Establish A Routine With Them
The world is often a confusing and anxiety-inducing place for autistic children. This is why they find great comfort in a predictable and stable routine. Fortunately, the structured nature of school is perfect for this, but you need to find a way to make their daily routine clear to them.
Creating a visual timetable is an effective and widely-used method for doing so. This involves placing images and simple words on a timetable, in chronological order, to describe the activities and transitions in the childs day. Having this visual aid gives the child a sense of security, while also acting as a reminder for those who support them.
Do Symptoms Of Autism Change Over Time
For many children, symptoms improve with age and behavioral treatment. During adolescence, some children with ASD may become depressed or experience behavioral problems, and their treatment may need some modification as they transition to adulthood. People with ASD usually continue to need services and supports as they get older, but depending on severity of the disorder, people with ASD may be able to work successfully and live independently or within a supportive environment.
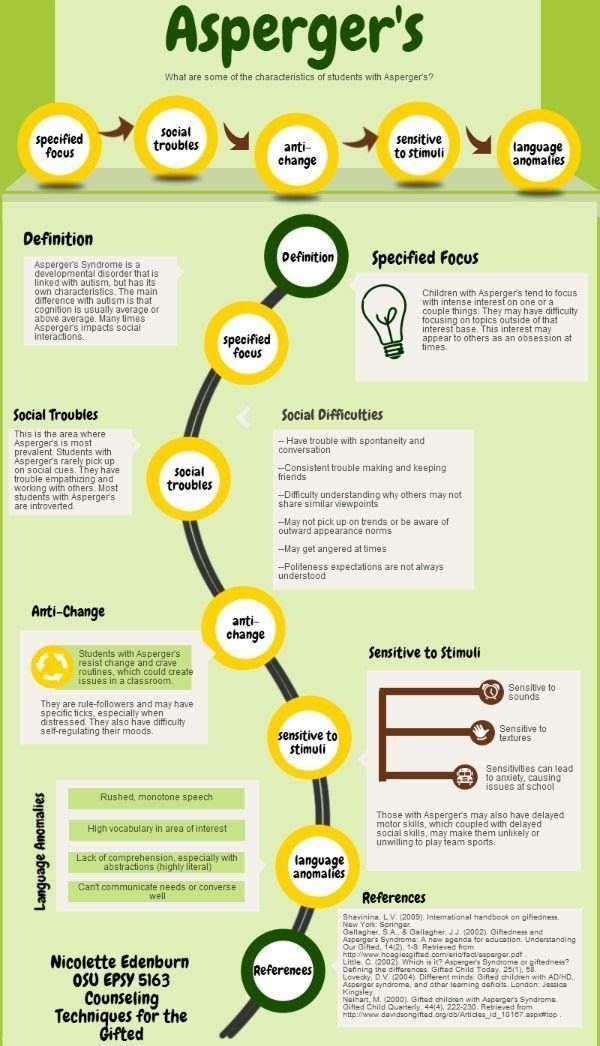
Language Communication And Autism
Many autistic children develop language skills at a different rate and in a different order from typically developing children. This means they might not understand what you say to them or might have difficulty following instructions. Some autistic children can find it difficult to use spoken language to ask for things, or tell other people what theyre thinking or feeling.
Differences in communication can make social situations like playing with other children a little more difficult.
Read Also: Are There Doctors With Autism
Ways Autism Can Affect Learning
Children with autism may have average or above-average intelligence, but autism can still affect learning in a number of ways. Some of these learning difficulties can be effectively addressed, particularly with early interventions, and in some cases, these learning difficulties are also accompanied by strengths unique to autistic children.
Related resource:;Top 15 Best Online Applied Behavior Analysis Programs
Interaction Joint Attention And Autism
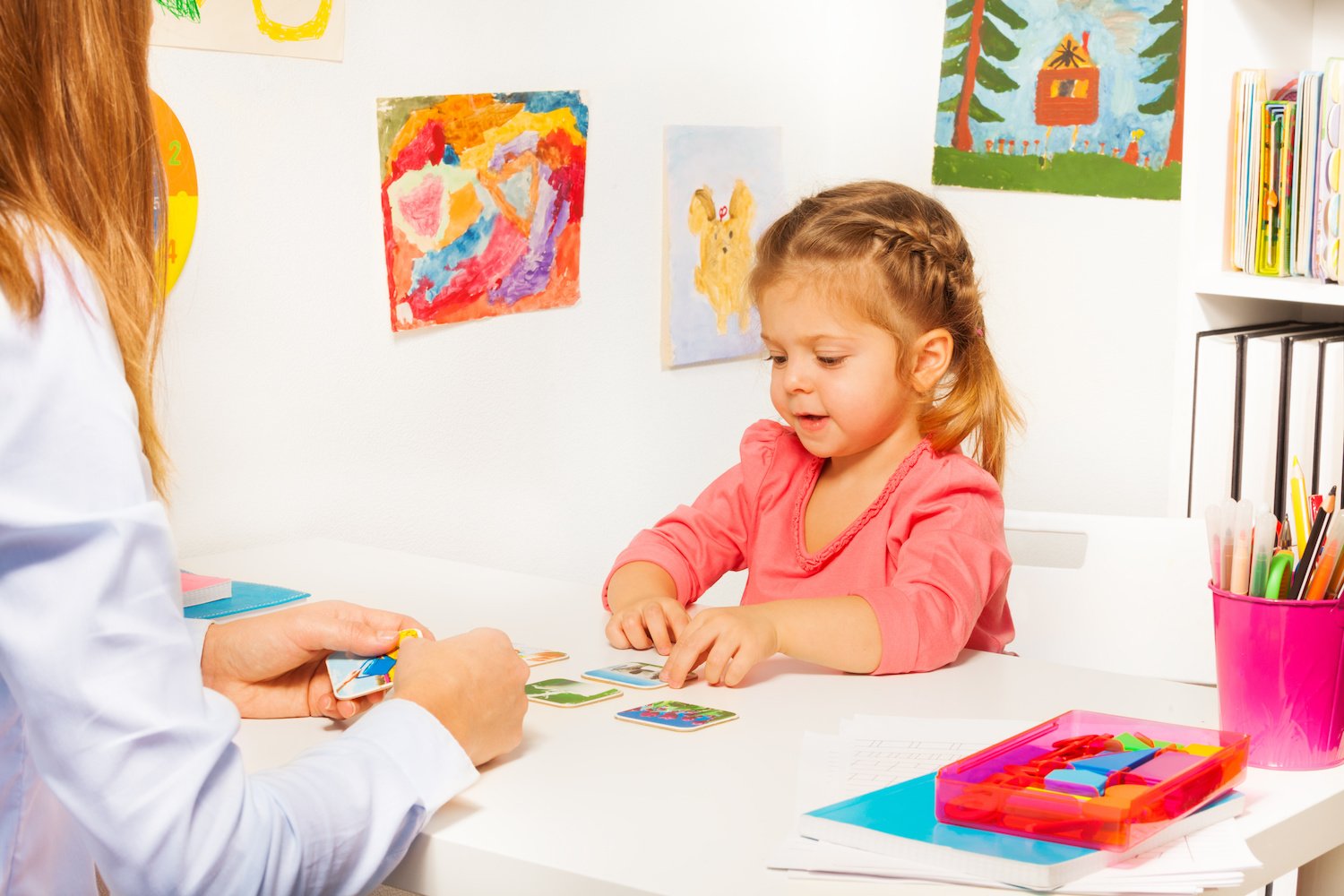

Autistic children might interact with people in a different way from typically developing children.
For example, autistic children might not respond to their own names, smile when someone smiles at them, or notice facial expressions. But they often develop their own way of letting their parents know what they want, although they might not use the gestures that typically developing children use. For example, they might lead their parents by the hand rather than pointing to show their carers something interesting.
Autistic children often have difficulty with joint attention, which is using eye contact and gestures to share experiences with others. These difficulties;;can make it harder for autistic children to develop communication and language skills. For example, if a parent is pointing to a picture of a dog, but the child is interested in another part of the picture, it might be harder for the child to learn the link between the picture of a dog and the word dog.
Attention is a skill that develops over time. Our article on learning to pay attention explains how you can use play to help your autistic child build this skill.
Read Also: Is Aspergers Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism In The Classroom: One Size Doesnt Fit All
The parents and the professionals all agree that it takes lots of hard work to help a child with autism get the most out of the classroom experience. It also takes, they say, a good dose of structure and the understanding that every child with an autism spectrum disorder is unique. That means each child has different symptoms as well as styles of learning.
“Autism isnât like diabetes,â psychologist Kathleen Platzman tells WebMD. âWith diabetes, we have two or three things that we absolutely know about every kid who has it. But since itâs not that way with autism, we need an educational model wide enough to take in the whole spectrum. That means itâs going to have to be a fairly broad model.â
Platzman works with autistic children and their families in Atlanta. She says every child with an ASD needs individual attention.
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
Read Also: What Does It Mean To Be Autistic
Impact Of Autism On A Students Life
Every person on the autism spectrum is unique and their needs will be reflected differently.
Challenges experienced interacting socially and communicating with others are common among students on the spectrum, and will have an impact on every aspect of their lives.
These challenges can lead to levels of stress, anxiety and depression that are much higher than for other students. Up to 72% of students on the autism spectrum have additional mental health needs.
Classrooms are social environments that rely heavily on being able to interact, socialise and communicate with others effectively. This can intensify the stress, anxiety and depression students on the spectrum may experience.
This can present unique challenges for schools and teachers, with students on the spectrum being four times more likely than their peers to require additional learning and social support services.
Research shows the importance of understanding the link between academic learning and social and emotional competence.
A lack of social-emotional competence can lead to not only a decrease in a students connection with school, but also academic performance.
This reinforces the notion that social-emotional learning has a critical role to play in learning, as well as in school attendance, classroom behaviour, and academic engagement for all students.
Social Skills And Autism
Many children and adults on the autism spectrum need help in learning how to act in different types of social situations. They often have the desire to interact with others, but may not know how to engage friends or may be overwhelmed by the idea of new experiences.
Building up social skills with practice can help enhance;participation in the community and support;outcomes like happiness and friendships.;We have compiled social skills tips and;information from experts, teachers, and families, along with useful tools to help enhance opportunities to be part of the community.
Don’t Miss: Is There Different Types Of Autism
Article 4: Visual Structure In The School Setting
This article describes the visual structure component of the Structured Teaching pyramid.; Visual structure adds a physical or visual component to tasks to assist students in understanding HOW an activity should be completed.;
Thank you to the Indiana Resource Center for Autism for permission to publish this article. Visit the IRCA website to browse their complete library of articles and visual supports.
References And For Further Reading
Butera, G., & Haywood, H.C. . Cognitive education of young children with autism. In E. Schopler & G.B. Mesibov ,;Learning and cognition in autism;. New York, NY: Plenum Press.
Charlop, M.H., Kurtz, P.F., & Casey, F.G. . Using abberant behaviors as reinforcers for autistic children.;Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 23, 163-181.
Dyer, K., Dunlap, G., & Winterling, V. . Effects of choice making on the serious problem behaviors of students with severe handicaps.;Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 23, 515-524.
Frea, W.D. . Social-communication skills in higher functioning children with autism. In R.L. Koegel & L.K. Koegel ,;Teaching children with autism: Strategies for initiating positive interactions and improving learning opportunities;. Baltimore, MD: Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.
Koegel, R.L., Koegel, L.K., Frea, W.D., & Smith, A.E. . Emerging interventions for children with autism: Longitudinal and lifestyle implications. In R.L. Koegel & L.K. Koegel ,;Teaching children with autism: Strategies for initiating positive interactions and improving learning opportunities;. Baltimore, MD: Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.
Koegel, R.L., Koegel, L.K., & Parks, D.R. . Teach the Individual: Model of Generalization. In R.L. Koegel & L.K. Koegel ,;Teaching children with autism: Strategies for initiating positive interactions and improving learning opportunities;. Baltimore, MD: Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.
You May Like: Is Aba Therapy Only For Autism
Choosing The Appropriate School
As with many disabilities, in the past students on the autism spectrum were kept separate fromn ‘normal’ children as much as possible. However, the past few decades have seen a trend to integrate these students into the regular system as much as possible. Debate exists on whether this is the best option given the specific needs of children with Autism Spectrum Disorders . Some teachers in both the specialized and regular education systems believe that integration into regular schooling is often let down by inadequate training, support and resources .
The choices of education systems available may be limited. Parents may live in a country or rural area where nothing exists other than the regular school system. Parents may opt for home-based schooling if they have the time, commitment and willingness to learn all the strategies they will need to teach effectively. Costs can also be a major factor if specialized schools or support need to be paid for.
In some cases, a child on the autism spectrum can be taught partly in both a special education program and the regular classroom. This is an example of an integration model where the student has specialized or home-based education but is increasingly included in regular schools as the child can cope.
Will Having Autistic Students In My Kids Class Impact Their Learning
The day their daughter came home crying was the day Robert and Sara Soncini learned there was a problem in her second grade classroom in Las Vegas.
Every parent of a 7-year-old learns to roll with the crying jags and the hurt feelings that come from fitting into a sometimes unruly classroom environment. But something about this episode was different, as the Soncinis would soon learn.
Another student, an 8-year-old boy, had pushed and punched their daughter, then threatened her with scissors. And their daughter wasnt the only one. Other students in class had been subject to the same behaviors and even the teacher had been a victim. The situation had escalated to the point where the teacher had created a code word for the other students to evacuate the classroom when the boy got out of hand.
As a special needs student, the school district was required under the 1990 Individuals with Disabilities Education Act to put the boy in the least restrictive environment available to serve his educational needs. But to the Soncinis, if that meant the needs of the rest of the class were not being met, there was a problem.
After meeting with the school district and finding no mutual solution, the Soncinis took the unusual step of filing for a restraining order against the boy in Clark County Superior Court. The motion had the desired effect: the school district removed the boy from the classroom.
You May Like: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Autism In The Classroom: How To Handle Behavior Challenges
Children with autism typically use behaviors to communicate their wants, needs, anxieties, and frustrations.;
These behaviors can include:;
- Refusing to follow directives
- Eloping
While behaviors are important communication tools, some behaviors can disrupt learning in a classroom setting. Various interventions teach children with autism new skills that help them develop acceptable ways to communicate, socialize, and function.
Autistic Spectrum Disorders In The Classroom
With behaviors and actions ranging from mild to extreme, autistic spectrum disorders in the classroom can be challenging for any educator. But as we become more and more aware of the information surrounding autism and how we can support students its easier than ever for teachers to assist students with these disorders effectively, practically and functionally.
With behaviors and actions ranging from mild to extreme, autistic spectrum disorders in the classroom can be challenging for any educator. But as we become more and more aware of the information surrounding autism and how we can support students its easier than ever for teachers to assist students with these disorders effectively, practically and functionally.
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Autism In 30 Days Book
Autism In The Classroom: Tips From A Parent
Atlanta resident Leslie Wolfe and her husband, Alan, struggle with whether to tell people their son Joshua has autism. The bright 7-year-old did so well in his public school’s first-grade class that many of his classmatesâ parents didnât know Joshua needed extra help.
Wolfe says one reason Joshua is thriving in public school is that the family got started early to help him get ready.
Joshua attended Emory Universityâs Walden School. Walden School is a preschool for children with autism. Each classroom has up to 18 children. There are two âtypicalâ children in the classroom for every one child with autism. The idea is to help the children with autism learn from the behavior of their classmates. Another aim of the Walden School is to help families learn how to deal with autism spectrum disorders.
Wolfe offers these other tips for helping your child with an ASD do well at school.
She suggests showing up a week before school starts. Practice walking to school. Once there, show your child their new classroom. Also show your child with autism how to get to the water fountains and the bathrooms.
Burkhart Center For Autism Education And Research
The Burkhart Center is housed in the Texas Tech University College of Education. It provides a variety of resources in the areas of adult transitions, technical assistance in implementing evidence-based interventions for children, and community outreach services. The Center also supports Masterâs and Doctoral Students with scholarships, graduate assistantships, and opportunities to work with individuals on the spectrum.
Web: www.ladders.org
Read Also: How To Give Autistic Child Medicine
Autism Treatment Network Research On Challenging Behavior
Researchers with the Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network study challenging behavior in kids and teens with autism. Many children with autism have behavior problems. These can be hard on both the child and the family and caregivers. More than half of kids and teens with autism may be physically aggressive toward caregivers or other kids and grown-ups. This can include hitting, kicking and biting. Other behavior problems can include:
- being hyperactive, anxious and worried
- hurting themselves by banging or hitting their heads
- biting their hands and fingers
Behavior problems happen more often if the child has trouble sleeping. This is more likely if they wake up in the middle of the night. Younger kids are more likely to hurt other people. But older kids and teens are more likely to hurt themselves, especially if they have trouble talking.
For the full reference list and more Frequently Asked Questions addressed by ATN research on challenging behavior, visit asatn.org.
Structured Teaching Strategies For Students With Autism Spectrum Disorder
Learn about four strategies for structured teaching to support students with ASD: physical structure, visual schedules, work systems, and visual structure.
This series of four articles can be used as a set or separately depending on the needs of the staff/students. Each article will review the rationale for the use of structured teaching, as well provide as a brief description of the TEACCH model.
You May Like: Can You See Autism In Infants
Work With Their Parents/carers
Parents and carers are the true experts on their autistic children. To fully support the child in and out of school, you should therefore coordinate and share knowledge with them. Both of you can suggest interventions that have worked at home or in school for the child and can integrate these into their routine.
Not only will building a relationship benefit the autistic child, but it will also help the parents and carers feel at ease about their childs education. Your commitment to working with them will build their confidence in the schools ability to support their child.
Set & Explain Realistic Expectations

Most children function better when they know whats required of them and when they have the skills to meet those expectations. Children with autism are no different, especially since they can think in very literal and concrete terms.
Carefully set realistic expectations, and explain those expectations clearly to reduce autism behavior problems in the classroom.;
For example, teachers may need to show students visually what they must do and use simple instructions. Have the child repeat the instructions back to the teacher, too, to ensure understanding and reduce outbursts.
Recommended Reading: Does Chelation Therapy Work For Autism
What Research Is Being Conducted To Improve Communication In Children With Asd
The federal governments Autism CARES Act of 2014 brought attention to the need to expand research and improve coordination among all of the components of the National Institutes of Health that fund ASD research. These include the National Institute of Mental Health , along with the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders , the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development , the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences , the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke , the National Institute of Nursing Research , and the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health .
Together, five institutes within the NIH support the Autism Centers of Excellence , a program of research centers and networks at universities across the country. Here, scientists study a broad range of topics, from basic science investigations that explore the molecular and genetic components of ASD to translational research studies that test new types of behavioral therapies. Some of these studies involve children with ASD who have limited speech and language skills, and could lead to testing new treatments or therapies. You can visit the NIH Clinical Trials website and enter the search term autism for information about current trials, their locations, and who may participate.