The Facts About Autism And Common Misconceptions
Are you finding that well-meaning family and friends, media commentators even some health professionals are making you more concerned and confused about your own or your childs autism or suspected autism?
Misinformation and mixed messages can lead to feelings of guilt and isolation and can work against a proactive diagnosis and support program. Although the global understanding of autism is constantly evolving, here are some of the commonly understood facts, to help you put some of these misconceptions about autism to bed.
Be Careful About Changing Your Childs Diet
Talk to your doctor before trying something different, like a special diet. Thereâs no hard evidence that special diets help children with ASD. Autism is a complex brain disorder. While it may seem that cutting out certain foods could relieve your childâs symptoms, it might actually cause more harm.
For example, children with autism often have thinner bones. Dairy products have nutrients that can make their bones stronger. Studies on a protein in milk products called casein have found that many children performed the same whether or not they ate foods with this protein. Their autism symptoms didnât change in any remarkable way.
Some evidence shows that people with autism may have low levels of certain vitamins and minerals. This does not cause autism spectrum disorder. But supplements may be suggested to improve nutrition. Vitamin B and magnesium are two of the supplements most often used for people with autism. But people can overdose on these vitamins, so megavitamins should be avoided.
However, some diet changes may help with certain symptoms of autism. Food allergies, for example, may make behavior problems worse. Removing the allergen from the diet may improve behavior issues.
Some children with autism have digestive problems like constipation, belly pain, or nausea and vomiting. Your doctor can suggest a diet that wonât make them worse.
Show Sources
The Train Analogy: Understanding How We See The World
Imagine what it would be like if you were to be picked up suddenly and dropped into the middle of a packed rush hour subway in downtown Tokyo.
To begin with, you are overwhelmed by the number of people in your personal space the subway is so packed that you literally cannot move. Lots of people are talking to each other at once, to the point that you can barely hear yourself think. One person standing next to you may wear very strong perfume. Another person may have bad breath from forgetting to brush their teeth. The environment around the subway makes you extremely uncomfortable on a sensory level and you cannot wait to get off and out into the city.
The subway arrives and everyone disembarks. Every other person begins to walk in the direction they need to go in. But you find the signs around the station very confusing and you dont know how to leave the station. Doing the logical thing, you approach another passenger to ask for directions. You cant tell from his body language or facial expression whether he is happy to help or annoyed to be stopped. He is speaking very quickly in Japanese and is using local expressions you know nothing about you cannot follow his instructions as you are unsure about what he is saying to you.
Also Check: Low Level Autism
How Autism Is Diagnosed
There is no known biological marker for autism. That means that no blood or genetic test can diagnose the disorder. Instead, clinicians rely on observation, medical histories, and questionnaires to determine whether an individual has autism.
Physicians and specialists may use one or several of the following screening tools:
- Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised , a 20-question test designed for toddlers between 16 and 30 months old.
- The Ages and Stages Questionnaire , a general developmental screening tool with sections targeting specific ages used to identify any developmental challenges a child may have.
- Screening Tool for Autism in Toddlers and Young Children , an interactive screening tool, comprising 12 activities that assess play, communication, and imitation.
- Parents Evaluation of Developmental Status is a general developmental parent-interview form that identifies areas of concern by asking parents questions.
The American Academy of Pediatrics encourages autism screening for all children at their 18 and 24-month well-child checkups. Parents and caregivers can also ask their pediatrician for an autism screening if they have concerns. In rare cases, individuals with autism reach adulthood before receiving a diagnosis. However, most individuals receive an autism diagnosis before the age of 8.
How Autism Has Changed From Dsm To Dsm
The first edition of the DSM was published in 1952. It was 130 pages and contained 106 diagnostic descriptions. The most recent edition, the DSM-5, published in 2013, is 947 pages and covers roughly 300 disorders. As the DSM has gotten bigger and broader, so too has the definition of autism.
Before 1980, the word autistic appeared in the DSM only as a trait to describe schizophrenia. But that doesnt mean diagnostic criteria for autism didnt exist. A 1956 article by Leo Kanner and Leon Eisenberg focused on two criteria: aloofness and a significant resistance to changes in routines, noticeable in a child by 24 months of age. These traits are still present in diagnostic criteria today, and are sometimes called classic autism or Kanners autism.
The DSM-III, released in 1980, introduced infantile autism, officially creating a separate diagnosis for autism for the first time. Seven years later, a revised edition, the DSM-III-R, changed the name to autistic disorder and placed it in the category of Pervasive Developmental Disorders along with other related conditions like Aspergers Disorder and Pervasive Developmental Disorders – Not Otherwise Defined .
The 1994 DSM-IV dropped the number of required traits for a diagnosis from eight to six. And the majority of behavioral examples included in earlier versions of the manual were removed, meaning that physicians had to interpret behavioral descriptions with less guidance.
Don’t Miss: Does The Good Doctor Really Have Autism
How Is Autism Diagnosed
Fortunately, the way autism is diagnosed has changed and improved over the last 80 years.
We now recognise a wider range of signs and characteristics as forming part of the autism spectrum.
As awareness increases, parents and professionals are getting better at identifying early signs of autism and are more likely to seek an autism assessment.
This explains why people think autism is more prevalent today than it was ten or twenty years ago.
Highly Focused Interests Or Hobbies
Many autistic people have intense and highly focused interests, often from a fairly young age. These can change over time or be lifelong. Autistic people can become experts in their special interests and often like to share their knowledge. A stereotypical example is trains but that is one of many. Greta Thunberg’s intense interest, for example, is protecting the environment.
Like all people, autistic people gain huge amounts of pleasure from pursuing their interests and see them as fundamental to their wellbeing and happiness.
Being highly focused helps many autistic people do well academically and in the workplace but they can also become so engrossed in particular topics or activities that they neglect other aspects of their lives.
Take a look at the Spectrum magazine, written for and by autistic people
Also Check: High Functioning Autism Vs Low Functioning Autism
Examples Of Autism In A Sentence
autism ajcautism NBC NewsautismSan Diego Union-Tribuneautism Scientific Americanautism CNNautismchicagotribune.comautism The Salt Lake Tribuneautism Fox News
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘autism.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
What If I Think Someone Has Autism
Your approach will vary depending on the person.
If it is for your own child, you may like to refer to our guide for getting an assessment. If it is for an adult or another persons child, and you feel that they may be receptive to your thoughts, you may want to share that you think the challenges the person is having may be due to a neurological difference. If they appear open to further discussion, you may like to suggest autism. You could suggest that, if they would like to investigate this possibility further, they could consider visiting the Autism New Zealand website for information on autism and on how to go about obtaining a formal assessment. It is possible that the characteristics you observe may not be autism, and perhaps there is another explanation for them.
Read Also: Can A Child Outgrow Autism
Does Autism Affect Intelligence
Intelligence are not inherently affected by autism however, other conditions that do affect IQ, such as intellectual disabilities or savant syndrome, can co-occur with autism.
This means that autistic people are statistically more likely than neurotypical people to sit on the extreme ends of the intelligence bell curve. It is important to realise that above or below average intellectual ability, if present, is generally due to a separate diagnosis, not the autism itself.
Films like Rain Man have promoted the stereotype of autistic people having savant abilities, and contemporary research in medical biography posits historical figures like Mozart, Einstein, Darwin, and Newton as having been on the autism spectrum. This has contributed to creating an expectation of autism being correlated with giftedness, special talents, and superior intelligence. In reality, while savantism is more common in autistics than in the neurotypical population , it is far from the norm.
Instead, people with autism may have higher aptitude in specific types of tasks that require visual thinking or pattern recognition, which can make it easier to learn certain skills such as foreign languages, musical instruments, or maths. The typically autistic intense focus on a single topic, and relentless study as well as practice, may also contribute to what looks like a special talent.
Asd Surveillance System And Data
The ADDM Network conducts ASD surveillance in multiple geographically defined communities in the United States every 2 years. The surveillance protocol involves requesting health and special education records for children aged 8 years who are living in the study area during the surveillance year. Health records are requested from medical sources if they are assigned specific International Classification of Diseases billing codes relevant to developmental disabilities, and special education records are requested from schools based on special education exceptionality codes. The ADDM Network sites then send trained record abstractors into the field to review the records for different types of ASD behavioral symptoms, ASD tests, or suspected or confirmed ASD diagnoses .
Don’t Miss: What Is The Symbol For Autism
Domain A: Social Communication And Social Interaction
Differences or challenges relating to language and social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, both currently or historically. These include difficulty or differences in:
- Social-emotional communication and personal exchanges.
- Non-verbal communicative behaviours used for social interaction.
- Developing, maintaining and understanding relationships.
World Health Organisation Updates Classification Of Autism In The Icd

Last modification: 21/06/2018
On the 18 June 2018, the World Health Organization released its new International Classification of Diseases . The ICD catalogues different pathologies and conditions in order to provide a common language to inform and control their development, as well as comparing and sharing data following standard criteria between hospitals, regions and countries in different time periods. To do this, the diagnostic terms are converted into around 55 000 unique alphanumeric codes.
The ICD-11 is the result of ten years of work and replaces the previous classification, , with the intention of offering an updated view of the different health and disease conditions. There has been unprecedented involvement of health care workers in the elaboration of this 11th edition of the ICD. They have joined collaborative meetings and submitted proposals. The ICD team in WHO headquarters received over 10 000 proposals for revisions. ICD-11 will be presented at the World Health Assembly in May 2019 for adoption by Member States, and will come into effect on 1 January 2022.
Don’t Miss: Comorbid Autism And Adhd
What Is The History Of Autism
The understanding of autism has developed over a number of decades. While the term autism was defined by Kanner, there is varying evidence that other professionals, including Grunya Efimovna Sukhareva and Paul Bleuler, had recognised the unique presentation of symptoms much earlier than this. Since the 1940s the diagnostic criteria has evolved and shifted as we learn more but now autism is widely understood as a spectrum of conditions with wide-ranging degrees of impairment
Autism Redefined In New Manual Of Mental Disorders
Q: Can you give us a quick overview of autism?
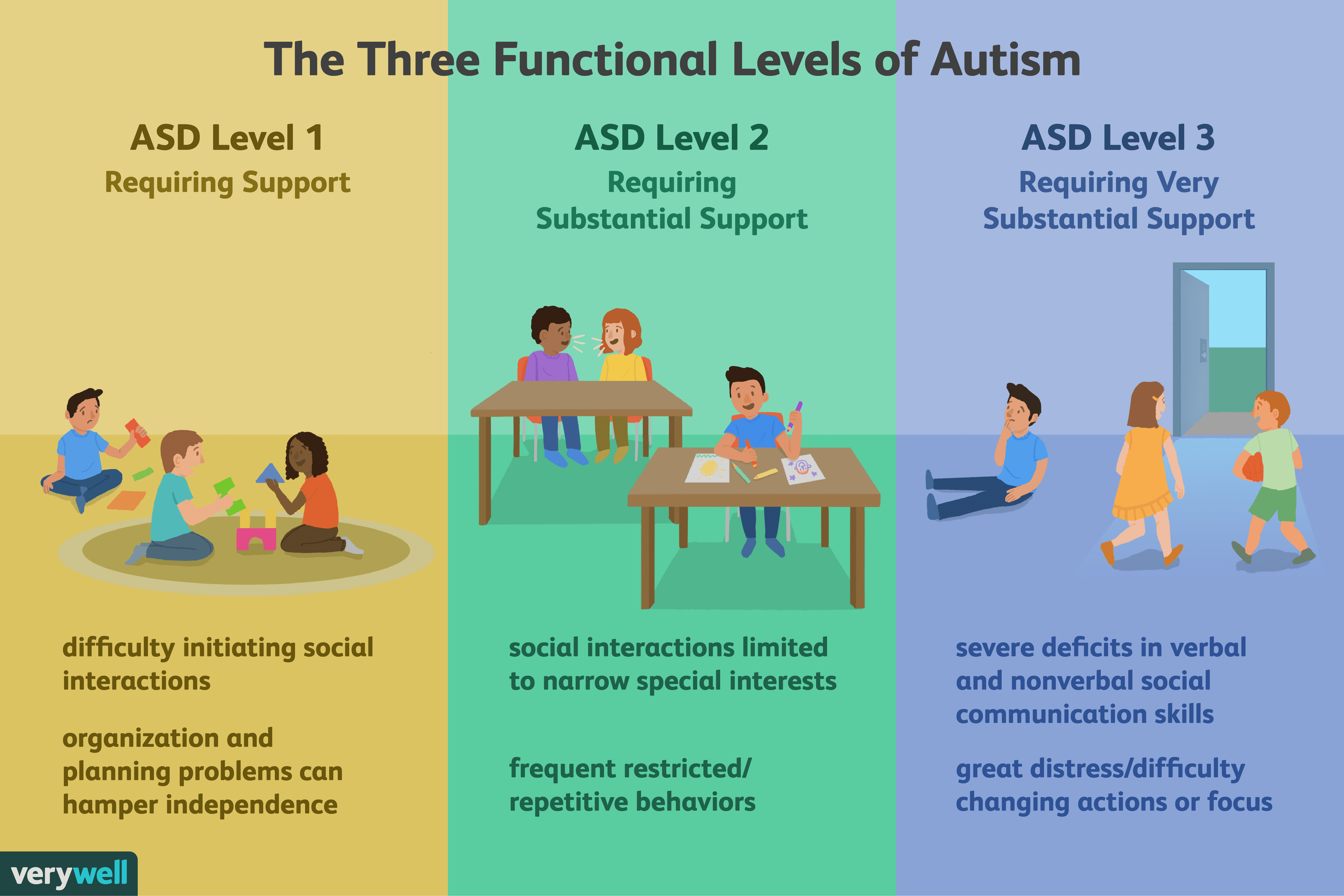
A: Autism is a developmental neurobiological disorder, characterized by severe and pervasive impairments in social interaction and communication skills , and by restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests or activities.Q: What are the autism-related changes in the new edition of the DSM?A: Under DSM-5, the separate diagnostic subcategories under PDD in DSM-IV will now be subsumed under one category Autism Spectrum Disorder. This puts autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified and childhood disintegrative disorder ALL under ASD.The new ASD diagnostic category will include specifiers for severity and verbal abilities, and will also include associated features such as known genetic disorders, epilepsy and intellectual disability. Severity levels are based on the amount of support needed by an individual with ASD e.g., an ASD patient could be considered level 1, level 2 or level 3.The new ASD diagnostic category will also combine the current three domains of autism symptoms into two domains .Q: Ive read that a lot of people are concerned with these changes, can you explain why?
A:Q: What is the APAs rationale for these changes?A:Q: What autism services and treatments are offered at the Center for Autism and Developmental Disorders at Western Psychiatric Institute and Clinic of UPMC?A:
Don’t Miss: Autism Awareness Month Symbol
Broad Diagnoses Change Our Concept Of Normal
When the DSM-5 was released, it sparked a petition signed by over 15,000 psychologists. The petition argued that the manual placed the diagnostic threshold for many conditions too low, making it easier to apply a psychiatric label to a wider range of people. That also means the DSM has the power to make people more eligible for treatment with drugs whose effects, especially long-term, are not fully studied.
Allen Frances, the chair of the DSM-IV task force, has highlighted the risk that normal people are being diagnosed with mental conditions they do not have, thanks to overly broad diagnostic criteria in the DSM-5. This almost exactly mirrors criticisms over the broadening definition of autism.
And as the definition of autism get broader, it narrows what is considered normal. People who would not previously have had a diagnosis are now being pathologized. We are constructing a new reality of the disorder that does not accurately represent the most affected population. This could divert attention and resources from the people who need it the most the significantly disabled.
Rates of people with less significant forms of autism will rise and become the autistic norm, as we see in media portrayals in TV shows like Parenthood and or books like The Curious Incident of the Dog in Nighttime. When this becomes the autistic norm, people who are more significantly autistic appear super-disabled, and then become super-stigmatized.
Social Communication And Social Interaction Challenges
Social communication
Autistic people have difficulties with interpreting both verbal and non-verbal language like gestures or tone of voice. Some autistic people are unable to speak or have limited speech while other autistic people have very good language skills but struggle to understand sarcasm or tone of voice. Other challenges include:
- taking things literally and not understanding abstract concepts
- needing extra time to process information or answer questions
- repeating what others say to them
Social interaction
Autistic people often have difficulty ‘reading’ other people – recognising or understanding others’ feelings and intentions – and expressing their own emotions. This can make it very hard to navigate the social world. Autistic people may:
- appear to be insensitive
- seek out time alone when overloaded by other people
- not seek comfort from other people
- appear to behave ‘strangely’ or in a way thought to be socially inappropriate
- find it hard to form friendships.
Read more about social communication and social interaction challenges here
Read Also: Does Gestational Diabetes Cause Autism
How Should I Refer To A Person Diagnosed With Autism
Autism New Zealand recognises the importance of autistic-guided language. Language is constantly evolving, and many terms used in the past to describe autism have been largely rejected by the autistic community.
It is important to use and respect each persons preferred terminology its always best to ask the person how they would like to be referred to.
When speaking more generally about autism listening to the preferences of the autistic community, this means using identity-first language for autism instead of person-first language . Person on the autism spectrum is often preferred over traditional person-first language and may be used in conjunction with identity-first language. Identity-first language is preferred because many people consider their autism an intrinsic part of their personhood.
Autism New Zealand does not use terms that categorise functioning or severity . This is because functioning and severity labels do not represent the autistic persons experience of being autistic they represent how society experience autistic people. Instead it is preferred that an individuals specific support needs are described when needed. If simplification is required level of need can be used .
Autism In Pop Culture
Movies and books featuring characters with autism have helped bring autism spectrum disorder into the public consciousness. Some have ignited controversy others have increased the publics general understanding of autism. A few have done both. At ARI, we hope that people will rely on evidence-based research to understand autism spectrum disorder better.
Learn more about autism spectrum disorder by watching one of our expert-led webinars. They help you learn about ASD from clinicians, researchers, and therapists who research autism and support individuals with ASD.
Also Check: Cluttering And Autism