Autistic People May Act In A Different Way To Other People
Autistic people may:
- find it hard to communicate and interact with other people
- find it hard to understand how other people think or feel
- find things like bright lights or loud noises overwhelming, stressful or uncomfortable
- get anxious or upset about unfamiliar situations and social events
- take longer to understand information
- do or think the same things over and over
If you think you or your child may be autistic, get advice about the signs of autism.
Causes And Risk Factors
We do not know all of the causes of ASD. However, we have learned that there are likely many causes for multiple types of ASD. There may be many different factors that make a child more likely to have an ASD, including environmental, biologic and genetic factors.
- Most scientists agree that genes are one of the risk factors that can make a person more likely to develop ASD.4, 19
- Children who have a sibling with ASD are at a higher risk of also having ASD. 5-10
- Individuals with certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis, can have a greater chance of having ASD. 11-14, 20
- When taken during pregnancy, the prescription drugs valproic acid and thalidomide have been linked with a higher risk of ASD.15-16
- There is some evidence that the critical period for developing ASD occurs before, during, and immediately after birth. 17
- Children born to older parents are at greater risk for having ASD. 18
ASD continues to be an important public health concern. Like the many families living with ASD, CDC wants to find out what causes the disorder. Understanding the factors that make a person more likely to develop ASD will help us learn more about the causes. We are currently working on one of the largest U.S. studies to date, called Study to Explore Early Development . SEED is looking at many possible risk factors for ASD, including genetic, environmental, pregnancy, and behavioral factors.
Level : Requiring Support
The communication issues that a person with Level 1 ASD may face include:
- difficulty initiating social interactions
The repetitive behavioral issues a person with Level 1 ASD may face include:
- inflexible behavior that interferes with general functioning in one or more contexts
- problems switching between activities
- issues with organization and planning, which can impact independence
Also Check: What Disability Does Collin Gosselin Have
How Do Doctors Describe Autism Right Now
Doctors use the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders when placing patients into diagnostic categories. In the fifth edition, issued in 2013, the autism world changed dramatically.
Prior versions included several conditions, such as:
- Autism.
- Childhood disintegrative disorder.
- Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified .
The borders between these conditions were porous, experts explain. Someone visiting one doctor could get a diagnosis of autism. The next day, that same person might get a diagnosis of PDD-NOS from a different doctor.
Diagnostic confusion leads to blurred treatments and stressed families. They dont know which label is true, and they dont know whom to trust.
In the DSM-5, these conditions were replaced with one term: autism spectrum disorder. That language encompasses the many commonalities these conditions share. The use of the word spectrum recognizes that some people have much deeper impairments than others.
Doctors will use the term autism spectrum disorder when discussing patients. Despite this, you might hear families discussing Aspergers syndrome or PDD-NOS in casual conversation, says the Autism Society. These terms are still widely circulated.
Conditions Related To Autism
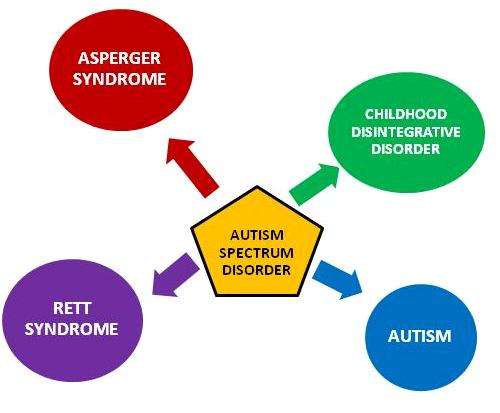
Autism diagnosis doesnt just begin and end with these 5 conditions though as, like the 2 previous conditions demonstrate, there are many MANY types of diagnosis out there which overlap in the causes and effects of autism.
As such, while you may have seen many things labelled a rare type of autism in a newspaper or journal, the reality is that many of these condition are close to the spectrum but not on in. These include:
You May Like: Best Pet For Autistic Child
What Are The 5 Types Of Autism
Autism refers to a wide range of neurodevelopmental disorders. If your child is living with autism, it is important for you to understand the various types of autism and the symptoms presented by each.
Understanding the unique challenges presented by each type of autism will guide you in helping your child cope with the disorder. There are five major types of autism which include Aspergers syndrome, Rett syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, Kanners syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified.
Pervasive Development Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
This mouthful is one of those strange parts of autistic diagnosis that shows why the DSM thought it might be a good idea to reorganize the whole disorder: it’s literally defined as “not fitting into the other categories properly”. It’s regarded as one of the “milder” forms of autism, and is sometimes called atypical autism, but exactly why is, well, complicated.
Basically, people with PDD-NOS don’t quite fit into a diagnosis either of full Asperger’s or of autistic disorder. They tend to be high-functioning, but their particular symptoms include childhood developmental delay, which means Asperger’s isn’t the right diagnosis. They may also have a range of autistic disorder symptoms, but only in mild forms or have some of the symptoms, but not enough of them to fully qualify. Basically, it’s the outlier. PDD-NOS children and adults are often socially oriented, for instance, but it’s tricky to outline exactly what the symptoms are because there’s so much variation.
Recommended Reading: Visual Calendar Autism
Behavior Activities And Interests:
- Repeating the same movements constantly, such as clapping their hands, stomping their feet or rocking back and forth. Often these movements are done out of a state of relaxation or as a coping method.
- Ways of moving may seem out of the ordinary, such as being aggressive in certain actions such as being too rough with a simple hug or being too aggressive during play time with other children.
- Obsessive actions and thoughts towards certain things are not uncommon. They may obsess over a certain corner of a house, a toy that they love or a specific person. Failure to have this object or person around them may result in a breakdown, commonly with crying, screaming or tantrums.
- Focusing on one specific topic all the time can prevent other topics of conversation from coming into play. Often individuals on the Autism spectrum will obsess over a certain topic, such as airplanes or trains. It can be extremely hard for them to engage in any sort of conversation that is not directly related to the object they are interested in.
- Sensitivity to certain sensory experiences may vary. Some individuals are hypersensitive to sensations such as cold, textures, sounds, etc. whereas others are hyposensitive to them.
Managing Autism Spectrum Disorder
Numerous therapies and behavioral interventions can help improve the specific challenges that autistic people face.
Healthcare professionals often recommend that ASD therapies begin as soon as possible after a child receives their diagnosis. Early intervention can reduce their difficulties, allowing them to adapt and learn new skills.
Management strategies for ASD may include:
- educational and developmental therapy
- behavioral therapy to help learn life skills and overcome other challenges
- speech, language, and occupational therapy to help with social, communication, and language skills
- medication to tackle accompanying mental health issues, such as irritability, aggression, repetitive behavior, hyperactivity, attention issues, anxiety, and depression
- psychotherapy to help a person increase or build upon their strengths
- supplements or changes in diet
It is important to note that ASD is a spectrum disorder, meaning people can experience a varying range of these differences. After an ASD diagnosis, many children go on to live productive, independent, and fulfilling lives.
Read Also: Can Autistic Person Drive
Getting Evaluated For Autism Spectrum Disorder
Parent interview In the first phase of the diagnostic evaluation, you will give your doctor background information about your childs medical, developmental, and behavioral history. If you have been keeping a journal or taking notes on anything thats concerned you, share that information. The doctor will also want to know about your familys medical and mental health history.
Medical exam The medical evaluation includes a general physical, a neurological exam, lab tests, and genetic testing. Your child will undergo this full screening to determine the cause of their developmental problems and to identify any co-existing conditions.
Hearing test Since hearing problems can result in social and language delays, they need to be excluded before an Autism Spectrum Disorder can be diagnosed. Your child will undergo a formal audiological assessment where they are tested for any hearing impairments, as well as any other hearing issues or sound sensitivities that sometimes co-occur with autism.
Observation Developmental specialists will observe your child in a variety of settings to look for unusual behavior associated with the Autism Spectrum Disorder. They may watch your child playing or interacting with other people.
Lead screening Because lead poisoning can cause autistic-like symptoms, the National Center for Environmental Health recommends that all children with developmental delays be screened for lead poisoning.
Treatment And Intervention Services For Autism Spectrum Disorder
Treatment and Intervention Services for Autism Spectrum Disorder
At present, no treatment has been proven to treat ASD However, several strategies have been designed and tested to be used with children. The interventions can help reduce symptoms, enhance cognitive abilities and daily living abilities, and increase the capacity children to participate and contribute to the world.The different ways ASD affects every person is that individuals with ASD possess
Don’t Miss: Autism Schedule Board
Terms For Types Of Autism That Are No Longer Used Today
When autism was categorized by types, the lines between the different types of autism could be blurry. Diagnosis was, and still is, complicated and often stressful for families.
If you or your child received a diagnosis before the DSM-5 changed, you may still be using the older terminology . Thats OK. Your doctor may continue to use those terms if they help.
Thimerosal And The Asd Hypothesis

Thimerosal is a mercury-containing compound that has been used as an additive to vaccines to prevent bacterial contamination. In 1997, the United States Food and Drug Administration called for assessment of the risk of all mercury-containing foods and drugs. This action stimulated the United States Public Health Service and the American Academy of Pediatrics to issue a joint statement in 1999 calling for the removal of thimerosal from the vaccines. This action was undertaken as a precautionary measure. There was no evidence that mercury was harmful at the doses being administered in the vaccines. The evidence from these studies does not support and favors rejection of a causal relationship between thimerosal-containing vaccines and autism., Further evidence contradicting this hypothesis is that rates of autism have continued to increase despite the removal of thimerosal from vaccines in 1999.,
Recommended Reading: What Color Is The Autism Ribbon
What Are The Treatment Options For Autism
Autism spectrum disorder has no cure, and there is no clear-cut treatment for it. Treatment of ASD depends on the symptoms of an individual.
Treatment options for ASD may include:
- Behavioral and communication therapy: These programs educate children on how to behave and improve communication skills. A reward-based incentive system may improve learning abilities and apply these skills to various settings.
- Educational therapy: Highly organized educational programs may improve social skills, communication, and behavior. Children who received such programs in preschool have shown good results.
- Family therapy: Family members are counseled to take an initiative to interact with children and teach them social skills, discipline, daily living, and communication.
- Other therapies: A psychologist can advise you on how to deal with problematic conduct. Speech therapy and physical therapy may improve communication skills and improve mobility that helps with daily living.
- Medications: There is no medicine to cure ASD. However, the child may be given certain medications such as antipsychotic drugs and antidepressants depending on their symptoms.
Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder
In order to determine whether your child has autism spectrum disorder or another developmental condition, clinicians look carefully at the way your child interacts with others, communicates, and behaves. Diagnosis is based on the patterns of behavior that are revealed.
If you are concerned that your child has autism spectrum disorder and developmental screening confirms the risk, ask your family doctor or pediatrician to refer you immediately to an autism specialist or team of specialists for a comprehensive evaluation. Since the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder is complicated, it is essential that you meet with experts who have training and experience in this highly specialized area.
The team of specialists involved in diagnosing your child may include:
Need urgent help? .
Recommended Reading: Is The Good Doctor A Good Representation Of Autism
Clinical Development And Diagnoses
Leo Kannerearly infantile autism
The word autism first took its modern sense in 1938 when Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital adopted Bleuler’s terminology autistic psychopaths in a lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD now known as Asperger syndrome, though for various reasons it was not widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981.Leo Kanner of the Johns Hopkins Hospital first used autism in its modern sense in English when he introduced the label early infantile autism in a 1943 report of 11 children with striking behavioral similarities. Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner’s first paper on the subject, notably “autistic aloneness” and “insistence on sameness”, are still regarded as typical of the autistic spectrum of disorders. It is not known whether Kanner derived the term independently of Asperger.
Kanner’s reuse of autism led to decades of confused terminology like infantile schizophrenia, and child psychiatry’s focus on maternal deprivation led to misconceptions of autism as an infant’s response to “refrigerator mothers“. Starting in the late 1960s autism was established as a separate syndrome.
Strategies And Interventionsadvice & Support For:
This section looks at a range of approaches that can support autistic people to reach their full potential.
Autism is a lifelong disability and the concept of a cure is controversial for many autistic people and their families. However, there are a range of approaches that can support autistic people to reach their full potential.
Many different approaches exist, making it difficult to decide which is best to use. There is a lot we dont know about their effectiveness, as few have been independently or scientifically evaluated.
Bold claims are often made about interventions and therapies for autistic people without any evidence to back them up. This is irresponsible and inappropriate, and we try to keep people aware of current concerns in . It is therefore vital that autistic people and parents/carers can access reliable information and advice both after and on an ongoing basis.
Autism is complex and what helps one person may not help others, so it is vital that each person is supported as an individual and that any interventions are adapted to their specific needs.
A range of communication-based, behavioural and educational approaches exist such as:
- PECS
- SPELL
- TEACCH
- Social Stories
- speech and language therapy.
The National Autistic Society believes that interventions need to be adapted to the needs of the person and monitored for impact.
NICE guidelines are reviewed every three years taking into account any new evidence.
Read Also: Mild Autism Prognosis
What Parents Should Know About An Asd Diagnosis
While doctors will generally now diagnose someone with ASD and a level, doctors might still refer back to pre-2013 diagnoses in an informal way, especially if they are trying to help a family better understand the kind of support their child might need, according to Frazier.
For instance, when Huftons older son was diagnosed, her childs psychologist told her that he was considered low-functioning because he required so much assistance to make it through the day. But when her younger son was diagnosed two years later, she had come to focus less on labels and more on her sons unique traits.
Given her experience, Hufton encourages parents to consider their child as an individual. My childrens future is not based on where they fall on the spectrum, she says. My childrens future is based on what we help them achieve. What their interests are and what their strengths are. The extra labels have nothing to do with that. As a parent, I advocate for them to get accommodations and services that will help them based on what I observe about them individually.
When it comes to fixating on a specific label, Shore couldnt agree more. Its up to educators, therapists, parents and others in allied fields to avoid thinking of autism as a series of deficits, disorders and disabilities, Shore says. The potential of people on the autism spectrum is the same as everyone else: unlimited.
Level : Requiring Substantial Support
The communication issues that a person with Level 2 ASD may face include:
- noticeable issues with verbal and nonverbal social communication skills
- social issues being apparent despite supports in place
- limited initiation of social interaction
- reduced response to social interactions from others
- interactions that are limited to narrow special interests
- more significant differences in nonverbal communication
The repetitive behavioral issues a person with Level 2 ASD may face include:
- inflexible behavior
- struggling to cope with change
- restricted or repetitive behaviors that are obvious to a casual observer and interfere with functioning in several contexts
- difficulty changing focus or action
Read Also: Autism Awareness Month Symbol
How Common Is Autism
An autism diagnosis occurs in one of every sixty-eight births. An early intervention program can be helpful when autism is discovered in younger children. In some cases, with the right treatment program, a child can even outgrow some of the issues associated with autism and begin to display better social and communication skills.
Different Types Of Autism
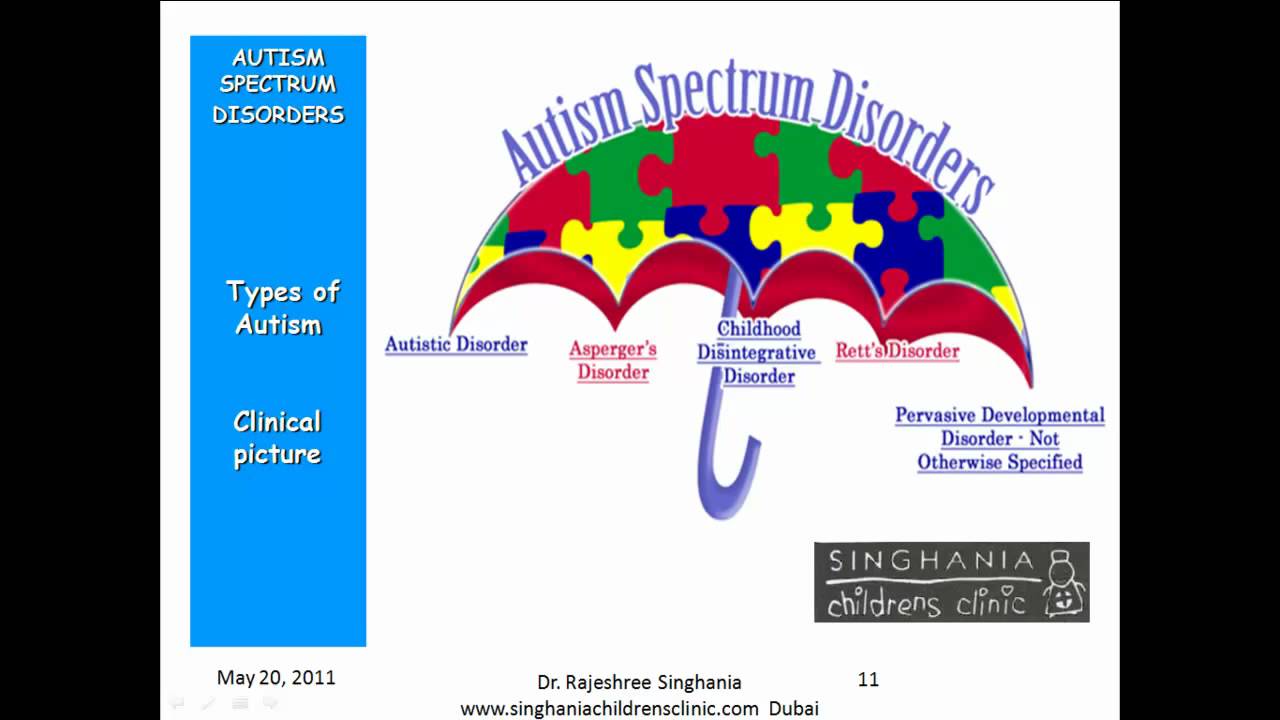
The 5 main types of autism spectrum disorder include:
Recommended Reading: Is The Good Doctor Really Autistic