Providing Genetic Counselling For Families
Genetic counsellors may be asked to advise on the recurrence risk of ASD among families who have one or more offspring already diagnosed with ASD. In families generally, the risk of having a child with ASD is related to the population prevalence, currently in the region of 1 per cent. Among those children deemed âhigh-riskâ by way of an older sibling being diagnosed with ASD, 18.7 per cent are subsequently diagnosed with ASD. Moreover, with two older siblings with ASD, this figure goes up to 32.2 per cent.
Figure 2
Challenges And Future Perspectives
The field of imaging genetics has exponentially grown in recent decades from its candidate gene studies to large-scale longitudinal studies, cross-modal investigations, and translational animal models of various psychiatric disorders. In addition, imaging genetics has begun integrating transcriptomic data and analytical methods for assessing pathway enrichment, such as the score system for pathway regulation. Of addition to translational animal research and pharmacological intervention in vitro and in vivo, imaging genetics can also provide an insight into various behavioral and genetic factors that contribute to the risk of ASDs.
One of the challenges facing imaging genetics is the conceptualization of endophenotypes, which states that endophenotypes are heritable and associated with psychiatric disorders and may impede research on brain-based associations by limiting imaging genetic research to genes previously associated with a psychiatric disorder. It is important to properly replicate the studies, particularly those with false-positive results, to address the impact of a genetic variation in a disease, and this problem can be solved by correcting genome-wide associations with large sample size imaging phenotypes.
Transcriptional Regulation And Chromatin
The processes that encompass transcriptional regulation and chromatin-remodeling are complex. In short, these two processes control which genes can be expressed to form the corresponding protein.
Accurate follow-through of these processes is important as, if any of the steps involved during either transcriptional regulation or in the chromatin remodeling pathway are affected, it will bring rise to the formation of risk genes, some of which have been potentially linked to autism.
For example, the process of transcriptional regulation converts DNA to RNA. Once RNA is transcribed, it goes through cellular processes to coordinate cellular activity. When RNA is transcribed, RNA editing or modification can occur whereby discrete changes can take place within the RNA molecule. In the study by Tran et al. , it was found that mutations such as FMRP and FXRP1 can cause abnormal RNA modification activity.
According to Rylaarsdam, et al. , the genes that impact transcription and chromatin-remodeling pathways include MeCP2, UBE3A, chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 8 , activity dependent neuroprotector homeobox , pogo transposable element derived with ZNF domain , fragile X mental retardation protein , and RNA binding forkhead box genes.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Asd And Associated Genetic Conditions
Autism Spectrum Disorder and features of ASD can occur as part of some genetic conditions. Approximately 20% of children with ASD will have a diagnosable genetic syndrome. These syndromes can be due to missing or extra stretches of DNA, misspellings in genes, or biochemical abnormalities.
Some of these conditions are easy for a general pediatrician to recognize , while other conditions can be subtle and require specialized testing . For this reason, the American College of Medical Genetics recommends that anyone with an ASD diagnosis receive an evaluation by a clinical geneticist. Accurate diagnosis is important because there can be other health implications for the affected child, as well as differences in the risk of having another child on the autism spectrum.
In addition to genetic causes of ASD, exposure to certain medications during pregnancy can cause ASD. During your childs visit with a clinical geneticist, they will review any medications that you may have taken during pregnancy.
Examples of genetic abnormalities that can be associated with ASD are listed below.
22q deletion syndrome
Angelman syndrome
CHARGE
Cornelia de Lange syndrome
Down syndrome
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Fragile X
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition that causes a range of developmental delay. Usually males are more severely affected than females. Children may be hyperactive or have a secondary diagnosis of ADHD.
Prader-Willi syndrome
Rett syndrome
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
Do Vaccines Cause Autism
The subject of whether or not vaccines cause autism has been a heated debate for a long time.
The rumor started back when Dr. Andrew Wakefield and his colleagues published an article in 1998 linking measles, mumps and rubella vaccines to autism.
The article has since been retracted due to the article not being correct.
People have had concerns that autism could be linked to the vaccines children get. However, an abundance of studies have shown that there is no link between getting vaccinated and developing ASD.
CDC has conducted in 2013 that showed that vaccines do not cause autism spectrum disorder.
The study investigated various substances in vaccines that cause the bodys immune system to produce antibodies within the vaccines in the first two years of life.
The studys results stated that the total amount of antigen from vaccines was the same between children with autism spectrum disorder and those who did not have ASD.
, a controversial vaccine ingredient that has been researched specifically, is a mercury-based preservative.
It is used to prevent contamination of vaccines. Studies showed that thimerosal does not cause autism.
CDC has nine studies on this matter and none of them found any link between vaccines containing thimerosal and autism spectrum disorder.
And these studies also failed to find any connection between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine and autism spectrum disorder in children.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Autism
Epigenetics And The Environment
Autism susceptibility is currently estimated to be 4080% genetic. Environmental factors likely acting through epigenetic regulation as the major mechanism presumably compromise the remainder of the risk. Hundreds of potential environmental factors have been suggested to contribute to risk, such as increased parental age , maternal complications or infections during pregnancy, or prenatal exposure to anticonvulsants . In-depth reviews of these findings can be found elsewhere . In this review, we will only discuss the epigenetic modifying effects of valproic acid an anticonvulsant as one example of the widespread modifications that an environmental factor can induce. Valproic acid has been hypothesized to modify gene expression through histone deacetylase inhibition activity and is sometimes used to induce an autistic phenotype in animal models . Examples of its far-reaching effects include apoptotic cell death in the neocortex, decreased proliferation in the ganglionic eminence, increased homeobox A1 expression, abnormal serotonergic differentiation via Achaete-Scute family BHLH transcription factor 1 silencing, disrupted serotonin homeostasis in the amygdala, dendritic spine loss, reduced prefrontal dopaminergic activity, and disruption of the glutamatergic/GABAergic balance .
What Is Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is a form of medical test used to identify changes in the DNA sequence or chromosomes. It is an effective method to determine if a person is prone to a certain disease or disorder.
Genetic testing is a complex but effective means of determining the existence of medical conditions which could potentially alter the development of the fetus or infant. Genetic testing can be conducted prenatally and postnatally. There are three forms of a genetic test: the first is prenatal testing, the second is preimplantation genetic diagnosis on embryos produced through IVF, and thirdly, postnatal diagnostic testing.
Biological scientists have studied genes for several decades and it has become easier to detect some medical conditions very early. This can assist families in making informed parental decisions and choosing the most effective interventions to assist in daily living.
Read Also: Aspergers Prognosis
Genetic Causes Of Autism: Rare And Common Genetic Variants Associated With Asd
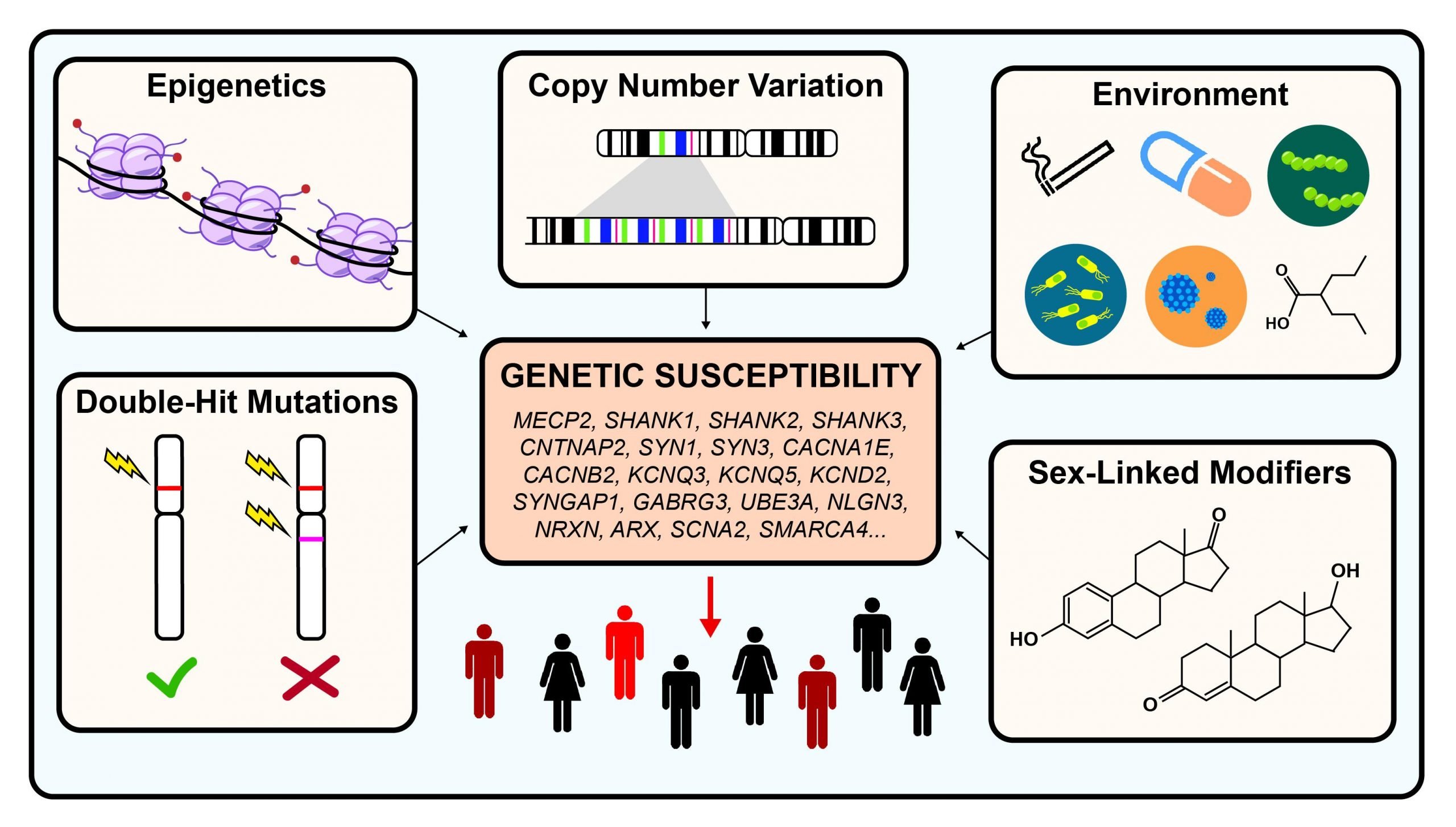
Although a substantial genetic contribution to ASD is well recognized, its genetic architecture is exceedingly heterogeneous and reflects a spectrum of genetic loads between two extremes: on the one hand a complex and still only poorly characterized burden of low-risk variants, mostly single nucleotide polymorphisms , and on the other hand a large number of highly penetrant rare variants, often copy number variations , whose expressivity is however also influenced by the heterogeneity of genetic backgrounds .
Several large consortia have been established with the purpose to investigate the genetic causes of NDDs by genotyping large cohorts of patients. This has resulted in the generation of knowledge bases and repositories openly available online that represent valuable resources to explore the genetic cause of NDDs the most relevant of them are listed in Table .
Table 1 Knowledge bases for NDD-relevant genes and patient cohorts
Autism Is A Complex Genetic Disorder
First-degree relatives of ASD probands have an increase in behavioral or cognitive features associated with autism, such as social or language dysfunction, albeit in lesser forms, when compared with the population prevalence . This has been called the broader phenotype and includes restrictive repetitive behaviors and sub-threshold deficits in social cognition, as well as language dysfunction . For example, language delay is observed in a significant proportion of non-autistic siblings of autistic probands . Similarly, autistic-like social impairment clearly is heritable and increased in unaffected parents and children of autistic probands . Studies using multiple measures of sub-threshold autistic traits in population cohorts suggest that different components, separately representing language, social function and repetitive or stereotyped behaviors contribute to ASD . On aggregate, these data suggest that different features of autism represent a quantitative continuum of function that may be inherited in distinct patterns. This is consistent with the knowledge that specific genetic factors contribute to the development and function of specific brain structures, and that distinct brain circuits may underlie different components of autism .
Common and Rare Variants
You May Like: Dylan Chills Autism
Autism Is Not An Illness
Being autistic does not mean you have an illness or disease. It means your brain works in a different way from other people.
It’s something you’re born with or first appears when you’re very young.
If you’re autistic, you’re autistic your whole life.
Autism is not a medical condition with treatments or a “cure”. But some people need support to help them with certain things.
Indirect Evidence Suggesting A Contribution Of Environmental Factors
Prevalence
Prevalence studies of autism spectrum disorders conducted in recent years have been the source of an important debate because of a steady and highly significant increase of estimates of the total prevalence of pervasive developmental disorders. Indeed, while the prevalence was estimated at 6 per 1000 in a population of school children in 2005, recent studies have gone so far as to estimate the prevalence to be one child in 38.The last prevalence estimates in the United States, released by the Centers for Disease Control recently, reached 1 in 88 child in 2008, while their previous estimate was one in 110 in 2006. However, most of the studies are not comparable in method or in the populations studied. One hypothesis is that this increase is the result of enlargement of diagnostic criteria, and the growing importance of screening for ASDs. The results of an epidemiological study from England, based on a national sample from 2007, support this hypothesis. Indeed the authors found a rate of about 1% in adults across the entire age range, without a significant reduction in the older part of the sample, as one would expect if the prevalence had increased in recent years. However, another study suggested that diagnostic substitution, especially for the most severe cases, and better ascertainment, especially for children at the less severe end of the spectrum, explain only a part of the linear increase observed in the California registry.
Immune dysfunction
Transcriptome
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Genetic Conditions And Asd
There are genetic conditions associated with autism. Chawner said its still unknown whether different conditions cause different types of autism.
Many in the field have previously hypothesized that different genetic conditions lead to different types of autism, he said. We, in fact, found small differences between genetic conditions, and we were surprised how variable clinical outcomes are within a genetic condition.
Chawner also found that the differences in clinical outcomes within a genetic condition were greater than the differences between genetic conditions.
To us this indicates that other factors are likely to play a more important role than the type of genetic condition in explaining outcome, he said. These possibly include additional genetic factors that modify clinical outcomes or environmental factors, such as access to healthcare and early educational support, and prenatal factors.
Read Also: Autism Puzzle Piece Colors Meaning
Are There Treatments Options Available
There is no cure for autism, but many treatments are available that may ameliorate some of the more challenging aspects of the disorder. Education can help parents learn to deal with their childs behavioral and emotional concerns, and will allow them to train their child to live a more independent lifestyle. However, it is important to remember that all autistic children are different, and no single treatment will work for all children.
Nebula Genomics Dna Report For Autism
Is autism genetic? We created a DNA report based on a study that attempted to answer this question. Below you can see a SAMPLE DNA report. To get your personalized DNA report, purchase our Whole Genome Sequencing!
| This information has been updated to reflect recent scientific research as of April 2021. |
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
The Role Of Rare Mutations Versus Common Polymorphisms In Asd
A series of important findings over the last four years clearly challenges the notion that autism is mainly caused by combinations of common variants by identifying a large number of rare, recurrent, and non-recurrent mutations that lead to ASD. At the same time, whole genome association studies with common variants, while identifying a few loci with very small effect sizes, have not yielded independently replicated results . These rare mutations, mostly in the form of sub-microscopic chromosomal structural variation, called copy number variants , are now known to account for up to 10% of cases of idiopathic autism . Since many of these CNV have large effect sizes and thus are thought sufficient to cause ASD, they are predicted to significantly reduce reproductive fitness. Consistent with this, these causal CNV are often not transmitted from the parent, but instead occur de novo in the germline . However, in some cases, such as CNV at 16p11 and 15q11-13, the CNV are transmitted from an unaffected parent to cause the disorder in an offspring . The genetic or epigenetic mechanism for the reduced penetrance for ASD in the mutation-carrying parent is not known. However, it is also very likely that the parent carriers of such CNV have more subtle neuropsychiatric or cognitive phenotypes that have not yet been systematically identified.
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism
Autism usually develops before 3 years of age and affects each individual differently and to varying degrees. It ranges in severity from relatively mild social and communicative impairments to a severe disability requiring lifelong parental, school and societal support.
The hallmark symptom of autism is impaired social interaction. Children with autism may fail to respond to their name and often avoid eye contact with other people. They have difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling because they don’t understand social cues provided by tone of voice or facial expressions and they don’t watch other people’s faces to pick up on these cues.
Many children with autism engage in repetitive movements such as rocking, spinning, twirling or jumping, or in self-abusive behavior such as hand biting or head-banging.
Of children being diagnosed now with an autism spectrum disorder, about half will have intellectual disabilities defined by nonverbal IQ testing, and 25 percent will also develop seizures. Though most children show signs of autism in the first year of life, about 30 percent will seem fine and then regress in both their language and social interactions at around 18 months of age.
About 30 percent of children with autism have physical signs of some alteration in early development such as physical features that differ from their parents , small head size or structural brain malformations.
Don’t Miss: Can You Outgrow Autism
Online Mendelian Inheritance In Man
| Content |
|---|
| Catalog of all known human genes and genetic phenotypes. |
| Data types |
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man is a continuously updated catalog of and and , with a particular focus on the . As of 28 June 2019, approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented the rest represented , many of which were related to known phenotypes.
Terminology And Distinction From Schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism while in 2007 it was believed to be one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed, parents continue to feel social stigma in situations where their child’s autistic behavior is perceived negatively, and many primary care physicians and medical specialists express some beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely.Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
You May Like: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism