Diagnostic Criteria For 29900 Autism Spectrum Disorder
To meet diagnostic criteria for ASD according to DSM-5, a child must have persistent deficits in each of three areas of social communication and interaction plus at least two of four types of restricted, repetitive behaviors .
Specify current severity:
Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior.
Diagnosis Of Autism From Kanner To Dsm
The condition known as autistic disorder, childhood autism, or infantile autism was first described by Kanner in his report of 11 children with what appeared to him to be a novel condition characterized by two essential features of autism; a lack of interest in the social world, and a group of behaviors he referred to as resistance to change or insistence on sameness . Kanners thoughtful clinical description noted many of the features still commonly included in diagnostic criteria for the disorder, and his emphasis on the centrality of social difficulties remains a hallmark of the condition. Early research was confused by some false leads and a lack of clarity about the validity of autism . By the 1970s longitudinal and other studies strongly suggested the validity of the condition, its frequent association with intellectual disability, and its strong brain and genetic basis .
In DSM-III autism was included in a class of conditions called pervasive developmental disorder ; this term had the advantage of no previous history. The DSM-III definition was very focused on infantile autism and developmental change was only cursorily addressed, although other categories for late-onset autism were also included .
Diagnosis Of Other Co
Sometimes autism comes with other conditions. These are called co-occurring conditions.
If children have signs or characteristics that meet the criteria for other conditions, theyll be diagnosed as having two or more conditions for example, autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or intellectual disability.
You May Like: Life Expectancy With Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnostic Criteria 29900
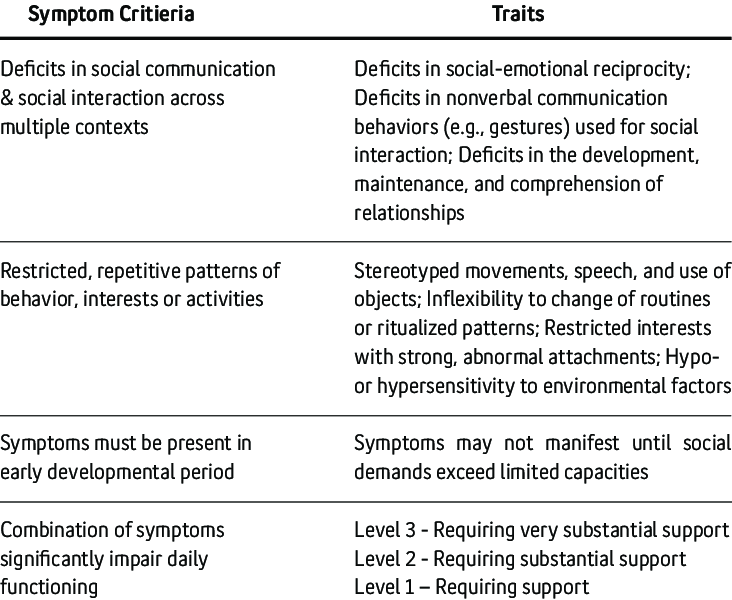
A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by all of the following, currently or by history :
1. Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back-and-forth conversation; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect; to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions.
2. Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction, ranging, for example, from poorly integrated verbal and nonverbal communication; to abnormalities in eye contact and body language or deficits in understanding and use of gestures; to a total lack of facial expressions and nonverbal communication.
3. Deficits in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships, ranging, for example, from difficulties adjusting behavior to suit various social contexts; to difficulties in sharing imaginative play or in making friends; to absence of interest in peers.
Specify current severity: Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior .
B. Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history :
1. Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech .
2. Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior .
Specify if:
What Is The Dsm
Diagnostic criteria
The definition of ASD in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition encompasses the previous manual’s autistic disorder , Asperger’s disorder, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. ASD is characterized by the following:
-
Deficits in social communication and social interaction
-
Restricted repetitive behaviors, interests, and activities
These symptoms are present from early childhood and limit or impair everyday functioning. Both components are required for diagnosis of ASD.
Recommended Reading: Autism Life Expectancy
About The Dsm And Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis
When diagnosing autism, professionals like paediatricians, psychiatrists, psychologists and speech pathologists use the Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders , or DSM-5, produced by the American Psychiatric Association.
The DSM-5 lists the signs and symptoms of autism and states how many of these must be present to confirm a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. The DSM-5 refers to signs and symptoms, but this article talks about signs and characteristics.
To find out whether a child has autism signs and characteristics and meets DSM-5 criteria, professionals also need to do extra tests. These tests are called adiagnostic assessment.
Terms For Types Of Autism That Are No Longer Used Today
When autism was categorized by types, the lines between the different types of autism could be blurry. Diagnosis was, and still is, complicated and often stressful for families.
If you or your child received a diagnosis before the DSM-5 changed, you may still be using the older terminology . Thats OK. Your doctor may continue to use those terms if they help.
Recommended Reading: Does Autism Shorten Life Span
Autism New Jersey Stated These Recent Changes To The Diagnostic Criteria
In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association revised the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , which includes changes to its definition of autism. The previous version of the DSM listed Autistic Disorder, Aspergers Disorder and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified as distinct diagnoses under the broader category of Pervasive Developmental Disorders. DSM-5 includes these separate diagnoses under a single umbrella term, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and makes changes to the way ASD is diagnosed.
The DSM-5 advises that individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnosis of autistic disorder, Asperger’s disorder, or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
The DSM-5 requires an individual to meet a specific number of criteria from two major categories. To be diagnosed with ASD, a person must have difficulty with social communication and interaction, and display restricted repetitive behaviors, interests and activities. The diagnostician will rank the characteristics based on level of severity and describe the support the individual needs.
Autism Spectrum Diagnosis according to DSM-5:
- Symptoms Must Be Present In The Early Developmental Period
- Symptoms Cause Clinically Significant Impairment In Social, Occupational, or Other Important Areas of Functioning
- Severity Levels are Measured Based on Level of Support Needed
Risk And Prognostic Factors
The best established prognostic factors for individual outcome within autism spectrum disorder are presence or absence of associated intellectual disability and language impairment and additional mental health problems. Epilepsy, as a comorbid diagnosis, is associated with greater intellectual disability and lower verbal ability.
Environmental. A variety of nonspecific risk factors, such as advanced parental age, birth weight, or fetal exposure to valproate, may contribute to risk of autism spectrum disorder.
Genetic And Physiological. Heritability estimates for autism spectrum disorder have ranged from 37% to higher than 90%, based on twin concordance rates. Currently, as many as 15% of cases of autism spectrum disorder appear to be associated with a known genetic mutation, with different de novo copy number variants or de novo mutations in specific genes associated with the disorder in different families. However, even when an autism spectrum disorder is associated with a known genetic mutation, it does not appear to be fully penetrant. Risk for the remainder of cases appears to be polygenic, with perhaps hundreds of genetic loci making relatively small contributions.
Also Check: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Autism Spectrum Disorder: A New Umbrella Term
One of the biggest changes in the DSM-5 is the revised diagnosis of individuals with autism-related disorders.
Prior to the revision, patients could be characterized as having one of four disorders: autistic disorder, Aspergers, childhood disintegrative disorder or an unidentified developmental disorder not otherwise specified. After medical and scientific review, researchers found that these labels were not consistently applied across clinics and treatment centers. The DSM-5 has therefore done away with the prior mentioned labels and has redefined these symptoms under one umbrella term. In doing so, they hope it will improve diagnoses without limiting criteria or changing the number of individuals being diagnosed.
People with autism spectrum disorder tend to display the following traits:
- Communication deficits
- High sensitivity to changes in their environment
Why This Terminology Is No Longer Used By Doctors
The spectrum illustrates a broad range of developmental delays and symptom severity.
ASD includes people who have a few mild autistic traits to those who need help with day-to-day functioning. It represents every intelligence level, as well as varying degrees of communication and social abilities.
The differences between one type and another type can be subtle and difficult to determine.
Don’t Miss: Aspergers And Stuttering
Research To Drive The Future Of Autism
Nevertheless, no matter how controversial these changes are, they were based on sound research, analysis and expert opinion. The aim of the changes to the DSM 5 for Autism Spectrum Disorder, were made in the hope that diagnosing Autistic disorders would be more reliable, more specific and hold more validity by standing the test of time.
There is apprehension as to how the changes will impact people who will no longer meet the stricter criteria for diagnosis, especially people at the higher end of the spectrum. Will they still be eligible for the support that they have had within education? This is concerning especially as it is likely that they also have additional learning difficulties.
Obviously, these changes will have an impact not just on the people who are diagnosed with Autism, but also their families.
Since the publication of the Autism Spectrum Disorder DSM 5, scientists have found that there is distinct brain connectivity difference between children with Autism in comparison with children who have other forms of Autism. A specific example is where that children with Aspergers do not have a speech delay but children with other forms of Autism do.
Does Aspergers Syndrome Still Exist In Dsm 5
With the new model of Autism, it means that Aspergers Syndrome which was added to the DSM ;back in 1994 and has existed for a period of time, was removed in May 2013. Which begs the question does Aspergers still exist? In official terms no, because the diagnosis would be Autistic Spectrum Disorder Level I.
The reason for diagnosing what was Aspergers as Autistic Spectrum Disorder Level I is that in general terms the need is of a low level of support. On the face of it, that is correct, but the type of low-level support that is needed has to be of a different genre than for someone who is ASD Level III.
However, to just give a label of ASD Level I, is not sufficient. Autism, at different;level, affects each child or adult differently. On a personal experience, I have encountered clients with similar autistic traits but how the traits impact on their lives will depend on their personality; levels of sensitivity; resilience and the effectiveness of their support.;To counteract the impact of ASD labelling, there should be specific descriptors to highlight individual signs and symptoms.
Aspergers may not exist as a definitive within the DSM 5 Autism Spectrum Disorder, but clinicians will still carry on using the international coding system especially when they are dealing with medical insurance companies , as Aspergers is still included in that system. Groups and organisations that support their members that have Aspergers will continue to use the descriptor.
Read Also: Symmetra Overwatch Autistic
Deficits Or Difficulty With Social Communication
According to the manual, a child should have ongoing difficulties in all three areas of social communication and interaction.
What Are The New Criteria For Diagnosing Autism
The DSM-5 criteria for autism fall under two categories:
In addition, clinicians are asked to rate the severity of these problems, based on the level of daily support they require.
Read the full text of the DSM-5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder.
How will these DSM-5 changes affect people already diagnosed with Asperger syndrome, PDD-NOS or other previous autism categories?
The DSM-5 states, Individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnoses of autistic disorder, Aspergers disorder or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
What if I or my child want to keep the diagnosis of Asperger syndrome?
Many people strongly identify with their diagnosis of Asperger syndrome. Healthcare providers can still indicate a diagnosis of Asperger syndrome in a patients medical record, alongside the current DSM-5 coding for autism spectrum disorder. Colleges and school districts may vary in their policies for educational records.
What is the new diagnosis of social communication disorder? Who will it affect?
This new diagnosis applies to people who have persistent problems with the social use of language, but dont have restricted interests or repetitive behaviors.
You May Like: Does Gestational Diabetes Cause Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder: Dsm 5 Criteria
According to the Centers for Disease Control , the 2014 statistics for the prevalence of autism ran at 1 in 59 children, based on the Autism DSM 5 criteria. While the number varies somewhat depending on the source, most sources seem to agree that the overall rate of diagnosis is increasing, at a seemingly startling rate .
Experts disagree about why the number of children diagnosed with autism continues to increase. Due to changing diagnostic criteria to Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition , its now impossible to know for sure.
Changing Diagnoses: Autism Dsm 5 Criteria
The publication of the DSM 5 sparked a sharp change in the way clinicians diagnosed autism. Rather than needing all 3 of the above criteria, individuals only needed 2:
- Restricted and repetitive interests and/or movements
- Social deficits
The DSM 5 included a separate diagnosis for those children presenting with communication deficits. Individuals no longer needed significant impairments in communication to qualify for an autism diagnosis. This resulted in an autism diagnosis for many individuals who experienced serious social deficits with restricted interests but not the accompanying communication challenges.
With the publication of the DSM 5, individuals who have an intact communicative repertoire but struggle socially and engage in repetitive behaviors began to receive an autism diagnosis. The increase in children diagnosed with autism also gave these children access to much needed services they may not have been able to receive otherwise.;
Six years after the publication of this manual, we still feel the effects of these critical distinctions in the prevalence of autism.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Of Autism
Other Terminology You May Have Heard For Types Of Autism
Terms like mild or high functioning arent official diagnoses. Some people find these terms useful, but many in the autistic community havent found them to be helpful or accurate, largely due to the range of abilities that can be present in an autistic person.
You may also have heard about three levels of autism, with level 1 being the mildest and level 3 the most severe.
Dsm 5 Autism Spectrum Disorder
In on of the previous articles, we looked at the detailed autism symptoms checklist that can help in an;accurate diagnosis of Autism. To provide a common framework;that can be applied;to test the presence of Autism, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5 has been adopted by psychologists across most major nations.; The DSM 5 also eludes to;diet recommendations and;medication;for autism and similar neuro-behavioral disorders.
A comparison of DSM 4 Vs DSM 5
Over the years there have been changes to the DSM 5 manual. Recent;concerns being that there have been changes to the categories for Autism.; This has given rise to the concern that some of the psychological and screening tools;that have traditionally been;used to determine a diagnosis of;Autism are now either too simplistic or archaic.
The changes in the fifth edition of the manual now mean that Aspergers, Pervasive Development Disorders, and Autism are now diagnosed as Autistic Spectrum Disorder Level I, II or III.
This now means that Retts Syndrome and Childhood Disintegrative Disorders are included in the Spectrum but are diagnosed by their severity of need within Social Communication and Ritualistic behaviors.
Table 1:;A Snapshot of Autism Spectrum Disorder Support Levels
You May Like: Autistic Life Expectancy
Is Rett Syndrome Autism
Rett syndrome or Rett disorder has also been called autism-dementia-ataxia-loss of purposeful hand use syndrome.
But its not included on the autism spectrum. Its a brain disorder caused by genetic mutations.
Classic Rett syndrome usually affects girls who display typical development for the first few months. Then, symptoms start to appear, involving issues with:
- language and communication
If you think your child might have symptoms of autism, speak with their pediatrician or a primary care physician. They can refer you to the appropriate specialist, such as a:
- developmental pediatrician
- psychiatrist or psychologist
You can also request an evaluation from your states public early childhood assistance center. Its free, and you dont need a doctors referral or diagnosis. Your local public school district can also provide assistance.
Theres no one medical test to diagnose autism spectrum disorder. A doctor can make the diagnosis with a comprehensive behavior evaluation and developmental screening.
Some people on the spectrum need minimal support services. Others require a lot. Either way, early intervention is associated with long-term positive effects.