
We have learned a lot about autism since it was first diagnosed in the 1940s by Dr. Kanner. There is still a lot we dont know but one thing that seems to be true about autism is that it does have some genetic tendency to run in families. To put it very simply without summarizing entire studies, the average risk of a subsequent child being born after one child with ASD has been born into a family is 10% based on group averages. This is a very loose number, but the point is that it has been well established that the tendency is there.
It is not unusual for therapists who work in the field to serve families who have more than one sibling who has been diagnosed with an ASD.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
Caregivers and teachers are often the first to recognize ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school. The schools special education team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend that a child undergo additional evaluation with their primary health care provider or a health care provider who specialize in ASD.
A childs caregivers may talk with these health care providers about their childs social difficulties, including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication differences may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. They also may have trouble forming friendships with peers.
Also Check: How Does Cbd Help Autism
Design Setting And Participants
Cross-sectional, population-based ASD surveillance based on clinician review of coded behaviors documented in childrens medical and educational evaluations from 14 geographically defined areas in the United States participating in the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network in 2006 and 2008. This study included 8-year-old children living in ADDM Network study areas in 2006 or 2008, including 644 883 children under surveillance, of whom 6577 met surveillance ASD case status based on the DSM-IV-TR.
Understanding Autism In Women
Autism is rarer in females than in males. In fact, one major researcher in the field, Simon Baron-Cohen, wrote that autism is a manifestation of the extreme male brain.
There does seem to be a real difference in the number of females who are actually diagnosed with autism versus the number of males. But this so-called “female protective effect” is still being explored.
In recent years, it has become clear that autism is underdiagnosed in females. There are a number of reasons for this:
- Girls are more likely to internalize anxiety related to autism instead of behaving aggressively, they are more likely to become depressed or anti-social.
- Most cultures make it acceptable for girls to be “shy” whereas shyness is less acceptable in boys.
- When girls with autism focus exclusively on a particular interest, they are more likely than boys to choose a socially acceptable fascination such as unicorns or dolls.
Because fewer females have autism, fewer females with autism have been included in studies. More attention is now being paid to how autism manifests in females.
You May Like: Why Is Autism Awareness Month Important