Why Is Autism Awareness Important
April 2 is World Autism Awareness Day. April has also become known as Autism Awareness Month in the United States. However, many community advocates have rightly called for the need to increase awareness about ASD year-round, and not just during 30 select days.
The Autism Society of America and other advocates have even proposed that April be designated Autism Acceptance Month instead.
Autism acceptance requires empathy and an understanding that ASD is different for everyone.
Certain therapies and approaches can work for some people but not others. Parents and caregivers can also have differing opinions on the best way to advocate for an autistic child.
Step : Interviewing Parents Family Members Or Other Caregivers
Information is obtained by asking semi-structured, open-ended questions, and may be integrated with information from a standardized questionnaire completed before or during the interview. Topics include:
- Reasons for referral, and when concerns first emerged
- Pregnancy, birth history, labour, with any delivery or other complications
- Childs developmental and behavioural history
- Childs current developmental functioning and behaviours
- Childs medical history, with focus on ASD-associated difficulties, such as sleep problems, unusual diet, self-injury
- Childs early intervention and educational history, when available
- Family medical and mental health history, spanning three generations, if possible. Inquire into any history of developmental disability, including ASD, learning difficulty, behavioural problems, as well as genetic conditions. Include psychosocial history, with focus on family violence or trauma, substance abuse, or neglect
- Family functioning, strengths, routines, and resources. Consider possible reactions to an ASD diagnosis, along with individual and family goals
| Table 1. Commonly used ASD diagnostic tools |
|
Diagnostic tool |
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
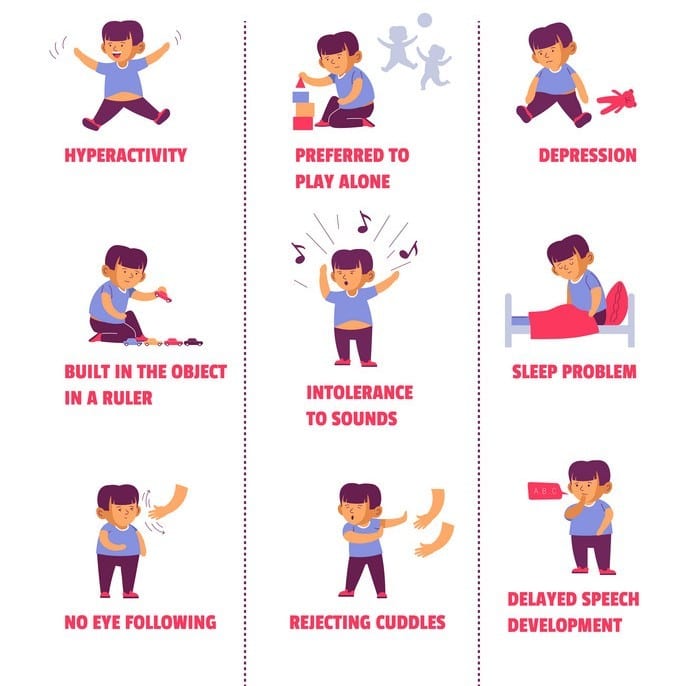
Every person with ASD is unique, so the timing and severity of the first signs and symptoms can vary widely. Some children with ASD show signs within the first few months of life. In others, symptoms may not become obvious until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD appear to develop normally until around 18 to 24 months of age and then stop gaining new skills and/or start losing skills.
During infancy , a child may show symptoms that include:
- Limited or no eye contact
- No babbling
- Appearing not to hear
- Playing with toys in an unusual or limited manner
- Showing more interest in objects instead of people
- Starting language skills but then stopping or losing those skills
- Showing repetitive movements with their fingers, hands, arms or head
Up to 2 years of age, there may be continuing symptoms from infancy. A child may also:
- Focus only on certain interests
- Be unable to have reciprocal social interactions
- Move in unusual ways, such as tilting their head, flexing their fingers or hands, opening their mouth or sticking out their tongue
- Have no interest in playing with other children
- Repeat words or phrases without appearing to understand them
- Have behavioural issues, including self-injury
- Have trouble controlling their emotions
- Like to have things a certain way, such as always eating the same food
Possible signs of ASD at any age:
Recommended Reading: Adhd Dyslexia Comorbidity
Autism: A Medical Primer
CHRISTOPHER D. PRATER, M.D., and ROBERT G. ZYLSTRA, ED.D., L.C.S.W., University of Tennessee College of Medicine, Chattanooga, Tennessee
Am Fam Physician. 2002 Nov 1 66:1667-1675.
Recognition of the disorder called autism may have its origin in Itard’s 1801 description of the wild boy of Aveyron, a violent child with no language skills who related to other people as if they were objects. It was not until 1943 that Kanner identified a complex set of characteristics for a syndrome he labeled autism.
Although Kanner theorized that a single, biologically based defect was responsible for the development of autistic disorders, treatment in the 1950s and 1960s was dominated by the psychodynamic theory of the etiology of autism that charged that pathologic parenting was responsible for the withdrawal of children from their environment. Following the 1970s discovery of neuroreceptors, endogenous neurohormones, and the stereospecific binding sites of neuropeptides to neurons, clinicians have discounted the psychodynamic theory of autism and repostulated Kanner’s original supposition that biologically based deficits are responsible for the etiology of autism.
How Is Autism Managed

If your child is diagnosed with autism, you will be guided through the various treatment options. There are education programs and support services available for children with autism and their parents or caregivers from a number of organisations such as Autism Spectrum Australia.
Treatments used to manage autism are best started as early in a persons life as possible. Specific symptoms and social skills can be improved with the right support and programs. Because everyone with autism is different, the best results are obtained from a treatment program specifically tailored to their individual needs.
Language and social skills are taught through intensive educational programs and behavioural therapies. Speech pathology focuses on developing communication and social skills. Occupational therapy concentrates on sensory motor development, such as learning play and fine motor skills, as well as how to cope in social situations.
Public and private schooling options are available for children with autism. Find out more about schooling options on the Autism Awareness website.
Sometimes claims are made about treatments that are misleading. Avoid treatments that offer a cure or recovery as there is no evidence to support these claims. Ensure that the treatments and supports you choose are informed by evidence.
Autism Awareness Australia provides self-care tips and helpful links and resources.
Also Check: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
When Should I See My Doctor
It’s important to seek help if you are concerned you or your child has autism. Early intervention offers the best outcomes, no matter what type of autism a child has.
There may be different signs of autism in different ages.
In the first year, a baby with autism might not be interested in other people and may not make eye contact with their parents. They may not smile or gesture like other babies.
As toddlers, children with autism might not respond to their name, or might focus on activities like lining up toys. They may not be interested in playing with other children or might speak in a monotone way.
Older children with autism might have difficulties in social situations, following instructions or making friends.
Sometimes people are not diagnosed with autism until they are adults. They may spend their lives feeling like they dont quite fit in. They may have difficulties with relationships, work and social situations. They may also have mental health conditions like anxiety or depression.
Autism Awareness Australia provides information about signs of autism in people at different ages.
Clinical Development And Diagnoses
Leo Kannerearly infantile autism
The word autism first took its modern sense in 1938 when Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital adopted Bleuler’s terminology autistic psychopaths in a lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD now known as Asperger syndrome, though for various reasons it was not widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981.Leo Kanner of the Johns Hopkins Hospital first used autism in its modern sense in English when he introduced the label early infantile autism in a 1943 report of 11 children with striking behavioral similarities. Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner’s first paper on the subject, notably “autistic aloneness” and “insistence on sameness”, are still regarded as typical of the autistic spectrum of disorders. It is not known whether Kanner derived the term independently of Asperger.
Kanner’s reuse of autism led to decades of confused terminology like infantile schizophrenia, and child psychiatry’s focus on maternal deprivation led to misconceptions of autism as an infant’s response to “refrigerator mothers“. Starting in the late 1960s autism was established as a separate syndrome.
You May Like: Is Stuttering A Sign Of Autism
How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosed
There are no laboratory tests to determine ASD. However, certain healthcare providers receive specific training and can do screenings and evaluations if needed and who might ask parents or teachers to record observations. These providers might include specialized physicians, psychologists and speech-language pathologists.
Is Rett Syndrome Autism
Rett syndrome or Rett disorder has also been called autism-dementia-ataxia-loss of purposeful hand use syndrome.
But its not included on the autism spectrum. Its a brain disorder caused by genetic mutations.
Classic Rett syndrome usually affects girls who display typical development for the first few months. Then, symptoms start to appear, involving issues with:
- language and communication
If you think your child might have symptoms of autism, speak with their pediatrician or a primary care physician. They can refer you to the appropriate specialist, such as a:
- developmental pediatrician
- psychiatrist or psychologist
You can also request an evaluation from your states public early childhood assistance center. Its free, and you dont need a doctors referral or diagnosis. Your local public school district can also provide assistance.
Theres no one medical test to diagnose autism spectrum disorder. A doctor can make the diagnosis with a comprehensive behavior evaluation and developmental screening.
Some people on the spectrum need minimal support services. Others require a lot. Either way, early intervention is associated with long-term positive effects.
You May Like: Can Autism Be Passed Down
How It All Fits Together
Diagnosing ASD can be very difficult, mainly because the condition starts to manifest itself early. The families of people living with the condition have to watch for early signs and symptoms in their children from as early as 18 months old.
They should also do a developmental screening test with a certified healthcare professional who will put their child through a series of questionnaires and checklists. An ASD diagnosis helps the families of autistic people understand their needs and how best they can support them.
For an adult who has lived for years with the condition, a diagnosis of ASD could finally answer any questions theyve had for most of their lives. Theyll understand why they find doing certain things harder than most people or find it challenging to communicate with people or be comfortable in social settings.
A New Understanding Of Asd
After reading and researching ASD and feeling certain this information describes yourself, you may experience an identity shift towards one that is autistic. Reflecting back on moments in your life, you may view things that happened in a different context, through the lens of autism. Retelling the story of your life may now have the ASD perspective. Remembering your stories, reflecting on them, and receiving feedback will change your narrative. This process of self-discovery helps to make sense of whats happened in your life how having ASD has shaped the way you think, react and feel. Maybe some of the confusion is gone, you understand yourself better, and in time you can share this discovery with people you trust.
This new identity may also cause feelings of loss, resentment or anger. Its OK to feel this way as this is a life changing event and it can feel overwhelming. Try to think about the positive things such as your strengths. People continue to grow, change and adapt throughout their lifespan. You can learn new skills and find new ways to do things that may make life easier and more comfortable.
Read Also: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Some People Use Other Names For Autism
There are other names for autism used by some people, such as:
- autism spectrum disorder the medical name for autism
- autism spectrum condition used instead of ASD by some people
- Asperger’s used by some people to describe autistic people with average or above average intelligence
Unlike some people with autism, people with Asperger’s do not have a learning disability.
Some people call this “high-functioning” autism.
Doctors do not diagnose people with Asperger’s anymore.
But if you were diagnosed with it before, this will stay as your diagnosis.
Who Should Diagnose Autism Spectrum Disorders

It seems that everyone, including the lady at the grocery store, can spot autism when they see it. But of course, it’s not that simple. Autism is not just a collection of personality traits and personal interests, and not everyone who prefers solitude and comic books is autistic. In fact, autism is a serious developmental disability, and diagnosis requires testing, evaluation, and an in-depth understanding of the disorder.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Are Siblings At Greater Risk For Autism Spectrum Disorder
The truth is that genetics do play a role in autism. When one child is diagnosed with ASD, the next child to come along has about a 20% greater risk of developing autism than normal. When the first two children in a family have both been diagnosed with ASD, the third child has about a 32% greater risk of developing ASD.
Autistic People May Act In A Different Way To Other People
Autistic people may:
- find it hard to communicate and interact with other people
- find it hard to understand how other people think or feel
- find things like bright lights or loud noises overwhelming, stressful or uncomfortable
- get anxious or upset about unfamiliar situations and social events
- take longer to understand information
- do or think the same things over and over
If you think you or your child may be autistic, get advice about the signs of autism.
Don’t Miss: Puzzle Piece Autism Meaning
How Is Asd Diagnosed
There is no simple medical test for diagnosing ASD.
To diagnose a child with ASD, a healthcare professional observes the childs levels of:
- communication
This could include the childs:
- verbal skills
- how they relate to others
- behaviours related to their interests and activities
- repeated actions related to how they speak, move or use objects
To determine the severity of ASD, the healthcare professional observes the amount of difficulty the child has with:
- social communication
Medical professionals use the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders to evaluate ASD.
If a health care provider thinks that your child may have ASD, get a referral for a diagnosis. A specialist will create a detailed description of your child’s strengths and challenges. A team of health professionals may work together for this assessment.
Testing for ASD will also make sure that this is not a different condition. For instance, sometimes hearing loss can explain your childs unresponsiveness in social situations or when their name is called.
Medical Diagnosis Vs Educational Eligibility For Special Services: Important Distinctions For Those Diagnosed With Asd
Parents are often surprised to learn that a medical diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder does not automatically entitle a student to special education services under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act . Eligibility for special education services is based, rather, on an educational determination of a disability, which includes meeting not just the criteria for a specific disability , but also finding that a student is in need of special services. Understanding the differences between a medical diagnosis and an educational determination of eligibility for special education services can help parents become better advocates for their children.
By contrast, educational eligibility is decided by a team comprised of various school professionals and a students parents. The team must find that the student qualifies for services under IDEA. To be eligible, IDEA requires that a student have at least one of 14 specified disabilities and be in need of special services. Autism is one of the 14 categories, but the definition of autism varies from state to state. Some states follow the medical definition found in the DSM, but others have their own definitions. In fact, some states exclude students with diagnoses of Aspergers Disorder or PDD-NOS from the autism category
Impact on Services
Related Articles:
Read Also: Can A Child Outgrow Autism
Serotonin Modulators And Stimulators
, sometimes referred to more simply as “serotonin modulators”, are a type of with a multimodal action specific to the system. To be precise, SMSs simultaneously modulate one or more and inhibit the of serotonin. The term was coined in reference to the of the serotonergic antidepressant , which acts as a , of the , and of the and . However, it can also technically be applied to , which is an antidepressant as well and acts as an SRI and 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.
An alternative term is serotonin partial agonist/reuptake inhibitor , which can be applied only to vilazodone.
What If I Or My Child Want To Keep The Diagnosis Of Asperger Syndrome
Many people strongly identify with their diagnosis of Asperger syndrome. Healthcare providers can still indicate a diagnosis of Asperger syndrome in a patients medical record, alongside the current DSM-5 coding for autism spectrum disorder. Colleges and school districts may vary in their policies for educational records.
Read Also: Comorbid Autism And Adhd
How Does The Dsm
Six major changes include:
1. Four previously separate categories of autism consolidated into one umbrella diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
Previous categories:
- Pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified
2. Consolidation of three previous categories of autism symptoms into two categories of symptoms.
Previous categories:
- Persistent deficits in social communication/interaction and
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior
3. The addition of sensory issues as a symptom under the restricted/repetitive behavior category. This includes hyper- or hypo-reactivity to stimuli or unusual interests in stimuli
4. A severity assessment scale based on level of support needed for daily function.
5. Additional assessment for:
- Any known genetic causes of autism
- Language level
- Intellectual disability and
- The presence of autism-associated medical conditions
6. Creation of a new diagnosis of social communication disorder for disabilities in social communication without repetitive, restricted behaviors.
Is There A Test For Asd In Adults
Clinicians have developed different tests that can help diagnose ASD in adults. These include diagnostic tests such as ADOS 2 Module 4, ADI-R, and 3Di Adult.
However, it is not clear how reliable these tests are for adults. The reasons for this include:
- Researchers who look at the reliability of ASD tests often use a small number of study participants.
- Not many research studies on testing for adult ASD include enough participants from historically underserved groups, such as People of Color or people who are LGBTQIA+. This means the results of studies looking at ASD testing methods may not represent a true population of autistic adults.
- Many clinicians may not be familiar with the signs of ASD in adulthood. This is especially true if the patientâs symptoms are not severe or if the patient also has other conditions, for example, anxiety.
Autistic people may have of co-occurring conditions, such as anxiety or depression, than those in the general population.
Also Check: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic