What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
What Is The Outlook For People With Autism Spectrum Disorder
In many cases, the symptoms of ASD become less pronounced as a child gets older. Parents of children with ASD may need to be flexible and ready to adjust treatment as needed for their child.
People with ASD may go on to live typical lives, but there is often need for continued services and support as they age. The needs depend on the severity of the symptoms. For most, it’s a lifelong condition that may require ongoing supports.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Through research, there has been much that has been learned about autism spectrum disorder over the past 20 years. There is ongoing active research on the causes of ASD, early detection and diagnosis, prevention and treatments.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/29/2020.
References
Social Behavior And Social Understanding
Basic social interaction can be difficult for children with autism spectrum disorders. Symptoms may include:
- Unusual or inappropriate body language, gestures, and facial expressions .
- Lack of interest in other people or in sharing interests or achievements .
- Unlikely to approach others or to pursue social interaction comes across as aloof and detached prefers to be alone.
- Difficulty understanding other peoples feelings, reactions, and nonverbal cues.
- Resistance to being touched.
- Difficulty or failure to make friends with children the same age.
Recommended Reading: Autism Puzzle Piece Colors Meaning
How Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder Play
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder tend to be less spontaneous than other kids. Unlike a typical curious little kid pointing to things that catch their eye, children with ASD often appear disinterested or unaware of whats going on around them. They also show differences in the way they play. They may have trouble with functional play, or using toys that have a basic intended use, such as toy tools or cooking set. They usually dont play make-believe, engage in group games, imitate others, collaborate, or use their toys in creative ways.
Repetitive And Restrictive Behaviour
With its unwritten rules, the world can seem a very unpredictable and confusing place to autistic people. This is why they often prefer to have routines so that they know what is going to happen. They may want to travel the same way to and from school or work, wear the same clothes or eat exactly the same food for breakfast.
Autistic people may also repeat movements such as hand flapping, rocking or the repetitive use of an object such as twirling a pen or opening and closing a door. Autistic people often engage in these behaviours to help calm themselves when they are stressed or anxious, but many autistic people do it because they find it enjoyable.
Change to routine can also be very distressing for autistic people and make them very anxious. It could be having to adjust to big events like Christmas or changing schools, facing uncertainty at work, or something simpler like a bus detour that can trigger their anxiety.
Read more about repetitive behaviours and dealing with change here
Also Check: Real Doctor With Autism
Terminology And Distinction From Schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism while in 2007 it was believed to be one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed, parents continue to feel social stigma in situations where their child’s autistic behavior is perceived negatively, and many primary care physicians and medical specialists express some beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely.Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
How Common Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Based on most recent CDC report, ASD is estimated to affect about 1 in 54 children, with boys being more likely to have ASD than girls. There were more than 5 million adults in the US, or 2.21% of the population, with ASD as of 2017. Government statistics suggest that the prevalence of ASD has risen 10% to 17% in recent years.
Read Also: Dan Jones Sleep Hypnosis Youtube
Restricted Or Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior Or Activities
In addition to the communication and social issues mentioned above, autism also includes symptoms related to body movements and behaviors.
These can include:
- repetitive movements, like rocking, flapping their arms, spinning, or running back and forth
- lining objects, like toys, up in strict order and getting upset when that order is disturbed
- attachment to strict routines, like those around bedtime or getting to school
- repeating words or phrases they hear someone say over and over again
- getting upset over minor changes
- focusing intently on parts of objects, like the wheel of a toy truck or the hair of a doll
- unusual reactions to sensory input, like sounds, smells, and tastes
- obsessive interests
- exceptional abilities, like musical talent or memory capabilities
How Would You Describe Someone With Autism
In the autism community, many self-advocates and their allies prefer terminology such as Autistic, Autistic person, or Autistic individual because we understand autism as an inherent part of an individuals identity the same way one refers to Muslims, African-Americans, Lesbian/Gay/Bisexual/Transgender/
You May Like: Stage 3 Autism
Development Into A Health Profession
The health profession of occupational therapy was conceived in the early 1910s as a reflection of the . Early professionals merged highly valued ideals, such as having a strong work ethic and the importance of crafting with one’s own hands with scientific and medical principles. The National Society for the Promotion of Occupational Therapy , now called the , was founded in 1917 and the profession of Occupational Therapy was officially named in 1921., one of the founders of NSPOT and visionary figure in the first decades of the profession struggled with “the cumbersomeness of the term occupational therapy”, as it lacked the “exactness of meaning which is possessed by scientific terms”. Other titles such as “work-cure”, “ergo therapy” , and “creative occupations” were discussed as substitutes, but ultimately, none possessed the broad meaning that the practice of occupational therapy demanded in order to capture the many forms of treatment that existed from the beginning.
The profession has continued to grow and expand its scope and settings of practice. , the study of occupation, was created in 1989 as a tool for providing evidence-based research to support and advance the practice of occupational therapy, as well as offer a basic science to study topics surrounding “occupation”. That said, occupational science continues to be largely theory driven to the present day, and its application to clinical practice is frequently questioned.
Share Suggested Ways To Interact With Your Child
When you first start explaining autism to friends, family, and kids, they might not understand all of the jargon and behaviors you identify. For example, they still might have trouble understanding the meltdowns, necessity for routine, or other behaviors your child exhibits. For this reason, you might want to share suggested ways to interact with your child.
You wont need to share your childs treatment plan with everyone, but sharing the dos and donts for your child may be important for adults who care for your child regularly, like a grandparent or teacher. So, walk them through your childs schedule and make a note of the importance of sticking to it for your child. Let them know of any sensory sensitivities your child has with certain types of foods. Make them aware of any goals you are working on with your child, such as looking others in the eyes, and how to provide positive feedback and reinforcement. Any suggested ways of interacting can help others better know how to communicate and care for your child.
If you have any questions about explaining autism to family or friends, contact us at Carmen B. Pingree. We offer various autism programs for children and will be opening an adult autism center in the Summer of 2020. We are dedicated to helping those with autism receive quality treatment and work towards independence and increased quality of life. Discover all of the programs we offer today!
Recommended Reading: Symbols For Autism
Getting An Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis
The road to an ASD diagnosis can be difficult and time-consuming. In fact, it is often two to three years after the first symptoms of ASD are noticed before an official diagnosis is made. This is due in large part to concerns about labeling or incorrectly diagnosing the child. However, an ASD diagnosis can also be delayed if the doctor doesnt take a parents concerns seriously or if the family isnt referred to health care professionals who specialize in developmental disorders.
If youre worried that your child has ASD, its important to seek out a clinical diagnosis. But dont wait for that diagnosis to get your child into treatment. Early intervention during the preschool years will improve your childs chances for overcoming their developmental delays. So look into treatment options and try not to worry if youre still waiting on a definitive diagnosis. Putting a potential label on your kids problem is far less important than treating the symptoms.
Related Signs And Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder

While not part of autisms official diagnostic criteria, children with autism spectrum disorders often suffer from one or more of the following problems:
Sensory problems Many children with autism spectrum disorders either underreact or overreact to sensory stimuli. At times they may ignore people speaking to them, even to the point of appearing deaf. However, at other times they may be disturbed by even the softest sounds. Sudden noises such as a ringing telephone can be upsetting, and they may respond by covering their ears and making repetitive noises to drown out the offending sound. Children on the autism spectrum also tend to be highly sensitive to touch and to texture. They may cringe at a pat on the back or the feel of certain fabric against their skin.
Emotional difficulties Children with autism spectrum disorders may have difficulty regulating their emotions or expressing them appropriately. For instance, your child may start to yell, cry, or laugh hysterically for no apparent reason. When stressed, they may exhibit disruptive or even aggressive behavior . The National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities also notes that kids with ASD may be unfazed by real dangers like moving vehicles or heights, yet be terrified of harmless objects such as a stuffed animal.
Savant skills in autism spectrum disorder
Don’t Miss: Is Freddie Highmore A Genius
Are There Positive Things To Say About Autism
That post had over 300,000 views and 4,000 shares which got me to thinking people really want to highlight and talk about the positive aspects of autism and stop dwelling on what is perceived to be the negative ones. Thinking about autism in more favorable terms will change your thinking and responses towards someone with autism.
Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
People with ASD have difficulty with social communication and interaction, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The list below gives some examples of the types of behaviors that are seen in people diagnosed with ASD. Not all people with ASD will show all behaviors, but most will show several.
Recommended Reading: Autism Awarness Symbol
Autism Is Not An Illness
Being autistic does not mean you have an illness or disease. It means your brain works in a different way from other people.
It’s something you’re born with or first appears when you’re very young.
If you’re autistic, you’re autistic your whole life.
Autism is not a medical condition with treatments or a “cure”. But some people need support to help them with certain things.
What Causes Autism Spectrum Disorder
There is no clear-cut cause of ASD. Some causes that are supported by research include genetic and some environmental factors. Specific genetic causes can only be identified in 10% to 20% of cases. These cases include specific genetic syndromes associated with ASD and rare changes in the genetic code.
Risk factors include older parental age, low birth weight, prematurity and maternal use of valproic acid or thalidomide during pregnancy, among others. This field of study is an active one for reasearch.
You May Like: What Color Represents Autism
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school are often first recognized by parents and teachers and then evaluated by the schools special education team. The schools team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend these children visit their primary health care doctor or doctors who specialize in ASD for additional testing.
Parents may talk with these specialists about their childs social difficulties including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication issues may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. Parents may also find that their child has trouble forming friendships with peers.
Do Use Metaphors And Picture Books
hairdryer brain vs toaster brain explanation1. “Autism is…?”Target audience:Description2. Ian’s WalkTarget audience:Description3. Can I tell you about autism?Target audience“Can I tell you about Asperger Syndrome?”Description:4. Different Like Me: My Book of Autism HeroesTarget audienceDescription:5. Autistic PlanetTarget Audience:Description
Recommended Reading: Hypnosis And Autism
Why Is Autism Awareness Important
April 2 is World Autism Awareness Day. April has also become known as Autism Awareness Month in the United States. However, many community advocates have rightly called for the need to increase awareness about ASD year-round, not just during 30 select days.
The Autism Society of America and other advocates have even proposed that April be designated Autism Acceptance Month instead.
Autism acceptance requires empathy and an understanding that ASD is different for everyone.
Certain therapies and approaches can work for some people but not others. Parents and caregivers can also have differing opinions on the best way to advocate for an autistic child.
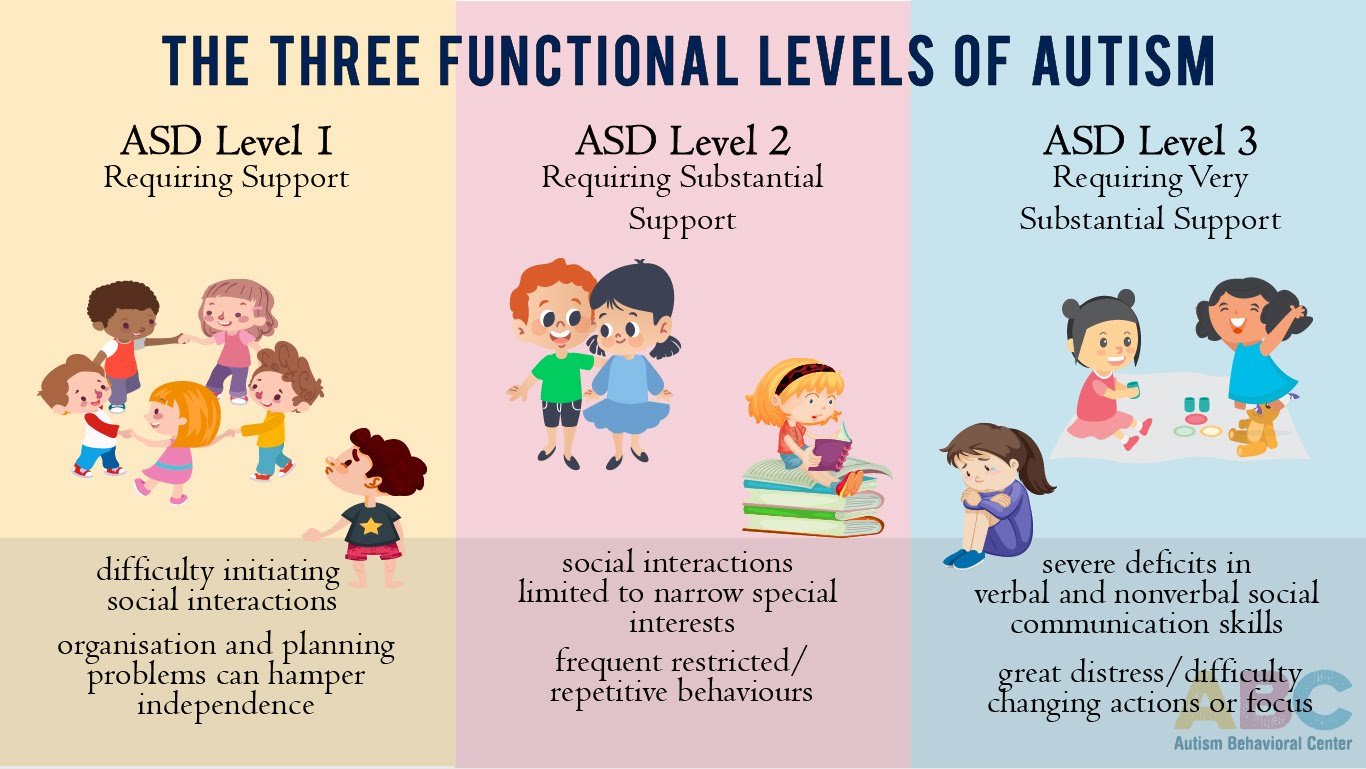
Level : Requiring Substantial Support

People who meet the level 2 criteria need more support than those with level 1 autism. Social challenges can make holding a conversation very difficult.
Even with support, the person may find it hard to communicate coherently, and they are more likely to respond in ways that neurotypical people consider surprising or inappropriate.
The person may:
- only discuss very specific topics
- have difficulty understanding or using nonverbal communication, including facial expression
For example, they may face away from the person with whom they are communicating.
People with level 2 autism may also find daily functioning difficult due to the challenges of coping with change. Facing change might cause them to experience significant distress.
Don’t Miss: Symbols Of Autism
Not Right For Everyone
Recently, together with the National Autistic Society, my colleagues and I asked 3,470 autistic people, parents and their broader support network, about the words they use to describe themselves, their children or the people with whom they work. Did they prefer to use autistic person? Or person with autism? Or person who has autism?
The results clearly showed that people use many terms when talking about autism. The words autism and on the autism spectrum were clear favourites among all the groups added together. But there was much disagreement on the use of several words and phrases. Professionals preferred to use person with autism while autistic adults and family members preferred on the whole to use is autistic. They thought that the term allowed them to describe the centrality of autism to their lives.
One autistic woman said:
In describing someone whos autistic as a person with autism/person who has autism/ person who suffers from autism you imply that autism is separate from a person, and behind their autism is a normal person.
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Recommended Reading: Autism Level 2 Prognosis